What is the periosteum and where is it located?
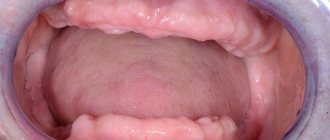
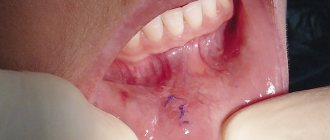
Periosteum (periosteum) is a connective tissue that lines the outer surface of the bone, including the jawbone. It is penetrated by a large number of vessels and nerve fibers and, in fact, connects the tooth with the surrounding ligaments and muscles. When an infection penetrates into this vascular tissue or damage occurs, an inflammatory process occurs. In professional terminology, this diagnosis is called periostitis, and people usually say that a flux has popped up. What the tooth and gums look like in the area of the inflamed periosteum is shown in the photo below.
The photo shows a gum and tooth with inflammation of the periosteum
Most often, inflammation of the periosteum is accompanied by severe symptoms, and the patient experiences severe pain. But if you leave all these signs unattended, drowning out the acute symptoms with painkillers, the pathology risks leading to the formation of an abscess or phlegmon, the development of osteomyelitis, or even blood poisoning. Timely seeking qualified help will allow you to quickly stop the pathological process, eliminate its cause and all factors that can lead to relapse.
Causes of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth
Inflammation of the periosteum is most often provoked by various inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. These are caries, periodontitis, alveolitis, chronic inflammatory process in the teeth, cysts in the jaw, leading to suppuration. Less commonly, the causes of periostitis are:
- infectious diseases associated with the oral cavity (influenza, ARVI, tonsillitis);
- systemic infections (for example, tuberculosis);
- injuries (even minor chips of enamel or cracks in teeth lead to bacterial infection);
- incorrect actions after tooth extraction (usually non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations);
- allergic reactions (can be triggered by medications, incorrectly selected toothpaste or gum gel).
Inflammation of the periosteum can be provoked not only by trauma, but also by tooth extraction. A hole forms at this site, through which infection easily penetrates. Exactly following the recommendations will help you avoid this problem. Issued by the attending physician.
You should not try to cure inflammation of the periosteum at home. Such measures temporarily relieve symptoms, but do not remove the cause.
Symptoms of periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum
Periostitis of the tooth begins with an acute phase, which, if left untreated, gradually turns into a chronic form. The same is characterized by mild symptoms with periodic exacerbations. If we talk about acute inflammation, then in this case the patient usually faces the following unpleasant symptoms:
- redness of the mucous membrane in the area of inflammation,
- increasing pain that can radiate to the temple, ear or eye,
- severe swelling, in which the cheek swells and the face becomes asymmetrical,
- temperature rise to 38 degrees,
- headache and dryness of the oral mucosa as a consequence of general intoxication,
- the appearance of a white or grayish coating on the gums and inner surface of the cheeks,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- the formation of a dense cushion in the causative area - a purulent focus,
- the appearance of fistulas and bleeding,
- tooth mobility and changes in its position.
A symptom of the disease is the formation of a dense cushion and swelling.
As part of a professional diagnosis, a specialist can also detect signs of destruction of the pulp - a neurovascular bundle located in the cavity inside the tooth. This will be clearly visible on an x-ray. Also, with periostitis, a blood test may show an increased content of ESR and leukocytes1. Sometimes the pathology develops without severe pain and other acute symptoms, but usually this occurs already at the chronic stage of the disease.
Signs of inflammation of the periosteum with photos
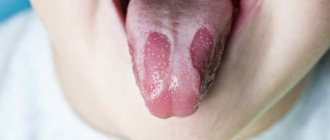
The photo clearly shows that the periosteum of a tooth is a thin connective film that almost completely covers its root. It contains a mass of vascular fibers and cells and serves as a connecting element between the tooth and muscle tissue and ligaments. Such close proximity leads to the fact that when the bone tissue becomes inflamed, the infection easily spreads further and causes periostitis.
Sometimes the connective tissue covering the bone becomes inflamed after a tooth is removed and appears red and loose. With insufficient oral care, microorganisms enter the hole formed in the periosteum, the activity of which activates the inflammatory process. It easily spreads to neighboring tissues and provokes suppuration and prolonged healing of the wound. When extracting a tooth, the doctor can damage the periosteum, which also provokes periostitis.
