490
The appearance of the first baby tooth in a newborn brings indescribable delight to his parents.
At the same time, quite often joy is replaced by anxiety and concern for the baby’s oral health.
This is due to a number of problems that require prompt elimination. Such diagnoses also include malocclusions in children.
Stages of development
The milk bite has two phases of development:
- developing occlusion – manifests itself in the phase from one year to 2.5–3 years. It is at this interval that all the child’s temporary teeth erupt, and the process enters the stage of their active growth;
- formed - the stage at which all the mammary organs protrude to the surface and are in their proper places.
This period is characterized by the rapid development of the jaw apparatus, preparing the ground for the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones. Such manifestations occur in the senior preschool age and last until approximately 13–14 years.
The formation process has its own specific features - the time parameters for the appearance of adult units, their pairing and the sequence of eruption.
Development of primary occlusion
The primary occlusion is one of the most important periods in the formation of the dentofacial system. The fact is that even the slightest deviation that occurs at this time can lead to the development of serious violations in the future.
To assess the correct development of the primary occlusion, the following characteristics are used:
- timing of eruption: normally, the first milk tooth erupts at 6 months, and the last at 30 months. The norm is also a deviation of 3-5 months. Violation of eruption juices is the main sign of the presence of anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus;
- pairing: during the period of primary occlusion, simultaneous eruption of antagonist teeth occurs on both sides of the jaw. Growth retardation of one of them for a period of no more than 1 month is the norm. A more significant violation of pairing may signal disturbances in the development of the jaw, for example, slow growth of bone tissue.
Timing of teething
By the end of the baby’s first year of life, all the central fragments of the jaw row should normally have erupted. As a rule, the first tooth will appear at 6-6.5 months.
A deviation of 8–10 weeks in one direction or the other is not a pathology; it is determined by the anatomical features of the structure of the facial apparatus and the general physical development of the child.
Only after this the lateral teeth begin to appear above the surface. This stage occurs quite quickly - within 4–5 months the baby already has at least eight lateral incisors.
Then the organs appear according to the following scheme:
- At about 18 months, molars erupt, followed by canines. At the same time, there is practically no risk of lack of space in the jaw row.
Long before the birth of the first molar, the canine is already localized in its proper place, in the inner part of the alveolar.If a mesial variant of the formation of a molar is observed, the click spontaneously moves it slightly back, giving room for the growth of the second tooth;
- the next molar erupts only after the canines emerge. In the baby, an increase in the bite becomes visible against the background of some lengthening of the lower jaw area;
- Replaceable molars mean a lot in the process of forming a correct bite . They adjust its height. That is why their structural and anatomical features play a primary role.
Malocclusion in children: when and how to correct it
— At what age is it easier to eliminate bite problems?
— A child grows actively from 7 to 12 years old, so removable devices for straightening teeth, called plates, can simply correct the pathology. The most optimal age for starting treatment for malocclusion is 7 years. The record is usually placed for 1 year.
- But it happens that children from a younger age wear removable plates - from 4-5 years old. Is it ineffective?
— At this age, there are still baby teeth, and bite correction is ineffective. Most often, children aged 4–5 years are given removable dentures in case of early tooth loss in order to restore chewing efficiency.
— Does a child feel any pain when a record is played on him?
— An orthodontist is the best dentist for children. He doesn't hurt. During installation and the entire treatment with the plate, the child does not experience any unpleasant painful sensations.
— How does the record “work”?
— This is a removable orthodontic device that is placed on the teeth. With the help of various elements built into it, the jaws expand, the bite is corrected and individual teeth move.
- How to care for her?
— The plate can be single-jawed or double-jawed - it all depends on the pathology. It is worn from 12 to 24 hours a day. A screw can be built into the device, which parents activate once every 4–7 days. The plate should be washed morning and evening with a brush and soap.
— Can orthodontic trainers help solve bite problems at an early age?
