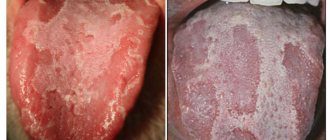
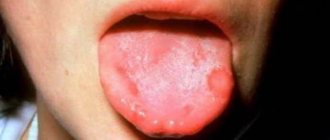
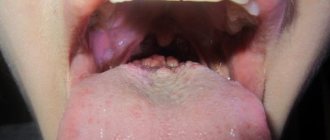
Ulcers formed on the oral mucosa can be both individual neoplasms and harbingers of various dangerous diseases. In general, ulcers on the tongue are not so terrible in their appearance for a person, but in various situations they can be harbingers of serious diseases that can cause serious complications. You can see the damage in more detail and understand what it is in various photos and videos.
The sore itself on the root of the tongue is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process that destroys soft tissue. It causes painful itching. Because of this, eating food turns into torture.
Ulcers on a child's tongue
The cause of sores on a child’s tongue can most often be either stomatitis or mechanical damage. It is also common for children under one year of age to develop cysts in the sublingual gland. But there is no need to be afraid of such an appearance. Most often, these cysts disappear on their own when the child is one year old.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
But still, when you need to find out why ulcers appear on the tongue and treatment methods for a child, it is best to play it safe. You should consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Causes of plaque
In normal condition, the surface of the tongue of a healthy child should be pink. The formation of a thin white or grayish coating, through which the papillae and the natural color of the tongue are visible, is also considered normal. This type of plaque usually appears in the morning, is easily removed with a toothbrush and does not have an unpleasant odor.
In summer it thickens slightly, acquires a yellowish tint, and in winter it becomes thin and white. If such a phenomenon occurs in hot weather due to extreme thirst, then to eliminate it it is enough to drink a sufficient amount of water.
In infants, a white coating on the tongue after feeding most likely means milk residues that can be easily removed. Other safe reasons for a white-yellow coating on a child’s tongue include:
- Consumption of certain foods: carrots, persimmons, strong tea and coffee, drinks with orange dyes.
- Taking certain medications: Furazolidone, sore throat lozenges, vitamins, antibiotics.
- Incorrectly selected milk formula.
- Overeating fatty, fried foods.
This plaque has a dense texture, is difficult to remove and is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth. The reasons for this phenomenon can be very diverse.
Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity
Inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa, which are commonly called stomatitis, are one of the common causes of the tongue covering with a whitish coating with grains. Depending on the type of stomatitis, symptoms may occur:
- round white sores on the oral mucosa;
- burning, pain, dry mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- bad breath;
- increased salivation;
- lethargy, weakness.
Sometimes there may be an increase in body temperature, swelling of the tongue, gums or cheeks. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Fungal diseases and dental caries
There are various microorganisms in the human mouth that do not cause harm. But in the presence of predisposing factors, fungi begin to actively multiply. Children are diagnosed with candidiasis, an oral disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida. A sign of this pathology is a white cheesy coating on the tongue.
Symptoms may occur:
- discomfort, pain during feeding;
- loss of appetite;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- itching, burning;
- plaque formation in the mouth;
- dry mouth.
A white tongue in a child means an advanced form of caries, which is an infectious focus. Proper oral care can prevent the progression of pathology.
Pathologies of the body's respiratory systems
The white surface of the tongue sometimes indicates the presence of pathological changes in the respiratory system of the body that are viral or bacterial in nature. If the cause is influenza or acute respiratory infections, the following symptoms are observed:
- redness of the throat;
- cough;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- runny nose.
If the tonsils are covered with a white coating, then a sore throat is diagnosed, and a change in the front part of the tongue may indicate bronchitis. As the disease progresses, the plaque becomes foamy, thickens, and acquires a darker color. Tonsillitis is characterized by inflammation of the tonsils and is manifested by whitish covering of the tonsils, pain when swallowing and hyperthermia of the body. With pharyngitis, a dense, bumpy whitish coating, redness and looseness of the throat may be observed.
