Why does dental health worsen during pregnancy?
As soon as a woman finds out she is pregnant, she should take extra care of her teeth and visit the dentist regularly. Caries at any stage is common, and it is important to prevent its occurrence or treat it at the initial stage.
In this article
- Why does dental health worsen during pregnancy?
- The effect of caries on pregnancy
- Treatments that are suitable for pregnant women
- Do pregnant women undergo anesthesia and X-rays?
- Features of caries treatment in different trimesters
- Is it possible to have teeth removed during pregnancy?
- Prevention of caries during pregnancy
Why are pregnant women’s teeth more susceptible to caries than others? There is an opinion that the fetus developing in the womb “takes” all the calcium from the mother’s teeth, which leads to caries in pregnant women. In fact, this is nothing more than a myth. And the real reasons for the development of dental caries during pregnancy are completely different.
- Changing eating habits
Pregnant women often change their taste habits and diet towards the “wrong” ones. Either they want something sweet, or they crave something sour. In the early stages of toxicosis, sometimes there is no desire to eat anything at all, and in the later stages, in order to drown out heartburn, the pregnant woman constantly chews something. Such changes in diet cannot but affect the condition of the teeth. The risk of developing caries during pregnancy especially increases when a woman eats a lot of carbohydrate and sweet foods. It serves as a food source for cariogenic bacteria, which convert sugar into acid that is destructive to tooth enamel. Frequent meals cause food to remain in the mouth for a long time and create excellent conditions for the growth of microbes.
- Toxicosis
This unpleasant condition in pregnant women is often accompanied by vomiting. These masses contain a large amount of hydrochloric acid, which is harmful to tooth enamel. It damages its structure, making it thinner, more fragile and permeable to bacteria. To prevent the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid on teeth, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a soda solution after vomiting.
- Hormonal changes
During pregnancy, the amount and composition of hormones in the female body changes. Against this background, a decrease in immunity occurs, and the composition of saliva also changes. If in normal times it has a powerful bactericidal effect and effectively fights cariogenic bacteria, then during pregnancy its disinfecting properties are noticeably reduced. This promotes the active proliferation of microorganisms in the oral cavity and increased formation of dental plaque.
- Improper hygiene
This is one of the most common causes of caries, and it is not always associated specifically with pregnancy. But it has been noticed that pregnant women, due to poor health, toxicosis, fatigue and other reasons, begin to pay less attention to proper teeth brushing and oral care, which can contribute to the development of caries.
- Lack of minerals
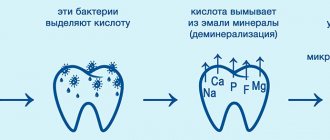
Although the fetus, as we already know, contains calcium from the mother’s teeth, this important microelement is extremely necessary for the development of its skeletal system. Therefore, from the nutrition that a pregnant woman receives, part of the nutrients goes to the development of the fetus. As a result, the concentration of minerals in the blood and saliva decreases, which leads to demineralization of the enamel - the first stage in the development of carious lesions. This is why it is so important during pregnancy to increase the intake of minerals into the body by adjusting the diet or taking special vitamin and mineral complexes.
Caries in pregnant women: causes
There is a widespread belief among women that rapid tooth decay during pregnancy is associated with the fetus’ increased need for calcium and phosphorus.
But the increased need for calcium is compensated by the mother’s body not by leaching it from the teeth, but primarily by increasing its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and reducing its loss in urine and sweat. This mechanism is hormonally determined. But besides this, the body has another mechanism that maintains a constant concentration of calcium in the blood of any person (including pregnant women). Maintaining normal calcium concentrations in the blood occurs due to slow osteoporosis of bone tissue. But the teeth do not suffer, and here's why. The fact is that mineralization of tooth enamel with calcium occurs due to calcium ions contained in saliva, the concentration of which in saliva is strictly tied to the concentration of calcium in the blood. And since, due to osteoporosis of bone tissue, its concentration in the blood is normal (and, accordingly, in saliva too), then the mineralizing function of saliva also does not suffer.
What then stimulates tooth decay in pregnant women?
Firstly, during heartburn and after vomiting, a large amount of gastric juice enters the oral cavity, i.e. hydrochloric acid, which helps wash out calcium from tooth enamel. Therefore, in case of heartburn and after vomiting, first of all you need to rinse your mouth with a soda solution (this will neutralize the acid), and it is not recommended to brush your teeth immediately. Immediately after exposure to acid, the surface layer of tooth enamel becomes porous and can be easily removed with abrasives.
