July 22, 2018
Averyanova Sveta
If we talk about the development of children, norms and deviations, then every parent knows for sure that their baby should not be like everyone else, grow and change according to a single pattern. But some indicators are still important for tracking disorders in nutrition, the functioning of internal organs, and the psyche.
This factor includes the number of teeth in and before one year of age. Why is it so important to know how many teeth a child should have at 1 year of age, and how this relates to the baby’s health, we’ll talk in our article.
Norms for the number of teeth before and after one year
The first milk teeth normally appear in newborns up to one year old - at 6 or 8 months, with rare exceptions at 3-4 or closer to 12. The order of their appearance in the mouth is usually the same for all babies, but the timing is determined by nature.
According to the average pattern for all babies, the incisors appear in the following sequence up to one year:
- at 6–10 months - two lower central teeth;
- at 8–12 months - two upper central incisors;
- Between 9 and 16 months, the upper and lower lateral teeth emerge sequentially.
Thus, by one year the baby becomes the proud owner of eight incisors. Although the normal number of baby teeth in a 1-year-old child is not established on a single scale.
After the first birthday, teeth grow more actively. The cutting table looks like this:
- by 13–19 months - molars from above;
- by 14–18 - molars from below;
- by 2 years - upper and lower canines;
- at 2.5–3 years - the second set of molars above and below.
A full-fledged jaw from baby teeth will be formed by 30 months, the child will have twenty teeth in his mouth.
They will change to native ones closer to first grade.
Parents do not need to remember the rules. There is an interesting formula for counting teeth by baby's age. There should be four less than the months of the baby’s life.
For example, a girl is 10 months old, subtract 4 from her age and get the result: after 10 months there should be 6 teeth in her mouth. Do not forget that the figure will be average, and the amount in a certain period depends on the individual characteristics of the newborn’s development and heredity.
How many teeth does your child have at 1 year old?
- Over 6 46%, 711 votes
711 votes 46%711 votes - 46% of all votes
- From 4 to 6 27%, 419 votes
419 votes 27%
419 votes - 27% of all votes
- From 2 to 4 16%, 245 votes
245 votes 16%
245 votes - 16% of all votes
- From 1 to 2 9%, 141 votes
141 votes 9%
141 votes - 9% of all votes
- Not at all 2%, 24 votes
24 votes 2%
24 votes - 2% of all votes
Total votes: 1540
14.08.2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Permissible deviations from the norm
The first incisors appear by 6 months, and at 3 years the child should have 20 baby teeth, which appear in sequence. If the baby has 20 teeth by the age of 2.5 years, and at 3 years old there will be 16-18 odontopagus teeth, then there is no need to panic, since small deviations are normal, each child develops individually.
You need to worry if less than 10 teeth have come out by 36 months. It is considered normal if by 12 months the baby has acquired one incisor. A deviation from the norm is considered to be up to 6 months up or down.
Often, a baby's first tooth appears too early. This is also considered normal. As statistics show, children born in winter-spring begin to grow teeth ahead of schedule, and those born in summer-autumn start growing later. But if by 10 months not a single tooth has come out, then you need to consult a doctor, as this may indicate problems with the endocrine system or other diseases.
There are rare cases when a baby is born with teeth. In this case, you should definitely consult an endocrinologist. During the development of the dentofacial apparatus, attention should be paid to the growth sequence of odontopagus. The incisors should appear first, followed by the lateral teeth, first molars, and then the canines and second molars.
A slight deviation from this sequence is not considered an anomaly, but in order to prevent the development of serious pathologies, you need to be periodically observed by a pediatric dentist.
Why don't teeth grow?
The absence of at least one tooth by the age of one year should cause concern on the part of parents. The anomaly may be associated with malfunctions of internal organs or serious diseases, indicating:
- lack of calcium, vitamin D;
- intestinal problems;
- infections;
- improper metabolism;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- distorted arrangement of teeth in the gums (horizontal, with a slope);
- dentition - a congenital mutation indicating the absence of dental germs.
More often, delayed eruption is associated with heredity. Ask your grandparents about how many teeth you had in childhood, find an outpatient card, entries in development diaries. If by the age of one year the father or mother was toothless, then there is no need to wait for their baby to have dental dentition soon.
If at 1 year of age the child has no teeth and there are no signs of early teething, consult a doctor to identify diseases and analyze the medical history.