Any pain is a reason to visit the clinic. Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth is no exception, especially since it passes brightly and painfully. The main symptoms of the acute form of the pathology include:
- severe localized gum pain,
- swelling of the affected sector, which can spread to the cheeks, lips,
- pain on palpation and enlarged lymph nodes,
- an abscess in the form of a dense cushion with purulent contents on the alveolar process,
- facial asymmetry,
- hot swelling in the tooth area,
- unbearable pain when pressing on the problematic tooth (it often spreads to neighboring units),
- Additionally, loosening of teeth in the affected area is possible.
Painful sensations
The main sign of inflammation of the periosteum is a sharp pain in the area of the bone tissue, going from the jaw to the ear, eye, temple. Initially, it occurs in the problem area where the source of inflammation is located. At the same time, the general temperature rises and suppuration increases.
After the flux has formed, the patient feels a little better, the pain dulls, but does not go away. It is in vain to suppress them with analgesics and hope that the tumor will go away. The infection spreads further, and the issue cannot be resolved without a dentist.
Swelling of the gums
Inflammation of the periosteum is localized on the upper or lower jaw, in the area of the jawbone, in the area of the anterior and posterior teeth. Depending on the place of occurrence, the severity of its clinical manifestations varies. The oral mucosa in the affected area is dry, red and hot. The gums swell, become loose, and the swelling quickly spreads to adjacent tissues, the cheek and lip.
Swelling of the cheeks, chin, lips
With advanced inflammation of the periosteum, swelling of the cheeks, lips, and chin is evident. It is especially noticeable when the process is localized on the upper jaw. It becomes painful to touch your face; cold on the affected area brings some relief. It is absolutely forbidden to heat inflammation, take hot drinks and meals. Swelling can be noticed visually, as well as by palpation and examination of the oral cavity. The danger of localizing flux in the upper jaw is that the infection easily spreads to the sinuses.
Hyperthermia of affected areas
When the source of inflammation is located in the upper jaw, the symptoms of periostitis are projected onto the area under the eyes, as can be seen in the photo. When an infection affects the lower jaw, the oval of the face changes. The appearance of a focus of suppuration leads to swelling and redness of the cheek, which is a classic sign of gumboil. At the same time, the temperature rises, chills and general malaise occur.
INTERESTING: what can gumboil mean in dreams?
Other symptoms
Acute periostitis has two stages - serous, when fluid accumulates at the site of the lesion, and purulent (a dense white ball forms at the site of inflammation). Pus can periodically come out through the hole, and the tooth hurts less. In the absence of timely assistance, the process becomes chronic, which is characterized by a sluggish course with periods of exacerbation, reminiscent of the acute stage of periostitis.
On X-ray, bone compaction is noticeable; upon visual examination, facial asymmetry is observed. In the oral cavity on the side of the affected area, hyperemia and swelling are expressed. The chronic form of the disease is much more difficult to treat, since over time the bone tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue.
Factors that provoke inflammatory processes
We have found out what periostitis is and how it manifests itself, and now we will move on to consider factors that can provoke a pathological process in the periosteum. Experts grouped possible causes into three separate categories:
- odontogenic: in this case, inflammation becomes a complication of other dental diseases or complex pathological phenomena. So, for example, periostitis can develop as a result of prolonged eruption of wisdom teeth or, as a consequence, an enlargement of the cyst,
- traumatic: the inflammatory process often occurs against the background of trauma or damage to the periosteum, for example, with a fracture of the jaw or after a complex tooth extraction,
- hematogenous or lymphogenous: the infection enters the periosteum tissue from the inside, that is, through the lymphatic system or blood flow from other organs and systems affected by the pathological process. Quite often, periostitis develops against the background of diseases of the ENT organs.
One of the causes of the pathology may be a fracture of the jaw.
Thus, among the most common provoking factors are advanced dental diseases, in particular caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, complex tooth extraction, usually “eights”, sore throat, ARVI, sinusitis and other pathologies of the ENT organs , blows and injuries to the jaw, the appearance of neoplasms in the thickness of the oral mucosa, errors in the treatment and filling of canals. And this is only a small part of the reasons that can cause the inflammatory process. Therefore, prevention of this pathological phenomenon requires strict adherence to hygiene, timely treatment of dental diseases, as well as careful attitude to the health of teeth and the body as a whole.