— Trainers must be worn 12 hours a day. They are aimed at eliminating the tone of the muscles of the cheeks and lips, which inhibit the growth of the jaws. But if a child has mouth breathing, frequent ARVI or nasal congestion, then such a device will not be suitable, since it completely occupies the oral cavity and breathing is possible only through the nose.
— What are braces?
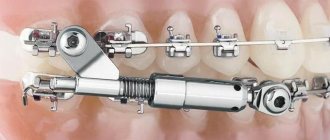
— From the age of 12, non-removable equipment - braces - is used to treat malocclusion. Braces can be metal or ceramic. With the former, treatment is faster, but they are less aesthetic compared to the latter.
On average, braces are installed for 1.5 years, but this period may increase depending on the complexity of the treatment. While wearing them, the patient must visit the orthodontist every 1-2 months for activation. There is no pain when installing them. But they may be in the first couple of days of wearing.
— There are also modern partial brace systems, which are used at an earlier age, but are attached only to molars...
— Children do not always follow the doctor’s recommendations for wearing removable orthodontic appliances; in such cases, partial braces can actually be installed. They can also expand the dentition and correct the bite. But this method is more expensive.
Subsequence
The growth of baby teeth always occurs in pairs. If this process fails due to defects in the formation of hard tissues of the jaw, the child is diagnosed with atypical development of dental elements.
As a rule, the organs of the lower jaw appear first, then the upper. The exception to the rule is the side fragments. Everything happens there in reverse order.
If the described growth method is disrupted, we can talk about abnormal processes of atypical growth of the entire dentofacial sphere.
What is tortoanomaly, and what methods are effective for correcting the pathology.
Let's talk here about the consequences of malocclusion in children.
Find out how to correct a deep bite here.
Deviations will be:
- Anterior position of the lower jaw (mesial bite) - as a result of impaired growth of the upper or lower jaw;
- Open bite - most often as a result of excessive sucking of fingers, pacifiers, pencils and impaired tone of the masticatory muscles;
- Crossbite - when the center lines of the jaws do not coincide due to a narrowing of the upper jaw and, as a result, displacement of the lower jaw.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Dental treatment for children under anesthesia.
These disorders are worth seeing an orthodontist. Slight crowding of primary teeth is not considered a pathology and does not require any intervention. So, from the age of 6 months to 6-7 years, the child has a milk bite. If you have an open bite or anterior position of the lower jaw at the age of 3-4 years, you can see an orthodontist.
Specifics of formation
Each of the previously discussed types of children's occlusion has its own distinctive features. So, at the formation stage it is characterized by:
- rather close localization of organs relative to each other. Sometimes this arrangement can be interpreted as crowding of the dentition;
- indelibility of the enamel surface;
- with complete closure of the jaw rows, there is no overlap of the lower fragments with the upper units.
A fully formed bite can be distinguished by the presence of the following signs:
- the enamel surface has focal manifestations of abrasion, in most cases quite pronounced;
- the appearance of cracks and diastemas in the frontal area of both the upper and lower organs;
- Behind the second molars, a void gradually begins to form, necessary for the appearance of the first pair of permanent teeth.
Changeable bite - what is it like?
Changeable or temporary dentition in children is characterized by the fact that at the same time there are both milk and permanent teeth in the mouth. This period begins at 5-6 years: from the moment teeth begin to fall out. Stages of formation:
- The first stage includes the appearance of incisors and sixes, it lasts up to 9-10 years.
- The second stage is characterized by the appearance of lateral teeth and lasts up to 12-13 years.
The shift period has its own characteristics. It is characterized by:
- active jaw growth;
- tooth mobility, root resorption.
A frequent phenomenon that causes concern among parents: baby teeth remain in the mouth, and permanent teeth begin to grow behind them. This is a common occurrence. To select an adjustment, you need the help of a specialist. In cases where a baby tooth is displaced by a permanent one, the dentist will recommend removal. But there are cases in which no action needs to be taken.
The loss as well as the increase in shifts must be closely monitored.