To exclude congenital edentation, an x-ray examination is performed.
The picture shows the beginnings of baby teeth and molars awaiting their turn. If a serious illness is diagnosed, the baby will have to have implants extended or inserted.
Interesting fact! According to research by pediatricians, girls develop teeth faster than boys.
And here is what the famous doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky thinks about this. Watch a short video:
Causes of abnormal teething
Timely teething is a sign of good child development. But if teeth appear prematurely or a little later, then this is also considered the norm, because each baby develops individually. But sometimes various kinds of deviations arise that require treatment. The causes of abnormal teething are:
- deficiency of calcium, potassium, vitamin D,
- disrupted metabolic process,
- rickets, gastrointestinal problems,
- chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx,
- congenital or acquired diseases,
- poorly developed gum muscles,
- curvature of the lower limbs,
- developmental delay,
- chromosomal abnormalities.
Early eruption of odontopagus may indicate impaired functioning of the endocrine system, a growing tumor, and may also occur as a result of excess calcium intake during pregnancy. The reason for the late appearance of incisors may be an infectious disease or a disease transmitted to the mother during gestation.
If by 12 months not a single tooth has appeared, then the reason for this may be the absence of rudiments, which can be diagnosed by a dentist. It is possible to find out the cause of abnormal teething in a child only after a thorough examination.
What microelements are needed for teeth growth?
Vitamins and microelements are a necessary component for the development and normal functioning of the child and adult body. The formation of dental tissue cannot do without:
Fluorine
Strengthens enamel, makes incisors resistant to bacteria, the destructive effects of acids, and prevents caries. Fluoride is taken in tablets or drops when a deficiency is diagnosed. Enters the body with sea fish, nuts, grape juice, spinach, and most vegetables.
Toothpastes with fluoride are not approved for use by children under 4–5 years of age. Children aged 1.5–3 years swallow the tasty mass when cleaning their mouths, and an excess of the element is formed in the blood. For foolish children, choose toothpastes without fluoride to protect them from the negative consequences of hygiene procedures.
Calcium
It is the building material of infants' teeth. Without calcium, mineralization in tissues is impossible. After finishing breastfeeding, a one-year-old child should receive dairy products daily, greens and fish at least three times a week.
Vitamin K
Necessary for complete absorption of calcium and protein synthesis. Found only in natural dairy products (cottage cheese, sour cream and others).
Teething for young parents seems like an extremely difficult and nervous process. They prepare for it mentally, they are afraid of hysterics and hyperthermia.
Young and inexperienced parents do not need to worry or be negative. It is better to study the issue of dentition in infancy in order to arm yourself with knowledge and understand why the baby cries and is nervous. In this case, jaw development will be perceived as a normal physiological stage of growth, which will be experienced easily and quickly.
Possible problems of the chewing apparatus in children aged 3 years
A significant lack of baby teeth in a child may indicate a lack of vitamins and minerals in the baby’s body, metabolic disorders and problems of the nervous, endocrine or cardiovascular systems. Of course, this is a reason to visit a doctor. Any deviations and pathologies must be identified and treated in a timely manner.
Along with the number of mammary odontopagus in the child, parents should be concerned about their condition. It is at the age of three that children begin to experience the first problems with their teeth, such as caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, as well as other problems of the masticatory apparatus:
- Teeth with black edges indicate a lack of iron in the baby’s body.
- The presence of a large gap between the upper incisors is an anatomical defect and is corrected by an orthodontist.
- Darkening of tooth enamel occurs as a result of the mother’s treatment with antibiotics during pregnancy, and a greenish tint indicates problems with metabolism, metabolism, or diseases of the baby’s circulatory system.
- Hypoplasia (gray soft dental tissue) is a consequence of poor nutrition of the mother while expecting a child.
- A child’s malocclusion also needs to be corrected; this problem will not be solved on its own and will grow with the baby. In adulthood it is much more difficult to eliminate.
Caring parents are advised to visit the pediatric dentist with their child at least once every three months, and conduct a weekly self-examination of their child’s oral cavity.
Time of start of eruption
The appearance of the first tooth is a holiday for the whole family, but only a loving mother and an attentive father know how much anxiety and worries are associated with this event. A couple of days, or even weeks, before the first external signs of teething appear, children cry, are capricious, and lose their appetite. Moms are having a hard time—sleepless nights.