Therefore, after heartburn or vomiting (as well as after drinking wine, fruit or fruit juice), it is recommended to brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush only after 30-40 minutes, using toothpaste with fluoride. Until this point, it is better for you to use a soda rinse, and after it you can immediately use a fluoride rinse. The second very important point is that studies show that 90% of pregnant women have worse oral hygiene (compared to the period before pregnancy).
The third reason is that insufficient hygiene is aggravated by eating disorders, i.e. constant snacking between main meals (anything containing flour, sugar and starch is especially harmful). Naturally, after snacking, people are not accustomed to brushing their teeth at all, and as a result, cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity receive constant 5-6 meals a day, while constantly producing organic acids that destroy teeth. At the same time, after the next snack, it is absolutely not enough to simply rinse your mouth and chew gum, because... this does not allow removing plaque, as well as food debris that has accumulated between the teeth.
The effect of caries on pregnancy
Another common reason for the development of caries in pregnant women is that women are afraid to have their teeth treated while pregnant. There is a popular myth that caries cannot be treated for any period of time, allegedly it can harm the fetus. As a result, a woman can walk with caries for nine months, which during this time can move from the initial stage of the stain to a complicated form or pulpitis.
American scientists conducted a study and found that there is a direct connection between the amount of cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity and premature birth or the birth of a child with low body weight. There is a hypothesis that the same bacteria contribute to the production of cytokines in the body of a pregnant woman - special substances that cause dilation of the cervical canal and contraction of the uterus itself. The greater the expansion of the canal, the greater the likelihood of premature birth.
Complications of caries, in particular pulpitis and periodontitis, can also affect the fetus. When the dental pulp becomes inflamed, the pathological process often spreads beyond the boundaries of the tooth. Toxins enter the blood and are carried by its current to other organs, in particular they reach the fetus and can negatively affect its development.
Thus, dental caries can be dangerous for a child, so diseased teeth should definitely be treated. Moreover, in pregnant women, the destruction of dental tissue occurs very quickly. It can take just a few weeks or months from the spot stage to deep caries.
When asked whether it is possible to treat teeth for pregnant women, dentists unanimously say: treatment of caries during pregnancy is acceptable and even necessary. The doctor will simply select methods and drugs approved for use in pregnant women.
Why is caries dangerous?
Tooth decay is a source of dangerous microorganisms right in your mouth. Neither the pregnant woman nor the fetus needs this dangerous source of infection. The infection can get into the blood. In this case, it will spread throughout the body.
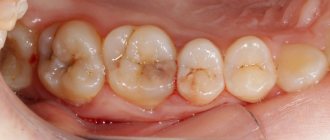
Caries is common in pregnant women. According to statistics, it is found in nine out of ten pregnant women. With toxicosis, this figure is even higher. Also at this time the sensitivity of the enamel increases.
According to statistics, caries is found in nine out of ten pregnant women.
It is generally accepted that treating a disease during pregnancy can cause more harm than the disease itself. Therefore, many women put off going to the dentist. This is a dangerous misconception. Caries can cause serious dental diseases. We will figure out how dangerous caries treatment is and whether it can affect the fetus.
Treatments that are suitable for pregnant women
If caries is detected at the spot stage, it can be treated with conservative methods without anesthesia, which will not cause the patient any pain or discomfort.
- Remineralization.
Tooth enamel is coated with gels containing large amounts of zinc, phosphorus, and calcium, while remineralizing compounds are applied not only to the lesion, but also to healthy enamel.
- Fluoridation.
The procedure is similar to the previous one, but the teeth are treated with fluoride-containing compounds. Fluorides strengthen tooth enamel and increase its resistance to cariogenic factors.
- Infiltration method.
A relatively new treatment method in which the stain is first treated with an etching gel, and after it is washed off and dried, a special substance, like a liquid filling, is applied to the surface, which seals the pores of the tooth. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with medium or deep stage caries, it is too late to treat with conservative methods. In this case, surgical treatment will be required. The carious cavity is prepared with a drill, the affected tissue is removed and, after preliminary preparation of the cavity, it is closed with a filling.
