general information
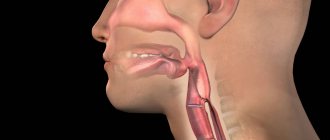
Salivation is known to be a normal process. Thus, approximately 2 mg of saliva is released every 10 minutes. However, in some cases, so-called hypersalivation may occur.
This pathology is popularly known as increased salivation. The causes in adults can be very different, ranging from oral diseases to serious neurological disorders.
It is also important to note that some patients perceive a normal amount of saliva as increased. Most often this occurs due to impaired swallowing function. In this case, a person simply cannot swallow saliva completely, and it constantly accumulates in the oral cavity. In fact, there is no need to talk about serious pathology here. Doctors call this hypersalivation false.
Increased salivation - types and causes
The process of salivation is important for humans, and the salivary glands located in the mouth are responsible for it. The production of saliva is constant - up to 2-5 ml of this liquid is produced in 5 minutes. In some cases, stronger salivation occurs, sometimes the oral cavity literally becomes overflowing. If in a child 3-6 months old (usually no more than one year old) this is a normal phenomenon, then in adults it is considered a problem. At the same time, other unpleasant symptoms may occur, such as nausea.
Depending on the time of onset, the causes of hypersalivation (or ptyalism) may vary:
| When the symptom occurs | Probable Cause | Other Possible Causes |
| During the day, while a person is awake | Pathologies of the nervous system | Gastrointestinal diseases |
| At night, during sleep or immediately after eating | Parasitoses | Diseases of the stomach, duodenum |
| After waking up in the morning | Severe hunger (normal) | Gastric ulcer, erosion, gastritis |
| While eating | Increased feeling of hunger (normal) | Pathologies of the small intestine |
| Attacks due to nervous tension | Consequences of stress | Nervous system diseases |
Hypersalivation can be true or false. In the first case, excessive saliva secretion in men and women is associated with an excess of its production, in the second it develops due to impaired swallowing of liquid. The norm is false ptyalism in children during teething; in adults it is somehow associated with pathologies of the brain or problems with the jaw muscles.
Primary symptoms
Saliva is constantly produced by special glands. The therapeutic norm is the production of liquid in the amount of 2 ml in approximately ten minutes. Increased salivation in adults can only be alarming when volumes exceed the 5 ml mark. In this case, there is too much liquid in the mouth, so there is a reflexive desire to swallow it.
Quite often, doctors associate this kind of problem with an inflammatory process in the oral cavity and various injuries to the tongue. In this case, the feeling of an abundance of fluid is false, since salivation is within normal limits.
The same sensations, not justified by dysfunction of the glands in the oral cavity, can occur in patients suffering not from neurological or dental problems, but susceptible to so-called obsessive states.
Quite rarely, hypersalivation is accompanied by a change in taste sensations (too strong or weak sensitivity). Some patients experience increased salivation and nausea at the same time.
Additional questions
Increased salivation during sore throat
With a cold or inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, including sore throat, hypersalivation may indeed appear, since during an illness an infection enters the mouth, which inflames the salivary glands. It is necessary to cure the underlying disease, after which increased salivation, one of its symptoms, will disappear.
Before or during menstruation
A rather rare symptom, it can be associated with changes in the hormonal balance of a woman during this period. If the frequency and amount of saliva in the mouth causes discomfort, you should consult a doctor.
Salivation and nausea
Nausea can actually be a source of this. During toxicosis in pregnant women, for example, the swallowing reflex is disrupted - a person begins to swallow less often and there is excess saliva in the oral cavity.
After eating there is a lot of saliva in the mouth - what to do?
Most likely, the glands react this way to too spicy or sour foods. This is not a very threatening phenomenon, but if it causes you severe discomfort, then you should consult a doctor.
Why does this pathology occur?
In a healthy person, saliva is secreted as a response to the aroma of food; taste analyzers also have nerve endings on the oral mucosa. Maximum irritation causes, accordingly, profuse salivation. For example, the more pleasant the smell, the faster your appetite flares up. The gastrointestinal tract thus communicates that it is ready to “work.”
The salivary glands are known to function constantly. They are designed to moisturize the oral cavity and protect the tongue, tonsils and nasopharynx from drying out. In just one day, about two liters of liquid are produced. A decrease in these volumes is usually observed during sleep, during dehydration and during stress.
