May 3, 2020 Last revised: February 1, 2020 Bite correction
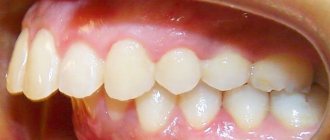
An open bite is an anomaly in the development of the dentition. It can be distinguished from other defects by its incomplete closure. Correcting such a bite is quite difficult.
Open bite teeth are most common in young patients. Below is the approximate frequency of occurrence of the disease in children:
- Children 7-11 months – 19%.
- Children 1-6 years old – 5.6%.
- Children 6-12 years old – 1.6%.
- Children 13-18 years old – 1.3%.
The adult population accounts for only 2%, and the percentage of the disease in patients 3-27 years old is 1.9%.
Based on the data presented, it can be judged that the dangerous period for the formation of an open bite is up to one year of age. The chances of acquiring such an anomaly drop sharply at the age of six and practically decrease by the age of 27.
Possible reasons
The disease can occur for the following reasons:
- Congenital disorders due to serious illnesses of the child's mother. These can confidently include heart disease, endocrine disorders, toxicosis, infections of various types, viral lesions and some other things.
- Bad heredity.
- Jaw injuries.
- Throwing back the head in sleep.
- Diseases of early age (for example, rickets).
- Improper breathing through the nose.
- The gap between the palate and the alveolar process.
- Increased size of the tongue and its improper functioning;
- Bad habits (biting objects, sucking fingers, holding the tongue in the gap from previously lost teeth, long-term habit of using a pacifier, biting nails).
- Atypical location of tooth germs.
What is this disease
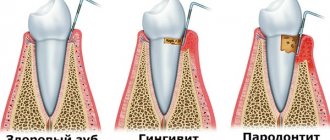
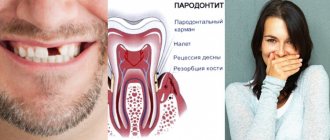
Open bite - this occlusion disorder is characterized by the absence of complete closure of the lower and upper incisors. With it, pronounced pathological changes in the dental system occur with loss of function, as well as gross aesthetic defects. Such malocclusion can be an independent disease; it is also often combined with other pathologies of occlusion and uneven dentition. There are combinations with distal and mesial disruption of teeth closure. It is recorded quite rarely, its prevalence among all occlusion anomalies is about 2%. The defect is most often detected in children under one year of age.
Classification
According to the etiological criterion, such disocclusion is divided into true (rickets) and false (traumatic). There are three degrees of open bite; the classification is based on the amount of space between the upper and lower teeth, due to the lack of closure (occlusion).
Degrees of severity of occlusion violation:
- The first is that there is a vertical interdental space of up to five mm, with a lack of closure in the area of the anterior teeth (canines, incisors).
- Second, this stage is characterized by the presence of a vertical gap with a size of five to nine mm, with the absence of contact between the incisors of the canines and molars.
- Third - there is a space between the teeth measuring more than nine mm; the front teeth, molars, and premolars do not touch each other.
Based on location, frontal (front) and lateral forms are distinguished. Lateral is divided into bilateral and unilateral. It is noted that this pathology can be asymmetrical as well as symmetrical.
Causes
The reasons for the development of this pathology are quite diverse. They are divided into acquired and congenital factors.
Congenital causes of anomaly development include:
- unfavorable heredity for this trait;
- infections suffered during pregnancy;
- exogenous toxic effects on the fetus;
- somatic diseases of the mother;
- birth injuries;
- effect of medications;
- pregnant woman's injuries.
All these influences together during intrauterine development cause an atypical position of tooth germs, the formation of cleft palate, alveolar process and upper lip. Deformation of the facial skeleton occurs.
Acquired factors include:
- bad habits (prolonged use of a pacifier, sucking on foreign objects);
- consequences of rickets;
- hypovitaminosis;
- pathologies of mineral metabolism;
- early loss of primary teeth;
- shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- macroglossia (enlarged tongue);
- late teething;
- diseases that cause difficulty in nasal breathing (adenoids, polyps, deviated septum).
To determine patient management tactics, it is necessary to identify the cause of the pathology. A single pathological factor may play a major role in its development, and it is also caused by a complex of causes.
Symptoms
Malocclusion has characteristic signs: facial, functional, intraoral.
Facial manifestations include;
- lengthening the lower part of the face;
- there is no fold between the lips and nose;
- constantly half-open or open mouth;
- smoothing the chin fold;
- presence of a sloping chin.
When examining the patient's oral cavity, characteristic signs can also be identified.
These include:
- lack of closure of the anterior or lateral upper and lower units;
- crowding;
- the shape of the closure defect (it repeats the shape of the object held in the mouth);
- severe dental caries;
- hypoplasia of the enamel layer;
- narrowing of the arch, asymmetry of the alveolar process;
- pronounced tartar;
- the shape of the upper palate is disrupted;
- dryness of mucous membranes in the oral cavity;
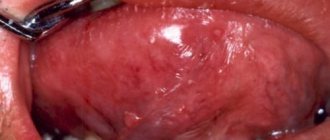
- signs of hypertrophic gingivitis (bleeding and swelling of the gums, enlargement of the gum papillae).
The following functional disorders are typical for this disocclusion:
- inability to bite off pieces of food;
- difficulty chewing;
- violation of diction (interdental sigmatism, defects in the pronunciation of labial and lingual sounds);
- difficulty in nasal breathing.