The central tooth below can grow even at eleven months. The timing of teething is individual for each baby. For almost all babies, only the symptoms of a tooth appearing remain the same. And even a professional doctor cannot determine exactly how many months the process of jaw formation will begin.
Features of the growth of permanent dental units
Up to 6 years of age, the first molars erupt in the free areas of gum formed as a result of jaw growth. You need to be wary if the teething period is 6 months longer than normal.
Due to the child's developmental characteristics or recent dental treatment, the loss of baby teeth may be delayed. Later than others (up to 25 years), 3 molars appear - wisdom teeth. Unlike other permanent teeth, which grow unnoticed, their appearance in most cases causes pain to the patient, which is why they are often removed.
It is not uncommon for permanent teeth to appear before baby teeth fall out. In this case, you need to remove the baby tooth as soon as possible. Gradually, under the pressure of the tongue, the permanent tooth will move into place. If you do not consult a doctor in time, the child’s bite will deteriorate, which will require long-term orthodontic treatment.
With the appearance of permanent dental units that are larger than baby teeth, the interdental spaces that form during jaw growth disappear. With small or no distances, the incisors and canines overlap each other. Curvature of the dentition also occurs due to mechanical stress. To prevent injuries during sports, the child needs to wear a special mouthguard.
Temporary teeth - canines, molars, lateral and central incisors, which are replaced by molars. Their appearance is a painful process, which is accompanied by a decrease in immunity. But they are also important for the baby. The purpose of temporary incisors, canines and molars is to:
- ability to chew food;
- proper speech development;
- formation of the facial skeleton and bite;
- acquiring chewing skills;
- aesthetics of the oral cavity.
First signs of teething
You can recognize the imminent appearance of a tooth in a baby by the following external signs and changes in behavior:
- Crawling babies put their fingers and everything they see into their mouths. Their gums itch.
- Saliva floods my blouse and prevents me from sleeping at night.
- Sleep and appetite are disturbed.
- The gums swell and turn red.
- A couple of days before teething, a runny nose appears and sometimes a cough.
- The stool becomes liquid, mushy with a yellow, green tint.
- The temperature rises within acceptable limits.
- Whims, tears, crying are suddenly replaced by laughter and good mood. The child does not know what he wants, often asks to be held, and worries without his parents.
A baby, even at one or one and a half years old, experiences stress. Mothers need to understand and forgive the baby for his whims and disturbing dreams. Try to help during this difficult period for everyone. Do not get angry or yell at your daughter or son under any circumstances. Newborns do not yet know how to patiently endure toothache and discomfort and require the attention and care of their parents.
Oral care for a three-year-old child
At the age of three years, the child is quite capable of brushing his teeth twice a day and rinsing his mouth after each meal. To do this, you need to start teaching your baby about personal hygiene from the age of one. Some tips for parents whose kids don’t like brushing their teeth:
- Carry out the procedure in a playful way and turn it into an exciting process for the baby.
- Go to the store with your child and buy a toothbrush and toothpaste that he likes. It should be remembered that a child's brush should be small in size with soft bristles, and the toothpaste should be age-appropriate, as children often swallow it. For a three-year-old, a pea-sized amount of paste will be enough for one cleaning.
- Brush your teeth yourself together with your child, because children try to imitate their parents in everything.
- While the baby does not have enough experience, after his independent attempts to carry out control cleaning with his own hands.
- Explain to the child the need for the procedure, read a book to him or watch a cartoon together about animals that did not brush their teeth and therefore got sick.
Taking care of a child's baby teeth is a fundamental basis for the formation of permanent dentition in a growing person.
While watching the video you will learn about teething in babies.
With the right approach from parents, the baby will very soon master the rules of oral hygiene and this useful habit will remain with him for the rest of his life. The child will grow up without fear of dentists, without toothache, and will constantly delight his parents with his shining Hollywood smile.
Peculiarities
Sometimes this appearance of teeth is accompanied by the following features:
- If the baby's jaw grows quickly or the frenulum of the upper jaw is deeply set, large interdental spaces may occur.
- Girls develop teeth earlier than boys.
- Too late teething in a small person may be associated with a disease such as rickets.
There is a pattern in the appearance of teeth in children born in different seasons. Spring and summer babies acquire teeth with a slight delay; autumn and winter children may develop teeth a little earlier.