Modern dentistry offers laser treatment as an alternative option. This method requires that the tooth is prepared not with a drill, but with a laser beam. The procedure is non-invasive and painless. The doctor determines which method is appropriate to use in each specific case.
Do pregnant women undergo anesthesia and X-rays?
Expectant mothers are frightened not so much by the fact of visiting the dentist as by the procedures that they consider dangerous for the child, in particular anesthetic injections and x-rays.
Medium and deep caries during treatment can cause severe pain, so in most cases it is treated with anesthesia. For pregnant women, local anesthetics are used that pass through the placental barrier to a lesser extent, are quickly eliminated from the body, and do not constrict blood vessels. Today, Ultracain, Alfacain, Ubistezin, and Artifrin are often used for pregnant women.
If teeth are treated by a professional dentist in a good clinic, properly selected anesthesia will not have a significant effect on the health of the fetus.
As for general anesthesia, it is not performed on pregnant women. Therefore, if treatment under general anesthesia is needed, it will have to be postponed until the postpartum period.
Radiography is usually not performed on pregnant women, but if necessary, it can be replaced by an alternative method - radiovisiography. It involves minimal radiation exposure and acts locally. This diagnostic method is used if there is a risk of developing an infection and the source of inflammation needs to be accurately determined.
How does it affect the woman and the fetus?
In the presence of infectious foci on the teeth, bacteria spread throughout the body, enter the bloodstream and contribute to various ailments. From such pathogenic effects, the fetus experiences a developmental delay, certain congenital diseases, and the child may be born with low weight or some abnormalities.
Also, from extensive caries, periodontal tissues or pulp become inflamed, which will lead to periodontitis, pulpitis and other diseases. And this, in turn, will be manifested by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- impaired functioning of the digestive system;
- appearance or exacerbation of toxicosis.
Separately, it is necessary to say about toothache. Its gradual increase will worsen the general psycho-emotional state of the woman, which will also negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the formation of the fetus. And the need to take painkillers will have a bad effect on the development of the embryo.
Those women who had caries during pregnancy and did not see a doctor know that it is much easier to cure it in the early stages than to allow various serious disruptions in the functioning of their or their child’s body. Therefore, you should not avoid visiting the dentist just because you are pregnant.
Features of caries treatment in different trimesters
- 1st trimester.
The period from the first to the 14th week is considered the most dangerous, since at this time there is a high risk of spontaneous abortion. The embryo is vulnerable and sensitive to the influence of stress factors and medications. Therefore, in the first trimester, teeth are usually not treated in order to avoid disturbances in the intrauterine formation of tissues and organs. The exception is emergency cases of acute pain or the development of a purulent inflammatory process. This usually occurs with complicated caries, turning into pulpitis.
- 2nd trimester.
During the period from 15 to 26 weeks of pregnancy, increased fetal growth occurs, but the risks associated with dental treatment are minimal. Therefore, during this period, caries can be treated and teeth professionally cleaned, taking into account the special situation of the pregnant woman.
- 3rd trimester.
In the period from 27 to 40 weeks, the weight of the fetus increases, it puts a lot of pressure on the internal organs of the pregnant woman, so it is difficult for a woman to sit in the dental chair. In addition, during this period the sensitivity of the uterus to external influences increases; there is a danger of premature birth due to stress if the patient is afraid to have dental treatment. Therefore, in the third trimester, as in the first, it is advisable to carry out dental treatment only for urgent reasons.
How to relieve toothache?
If you have any symptoms of an ongoing pathological process, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. But if it is not possible to do this immediately, then it is necessary to relieve the pain of a woman in a delicate position in safe ways. For this, folk recipes are offered:
- rinse the mouth with soda or saline solution;
- use decoctions of medicinal herbs for the same purposes - chamomile, sage, calendula, St. John's wort, etc.;
- apply chopped garlic wrapped in gauze to your wrist;
- you can hold a piece of lard in your mouth near the sore tooth;
- aloe leaf can also eliminate pain symptoms for a while;
- plantain and its juice have a similar effect.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, it is permissible to take painkillers, but in moderate dosage and for a short period. Among the safe medications are No-shpu, Tempalgin, Drotaverine, Pentalgin, Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Kalgel, Paracetamol, Grippostad (for the first trimester), Ketanov.
Before taking any of these medications, you should consult with your doctor or at least carefully study the instructions for the drug.