Understanding the classification of the disease
What is inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth, you now already know. Now we present to your attention the classification of periostitis.
| View | Peculiarities |
| According to the mechanism of occurrence |
|
| According to the nature of the flow |
|
Forms of periostitis (flux)
As mentioned above, periostitis begins with an acute form and gradually becomes chronic, of course, in the absence of treatment. At first, the pathology progresses very quickly: the gums turn red and swell, the cheek swells, and severe, increasing pain appears. It is simply impossible not to notice these symptoms. But some people prefer to numb the discomfort with painkillers and traditional medicine rather than go to the doctor. As a result, acute symptoms do subside, but this does not mean that the disease has receded. It has only become chronic, which is no less dangerous than the acute form, but much more difficult to treat.
Let's look at the main types of periostitis in a little more detail.
Acute serous form
Serous periostitis manifests itself in the form of rapidly increasing swelling of the mucous membrane and adjacent tissues. Literally within a day, the pathological process reaches its peak, but the pain may not be as acute as with the purulent form. This type of flux usually results from damage to soft or bone tissue. Easily treatable - signs of the inflammatory process can be completely eliminated in 5 days. In rare cases, complications are possible in the form of proliferation of fibrous tissue, deposits of calcium salts or neoplasms in the jaw bone.
Purulent periostitis in the acute stage
This form is characterized by acute pain, which gradually becomes throbbing. In the area of inflammation, severe swelling occurs, which is accompanied by hyperemia of the gums. The pain may radiate to the ear, temple or eye. The patient's temperature rises sharply - up to 38 degrees. As the inflammatory processes spread, the temperature will rise. Usually the disease develops as a result of infection of oral tissues.
The photo shows purulent periostitis
Diffuse acute periostitis
The development of pathology begins with the occurrence of acute pain and severe swelling in the area of the causative tooth. At the same time, the body temperature rises, and the patient develops weakness and general malaise, headache. It should be noted that this form of flux is much more difficult on the lower jaw than on the upper jaw. The lesion spreads over a wide area, and treatment requires surgery along with antibiotic therapy.
Symptoms of the disease also include weakness and general malaise.
Chronic stage of inflammation
In fact, the chronic form is quite rare. The inflammation is localized in the area of the alveolar processes, most often on the lower jaw. The mucous membrane turns red and swells a little, but only within the gums, that is, not spreading to the face. Swelling of the lymph nodes almost always occurs, and the bone tissue becomes denser at the site of the lesion. The development of the chronic stage can last from six months to several years. Exacerbations occur periodically.
Symptoms of ossifying and fibrous periostitis
Ossifying periostitis occurs in a chronic form, covering the periosteum and tissues adjacent to it. The disease can form as an independent inflammation or as a consequence of certain chronic diseases:
- osteomyelitis;
- arthritis;
- syphilis;
- bone tuberculosis;
- rickets.
Pathology of this type has minor manifestations. There are no pain sensations, there are no signs of intoxication. In the area of inflammation, slight swelling with an uneven surface is visible due to the proliferation of bone tissue.
Fibrous inflammation of the periosteum is characterized by slow development, when for several years it is constantly irritated as a result of some concomitant disease (bone necrosis, arthritis).
Its symptoms include:
- painlessness;
- slight swelling of the affected area;
- slight bone thickening.
The main danger of fibrous periostitis is its predisposition to transform into a cancerous tumor.
A correct and timely diagnosis will not allow the acute form of the disease to develop into chronic periostitis. And effective treatment can completely cure the patient.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis of acute periostitis is usually not difficult, since the symptoms are pronounced. As part of a visual examination, a specialist can detect noticeable swelling of the mucous membrane, its redness, and the presence of infiltrate. In the event that odontogenic inflammation occurs and the cause of its appearance is caries or pulpitis, the causative tooth will be partially destroyed or there will be a noticeable carious cavity on it.
In the chronic form of the pathology, the neoplasm will be clearly visible on the x-ray image. In this case, it will be necessary to carry out differential diagnosis to exclude lymphadenitis, osteomyelitis, sinusitis or periodontitis. To do this, a general blood test is performed, the results of which in case of periostitis will show an increased content of leukocytes and ESR.