The defect is usually accompanied by pathologies in the development of the paranasal sinuses of the skull, as well as the bottom of the nasal cavity.
Diagnostics
Before an open bite is corrected, a child will be thoroughly examined. The diagnosis is made by an orthodontist. He carefully examines the patient, listens, and analyzes his complaints. Studies and evaluates facial and oral signs of occlusion. The dentist measures the distance between the upper and lower teeth.
The doctor prescribes additional research methods.
These include:
- facial photometry;
- electromyography of the muscles of the head and face;
- orthopantomography;
- rheography;
- make casts of the jaws with subsequent study of diagnostic models;
- teleradiography of the skull with radiocephalometric analysis;
- tomography of the maxillary joint.
The patient requires consultations with specialized specialists: speech therapist, otolaryngologist.
Treatment
Methods for correcting open bite in children depend on the severity of the defect and the age at which correction begins.
Before the age of three years, mainly preventive measures are taken.
These include:
- stopping bad habits (sucking pacifiers, foreign objects);
- gymnastics for facial muscles;
- timely introduction of solid foods into the diet;
- consumption of foods rich in vitamins and microelements;
- prevention of rickets;
- timely treatment of caries;
- prevention of inflammation in the oral cavity;
- use of vestibular shields.
It is necessary to regularly visit the orthodontist and follow all his recommendations.
From the age of five to thirteen, corrective structures are prescribed.
The following devices are used:
- removable correction plates with tongue flap;
- Andresen–Goipl activator;
- Frenkel apparatus;
- trainers;
- Herbst-Cojocaru mouthguard device;
- Engle's apparatus;
- supradental vestibular arch.
To enhance the effect, continue to do gymnastics for the facial muscles. Children are recommended to visit a speech therapist to correct the pronunciation of sounds. Surgeries are performed to correct the lip frenulum. An otolaryngologist should treat diseases that make nasal breathing difficult.
In adolescence, starting from the age of thirteen, this defect is corrected using braces, aligners, and aligners. They are usually worn for 2 years to achieve the desired effect. In severe cases, surgical correction of the alveolar process is used. If sufficient jaw closure cannot be achieved, the teeth are ground down and crowns are placed on them.
Complications
If a child's open bite is not treated, serious complications develop.
It can be:
- appearance defects;
- diseases of ENT organs;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysfunction of the maxillary joint;
- headache;
- severe psychological disorders.
These problems can be avoided with timely treatment from an orthodontist and following all his instructions.
Prevention
Prevention of the formation of closure disorders is aimed at preventing the causes that are responsible for the development of the anomaly.
Recommended:
- carrying out the prevention of pathologies that complicate the course of pregnancy;
- prevention of rickets;
- elimination of diseases that impede nasal breathing;
- it is necessary to monitor the timely eruption of teeth;
- treat them for caries in a timely manner.
If there is a suspicion that a child has a closure anomaly, he should be regularly taken to the orthodontist for examination.
Forecast
The disease has a positive prognosis with early orthodontic correction of the defect. In this case, it is possible to make the appearance more attractive and prevent the formation of complexes and the emergence of psychological problems.
External manifestations
People with malocclusion are easy to identify. Their appearance has characteristic features:
- The mouth is slightly open.
- The lower part of the face is larger than the correct size (symmetry is not observed).
- The folds between the lips and nose are smoothed out.
- The face looks small in comparison with the skull, the person has an infantile appearance.
- When the lips close, a very pronounced tension appears on the face.
- You can clearly hear that the person has a lisp.
Ugly external features are not as bad as subsequent health problems. Potential dangers include:
- In gastrointestinal diseases that arise due to poorly chewed food.
- Severe speech impairment.
- In constant diseases of the ENT organs.
What it is
In the dental field, the word "occlusion" is used to describe the method of closing and opening the upper and lower arches of teeth. Usually, by the time a person reaches a certain age, a complete formation of a physiological bite occurs, which is accompanied by certain qualities:
- Each of the units of the dentition must close with two antagonists in a certain position;
- The upper incisors provide overlap with the lower incisors;
- There is slight obstruction of the lower canines by the upper ones.
If any symptom is not fulfilled, then in this case it is worth talking about the development of a pathological process. An open bite is a pathological disorder during which complete closure is not observed in the upper and lower dentition.
An open bite is an anomaly in the development of the dentition. It is characterized by a pronounced defect - incomplete closure of the jaws. Correcting such a bite is quite difficult.
This pathology not only spoils the appearance, but can also cause serious harm to health.
Important! An open bite can cause a variety of ENT diseases and can also be a major factor in speech problems. Loose teeth can cause great difficulty in chewing food, which can result in disruption of the digestive tract.
An open bite is often observed in the anterior part of the dentition. Sometimes this pathology occurs in the lateral rows of teeth. Many dentists advise regularly visiting the dental office. Upon examination, pathologies can be identified at an early stage of development and can be easily eliminated. Otherwise, delay can lead to serious disorders in the body and severe, long-term treatment.
Types of open bite
Depending on the form of localization, bites are distinguished:
- Open front.
- Open side.
The first form is more common than the second. It appears independently for the reasons described above or becomes an accompaniment of another disease.
The second form is very rare. Lateral has subtypes: one-sided and two-sided.