Infectious diseases
If the white coating on the surface of the tongue is infectious in nature, then it is quite difficult not to notice, since the pathology usually has severe symptoms in the form of high fever and signs of intoxication. This manifestation is characteristic of scarlet fever and diphtheria. With scarlet fever, the tongue becomes covered with a white film with small red spots, symptoms are observed:
- rash on the body;
- lymphadenitis;
- throat hyperemia;
- change in color of the tongue and tonsils to white-yellow;
- severe intoxication.
Other causes of plaque on the tongue
The formation of a white or yellow coating on the surface of a child’s tongue may indicate the presence of pathological conditions:
- allergic reaction;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- metabolic disease;
- pathologies of the kidneys, liver, lungs;
- frequent constipation;
- dehydration of the body;
- helminthic infections;
- food poisoning;
- autoimmune diseases.
The reason is a weakening of the immune system, which can result in colds and infectious diseases. As you can see, the causes of plaque on a child’s tongue can be very diverse. To make an accurate diagnosis, you must contact a medical facility.
Treatment of ulcers on the tongue of a child
When the tongue ulcer is small or there is the same inflammation on the oral mucosa, then for treatment you should use an antiseptic gel purchased at a pharmacy. It must be applied to the sore every three hours. Such a gel should quickly cure the disease in 5 days, but it can be used for longer only on the recommendations of a doctor.
| Folk remedy | Recipe | Method of use |
| Coriander | 1 tbsp. l. coriander, pour 250 ml of boiling water, cook for half an hour over low heat and leave for a couple of hours. Strain before use | Rinse your mouth with the decoction several times a day |
| Lemon juice | Squeeze fresh lemon juice | Soak a cotton pad in juice and apply to sore spots for 2-3 minutes |
| Potato | Peel the potatoes and cut into wedges | Apply a piece of potato to the ulcer and hold for 5-7 minutes |
| Aloe and olive oil | Squeeze juice from aloe leaf and mix with the same amount of oil | Treat inflamed mucous membranes; you can also apply a bandage soaked in the mixture |
| Propolis | Pour 2-4 small pieces of propolis with water and boil for half an hour | Rinse your mouth with warm broth up to 10-12 times a day |
As for traditional methods of treating ulcers on a child’s tongue, a soda solution is used here. It is necessary to dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda in 150 ml of water. This method is suitable for children from 5 years old and even adults.
To prevent the occurrence of ulcers on a child’s tongue, the following rules must be observed:
- Teach your child to brush their teeth correctly and thoroughly and monitor this.
- Do not skip routine pediatric and dental examinations.
- Take multivitamin complexes during periods of acute vitamin deficiency.
- Protect your child from stress as much as possible.
- Remove sharp and dirty objects from the child’s free access.
- Wash your face and hands after going outside.
Causes
Causes of tongue ulcers in children:
- Stomatitis (aphthous, herpetic, necrotic);
- Thrush;
- Thermal burn, injury;
- Afta Bednar;
- Diseases of internal organs;
- Rashes caused by taking medications;
- Reduced immunity.
The type of rashes and methods of their treatment depend on the disease that caused them.
Reds
Red ulcers occur in diseases such as:
- Stomatitis;
- Glossitis;
- Bacterial dermatosis;
- Herpetic infection.
The appearance of ulcerative wounds on the tongue can be caused by an allergic reaction of the body to foods or fruits and vegetables that are red or orange in color. Sometimes it is worth analyzing the child’s diet so that there is no unnecessary cause for concern.
Infectious diseases in which red sores appear are accompanied by pain and increased salivation. The child is capricious and refuses to eat and drink. Body temperature rises. Treatment is carried out with the use of antiseptics, which are used to treat the surface of the tongue.
White
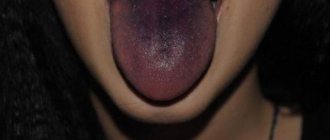
White ulcers on the tongue or a whitish coating may appear with non-infectious glossitis. The disease is associated with hormonal imbalance, worms, and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. With glossitis, the ulcers can change locations, but do not cause discomfort.
How to treat ulcers in this case? Sometimes it is enough to enrich the baby’s diet with vitamin complexes or treat the affected areas with antiseptic agents.
Ulcers appear randomly. At the tip of the tongue, later found in the larynx area. They are not painful and are covered with a coating reminiscent of curd masses.