The mechanism of change looks like this: the root endings are gradually destroyed due to the fact that the germ of a permanent adult tooth is adjacent to them. The vessels appearing in the hole contribute to the active destruction and resorption of the root.
The replacement stage of development ends only when all baby teeth fall out.
Peculiarities
Factors determining the condition of the primary occlusion:
- the upper jaw row is always larger than the lower one;
- the shape of the facial apparatus is regularly semicircular, with a pronounced increased upper radius;
- if you mentally draw lines between the frontal lower and upper incisors, normally they will be located in the same plane;
- each unit of the jaw row autonomously contacts a pair of antagonists. This statement does not apply to the upper second pair of molars and lower frontal incisor units - they come into contact with only one antagonist;
- The upper first molar overlaps the lower second analog fragment by a third and the lower first by two thirds. At the same time, it completely closes with the lower molar pair;
- the frontal units and molars, the surfaces responsible for the function of chewing food, are located in the same plane.
Number of units
The speed at which the first teeth appear is determined by the amount of hormone produced by the thyroid and pituitary glands, the age of the child’s parents, and even gender.
It has been scientifically proven that boys are quicker to bite than girls. At the same time, the time of appearance of the mammary organs does not affect their health in any way.
So, what should their number be at a certain stage of the baby’s growth? Average:
- the very first tooth will appear in about six months;
- by nine months the upper two units will have erupted;
- at 10–11 months, the upper lateral fragments, located adjacent to the frontal incisors, will be visible on the surface;
- by one year the baby will have 8 units;
- By the age of two, the child’s oral cavity will be replenished with two dozen temporary elements - these will be incisors (4 pieces), molars (4 pieces), canines (2 pieces). Taking into account the fact that the eruption process proceeds symmetrically, there will be 10 teeth in each jaw row.
Upon reaching the age of three, children’s occlusion is almost complete and includes 20 units. Thus, both rows, top and bottom, are considered filled.
Permanent teeth
The beginning of the formation of a permanent dentition is considered to be the appearance of the first permanent molars. Stages of development:
- Eruption of the last permanent molars.
- Pre-formulation stage. Development of jaw arches, appearance of wisdom teeth.
- Formed. The processes of restructuring and the formation of jaw bones stop.
The approximate mark for the completion of the formation of a permanent dentition is 25-26 years.
Teeth are divided into 4 types, each of them has an individual shape and performs its own functions:
- incisors (8 pieces), with their help a person bites off food;
- fangs (4 pieces), located behind the incisors, they are characterized by sharp edges, with their help the structure of food is torn;
- premolars (8 pieces), located sequentially behind the fangs, facilitate chewing and grinding food;
- molars (12 pieces), the most of them in the mouth, help to completely grind and crush food.
What the units in the formed jaw row will look like determines the course of the previous stages of development, so it is important to monitor the situation and also solve problems in a timely manner. The size of the dentition decreases with age, this is due to the abrasion of the enamel.
An incorrect permanent bite develops if failures occur at any stage of development. Corrections are carried out by orthodontists. Techniques that help correct the situation are:
- wearing braces;
- use of silicone caps.
These methods are recommended when the permanent dentition is not yet fully formed.
Main differences
The main difference between a child’s bite and a permanent one is the number of units that should normally erupt. An adult has 32 teeth, a child has 20.
There are also not so specific differences that separate both of these states:
- The milk units are more convex, their relief is clear and bumpy , while the crowns of an adult are smoother, almost even surfaces.
- The zone where the coronal part borders the neck is more pronounced in replaceable units;
- Temporary teeth are somewhat smaller in size , and not only the part that is on the surface, but also the root system. That is why their removal is almost painless, and soft tissue trauma at the time of amputation is minimal.
- Color - temporary elements are bluish-white and shiny, while permanent elements are distinguished by increased yellowness or a slightly earthy tint.
- Susceptibility to external negative factors in milk fragments is more pronounced - babies more often suffer from caries and damage to periodontal tissue.