Depending on the symmetry of the location, symmetrical and asymmetrical bites are distinguished.
Based on jaw location, bites are divided into:
- Combined.
- Mandibular.
- Maxillary.
According to etiology they distinguish:
- True.
- False.
A child who has suffered rickets has a true open bite. This type of bite is also called rachitic. The appearance of rickets is influenced by the following factors:
- Ecological. Due to unfavorable conditions, large amounts of zinc, strontium and lead may be present in water and soil. Once inside the body, they lead to a complete replacement of calcium, which is so necessary for our bones.
- Hereditary. Rickets occurs as a result of improper metabolism of vitamin D, calcium and phosphorus.
- Perinatal. Rickets often occurs in children born before 30 weeks due to a lack of necessary elements through the mother's body. The second reason: placental insufficiency.
- Food. These include taking low-quality mixtures that lack vitamin D3; being breastfed for a long time; feeding the child only vegetarian products; late addition of regular foods to the diet.
- Physical. Complete absence of physical activity, massage and gymnastics (especially up to a year). Blood can flow to the bones only during muscle activity.
- Intestinal. Long-term dysbiosis and constant diarrhea lead to the removal of calcium from the body.
- Various diseases and their long-term treatment. Some forms of illness and prescribed medications add speed to the body's absorption of vitamin D and its rapid elimination. The result is a deficit.
People with a rachitic bite have the following symptoms:
- Breathing is difficult.
- Speech is slurred.
- It is difficult to chew food well.
- The mouth is open.
- The face is deformed.
- The oral mucosa constantly becomes dry.
A false bite is formed as a result of injury. It has another name: traumatic. Most often, the bite deteriorates due to trauma in children with milk teeth. Correcting open bites in children is easier and more productive for orthodontists than for adults.
An open bite in a child begins to develop during tooth loss. At this time, children begin to stick their tongue into space and constantly suck fingers and toys. If you do not wean your child off the wrong behavior and do not immediately correct the formed defect (before permanent teeth appear), then complex treatment of an open bite will be required. It is possible that in addition to the orthodontist, a periodontist will be involved in the problem.
Types and consequences of pathology
Depending on the causes and location, there are several classifications of malocclusion. There are frontal and lateral types. The first option is located in the area of the front teeth, causing a change in diction, loose lips closing and difficulty in biting food. The lateral version differs in that the lateral teeth do not close together. Food is processed poorly, swallowing and the functions of the lower jaw joint are impaired. Occlusion is located on both one and two sides.
Types of open bite:
- True (rachitic). The teeth are not fully developed, and this type is considered the most severe form of the defect. Complex and complex treatment is required, most often surgery and correction with orthodontic medications.
- False (traumatic). This type is common in children with baby teeth (from 4 to 8 years old). The main reason is the absence of one or more teeth, sucking on hard objects, and protruding tongue.
According to the jaw location, the bite can be combined, mandibular and maxillary. Some patients purse their lips tightly to hide the defect. Changes are determined by tense cheeks and muscles. The face becomes less attractive, which causes discomfort in the person and many complexes.
If the correct bite is not corrected, the pathology causes serious complications:
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines due to improperly chewed food.
- Speech disorders and defects.
- Diseases of the ENT organs.
- Breathing problems.
An open bite is always accompanied by breathing through the mouth. The amount of carbon dioxide increases and the oxygen content decreases, the composition of the blood changes, the outflow of blood from the veins worsens, and the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted.
Occlusion is established already in childhood, so it needs to be corrected at the initial stage. A pathological bite causes hypertrophy of the tongue, which seriously affects the appearance.
Diagnostics
In the orthodontist’s office, a visual examination, instrumental examination is carried out, and the full clinical picture of the disease is assessed. The process covers the following points:
- Complaints are heard.
- A detailed conversation is held with the patient.
- The oral cavity is visually inspected.
- Facial defects are assessed.
- The intermediate distance between the incisors is measured.
- The type of bite is determined.
- It is decided what degree of bite is inherent.
In dentistry, it is customary to distinguish three degrees of open bite, by which the severity of the defect is judged:
- 1st degree: the vertical gap is no more than 5 mm;
- 2nd degree: vertical gap is 5-9 mm;
- Grade 3: vertical gap greater than 9 mm.
In case of problems with speech, the patient is referred to a speech therapist, and in case of problems with nasal breathing - to an otolaryngologist.
The situation is complicated by the oral characteristics of the dentition. These include crown deformation, lateral compression, anomaly of location, and narrowing of the dental arches. Upon examination, you can see strong tartar and bleeding on the tongue.
The diagnosis ends with the conclusion: is open bite an independent pathology or is it closely related to other defects. Most often, the bite is combined with other anomalies.
All forms are characterized by changes:
- The plane of the sky is shifted down and back.
- The angle between the Frankfurt horizontal line and the sky plane is negative.
- The temporomandibular joint is located high.
- Low height of the alveolar process of the lateral section.
Open bite - causes and consequences
Open disocclusion, or, as it is also called, open bite, is not the most common type of dental anomaly, but one of the most problematic. Those with this curvature have difficulty chewing food and pronouncing some words, and their facial expression always seems surprised. Read our article about what treatment an open bite requires, whether it is possible to cure open disocclusion once and for all and avoid all the consequences described above.