If rashes on a child’s tongue are accompanied by pain, anxiety, and high fever, fungal diseases can be suspected. To get rid of thrush, it is enough to treat the surface of the tongue with a weak soda solution. In other cases, more serious antifungal treatment is required.
Purulent
Purulent ulcers on the tongue appear with stomatitis. First on the tip of the tongue, gradually spreading over the entire surface of the mucous membrane, capturing the inner surface of the cheeks. Plaques are painful, purulent, white with a red edge.
The main reason is most often associated with failure to comply with basic hygiene standards. This explains why the pathology occurs in older children.
In addition to regular oral hygiene, it is necessary to treat purulent rashes with antiseptics. This is an elementary practice that allows you to get rid of the disease and is used as a preventive measure.
The same symptoms may appear after a thermal burn or against the background of an allergic reaction. The curiosity of children in the first years of life leads to dangerous objects, powders or liquids appearing in the mouth.
On the tip
Small single ulcers on the tip of the tongue most often occur due to trauma. The baby can damage the tip by biting it. It is possible that the injury was caused by sharp cutlery. Such ulcers on a child’s tongue do not require special treatment. It is enough to carry out hygiene procedures, avoid hot foods and drinks until complete healing.
An ulcer on the tip of the tongue, especially an old one, may indicate an infectious disease. Small ulcers on the tip of the tongue appear with the following diseases:
- Stomatitis;
- Glossitis;
- Liver or gastrointestinal diseases.
Even if this does not cause any discomfort to the baby, it is necessary to see a pediatrician and undergo an examination.
Side
A lack of vitamins B6 and B2 in a child’s body can cause ulcers to appear on the side of the tongue and at the same time on the lips or in the corners of the mouth. If the whites of the baby's eyes turn red and dandruff appears, this confirms vitamin deficiency. Ensuring a complete supply of B vitamins is quite difficult. This requires complex vitamin therapy.
How to treat ulcers on the tongue of an adult?
It is possible to cope with such a problem on your own only in the case when the ulcers are located only on the mucous surface of the mouth, that is, they are focal in nature. In this case, the patient either has stomatitis or a trivial injury. But still, there are a number of factors in which you should not postpone a visit to the doctor until later:
- In addition to the oral cavity and tongue, other parts of the body are affected;
- a huge wound on the tongue;
- ulcers do not heal for a long time;
- heat;
- dizziness;
- itching;
- redness of the eyes.
Also, depending on the cause of the ulcers, it is necessary to determine which doctor can help:
- Dentist. It can help if the oral cavity is affected. For example, a patient accidentally bit his tongue and, as a result, an ulcer appeared.
- Gastroenterologist. If the damage occurs due to aphthous stomatitis.
- Venereologist. When syphilis is detected in a patient.
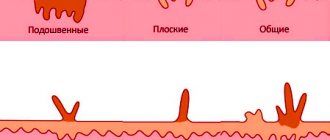
Types of sores
The most likely causes of ulcers on the tongue or mucous membranes of a child include infectious diseases. Dirt gets into the toddler's mouth easily - he constantly pulls toys and hands into it. Another child who already has an oral infection can also serve as a source of provoking the disease. The following oral diseases are most often diagnosed in childhood.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis means inflammation of the oral mucosa. During this disease, the inner surfaces of the cheeks become red, a white coating appears on the tongue, and painful ulcers form. Stomatitis develops due to the spread of pathogenic bacteria. The risk group includes children with weakened immune systems and untreated teeth.
It is rare that a child does not suffer from stomatitis
Depending on the causes of occurrence, the following types of stomatitis are distinguished:
- viral (accompanied by severe intoxication of the body, the temperature may rise);
- infectious (often develops against the background of pneumonia, sore throat or sinusitis, the disease is seasonal);
- traumatic;
- allergic.
Thrush
Thrush, or candidiasis, of the oral cavity most often affects children in the first year of their life. The causative agent of the disease is Candida yeast. Their active reproduction is facilitated by dysbacteriosis, instability of the immune system and the use of antibiotics. The sore manifests itself in the appearance of white spots on the tongue and oral mucosa. In some cases, the throat is affected.