Causes of nausea
There are many reasons that cause nausea. To get rid of an unpleasant feeling, you need to find out and eliminate the source.
Factors that provoke nausea:
- Food poisoning. A feeling of discomfort in the stomach appears several hours after eating, ending with vomiting, undigested food is excreted with vomit. The process is accompanied by high fever and diarrhea.
- Toxicosis during pregnancy. Morning sickness in a woman is the first sign that indicates pregnancy. In the first trimester, hormonal levels change and malaise appears. The symptom goes away by the end of the first trimester. If it is not accompanied by excessive vomiting and deterioration of the body, then it does not harm either the expectant mother or the child.
- Reaction to medications, vitamins. All medications have side effects, nausea is one of them. Individual intolerance to components can provoke it.
- Alcohol in large doses. Causes poisoning of the body, the person becomes sick and ends with vomiting.
- Head injuries. A severe head injury can cause a concussion. Dizziness and vomiting occur. Immediate medical attention is required, possibly hospitalization.
- Menses. During menstruation, a hormonal imbalance occurs in the body. The woman feels anxiety, cramps and pain in the abdomen, and dizziness.
- Violation of the vestibular apparatus. When changing body position, darkening of the eyes, noise in the ears, and deterioration of health may occur.
- Diets. An unbalanced diet, an incorrectly selected diet disrupts the functioning of the digestive system, and a person receives insufficient amounts of vitamins and nutrients. There is a malfunction in the stomach.
- Sunstroke.
- Motion sickness in transport, seasickness.
- Psychological disorders, stress. Disruption of the central nervous system causes various reactions in the body, including ailments.
Sudden nausea occurs in diseases: meningitis, appendicitis, gastritis, ulcerative colitis, oncology, inflammation of the gallbladder, cholelithiasis, peritonitis, etc.
Why is salivation increased in adults? Main reasons
- Intoxication of the body. It is poisoning that is most often the main provoking factor causing the development of this pathology. In this case, the patient's age does not play a special role. Poisoning can be from food, alcohol or medication.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Acute gastritis, cholecystitis, stomach ulcers - these ailments are the fundamental factors in the emergence of such a problem as increased salivation.
- The reasons for the development of this type of pathology in adults often lie in the intake of certain groups of medications. There are many substances in medications that lead to hypersalivation. To exclude this cause, it is necessary to adjust the dose of the drug or select another remedy.
- Regular stressful situations, central nervous system diseases, mental disorders. In this case, there is a weakening of the muscles involved in the swallowing process. As a result, fluid constantly accumulates in the oral cavity.
- Vascular pathologies.
- Worms.
- Oral diseases (ulcerative stomatitis).
- Foreign bodies in the oral cavity (improperly installed dentures, braces, chewing gum). All these objects constantly irritate the nerve endings of the oral mucosa, causing increased salivation.
- Symptoms of this pathology very often appear in endocrine diseases. For example, diabetes, thyroid diseases, tumors - all these problems cause increased secretion of the salivary glands.
- Smoking. Active smokers actually very often have to deal with this pathology. Due to constant irritation of the oral cavity by nicotine, the salivary glands begin to reflexively produce more secretion.
Pathological causes of increased salivation
Doctors are often asked the question: if I have increased salivation, could some internal disease be the cause? Hypersalivation can be caused by the following diseases:
- When the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted (heartburn, gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and intestines, colitis), its mucous membrane periodically sends signals of inflammation to the brain, after which reflex salivation occurs.
- Neurological diseases (brain injuries and tumors, stroke), in which there is a disruption in the relationship between the mucous membrane in the mouth and the salivation center located in the medulla oblongata.
- Glaucoma, epilepsy and other diseases accompanied by convulsive attacks require the use of cholinomimetics and tranquilizers. A side effect of these drugs is hypersalivation.
- Poisoning with certain poisons (salts of heavy metals), in addition to worsening the general condition, causes excessive salivation.
How to cure ptyalism in this case? Since in this case it is only a consequence, it is quite obvious that it is necessary to eliminate the cause - the underlying disease. Doctors also answer that joint therapy of several specialists (dentist, therapist, neurologist, gastroenterologist) is absolutely necessary to select the right drug and adjust its dose.