The content of the article
Preventive measures
For preventive purposes, etiological causes should be excluded. These include the reduction or elimination of pathology during pregnancy, the prevention of rickets, ridding the baby of the habit of putting everything in his mouth and sucking objects, timely correction of the frenulum, strict control over the process of teething, and treatment of emerging caries.
The most important thing in prevention is to detect the pathology in time and contact an orthodontist, who will take action. With early treatment, it is possible to change the situation in a positive direction. Facial defects will become less pronounced or completely invisible, the jaw will begin to develop correctly, and the psycho-emotional background of the sick child will improve. Note that a false bite is corrected by orthodontists faster than a rachitic bite.
Predictions and prevention
Treatment of an open bite is the most difficult. As a rule, the correction period can last up to 4 years.
The duration of treatment primarily depends on the age of the patient. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the likelihood that the pathology can be stopped in a short time.
In some situations, the use of one technique gives only a minor effect. This picture is especially often observed when correcting advanced malocclusion in adults.
In this case, it is possible to completely restore the correct shape of the jaws only using a combined method, combining the use of braces (hardware) and surgical treatment.
Stages of surgical treatment of open bite, watch the video:
To avoid difficult and lengthy treatment, it is necessary to adhere to certain preventive measures :
- the diet should be balanced so that there is no lack of vitamins and minerals;
- promptly stop dental pathologies that can cause abnormal jaw growth: short frenulum of the tongue, extensive caries, etc.;
- form correct nasal breathing;
- under the age of one year, constant prevention of rickets is carried out using preparations with vitamin D;
- timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs plays a significant role;
- In case of premature loss of primary teeth, splinting of the included defect should be performed.
in childhood it is necessary to work to eliminate bad habits;
An open bite is a serious anomaly in the development of the jaw, which causes severe psychological discomfort and disruption of the functioning of certain body systems. Fixing this problem may take years and large investments.
A timely visit to the dentist will avoid a complex correction process.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Open bite treatment
Open bite in children. Treatment
How to correct an open bite? The whole process is reduced to 4 stages.
First stage: correction of milk bite
Treatment of open bite in children under three years of age is best started with disease prevention. Dentists advise:
- Eliminate all bad habits (they are described above).
- Treat baby teeth in a timely manner.
- Carry out oral sanitation in a timely manner.
- Strengthen the orbicularis oris muscles with myogymnastics.
- Feed your baby solid foods that develop jaw development.
- Contact an orthodontist promptly and follow his treatment.
A doctor usually prescribes wearing devices at a young age. Mouthguards and trainers are mainly used. Devices must be worn until the age of 13. Also widely used are plates that provide support under the tongue. The plates can be manufactured at the factory, or they can be made for each patient individually.
Appliances for treating open bites do not always bring results. Sometimes you have to resort to surgery.
Malocclusion in children will not be cured without the additional help of a speech therapist. Using special exercises, the speech therapist normalizes speech functions over time. If you do not follow the specialist’s recommendations, you may experience a relapse. For example, the orthodontist prescribed the wearing of plates, which over time corrected the bite. But the language remained in its old position. The patient ignored the recommendations and exercises of the speech therapist and did not follow them. When the plates were eventually removed, the tongue began to push the teeth back to their original position. There was a relapse.
The case shows that when correcting a child’s bite, parents should not shift responsibility from themselves.
Myogymnastics consists of performing special exercises. It is advisable to do it with children aged 3-7 years, when the task at hand can be clearly explained to them.
- First exercise. The baby holds his lips tightly, puffs out his cheeks strongly, presses his fists against them and begins to slowly squeeze out the air.
- Second exercise. The child blows strongly on a light object that is suspended in front of his face. He must try with all his might to displace it from its original point.
- Third exercise. The exercise involves whistling loudly.
- Fourth exercise. Fold the paper in half and let the child hold it between his lips for a long time (50 minutes). At this time, the child can study lessons or watch a program.
All exercises are performed daily.
You can check whether the baby breathes through his nose or not. To do this, you need to ask him to take water into his mouth and ask him to sit quietly for a while. If the baby sits, it means he can breathe through his nose.
Otherwise, you should teach your baby to breathe through his nose using exercises:
- In the morning, ask the child to take water into his mouth and forcefully push it out. Do this several times.
- Make the baby take water into his mouth and walk with it for a while.
- Place a ruler in the child's mouth and ask him to hold it for a long time.
- Let soap bubbles blow. In this exercise, folding the lips into a tube is very important (the orbicularis oris muscles are trained).
- Counteraction with buttons. Tie two buttons together at a sufficient distance from each other. The knots must be strong so that the baby cannot swallow objects. Place one button in the child's mouth, and hold the other button for an adult. Next, begin to pull the button out of the child’s mouth. The baby must resist and hold the object.
The domestic industry produces Schonherr and Kraus plates, double-jaw appliances, and individual plates that allow treating open bites in children.
Second stage: correction of the first period of mixed dentition
This kind of malocclusion can be treated with measures for milk malocclusion. Only fixed devices can be added to them. Their main function is to correctly move the dentition. To correct a row of one jaw, dental vestibular arches are used, fixed in tubes. The tubes are attached to rings on the permanent molars and first baby teeth. In the place where the arc does not contact the teeth, bend the device in a U-shape. Hooks and rings are attached to the teeth that need to be moved. Correction is achieved due to the generated traction.
During the period of mixed occlusion, arches, springs, and levers are mounted in plate devices, which ensure the elimination of anomalies.