Video: is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
Is it possible to have teeth removed during pregnancy?
Sometimes, with advanced or complicated caries, tooth extraction is required. For a pregnant woman, this procedure is stressful, so teeth are removed only in extreme cases.
Indications for removal may be:
- large cyst (over 1 cm in diameter);
- fracture of the crown or tooth root;
- acute pain that is not relieved by other treatment methods;
- deep caries with suppuration.
Pregnant women, as a rule, do not have their third molars, the so-called wisdom teeth, removed.
This is due to the fact that after such an operation inflammation of the socket often occurs. To prevent inflammation, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, and it is not advisable to use them during pregnancy.
Dental diagnostics during pregnancy
Treatment of pulpitis and tooth extraction during pregnancy cannot be done without diagnosis. Traditional radiography (sighted x-ray) is not the best option for pregnant women. Fetal cells are in the process of dividing, so they are especially sensitive to radiation.
But if there is a need for such diagnostics, it is better to carry it out in the second trimester. Be sure to cover your stomach and pelvic area with a protective lead apron.
The safest option for women during pregnancy is digital radiovisiography. This method is characterized by minimal radiation exposure - 90% less compared to film X-rays.
Prevention of caries during pregnancy
The goal of preventive measures during pregnancy is not only to improve and maintain the woman’s dental health, but also to provide prenatal prevention of dental caries in the child. If pregnancy is planned, then it is recommended to cure all the teeth and carry out a complete sanitation of the oral cavity at the preparation stage. In this case, the risk of developing caries during pregnancy is reduced significantly.
It is advisable to begin preventive measures immediately after a woman becomes aware of her status as a future mother.
- Visiting the dentist.
It is recommended to undergo routine examinations with a dentist several times during pregnancy:
- from 6 to 8 weeks, the dentist will conduct an initial examination, clean the tooth enamel from soft plaque and hard deposits, and, if necessary, coat the teeth with special compounds containing fluorides, phosphates, and calcium;
- from 16 to 18 weeks, a woman visits a dentist for a routine examination and professional teeth cleaning;
- from 26 to 28 weeks - repeated examination and another coating of teeth with mineral compounds;
- From 36 to 38 weeks, a routine examination and repeated hygienic cleaning are carried out.
If dental problems are identified at one of the first appointments, the appointment schedule is expanded. Most often, dental caries treatment is carried out in the second trimester of pregnancy.
- Multivitamins with macro- and microelements.
It is important that vitamin-mineral complexes include calcium, vitamin D, fluoride and other components beneficial to dental health. Pregnant women can use any vitamin preparations only as prescribed by a dentist.
- Careful oral hygiene.
Pregnant women are advised to brush their teeth after every meal. Toothpaste for pregnant women should be low-abrasive, contain fluoride and calcium; for gum inflammation, additional pastes with herbal extracts are recommended. At the same time, pregnant women should not use toothpastes with triclosan, because they destroy the healthy microflora of the oral cavity. Be sure to clean only the surface of the teeth, but also the interdental spaces. To do this, you can use dental floss, floss, or a modern device - an irrigator.
Important! If you have toxicosis after vomiting, you should not immediately brush your teeth. Enamel that has just been exposed to hydrochloric acid is very vulnerable and susceptible to wear. Dentists recommend rinsing your mouth with a soda solution immediately after vomiting, and brushing your teeth only after 30 minutes.
- Nutrition correction.
To minimize the risk of caries during pregnancy, it is recommended to normalize the diet. Firstly, limit the consumption of sweets and starchy foods, which contain large amounts of carbohydrates - a source of food for cariogenic bacteria. Secondly, avoid snacking on sugary foods. Thirdly, balance the diet with macro- and microelements in order to receive large amounts of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus and other minerals from food that help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent the development of caries.
- Correction of acid-base balance in the oral cavity.
Pregnant women may have increased acidity in the mouth, which can damage tooth enamel. To restore the acid-base balance, you can select individual hygiene products with the optimal composition together with your doctor.
- Professional oral hygiene.
It is recommended to visit a hygienist for professional teeth cleaning at least three times during pregnancy.
- Applications to restore the mineral composition of tooth enamel.
Remineralization of enamel using solutions of calcium gluconate, calcium phosphate gels, and fluoride-containing preparations helps strengthen the enamel and stop the development of caries at an early stage. By following these simple preventive measures, you can maintain dental health in pregnant women, prevent caries, gingivitis and a number of other dental diseases.