X-ray examination allows you to see hidden problems
Causes of periostitis
Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth occurs for many reasons, and the nature of dental care depends on them:
- advanced stage of caries,
- cyst on the root of a tooth (see also: cyst of a tooth root on an x-ray),
- jaw injuries,
- tooth extraction due to infections, colds,
- damaged the periosteum when removing a dental unit,
- hypothermia,
- complication or later treatment of periodontitis, pulpitis,
- poor oral hygiene,
- exacerbation of chronic periodontal diseases,
- sore throat, sinusitis, and other infections that enter the gum tissue through the circulatory system.
Principles of treatment of inflammation of the periosteum
Trying to cure inflammation on your own at home is strictly prohibited. Without consulting a specialist and making an accurate diagnosis, such arrogance will lead to even more serious consequences - the development of complications. Proper treatment must be carried out in several directions at once.
Surgical intervention
In the presence of purulent infiltrate, periostotomy is required. This is an operation that involves the opening of a neoplasm, and sometimes it is performed, including in the serous form of the pathology, to reduce internal pressure on the tissue. Surgical intervention involves the following steps:
- the specialist administers an anesthetic - local anesthesia is applied,
- makes an incision in the gum in the area of infiltration,
- opens the abscess, cleans out the purulent contents, carries out antiseptic treatment of tissues, fixes the drainage to ensure the outflow of exudate,
- At the same time, the doctor treats teeth that have become a source of infection. Sometimes they need to be removed
- open canals are filled with a special medicine and carefully sealed.
After removing the pus, drainage is installed
“My flux somehow jumped out, so my temperature jumped to 39. Naturally, my cheek swelled to incredible sizes. In addition to the fact that the tooth itself hurt terribly, my head was also pounding. I ran to the duty room, and from there they took me straight to the maxillofacial department. I had to cut almost half of my cheek, I still have a barely noticeable scar. If you feel something wrong in your gums, run to the doctor! Do not launch under any circumstances!”
Nelli7, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
Usually you have to visit the dentist several times - this is necessary to make sure that there is a complete absence of pus and that the infection is guaranteed to be eliminated. In this case, the patient is required to be prescribed antibiotics.
Drug therapy
In some cases, when the patient seeks help at the earliest stages of the disease, it is possible to do without surgical intervention. Regarding how to treat inflammation of the periosteum in such a situation, drug therapy with individually selected medications is used:
- antibiotics - Doxycycline, Lincomycin, Amoxicillin or Azithromycin. The latter has a milder effect, so it is sometimes prescribed to children and women during pregnancy, but only in emergency cases and with compelling reasons.
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs - “Cifran”, “Metronidazole”, “Nimesil”, “Diclofenac”,
- immunomodulatory and multivitamin complexes as maintenance therapy,
- antibacterial rinses, for example, Chlorhexidine,
- anti-inflammatory ointments and gels - “Cholisal”, “Metrogil-Denta”, “Levomekol”.
Medicines should only be prescribed by a specialist.
The therapeutic course usually lasts about 5-7 days. If, as a result, the desired effect is not achieved, you will have to move on to more radical measures. Also keep in mind that the affected area should never be heated - this will only accelerate the development of inflammatory processes and increase the risk of complications.
Physiotherapy as maintenance therapy
In order to speed up rehabilitation, maintenance therapy is carried out. Within this area, physiotherapeutic procedures are usually prescribed:
- laser therapy,
- UHF,
- darsonvalization,
- infrared irradiation,
- electromagnetic techniques.
The photo shows the use of a laser in the treatment of pathology.
The use of these techniques according to a correctly developed scheme allows you to achieve a noticeable effect. The affected tissues are restored much faster, and the healing processes of wound surfaces are accelerated.
Traditional medicine tips
You can resort to traditional medicine recipes only with the permission of your doctor. Sometimes the use of such drugs gives a good effect as maintenance therapy, but not as the main treatment. But without prior consultation with a specialist, independent attempts to relieve inflammation most often lead to the development of complications. And under no circumstances should you try to open a purulent abscess yourself - only an experienced specialist should do this.
So, the following tips will help relieve acute symptoms and alleviate the condition a little:
- rinse your mouth with a soda-salt solution - this will help relieve swelling and reduce pain,
- rinse your mouth with a decoction of medicinal herbs - chamomile, sage, calamus root and even green tea. The components of these plants have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect,
- from time to time apply a piece of ice wrapped in a handkerchief or gauze to the cheek on the side of the affected area - this will help slightly reduce the pain,
- In case of acute pain, you can take a painkiller.