Third stage: correction of the second period of mixed dentition
At this time, the narrowing of the dental arches increases. For this purpose, plates with a screw and a special support for the tongue are used. This period was characterized by the use of the Engle apparatus. It acts as an inter-maxillary rubber band. For alveolar shortening of the action of this device, it is more correct to use it with extraoral traction.
Stage four: correction of permanent bite
Here, in addition to plates with stops, arcs, springs and levers, non-removable devices are used. For example, the Engel apparatus.
The Herbst-Cojocaru apparatus is used if there is dentoalveolar lengthening in the anterior region and dentoalveolar shortening of the lateral teeth. The treatment will be much more effective if you add a compact osteotomy before using the device.
Interesting! After using functional devices, further use of retention devices will not be required. And after mechanical devices there will definitely be a long retention period, which will last 6-7 months.
Open bite treatment in adults
Previously, correcting open bites in adults required tooth extraction. Next, specialists installed removable dentures and lengthened the front teeth. Result: complete closure of the teeth. Modern dentistry helps avoid the use of such radical measures. However, the treatment still remains productive. The anomaly is corrected with effective braces. The devices are installed on both jaws at once and secured with reversible arches.
If the system is installed on the front teeth, then it is attached very close to the gum. Nickel-titanium thermoactive arches correct teeth well.
It is difficult to correct an adult bite, so surgery is sometimes the only correct solution.
Procedure for young patients
A set of various measures will help eliminate occlusion in a child. They wean the baby from bad habits, normalize the process of swallowing and nasal breathing, or treat rickets. It is important to take care of oral hygiene and implant dentures into the voids of lost teeth.
Corrections:
- Thrust plates.
- Myogymnastics.
- Klammt or Andresen-Goipl activator.
- Electrical stimulation.
- Overlays.
- Chin sling.
- Frenkel, Herbst or Schwartz apparatus.
- Orthodontic trainers or aligners.
- Vestibular arch.
In addition to the basic procedures, trimming the frenulum of the tongue and sanitation of the nasopharynx may be required. Correction of open bite in children under seven years of age begins with individual physiotherapy and myogymnastics.
During treatment, the child needs to wear special dental devices that normalize the closure of the teeth. For example, a palatal expander eliminates an anomaly, a chin sling and devices with intermaxillary traction move a protruding jaw, activators and bite plates, normalize the position of the tongue and muscle function, and relieve pressure from the cheeks and lips on the teeth. In difficult cases, some structures are installed simultaneously.
Andresen-Goipl activator
There are situations when it is possible to restore the closure of teeth by changing the height of the back teeth. This is done with the help of devices that restrain eruption or by grinding. In patients with open occlusion, the upper lip is located high, so bite blocks will help correct the pathology.
By the age of 12-13, patients are also fitted with braces. This is a very convenient way to correct a defect, because children will not be able to remove them. Older patients are fitted with mouth guards to straighten their teeth.
Correcting an open bite cannot be done by following only one scheme. The treatment algorithm for each patient is individual and depends on neglect and age.
Myogymnastics is used for primary and mixed dentition. The child regularly performs exercises that train the jaw muscles. The best results are achieved when using a Rogers shock absorber or a Friel interlabial disc. Photographs of the open bite before and after treatment will help evaluate the quality of therapy.
The activator consists of plates with a bite area into which the lateral teeth rest. The front side of the structure contains a tongue stop. In problematic situations, activators are equipped with metal arches, screws and springs.
In case of physiological normal occlusion or at a late stage of a replacement occlusion, orthopedic structures are used: mouthguards, braces, crowns, Engle apparatus. In difficult cases, the devices are used with surgical methods.
Surgery:
- Compact osteotomy.
- Removal of extra teeth.
In case of obvious speech development disorders, speech therapy procedures are prescribed. Bite defects are easier to prevent than to correct severe consequences. Parents should monitor teething and contact the dentist promptly.
Appliances for correcting open bite
There are:
- Plates (have flaps for the tongue).
- Trainers.
- Bracket systems.
- Andresen-Goipl apparatus.
- Frenkel apparatus.
Records
The plates are made from a material that does not cause allergies. This advantage allows the devices to be widely used in children. Plates are considered removable structures that include springs, arcs, screws and hooks. Dental plates are different and include the following elements in the design:
- Vestibular arch. A type of plate is used to straighten the front teeth. These devices differ from others by convenient additional bends (M and L shaped). These plates are often used to straighten canine teeth.
- Orthodontic lock. The plates expand and lengthen the dentition.
- Protracting springs. Used if the front teeth have a palatal position.
The plates are convenient because:
- Does not require constant wear. They can simply be worn while sleeping or not used while eating.
- They have a small price.
- They are very easy to care for.
If the treatment requires moving the teeth too much, then the plates will not cope with the task. Patients who are prescribed to wear them often forget to put them on. As a result, the treatment process stops. The bite with plates takes a year and a half to correct.
Trainers
These are devices that were simulated using a computer. They are made from silicone material. The devices eliminate the very cause of open bite and prevent recurrence.
Trainers have a fairly gentle effect on the dental jaw. If the treatment is simple, then they can be worn only 2 hours a day.
Important! Trainers do not allow talking while in the mouth.
There are bare trainers (they are gentle at the beginning of treatment) and pink trainers (they are hard to complete the treatment). The second trainers are allowed to be worn only during active times (during the day), and blue ones can be used at night. An open bite can be treated in this way for one year.