Treatment of caries at different stages of pregnancy: is it dangerous and how is it carried out?
Caries during pregnancy is not only possible, but also absolutely necessary. Sometimes, due to the risk of acute development of the disease, timely treatment for some pregnant women is the only way to prevent generalized caries. Of course, the management of the disease itself must take into account the patient’s situation.
The main danger that arises when treating caries during pregnancy is the risk of exposure of anesthesia drugs to the fetus. All anesthetics are absorbed into the blood and can pass through the placenta, and some of them are quite capable of having an adverse effect on the developing embryo.
This is why, by the way, it is so important to see a dentist throughout pregnancy - if caries is detected at the earliest stages of its development, treatment can be carried out using remineralization methods without anesthesia, without a drill and without discomfort. But already advanced caries without anesthesia will be really painful to treat.
Often it is impossible to do without anesthesia when treating complications of caries: with pulpitis or periodontitis, this approach is unacceptable, since a pregnant woman may experience painful shock.
As a rule, dentists prefer not to treat moderate caries during pregnancy, especially if the pathology is chronic, until the beginning of the second trimester. It is in the first 12-13 weeks that the formation of all organ systems in the fetus occurs, and the risk of negative effects of medications on it during this period is maximum, although still small. Already starting from 14-15 weeks, the use of special anesthetic drugs allows for safe sanitation.
On a note
Dental X-rays are strictly not used during pregnancy. If the cavity is hidden from view, they try to resort to other methods. They even try not to study the quality of canal filling using x-rays.
Modern radiography using a visiograph has several times less radiation exposure. If there is an urgent need, it can only be done from the second trimester of pregnancy on this device.
Using local anesthesia, regardless of the stage of pregnancy, acute pulpitis, purulent periodontitis and periostitis are treated. When treating caries, even deep ones, the doctor begins treatment without the use of anesthesia and gives an injection only if the patient begins to feel pain when excision of carious areas of dentin.
Specially adapted drugs are used as painkillers for the treatment of pregnant women in dentistry, for example, Septanest and Scandonest at a dilution of 1:200,000. Pregnancy is not a contraindication for their use, and already 3 hours after the injection they are not detected in the blood.
Dentist's opinion:
Pregnancy is not a contraindication for other medications, judging by the instructions. The fact is that reducing the concentration of adrenaline, and in Scandonest - also preservatives, minimizes risks, but does not eliminate them. In any case, I observed on popular portals the position that articaine-type drugs are positioned as relatively safe for local anesthesia with relative risks, therefore they are taken in case of emergency, one of which is pain!
Towards the end of pregnancy, therapy is further complicated by the fact that when sitting in a dental chair, due to the specific position of the fetus, the load on the inferior vena cava and aorta increases, which leads to a decrease in pressure and possible loss of consciousness in the patient. To avoid this, the pregnant woman lies down in the chair slightly on her side, which reduces the load on the fetus. At the same time, the risk of teratogenic effects of anesthetics on the fetus becomes minimal by the end of pregnancy.
It is also useful to read: Is it possible to get rid of dental caries at home?
You can take painkillers yourself at home only if the pain is completely unbearable and it is impossible to see a doctor at the moment. If it comes to this, the doctor should see the tooth as early as possible. A good dentist will do everything possible to cure the mother’s tooth and not harm the unborn baby.
If you decide to take a painkiller yourself, then keep in mind that taking almost any drug in some cases may well have negative consequences. You can select “self-medication” in an individual case so that even a single dose of a strong painkiller will affect the health of the mother and fetus. Do not forget about individual intolerance and side effects for each drug, especially since painkillers have a whole range of them.
Review
“At one time I went to a clinic where pregnant women did not have their teeth treated at all until the 20th week. Before pregnancy, I didn’t think about it, but when I came in the third month with initial caries, I was turned around. They said that I needed to walk around for another two months, and then they would treat me. This is a disgrace! At the spot stage, caries is treated without anesthesia and without any medications; nothing affects the fetus at all. And in two months they will open my tooth and put a filling, God forbid the nerves will be removed. I had to change the clinic, the tooth was cured, without a filling and without anesthesia. Now I’m already playing with my little one, but my tooth remains healthy.”
Anna, St. Petersburg