Chamomile decoction will help alleviate the condition.
All these actions are permissible only with the consent of the doctor. It is also recommended to refrain from taking painkillers and other blood thinning medications before visiting a specialist. Medicines can somewhat distort the overall picture and make diagnosis difficult.
Treatment methods for periostitis
If the periosteum hurts and is inflamed, you should immediately go to the dental office. Only a dentist can accurately diagnose and prescribe appropriate comprehensive treatment. Trying to solve the problem at home, basing a “diagnosis” on how the affected area looks compared to various photos from the Internet, is extremely unwise.
Depending on the form and severity of the disease, the specialist chooses the most effective treatment method. The entire course can consist of a number of different manipulations:
- surgical intervention;
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- traditional medicine methods.
The latter are auxiliary means that are aimed solely at alleviating the patient’s condition and speeding up recovery. Surgical intervention is used for the purulent form of periostitis.
Surgical
The operation to remove purulent compactions is called periostotomy. However, in some cases, the dentist can perform surgical intervention for other forms of the disease. The purpose of such manipulation is to reduce internal pressure on the tissue. The procedure itself is carried out in stages:
- local anesthesia is given;
- make an incision in the gums up to 2 cm in the problematic sector, through which the pus will be removed;
- carry out treatment with antiseptics and install drainage;
- treat dental diseases that have become a source of periostitis, sometimes diseased dental units are removed;
- The dental canals are closed and fillings are installed.
Conservative
A conservative treatment method with medications is relevant at the initial stage if the patient consulted a specialist as soon as the first signs of the problem appeared. In this case, the following medications are prescribed for 5–7 days:
- Antibiotics: Doxycycline, Lincomycin, Macropen, Amoxicillin. Their goal is to stop the spread of infection.
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory: Tsifran, Metronidazole, Tsiprolet, Diclofenac, Nimesil. They stop inflammation and relieve pain.
- Vitamin complexes and immunomodulators. Helps maintain normal functioning of the immune system.
- Antiseptics. Chlorhexidine, Miramistin for mouth rinse.
- Local anti-inflammatory gels. The most popular: Metrogyl-Denta, Cholisal, Solcoseryl.
Physiotherapy
One of the most effective ways to speed up the healing process and reduce the severity of unpleasant and painful manifestations is physiotherapeutic procedures. These include:
- UHF and microwave;
- laser treatment;
- darsonvalization (use of weak currents);
- iontophoresis;
- use of infrared rays;
- exposure to electromagnetic fields.
A prerequisite for the effectiveness of this technique is regularity and adherence to a specially selected scheme.
The result of physiotherapeutic procedures will be faster healing and better regeneration of damaged tissues.
ethnoscience
Measures that complement basic treatment include traditional medicine methods. They are aimed at reducing pain, relieving inflammation and restoring damaged tissue. At home they use:
- Soda-salt solution. They need to rinse their mouths.
- Herbal tinctures and decoctions. They are also used for mouth rinses. The most common herbs are: oak bark, chamomile, calendula, sage, calamus root, green tea, lemon balm.
- Cabbage leaf. It must be applied to the inflamed area.
- Cold compresses.
What complications can there be?
Even if some time after the onset of acute symptoms the pain and swelling disappear by themselves, this does not mean that the flux has passed. Without proper treatment, the pathology can only go into the chronic stage, and also lead to a number of serious complications.
Superficial or deep phlegmon
Superficial phlegmon is a neoplasm in the subcutaneous tissue. Deep phlegmon forms on muscle tissue. In fact, this is a consequence of inflammatory processes caused by staphylococci, dental spirochetes, streptococci and anaerobic bacteria. This is a serious pathological condition that requires urgent surgical intervention.
A complication of the pathology can be phlegmon
Purulent abscess
The formation of a purulent focus - a cavity in which inflammatory exudate gradually accumulates, which leads to a rapid increase in its size. In this case, the patient experiences severe pain, general malaise, and increased body temperature. If the abscess breaks, the pain will subside and the swelling will go away. But this situation is even more dangerous, because there is a risk of blood poisoning. Therefore, the abscess needs to be opened only surgically.