When the first tooth appears, signs of the beginning of eruption
Your baby's first tooth should begin to emerge at the age of 6 months.
You can notice the beginning of this process by a number of characteristic signs, such as:
- increased salivation;
- restlessness during sleep and its sensitivity;
- moodiness and tearfulness;
- increase in body temperature to 37.1 degrees;
- the appearance of clear snot;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- the baby is trying hard to scratch his gums using anything he can find - a toy or his own finger;
- If you look into your child’s mouth, you may notice the appearance of red or white stripes in the place where a tooth will soon appear.
The video below is an interview with a dentist, which talks about the process of teething in children. Filmed by the channel “Dentistry “All Yours”.
Possible problems
Sometimes the process of eruption occurs with significant deviations from the norm. In such cases, it is necessary to consult with a specialist to exclude concomitant pathologies in the child.
Parents should be wary if:
- the child was born with one or more teeth;
- first molars appear at the age of 2-3 months or do not appear until 1 year of age;
- the order of teeth eruption is disrupted;
- the teeth come out with a clear visible deviation from their place;
- the color or shape is different from the norm;
- the interval between the appearance of teeth is noticeably longer;
- teeth do not erupt in pairs;
- teeth grow unevenly or deviate to the side.
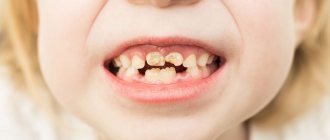
Several such cases are shown in the photographs below.
Premature emergence of a molar tooth
Hyperdontia - extra teeth in a row
Uneven row of teeth
How many baby teeth do children have?
Milk teeth and even some molars begin to form at the stage of intrauterine development. Of course, a child has no visible teeth at birth - they begin to erupt only after 6 months. During this six-month period, they are hidden under the gums, but slowly develop and form, beginning to move outward.
In total, a child grows 20 baby teeth:
- Central and lateral incisors – 8.
- Fangs – 4.
- First and second molars – 8.
Their main function is to form a space where molars will then grow.
The concept of baby teeth and what they look like
Milk teeth are the first teeth that fall out over time and are replaced by permanent teeth, starting around the age of six. At about six months, the process of teething begins and is completed by the age of three. Growth and loss, as a rule, coincides with the schedule, sometimes there are minor deviations, but this is normal. If a baby tooth erupts earlier or much later than scheduled, then this is a reason to visit a doctor and find out what’s wrong.
Parents often believe that their children’s teeth lack roots and nerves, since most often the child does not feel much pain when they fall out. He does not feel it if a tooth is pulled out by a doctor, at a time when tooth extraction in an adult can cause severe pain.
Baby teeth have everything, but the fact is that they tend to decay quickly , so by the time they fall out they are already very loose and fall out almost painlessly.
Mineralization of baby teeth begins during pregnancy, and their condition depends directly on the characteristics of its course. Then, during eruption, the crowns of the baby teeth are filled with salts, and the roots of the baby teeth grow. Then, when growth stops, a certain quiet period begins, and then the roots begin to dissolve and the milk teeth fall out.
After a few years, when the time comes to replace milk teeth with permanent ones, the latter, as they grow, begin to push away the milk teeth and provoke the destruction of the roots, as a result of which they easily become loose and fall out. If the tooth was subject to treatment, it will fall out more heavily; sometimes there are cases when it needs to be removed using an anesthetic, as when removing adult teeth.
In terms of their structure, children's teeth are practically indistinguishable from permanent teeth; they do not differ even in the number of roots. However, there are still differences and they are as follows:
- the crown is smaller than a regular one;
- the roots diverge due to the rudiments of permanent teeth that are located between them;
- the enamel is thinner;
- The pulp in children is larger in volume;
- wide root canals.
How many teeth should a child have?
It all depends on age. The maximum number of teeth in the period from birth to 5-6 years is 20 - these are milk teeth. Then, until the age of 15-16, the molars begin to erupt, pushing out the milk teeth. Ultimately, their number grows to 28.
The latest are the third molars. They grow only after 18 years of age, but not everyone has them.
It is worth noting that the period of formation and eruption of baby teeth is very individual. In some children, all 20 teeth grow by the age of 2, while in others - by 2.5 or later. Such delays within a year are considered normal and are not a developmental anomaly.
If teeth do not start cutting in the first year of the baby’s life, you should consult a doctor to find out the reasons.
To the list of posts