Thrush can be transmitted directly during childbirth (if the mother is its carrier), due to insufficient care of the baby after birth and disruption of the body's microflora. Treatment most often consists of regularly treating the mucous membrane with a baking soda solution.
Herpetic gingivitis
Herpetic gingivitis develops when the herpes virus gets into the oral mucosa. The risk group includes preschool children. Characteristic signs of the disease are bleeding and swelling of the gums, and the formation of ulcers on them.
If you suspect gingivitis, it is imperative to consult a specialist. If effective therapy is not selected in a timely manner, the disease can develop into periodontitis, which can lead to premature tooth loss.
Drug treatment
Regardless of the factors that preceded the formation of an oral ulcer, the treatment methods are similar. Treatment is aimed at preventing the process of inflammation and relieving pain in the oral cavity.
Before treating a wound on the tongue with an anti-inflammatory ointment, the mucous membranes are treated with an antiseptic. It is also recommended to take vitamins to restore tissue at the site of inflammation. If a white sore appears on the tip of the tongue and is very bothersome, then painkillers are also prescribed. How to treat tongue ulcers at home:
- Zelenka is an antiseptic that has been tested over the years, but the procedure itself is not pleasant.
- Hydrogen peroxide - allows you to treat wounds several times a day.
- Lidocaine in gel form – relieves pain.
- Aqueous solution of furatsilin.
Now let's look at situations where it is necessary to use more serious drugs:
- For fungal diseases, Nystatin or Levorin is prescribed. Such drugs can be dissolved or made into a rinse solution and taken at regular intervals.
- When affected by the herpes virus, Zovirax and Acyclovir are used.
- For ordinary stomatitis, propolis and chlorhexidine in the form of a spray or lozenges will help.
- For aphthous stomatitis, in addition to local treatment, the following drugs are also used: gels and ointments based on corticosteroids, painkillers containing benzocaine and lidocaine.
- It is recommended not to eat spicy or salty foods during treatment, so as not to further irritate the mucous membranes.
What can cause the disease?
Lesions on the tongue can have different causes; they can be divided into three groups:
- oral diseases;
- injuries;
- general diseases.
Stomatitis - factor No. 1
The sore most often appears with stomatitis of various types:
- Aphthous stomatitis can be chronic, so aphthae will become a constant companion throughout life, depending on the stage of the disease. During an exacerbation, the sore may pop up in only one place or a whole cluster of ulcers will appear on the tongue. Aphthae can be recognized by their pronounced borders, inflamed at the edges; they are extremely painful and interfere with eating and talking. The average healing time for an ulcer with aphthous stomatitis is a week; with prolonged treatment, a scar may remain in its place.
- With herpetic stomatitis, a large accumulation of watery blisters first appears, which quickly burst and turn into ulcers. They have blurred boundaries and may have a grayish coating in the center. More often, herpes appears on the lower surface of the tongue and heals in 7-10 days, leaving no scars.
- With simple and candidal stomatitis, small ulcers may appear, from one to several pieces, but this happens with a protracted form of the disease. In the first case, the central ulcer is covered with a yellowish-gray coating, in the second - with a white cheesy coating.
- Setton's aphthosis or recurrent necrotizing periadenitis is also accompanied by the appearance of ulcers on the tongue, as well as the inside of the cheeks and lips. With this disease, the sores are located mainly on the side. First, a thickening is felt under the mucous membrane of the tongue, which subsequently develops into dense ulcers with raised edges. Inside them there is an inflammatory infiltrate consisting of lymph, blood and cellular accumulations. Ulcers with Setton's aphthosis are very painful, difficult to treat and often do not go away for several months.
- Bednar's aphthae are common in children. The ulcers are covered with a light yellow coating and are localized on the tip of the tongue. They appear due to poor oral hygiene. With treatment, the disease goes away quickly, leaving no visible traces.
Traumatic factor
Ulcers caused by trauma are associated with external influences, such as:
- when biting the tongue;
- when using a hard toothbrush;
- due to cuts received during dental treatment;
- when scratching the tongue with a chipped tooth or a sharp filling, as well as poorly made dentures and braces;
- when the tongue is irritated by food or medications.