- Strength of enamel – despite the fact that children’s teeth look much smaller, their hard tissue is an order of magnitude stronger than an adult’s. They are less likely to crack and chip.
Indications for surgical correction of malocclusion, and patient reviews of the effectiveness of the operation.
In this publication we suggest looking at a photo of a child’s malocclusion.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/kak-vyirovnyat-zubyi-bez-breketov.html we will tell you how to straighten teeth in teenagers without braces.
The first functional period of the mixed dentition. Formation of occlusion, face, symmetry and asymmetry, correct occlusion and pathological, the influence of diction and posture.
, the first permanent molar erupts behind the temporary molars (it is never primary, but immediately grows permanent) . At the same time, the replacement of the front teeth begins. Permanent teeth have a more pronounced surface relief compared to milk teeth, so their eruption is characterized by the appearance of functional obstacles to the function of teeth. The bite is formed by changing the pattern of chewing movements. The palatal surface of the upper front teeth and the incisal edge of the lower ones determine the nature of the forward movement of the jaw, which contributes to the correct or pathological formation of the jaw joint and the parameters of the jaw itself. Therefore, during the period of 6 years, it is very important to conduct a functional diagnosis of the jaw joint and bite.
Drawing an analogy with the forward movement of the jaw in adults is incorrect, since at this age the angle of the articular path is very small due to the underdevelopment of the articular tuberosities (Kubcin-Mccscnburg). It is necessary to understand that the front teeth do not experience much load, because are not actually a “guide” (in mixed dentition), but provide only proprioceptive control.
The eruption of the first permanent molar (sixth teeth) behind the primary teeth finally changes the nature of the lateral and posterior movements of the jaw. After the completion of eruption of the first permanent molars and anterior teeth, the morphology of the entire system changes.
During this period, the dentist should carefully monitor the eruption of functional teeth.
Properly erupted mandibular molars have four primary functions: laterotrous guidance, retrusion protection, bolus movement, and soft tissue (tongue and cheek) protection. However, even in the event of improper eruption, compensating mechanisms ensure optimal functioning. In turn, these processes can lead to the development of dental-alveolar pathology and jaw asymmetry. Even so, they should be considered functional rather than pathological. The question is how they will function individually. In this connection, it is very important during this period to control the symmetry and certain laws of teeth closure.
In this period, the acceleration of the development of the lower jaw is of great interest. The growth of the lower jaw branch leads to an increase in the distance from the joint to the plane of closure of the teeth. The listed changes should be considered an adaptation to the morphology of the first permanent molars and anterior teeth.
Asymmetry of the dental arch can lead to malocclusion or malocclusion. If the inclination of the occlusal plane is different on the right and left, then the articular tubercles may develop asymmetrically, which in turn will affect the development of function and pathology with further age. It is obvious that asymmetry of the articular path can subsequently significantly complicate dental treatment. Timely diagnosis and treatment of asymmetry prevents such situations.
Correct posture during this period has a beneficial effect on the development of the masticatory organ. Poor posture, especially when reading and writing, can contribute to the development of dysgnathia. Writing and speech are closely related to the lateralization of the brain. In cultures with a horizontal writing direction, congenital alexia (dyslexia) leads to impaired posture and shape of the skull. When choosing a place for a child in the classroom, the dominant eye and ear are of great importance. The child tries to turn his dominant ear towards the teacher. From the standpoint of preventing pathology of the maxillomandibular system, a static position in the classroom is unacceptable.
In the first period of mixed dentition, speech development
.
It is significantly influenced by the position of the front teeth. Diction disorders lead to specific stress and certain stereotypical muscle contractions
. By the end of this period, the child’s diction is almost completely formed.
The roots of the teeth also develop not in a straight line, but in an arc corresponding to the slow verticalization of the system. As the height of the bite (occlusion) increases, the distance to the jaw joint increases, the inclination of the crowns of the teeth changes, and the roots of the teeth continue to develop along the axis of closure.