Abscess is quite a dangerous disease
Osteomyelitis – damage to bone tissue
An infectious lesion that is accompanied by purulent processes and spreads to the bone, bone marrow and periosteum, as well as adjacent soft tissue. Pathology leads to the gradual destruction of bone tissue, and this condition can be aggravated by diabetes, alcoholism, old age, weakened immunity, varicose veins and thrombophlebitis. Characteristic symptoms include a sharp rise in temperature up to 40 degrees, as well as severe pain, which reaches its peak approximately on the 2-3rd day of the development of the disease. Treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting.
The photo shows osteomyelitis
Sepsis - blood poisoning
The most serious of all possible complications is associated with general blood poisoning and poses a real threat to the patient’s life. The infection enters the bloodstream, and the entire body is affected. In such a situation, immediate hospitalization is necessary - very long and complex treatment will be required, which can last for months. Therapy involves the administration of large doses of antibiotics. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the chance of salvation.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease
Signs of inflammation of the periosteum in most cases are difficult to miss, because the disease is acute. But, nevertheless, they may differ depending on the nature of the inflammatory process.
Serous periostitis: the patient feels pain, the intensity of which can vary depending on the circumstances from moderate to unbearable. From the beginning of its development to the onset of severe symptoms, the disease progresses very quickly (in 3 days), resulting in the formation of a cystic neoplasm filled with serous fluid on the mucous membrane. At the same time, the surrounding tissues swell, and the cheek on the side where the affected tooth is located may also swell. You may also experience a general deterioration in health and loss of appetite.
Purulent periostitis: the pain is acute, radiating to the ears, head, and temples. Even when talking or trying to move your jaw or head, you will experience severe pain. What other symptoms are characteristic of this form of the disease: severe swelling of the soft tissues and cheeks, lips, enlarged lymph nodes, increased body temperature (up to 38 degrees). Temporary loss of sensation or numbness in the lips may also occur, and the affected tooth may begin to loosen. The resulting abscess, which can be easily seen on the mucous membrane, is filled with purulent contents. In some cases, pus may ooze out or the tumor will burst out completely - then you will experience relief, but the impression of lightness is deceptive and fraught with complications, so in no case should such a symptom be ignored.
Diffuse periostitis: this is the most severe form of the disease, which is characterized by severe symptoms. Firstly, the jaw swells very much. Secondly, body temperature rises sharply, which can reach 39 degrees. Thirdly, the patient experiences excruciating pain that spreads to the entire head. Fourthly, the patient cannot eat, speak, and even has difficulty swallowing. Fifthly, an unpleasant, even foul odor from the mouth appears from the mouth.
This type of pathology differs from purulent one in that the focus of inflammation here does not have a specific localization, and the infection begins to spread to all nearby organs and tissues.
As for the chronic form of the disease, it occurs with much less sparse symptoms: the swelling is local in nature and does not cause noticeable asymmetry of the face, the pain is barely noticeable and does not cause severe discomfort. However, this state of affairs does not mean that the pathology does not need treatment. The chronic form can be complicated by the fact that negative changes begin to occur in the structure of the bone tissue of the jaw, and it begins to thicken.
What can be done as a preventive measure
Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth is a rather complex and painful phenomenon, which most often requires surgical intervention and requires the mandatory use of antibiotics. But we can do everything possible to prevent such a nuisance. Experts in this regard recommend adhering to the following rules of prevention:
- brush your teeth 2 times every day - morning and evening,
- rinse your mouth after every meal, use floss, as well as an antibacterial rinse after morning and evening brushing of your teeth,
- take care of the health of your teeth and gums - avoid injuries and falls,
- when the first signs of a pathological process appear, immediately seek help from specialists,
- maintain immunity, take multivitamin complexes from time to time and try to lead an active lifestyle, eat right,
- use an individually selected brush and paste - you should consult your dentist about this,
- visit a specialist twice a year for prophylaxis and undergo the professional procedure with the same frequency. hygiene – removal of plaque and dental deposits.
Regular medical examinations will help to recognize the problem in time.
The prognosis of treatment mainly depends on how quickly the patient responded to the symptoms and sought help. Under no circumstances should you start a pathological process, because flux can not only cause acute pain, but also lead to very serious complications. The best preventative measure is to maintain oral hygiene and regularly visit the dentist for preventive maintenance - at least twice a year.
- Robustova T.G. Periodontitis, periostitis, osteomyelitis of the jaws. Guide to oral and maxillofacial surgery, 2000.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflamed periosteum
The doctor must diagnose the disease. It includes x-rays and a visual examination of the oral cavity. It is also necessary to differentiate periostitis from other serious pathologies: abscess, phlegmon, periodontitis and lymphadenitis.