Sores after injuries are not so painful. As a rule, unpleasant sensations arise only when they are exposed to irritants in the form of spicy, salty, sour, and hot foods. If the factor that caused the damage to the mucous membrane is eliminated, healing will occur quickly.
In the presence of chronic aphthous stomatitis, trauma can cause severe rashes.
Sores as a symptom of concomitant diseases
The third group of reasons why ulcers appear on the tongue is associated with common diseases. These include:
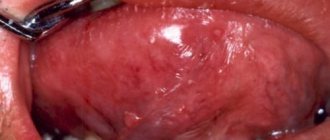
- Necrotizing gingivostomatitis is manifested by the appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa, in particular on the tongue. The cause of the development of the disease is viral infections, decreased immunity, allergic stomatitis, and hypothermia. In addition to formations on the tongue, the disease is accompanied by bad breath, excessive salivation, fever, and a yellow-gray coating on the gums. Ulcers caused by gingivostomatitis have uneven, blurred edges and a greenish coating. They often bleed, which causes severe pain.
- With pulmonary tuberculosis, bacteria often enter the oral cavity, causing a pathological effect on the tongue. At the initial stage, the mucous membrane is covered with small tubercles, which subsequently turn into small ulcers, rapidly increasing in size. Tuberculosis sores are loose and shallow, often bleed, and their edges are uneven. Additional symptoms of the disease are fever and general malaise.
- Treponema pallidum causes syphilis , and when it comes into contact with the mucous surface of the tongue during primary infection, it leads to the formation of a hard chancre. The latter is most often located on the back of the tongue, in rare cases - on its tip or side. The ulcers are absolutely painless and have a dense structure. Over time, the submandibular lymph nodes enlarge. The diameter of chancre is 5-10 mm, but there are both small, about 1 mm, and large, over 2 cm, ulcers. With primary infection, the healing period is 1 month, but if syphiloma is a manifestation of secondary syphilis, then the healing period is long, up to 4-5 months. After healing, star-shaped scars remain at the site of the ulcers.
- In 30% of cases, HIV is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers in the mouth. To a greater extent, the problem is localized on the gums, but sores also occur on the tongue, lips, palate, and cheeks.
- Malignant formations from squamous epithelial cells are more common in men. They appear 7 times more often than women. The causes are smoking, alcohol abuse, chronic mechanical injuries of the tongue, herpes and papilloma viruses.
In the photo there is an ulcer on the tongue with necrotizing gingivostomatitis.
There are three forms of the disease:
- Papillary - in this case, ulcers appear above the mucous membrane of the tongue.
- Ulcerative is accompanied by the appearance of bleeding wounds with jagged edges.
- The infiltrative form is manifested by pain. A dense, lumpy infiltrate appears on the tongue, palpable on palpation. Cancer often affects the side walls of the tongue; in rare cases, it occurs on the back, undersurface, or base. Additional symptoms at the initial stage are discomfort in the oral cavity. Subsequently, itching, burning, unpleasant odor, swelling of the face and neck occur. In the later stages, it is difficult for the patient to speak and swallow food, and the tongue begins to bleed.
How to treat ulcers using traditional methods?
A traditional medicine recipe cannot completely replace drug treatment, but it will help to achieve relief. Most methods will help numb tongue sores, prevent an increase in bacteria and viruses, and even promote the healing process.
Traditionally, to achieve an anti-inflammatory effect, folk medicine uses gargling with herbs such as chamomile, oak bark, calendula, St. John's wort and sage. To prepare the decoction, you need to add 1 tablespoon of the medicinal mixture to a glass of boiling water and let it brew for about half an hour. This decoction can be stored for no more than 12 hours.
How to treat a wound on the tongue using traditional medicine:
- Coriander tincture. To prepare the tincture, you need to pour 2 teaspoons of coriander into 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for half an hour and filter. It is necessary to rinse your mouth with coriander tincture every two hours.
- Glycerin paste is a mixture of turmeric and glycerin. To prepare the mixture, take 1 part turmeric and mix it with 2 parts glycerin. Apply this mixture to the sores 3 or 4 times a day.
- Collection of medicinal herbs. The collection most often contains chamomile, calamus, calendula and linden blossom. All herbs are crushed and steamed in a thermos. This decoction can be used not only as a solution for rinsing, but also for oral administration.