The shape of the crowns is determined genetically. The shape of the roots of teeth and the entire dentoalveolar complex is constantly changing. With asymmetrical development, the morphology of the roots is also asymmetrical, which affects dental treatment.
After the eruption of permanent front teeth, the principle of their functioning changes significantly. Movement of the mandible is controlled proprioceptively by the normal vertical overlap of the incisors. The front teeth do not experience significant mechanical stress.
Continued in the next part.
Important – marked in bold.
The formation of a child depends on his proper life support. Remember the documentary about African tribes who stretch the length of their necks from an early age with the help of rings. This is also how joint and jaw structures are formed or deformed during feeding and growth. The following articles will reveal more about the significance and value of a child’s functional formation.
READ ALL PARTS OF THE ARTICLE:
Part 1 /roditelyam-s-detmi-chast-1/ Part 2 /roditelyam-s-detmi-chast-2/ Part 3 /roditelyam-s-detmi-chast-3/ Part 4 /roditelyam-s-detmi-chast- 4/ Part 5 /smennij_prikus/ Part 6 /roditelyam-s-detmi-chast-6/ Part 7 /roditelyam-s-detmi-chast-7/
Diagnostics for joint treatment on the page (it can also be used by children over 5 years old): /concept/diagnostics/
As a doctor, I am often asked why our child, already at the age of 5, has certain disorders, as you say. Maybe it’s genetic or nature created it, so it must be so. This is a very big and in-depth question. My following articles and republications of world knowledge will open the curtain on all issues of the development and formation of the child’s body, starting from the first days of life. This knowledge will help to form an ideal person with great physical immunity. Levchenko Lev Vladimirovich. Follow the articles on Instagram (https://instagram.com/levchenkolev_com/) (#levchenkolevdental) and on my blog on the website: /blog/
Causes of pathologies
The main factors that negatively affect the condition of children's bite are:
- congenital anomaly - the disease can be transmitted to the child even at the stage of intrauterine development if one of the parents has a similar pathology;
- bad habits - using a pacifier for too long, ignoring the baby’s attempts to suck a finger, toys can form into a persistent dependence, and lead to deviations in the location of the dental organs.
What are malocclusions?
The curvature of the dentition can be identified independently.
The most optimal age for identifying anomalies in the development of the jaw arch is considered to be the age of 3 years, when the child has already grown all his milk teeth. At this stage, any orthodontist will be able to determine the presence of disorders, their nature and severity. But parents themselves may notice some deviations in the position of the teeth and consult a doctor at an earlier age.
Signs of malocclusion in a child may include the following:
- curvature of the dentition or certain areas;
- moving teeth forward or backward;
- incorrect location of one of the teeth relative to the entire dentition;
- interdental gaps.
Each of these external defects can be a symptom of a certain pathology, the most common of them are listed in the table:
| Bite pathology | Main features | Possible complications |
| The upper row of teeth is strongly pushed forward, overlapping the lower one. Appears due to developmental disorders of the lower jaw or excessive growth of the upper jaw (read more here). | Increased tendency to caries, periodontal disease, swallowing dysfunction, possible discomfort in the temporomandibular joint. |
| The lower row of teeth is pushed forward, and a visual distortion of the shape of the face occurs when the chin is slightly pushed forward. | Impaired chewing of food, a tendency to periodontal disease, possible clicking when using the jaw. |
| Strong overlap (more than half) of the lower dentition with the upper one due to underdevelopment of the lower jaw. Externally it manifests itself in shortening of the lower part of the face and curvature of the lips (read more here). | Difficulty in chewing food, high wear of incisors, accelerated tooth loss, headaches. |
| Both jaws develop unevenly, and obvious facial asymmetry appears | Tendency to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, difficulty chewing food. |
| When the jaws are closed, the dentition does not close, leaving a gap between the front or side teeth (read more here). | Impaired diction, chewing and swallowing food. |
| Displacement of one of the teeth in a row, or its position outside the dentition. | Discomfort, disturbances in the development of other teeth, injury to the gums, cheeks or tongue, inflammatory gum diseases. |
| The space between the teeth visually looks like a gap from 1 to 6 mm. | Speech disturbances, difficulty chewing food. |
Any pathology can have varying degrees of severity, and there can also be disorders of a mixed type.