Bracket systems
These systems are capable of moving teeth in three opposite directions.
Braces are made of metal and plastic. Sapphire and ceramic crystals are specially grown for them.
There are vestibular and lingual devices. The first type is installed on the front teeth. The second type is on the inner surface. Lingual systems are invisible to the interlocutor, but cause some inconvenience to the patient.
Discomfort is felt when talking and eating. Immediately after installation, sound pronunciation is greatly impaired.
The entire system consists of twenty elements, which are sequentially attached to the teeth with glue. Then these elements are interlocked with an arc. The process is long. The arc is inserted into the groove and firmly secured with a ligature. The entire structure is fixed with metal rings. The active element during correction is wire. It is she who sets the program for the teeth to be in the correct position. The entire procedure takes approximately 3 hours.
Braces correct very complex abnormalities. They are quite aesthetic in appearance. This is one of the best methods for correcting malocclusion in adult patients.
Unfortunately, braces systems are very expensive. They must be looked after conscientiously. During treatment, you should not eat foods that stick to your teeth or chew gum. Application causes pain in the neck, tongue, gums and teeth. Due to the complexity and responsibility of the event, constant visits to the orthodontist are required. Treatment for an open bite lasts two years.
Andresen-Goipl apparatus
The device easily copes with distal occlusion. This is a removable device, which consists of two plates for both jaws. The plastics are held together by plastic. The connection is made along the line of occlusion. The drug leads to a constructive bite. The activator actively moves the lower jaw into an extended position and activates its growth. Facial and chewing functions are normalized. The teeth change in three positions due to the inclination of the planes of the device.
Symptoms and external manifestations of open bite
This pathology is not secretive, so any deviations from the norm will either be visible externally or upon examination by a specialist.
Hardware diagnostics are necessary only to establish the severity of the disease and further develop a treatment plan. In the arsenal of orthodontists there are photometric studies, teleroentgenogram (TRG), orthopantomography and others.
All symptoms are combined into three large groups: facial, intraoral and functional.
Facial signs:
- The lower third of the face is modified. Its lower part is elongated;
- Displacement of the chin to any side;
- The mouth is constantly in an open or semi-open state;
- The nasolabial fold is deformed according to the smoothing type;
- Inability to close your lips or visible strong tension when trying to close your lips independently. If there is a malocclusion, the lip does not develop normally and becomes shorter;
- The patient's tongue tip and cutting surfaces of the front teeth are visible;
- The muscles around the mouth are noticeably overstrained or spasmed.
Intraoral:
- The oral mucosa is noticeably dry;
- The shape of the palate is changed, asymmetry of the jaw arches is visible;
- Gums look swollen and prone to bleeding;
- Hypoplasia of tooth enamel;
- The cutting part has a ribbed contour;
- There is a large amount of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Widespread caries often occurs;
- The gap between the upper and lower rows of teeth;
- Lack of closure of the teeth of the same name in the upper and lower jaws;
- Crowding of the front teeth is often observed;
- Changes in the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses are possible.
Functional:
- The patient feels difficulty biting food.
- Chewing function is significantly affected.
- Swallowing function suffers, as in newborns.
- Diction is broken.
- The patient breathes predominantly through the mouth.
- Complications arise with the mandibular joint.
Frenkel apparatus
Having analyzed the state of the bite, Frenkel proposed correcting it by reducing the pressure of the lips and cheeks on the rows of teeth and alveolar processes. As a result of the applied action, the process of closing the lips was normalized and the position of the tongue assumed the correct position. The functions of the tongue also returned to normal.
In practice, the author brought the vestibular plate to the skeleton and introduced a metal frame into the structure. As a result, the strength of the structure increased and the drug became lighter. A positive feature of the Frenkel apparatus was the openness of the frontal area. This made it easy to swallow and speak correctly. The Frenkel apparatus has several types. For open bite, type 4 is used. It removes the influence of soft tissues on the proper development of the jaw and differs from other types in the following:
- The palatal arch is prepared for retrusion of the superior anterior teeth.
- Lip pads are placed in the lower part.
- The vestibular arch is used for the frontal upper teeth.
- The lateral sections of the dentition have metal linings.
- The device not only separates the bite, but also shortens it.
Symptoms
An open bite is characterized by a change in the shape of the facial part and oral cavity. Also, a defect in the jaw row provokes functional disorders.
Pathology provokes:
- lengthening the lower part of the face;
- the formation of a large gap between the front teeth, through which the oral cavity is visible;
- curvature of the chin;
- lack of closure between the lips;
- reduction in the size of the upper lip, which does not completely cover the teeth of the upper row.
To hide such a noticeable defect, patients often press their lips tightly together. As a result, the cheeks are constantly in a tense state, and the skin on them is stretched. Because of this, the appearance of the face deteriorates, which leads to the formation of mental disorders (complexes).
In the case when an open bite was formed due to prolonged sucking of a certain object, the gap between the teeth takes on the shape of the latter.
Changes in the oral cavity arising due to the defect in question are characterized by the following phenomena:
- lack of contact between symmetrically spaced teeth;
- crowded teeth;
- frequent occurrence of caries;
- hypoplasia ;
- the presence of a nervous cutting edge on the front teeth;
- a large number of stones and plaque on the enamel surface;
- deformation of the upper palate;
- bleeding gums.