As for the treatment process, it may include a whole range of measures or be limited to individual events. It all depends on the form of the pathology. So, let's look at how inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth can be treated.
Drug treatment method
In the early stages of the disease, taking medications can be an independent measure, but if it does not produce results, then it is combined with other treatment methods. Also, medications are required to be taken regardless of what form of the disease is diagnosed in the patient.
Most often, doctors prescribe therapy, which consists of 5-7 days of antibiotics, antihistamines (for example, Erius or Claritin), anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesulide or Nimit), painkillers (Nurofen) and treatment with local antibacterial agents (“Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin”). Among antibiotics, Amoxiclav or Lincomycin give good results.
Surgical method of treatment
The first and second methods are often combined, because Independent drug therapy does not always bring a positive result, and the main task of the doctor here is not only to stop the inflammatory process, but primarily to remove the purulent exudate. For these purposes, the specialist gives the patient anesthesia, then opens the source of inflammation, cuts the gum and drains the wound, and excises dead tissue. Also, most often, a diseased tooth is removed in parallel, if it is the one that caused the development of the inflammatory process. Less often, a diseased tooth is treated, the canals are cleaned, medicine is applied and a temporary filling is placed. Next, after the drainage of pus, the wound is sutured, and the patient takes the prescribed medications at home.
If the cause of the flux is other organs or circumstances, the doctor must also sanitize the oral cavity, treat diseased teeth, and remove plaque. In the absence of these measures, the infection can linger in the oral cavity and the inflammatory process can easily resume.
Physiotherapeutic method
Most often, it is prescribed after complete surgical removal of the source of infection and only outside the acute phase of the chronic form of the disease. The main goal is to restore the condition of the damaged periosteum and mucosa, to force the tissue to regenerate faster.
Here the doctor may recommend undergoing procedures using electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound equipment, darsonvalization, ultraviolet radiation, hydromassage (for this purpose, be sure to additionally purchase an irrigator if it is not already in your home arsenal of oral care products), paraffin applications, and electromagnets.
What to do if the periosteum hurts
- Stop exercising. In the early stages, the problem with the periosteum can be solved by simply resting. Avoid shock loads on your feet so that damaged tissues have time to recover. If it is not possible to completely stop exercising, train without impact on your legs. Switch to a more gentle mode: replace running with swimming or cycling.
- Consult your doctor. An orthopedic traumatologist or sports medicine doctor will be suitable. The problem can be identified through examination or additional studies: x-ray or MRI. Do not try to diagnose and select treatment on your own. Trust your health to specialists.
How to treat periosteum
Restoration of the periosteum can take from 2-3 weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
For inflammation of the periosteum, the following is usually prescribed:
- RICE treatment (rest, ice, compression and leg elevation)
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- ointments with a “cooling effect”
- calf muscle massage
Prevention of pain in the periosteum
Strengthen your muscles . Most running injuries occur due to weak muscles that cannot handle the volume of running. Do strength exercises regularly, especially on stabilizer muscles, and strengthen your lower legs and feet. The more trained and stronger the muscles, the less stress is placed on the bones, ligaments and joints. This is why beginners have problems with the periosteum more often than experienced athletes.
Read:
- Exercises for the muscles of the foot and ankle
- Exercises for the Achilles: prevention and recovery
- Knee exercises
Increase volumes gradually . Overload in training is one of the main causes of health problems among athletes. Sometimes it seems that you are ready to run faster and longer - but this does not mean that the body is ready for high loads. To avoid injury, increase your training volume by no more than 10% per week.
Watch your running technique . Learn to run easier and take steps more often, place your feet correctly when landing. The quality of your running can be determined by your cadence. If it is low, your running is uneconomical. A cadence of 150 or lower for beginners indicates incorrect running technique . Long steps increase the impact load on the legs, which leads to ankle injuries.
Choose sneakers . It will not be possible to correct the anatomical features of the foot, but you can absorb the shock load by choosing the right sneakers . Almost every sports brand has sneaker models for people with flat feet and overpronation. Don't forget that sneakers have a lifespan after which they need to be changed. Usually it is 800-1200 km, maximum 1500 km. After such a run, the foam wears down and stops shock-absorbing, which can lead to injury.