Even if a child’s bite is initially formed correctly, visits to the dentist for examinations should be regular. Shifting teeth can occur at almost any age, for various reasons.
Correction Methods
If deviations were diagnosed at the stage of bite formation, then it can be corrected by using braces.
After eliminating the provoking factors, the organs will continue their growth and development in the direction specified by the design.
The use of leveling plates has a good effect . Made from soft material, the devices fragmentarily direct the fragments into the desired trajectory, preventing the pathology from progressing to an advanced stage.
At the stage of formation of the anomaly, you can limit yourself to a course of myotherapy - therapeutic muscle exercises.
Price
The cost of treatment is determined individually and depends on the following factors:
- clinical picture of malocclusion;
- chosen correction method;
- the material from which the structure will be made;
- region of residence;
- the status of the clinic where the treatment will be carried out.
On average, the service will cost:
- correction with braces – from 30,000 rubles
- use of leveling plates – 8,000;
- myotherapy – from 4,500 rubles.
Measures to prevent anomalies
At the stage when the formation of the primary occlusion begins, it is important for parents to remember the following rules:
- at the time of feeding, the breast or nipple should be positioned strictly perpendicular to the oral cavity;
- the supply of milk should not be too abundant;
- carry out regular prevention of rickets;
- exclude the development of bad habits in the baby - thumb sucking, toys;
- give the head the correct position at the time of sleep, it should not be thrown back;
- try not to use a pacifier when the baby is sleeping.
Regular visits to the dentist will help to diagnose the anomaly in time and take timely measures to eliminate it.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Causes of anomalies
The period of mixed occlusion implies the formation of anomalies of the masticatory system due to the uneven distribution of temporary and permanent units, therefore, at this age, dental control over the developing occlusion is especially important.
Due to the fact that temporary and permanent units have different densities, the mammary organs are erased much faster than newly formed ones.
This entails uneven development of the masticatory muscles, which can be compensated independently, or may require orthodontic intervention.
In addition, any removal of units before they are completely replaced leads to the formation of anomalies. For example, if one or more organs are removed before the age of 6 years, then asymmetry of the entire row will arise and the jaw will “move” towards the removed unit, because fragments erupting nearby will strive to occupy the free space.
If several units are removed on one side before the age of 12, then a pronounced asymmetry will be observed, which will affect not only the growth of bone organs, but also the formation of the masticatory muscles, facial contours, etc.
Excessive breastfeeding (more than a year) is also a factor in the formation of malocclusions. This also includes thumb sucking, toys, etc.
The rudiments of the permanent units are displaced, as a result of which the entire row (mainly the incisors) is deformed and shifted back. It is for this reason that it is important to maintain the health of primary teeth before replacing them yourself.
Many parents, believing that baby teeth “will soon fall out anyway,” do not treat caries in children, whereas this can lead to a defect in the permanent element of the row, which should erupt in place of the carious one. And given the systemic nature of the changes, just one defective fragment can lead to a change in the contours of the entire jaw.
What myogymnast exercises are used in orthodontics, and how effective the technique is.
From this publication you will learn what an orthodontist treats.
Here https://zubovv.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/nepravilnyiy-foto-i-formyi-litsa.html photos of all types of malocclusion with a detailed description are presented.
Reviews
Parents' fears about defects in the formation of primary occlusion, although often too exaggerated, still should not be ignored.
This phenomenon is not just an external flaw, it is a serious threat to the health and integrity of teeth, which over time will inevitably affect permanent units.
If you have encountered this problem in your own practice, you can leave a comment in the appropriate section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
tags milk bite bite
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Variants and specifics of classifications of toothless jaws
Next article
Specifics of the formation of a mixed bite and possible anomalies