On this topic
- Bite correction
Effective ways to correct your bite
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2020
The latter phenomenon indicates the course of hypertrophic gingivitis. Due to the fact that the patient is unable to bring his teeth and lips together, his oral mucosa often dries out, which leads to the development of many diseases.
Functional disorders in open bite are characterized by the following phenomena:
- speech problems (the patient is unable to clearly pronounce some sounds);
- violation of facial expressions;
- mouth breathing;
- difficulty biting, chewing and swallowing food;
- TMJ dysfunction and periodontal disease caused by the above disorders;
- changes in the shape of the bottom of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
The presence of an incorrect bite over time leads to the development of diseases of the internal organs. Due to this pathology, the gastrointestinal tract often suffers due to insufficient chewing of food.
Surgical method
In case of the following indications, surgical intervention is used:
- Serious anomalies;
- Injuries to the jaw area;
- Severe facial asymmetry.
Before the surgeon intervenes, orthodontists prepare. They install braces that force the teeth to move into the correct position. Often at this stage the frenulum and the necessary teeth are removed.
The correction process can take several years.
After alignment, it is performed before surgery. The doctor cuts the maxillofacial part in the right place, moves the bones into the correct position and secures them with dental devices. After the surgical procedure is completed, the orthodontist begins work. Braces are again helping the disease. After the braces are removed, a period begins in which the result is consolidated.
The joint work of two doctors makes it possible to correct serious cases. As a result, the patient’s breathing and speech are normalized and chewing functions are restored.
Many people are afraid of surgery for several reasons:
- Anesthesia. Both local and general. The procedure has not yet improved the health of a single person. It is impossible to predict how the patient will feel after it.
- During open surgery there is always a risk of unwanted infection.
- Severe bleeding may occur during the process.
- Allergies may occur due to the medications used.
- Much depends on the hands of a specialist surgeon.
How to eliminate an open bite in adults
In adults, correction takes longer and is more difficult. It is recommended to wear mouth guards to straighten the teeth, use braces, and install crowns to change the height of the bite. These correction methods are effective, but do not always help. In complex cases, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
The goal of orthognathic surgery is to return the jaw to its natural position. This is the fastest way to correct open disocclusion. The result will be noticeable immediately, but rehabilitation after surgery may take several months.
Reviews
Marina, 32 years old
My son has a terrible dental problem. It became very visible at the age of 2 years. The teeth in front began to close poorly. Between them there was an ugly gap about 1 cm high. Closer to the radicals, this ugly hole disappeared. Looking carefully with my eyes, I did not notice that his jaw was slightly pushed forward (the information was given by a specialist). Let's go to the orthodontist. Maybe we ended up with a bad specialist, but he didn’t tell us anything sensible. He offered to observe for a while. Yes, and I had a hope in my heart that when permanent teeth appeared, the problem would dry up on its own. But no. Improvement became noticeable only by the age of 5 years. The gap has been reduced by half. But now that my son is seven, new teeth have come out. And they are much smaller in height than the old ones. At first I thought that they would grow over time. No. They have been at the same height for more than three months now. I try to make sure my child gets plenty of calcium in his diet. I give him cottage cheese, cheese and calcium-containing supplements. The result is zero. New teeth only increased the distance. Now it is more than 1 cm. The dentist advised me to wait until the age of thirteen for the fangs to come out. But I'm in doubt again. Maybe I should have panicked earlier. I am very afraid that my baby will undergo surgery. It's a pity. I don't want anesthesia. But the bite needs to be corrected. You'll probably have to turn to other specialists. I hope they help.
Agripina, 18 years old
I have had an open bite since childhood. I don’t know who is to blame, heredity or bad habits. Everyone in our family has problem teeth. Dentistry is our permanent home. Even my little sister now wears braces. Her teeth resemble a wave. She really doesn't like the process. She is capricious with us, everything hurts her. My mother also told me that until I was three years old, I constantly sucked my thumb. I had it instead of a pacifier. They weaned me off, but until I grew up, I kept putting my finger in my mouth. Now my teeth are straight and I no longer experience the discomfort that I endured before. But before the happiness from teeth, there was a very long and sometimes intolerable process. I wore corrective braces and an apparatus (the name of which I don’t remember) for more than two years. I visited the dentist often. I really wanted to correct my bite, so I additionally performed special exercises that are indicated for children with a milk bite. I was interested in this and hoped for results. I want to say that experiencing discomfort when chewing and speaking poorly is a problem. I was very embarrassed about my condition. Now everything is normal. I laugh and talk out loud. The stomach from poorly chewed food no longer bothers you. I am a person who is now happy with everything. I advise people who have problems with their bite not to worry, but to go to the orthodontists. They are professionals and doctors from God. Therefore, orthodontists will make you healthy.
Olga, 25 years old
I had a distal open bite. I didn't avoid surgery. I also wore braces. Then I used special plates. To be honest, everything was terrible. The operation was difficult. Even though the doctor was a good specialist. My health was critical. My mouth hurt. I lost a lot of weight. With my excess weight, this was the only plus. But it's over. I have straight teeth. Everyone envy me.
Sources used:
Which brands of toothpastes have you used?