- Natural juice. Juice from black and white mulberry fruits will also be a salvation for mouth ulcers. Mulberry juice is taken 1 teaspoon once a day.
- Lemon is a strong natural disinfectant. It is used like this: the fruit is cut into two parts and the wound is treated with one of them. At first, the patient will feel an unpleasant tingling, but when the antiseptic juice penetrates into the inflamed area, it will disappear.
- Milk with honey and chicken egg yolk. To create the mixture you will need: 150 grams of milk, 1 teaspoon of honey and chicken yolk. All ingredients are mixed. Using a cotton swab, treat the affected surface with ulcers. This procedure is carried out 4 times a day. The course of treatment is three days.
- Almonds with honey. The nuts are crushed and mixed with honey. This paste is used to lubricate ulcers on the tongue.
- Elecampane. 4 tablespoons of this herb are poured into 1 liter of boiling water. The broth should sit for half an hour, then it should be strained. Next, rinse the area covered with ulcers with the decoction 2 times a day.
Therapy methods
If damage to the mucous membrane is detected, there is no need to self-medicate, as it can lead to serious complications.
You should immediately consult a doctor so that he can prescribe the appropriate course. Local therapy is used, which is aimed at pain relief and accelerated healing of ulcers, as well as a general approach that eliminates the cause.
A visit to a specialist is also necessary, because in this matter the doctor adheres to individual treatment, based on the patient’s age, stage of the disease, the presence of contraindications and restrictions.
When treating tongue ulcers in different cases, they resort to:
- antibiotics;
- antiviral drugs;
- immunostimulants;
- anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- anti-inflammatory ointments;
- antiseptics;
- anesthetics.
If you have sores on your tongue, be sure to treat them with painkillers and antibacterial agents, which are available in sprays, rinses and lozenges.
Popular in this group are Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Hepilor, Rotocan, Furacilin, Strepsils, Chlorphyllipt, Rivanol, Givalex, Orasept, Angilex.
Depending on the provoking factor, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Candidal stomatitis is caused by the spread of a fungus, so antifungal agents are necessary for treatment. These include Levorin, Nystatin.
- To combat viruses, in particular in the presence of herpetic sores , Viferon and Zovirax are prescribed. Gels are applied directly to the site of infection, since a huge accumulation of pathogenic cells is observed inside the vesicles. In more severe cases, when the disease is associated with bacterial activity, accompanied by elevated temperature and protracted nature, antibiotics are prescribed: Tsiprolet, Amoxicillin, Azithromycin.
- Gingivostomatitis is also treated with antibiotics, but antiallergic drugs are added during therapy. Vitamins and a high-calorie diet are required. Treatment is accompanied by removal of necrotic tissue under local anesthesia. Damaged areas are treated with antiseptics.
- Treatment of ulcers caused by trauma usually does not require specific therapy, other than local treatment with antiseptics and, if necessary, anesthetics. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed as painkillers. They are taken orally according to the instructions. The most popular are Lornoxicam, Ketoprofen, Voltaren. Cholisal-gel, Kamistad, Lidocaine and Strepsils plus are good for local anesthesia. To activate the immune system, Immunal is prescribed, as well as vitamin complexes.
- For tuberculosis , specific chemotherapy with rifampicin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide is prescribed. Treatment of infectious diseases: tuberculosis, syphilis and HIV is carried out under the supervision of a doctor in the clinic. Therapy is usually long-term and requires an integrated approach.
Malignant formations are dangerous due to the rapid spread of metastases, so treatment must be carried out promptly. After a series of tests and chemotherapy, the ulcers are surgically removed. Subsequently, it is necessary to regularly undergo a comprehensive examination in order to promptly detect remaining foci of cancer.
Preventing tongue ulcers
Everyone is susceptible to sores on the tongue, but if you are in good health and follow hygiene rules, you may not encounter such a problem. Main countermeasures:
- brushing and flossing teeth twice daily;
- visit the dentist twice a year;
- do fluorography annually;
- get rid of smoking and drinking alcohol;
- eat the right foods and vitamins;
- help strengthen the immune system.