- Colgate 32%, 29565 votes
29565 votes 32%29565 votes - 32% of all votes
- Splat 24%, 22195 votes
22195 votes 24%
22195 votes - 24% of all votes
- ROCS 16%, 15451 votes
15451 votes 16%
15451 votes - 16% of all votes
- Sensodyne 11%, 10446 votes
10446 votes 11%
10446 votes - 11% of all votes
- New pearls 11%, 10035 votes
10035 votes 11%
10035 votes - 11% of all votes
- President 6%, 5995 votes
5995 votes 6%
5995 votes - 6% of all votes
Total votes: 93687
Voted: 50514
17.01.2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
- Andreishchev, A.R. Combined dentofacial anomalies and deformities / A.R. Andreischev. — M.: GEOTAR-Media
- Atlas of radiographs of teeth and jaws in normal and pathological conditions. — M.: Medicine
- National Library of Medicine (USA)
SIMILAR ARTICLES
Author of the article:
Elena Vladimirovna Urakova (Author's page | All articles), Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of KSMA, Assistant Head. Department of Academic Affairs. Awarded the medal “Excellence in Dentistry” in 2016.
Open bite type: types, symptoms, causes
An open bite develops due to improper pathological formation of the jaw and dentition. The gap formed between the teeth characterizes the severity of the disease.
Most often, this anomaly occurs in infants. They make up a fifth of all cases. At the age of 7-11 months, babies have their first baby teeth, which cannot yet come into contact. Dentists call this period the period of bite formation.
Further, the problem may appear during the period of active growth of baby teeth. Over time, they will all change, and the bite will also change, which is why it is called temporary.
From the age of six, baby teeth begin to fall out and permanent teeth grow in their place.
The bite changes and is accordingly called interchangeable.
This process is usually completed by age 12. At this point, about one and a half percent of patients experience a problem with their bite.
In adolescence and older age, the incidence of problems with occlusion becomes less and less, and is associated with completely different reasons.
Depending on the causes of occurrence, there are two types of open bite:
- True - is considered the most difficult from a medical point of view, since irreversible bone changes occur in the jaw. Treatment is very difficult and requires a lot of time and effort from doctors and the patient. The symptoms in this case are very obvious and cannot be confused with something else. The patient is faced not only with an aesthetic problem. Very often, such a bite prevents breathing, eating and speaking normally. The mouth is constantly open, which causes the mucous membrane to dry out and become a target for pathogenic bacteria. In most cases, the problem can only be corrected through surgery. The second name for this pathology is rachitic bite.
- False type of open bite or traumatic. It is of an acquired nature. It may occur due to rapid and early loss of baby teeth, traumatic exposure, or bad childhood habits. Development occurs gradually, not always pronounced and noticeable. Therefore, regular visits to the pediatric dentist are important. Timely treatment during the growth of baby teeth is easy and painless. If you miss this moment, the treatment becomes longer, more complex and more expensive, with the need to wear special orthodontic appliances.
Another classification distinguishes bites by location:
- Anterior (frontal) is the most common option in patients with this pathology. From the name it is clear that this problem concerns the front teeth. In this case, four to eight teeth will be involved.
- Side. In this case, a gap is formed between the upper and lower premolars or molars. At least a couple of teeth create this gap. As a result, poor quality of chewing of food is observed, and problems with swallowing and the functioning of the jaw joint may occur.
An anterior or lateral bite can occur on one side or both. And finally, in dentistry, there are degrees of severity of bite, depending on the size of the gap or the number of non-occlusive teeth:
- I degree - the size of the gap does not exceed 5 mm, and only the front row of teeth, from the incisor to the canines, cannot close
- II degree – the gap is more pronounced and ranges from 5 to 9 mm. And not only the front teeth do not close, but also the first and second premolars (4th and 5th)
- Grade III is the most severe. The gap between the teeth can be 9 mm or more, and only the outer chewing teeth close together.
Causes of malocclusion in children
The main reasons contributing to the formation of malocclusion in a child are:
- untimely teething;
- problems with posture;
- Sucking on a pacifier, pacifier, or foreign objects for too long;
- mouth breathing (a consequence of ENT diseases. Normally, the child breathes through the nose, and the mouth should be closed);
- heredity;
- the predominance of soft foods that do not create the necessary load on the jaw apparatus.
Kinds
The classification of open bite is based on the influence of the etiological factor and clinical manifestations:
| Types of pathological occlusion | |||
| Impact of causes | External manifestations | ||
| Rachitic (true) | Traumatic (false) | Open anterior bite | Open lateral bite |
| Breathing and speech are difficult, difficulty eating. The face is deformed, the mouth does not close, the mucous membranes are dry. It is transmitted by heredity or due to diseases that deform the formation of the skeletal system during embryogenesis.
| It is most often formed in temporary occlusion, with early tooth loss. They are mainly provoked by bad habits: finger sucking, prolonged use of a pacifier. Often combined with cross pathology. | Separation in the frontal region, with a normal position in the lateral regions.
| The incisors have an incisal-tubercle contact, but there are gaps marked laterally. Can be one- or two-sided. |
Classification of open bite is also carried out according to the degree of separation of teeth:
- Type I: no more than 5 mm.
- II: 5-9 mm.
- III: more than 9 mm.
It is extremely rare for any one type of pathological occlusion to occur. Often the opening is also recorded during progeny. The degree of divergence in the contact of teeth with each other is also looked at in the sagittal direction.
Lack of jaw closure, combined with mesial shift of the lower jaw.