What is the cause of hypersalivation in children?
It should be noted that in the first year of a child’s life, this pathology is not considered a serious disease requiring treatment. Increased salivation in a baby is a normal process. In this case, the so-called unconditional reflex factor comes to the fore.
When the very first teeth erupt, excessive salivation is also not considered a disease and does not require surgical intervention.
It is important to note that older children should not suffer from hypersalivation. If a problem still exists, it is extremely important to consult a specialist.
At about three months, the baby's salivary glands begin to work. It is at this time that parents usually notice severe drooling. However, there is no need to panic for no reason, as it takes a baby some time to learn to swallow on its own.
Hypersalivation in children is often part of the work of the defense system. The thing is that along with the fluid that flows out of the mouth, various bacteria are removed.
Quite rarely, increased salivation is a sign of damage directly to the brain itself, which could have occurred in the perinatal period.
Causes for women and men
The causes of increased salivation in women and men can be illness, poisoning or lack of vitamins.
There are quite a lot of factors that stimulate the intensive work of the salivary glands. Among the main ones are:
- gastrointestinal diseases (ulcers, pancreatitis, gastritis);
- angina;
- intoxication;
- side effect from taking medications;
- stress;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- worms (cestodes, nematodes, trematodes);
- vascular pathologies;
- endocrine/infectious diseases;
- bad habits;
- menopause;
- removal of a tooth;
- foreign bodies (prostheses, braces, piercings, etc.).
Hypersalivation is observed in patients who do not control their behavior, infected with rabies and epidemic encephalitis. Sometimes excessive salivation is associated with a lack of nicotinic acid in the body.
Increased salivation is one of the symptoms of chemical poisoning (bromine, mercury, iodine, tin, copper).
Types of disease
- Drug hypersalivation. Most medications (for example, Nitrazepam) that affect salivation provoke the development of xerostomia.
- A psychogenic type of disease, which also entails increased salivation. The reasons for the development of this pathology in adults remain unknown. Sometimes drooling becomes so profuse that patients have to constantly carry a handkerchief with them.
- Hypersalivation in bulbar or pseudobulbar syndrome. Saliva is usually thick, and its volume can be up to 900 ml per day.
- Excessive drooling in patients with cerebral palsy is explained by dysfunction of the oral muscles.
Signs of increased drooling in adults
Drooling in adults (the reasons are determined by a therapist or a specialist doctor to whom the patient was referred on the recommendation of a therapist) is diagnosed by a number of signs, which can be noticed during a visual examination of the patient or during an analysis of the patient’s own feelings:
- volume released in 10 min. saliva increases to 5 ml (normally this figure should not exceed 2 ml);
- frequent urge to swallow accumulated fluid in the mouth;
- cough caused by irritation of the mucous membrane by an excessive amount of saliva entering the person’s throat;
- change in taste perception (products with a pronounced taste, for example, chocolate or citrus fruits, begin to seem tasteless or bitter, salty to the patient);
- irritation of the skin around the mouth or in its corners (usually the skin becomes dry, a small rash appears, causing itching);
- wet spots on the pillow after sleep;
- nausea or vomiting (caused by excess saliva entering the throat).
The diagram lists the causes of drooling in adults.
Despite the fact that hypersalivation in mild forms does not cause much discomfort to a person, ignoring its manifestations is extremely dangerous. If excessive salivation is caused by internal diseases, then, without starting timely treatment, you can not only encounter complications of existing pathologies in the future, but also undermine your overall health.
Increased salivation during pregnancy
As you know, a woman’s body undergoes various changes during pregnancy, including at the hormonal level. According to experts, it is in the early stages that many women notice the primary signs of hypersalivation.
Most often, this problem accompanies toxicosis. It is important to note that in some cases, hypersalivation is not associated with actual activation of the salivary glands. The thing is that a woman is constantly trying to suppress attacks of nausea and vomiting, thereby she begins to involuntarily swallow less often. As a result, there is a feeling that there is actually more saliva than there should be.
Often, increased salivation during pregnancy is somewhat aggravated by attacks of heartburn. In this case, the body conditionally receives a signal to soften the acid with saliva, which, due to its high bicarbonate content, is classified as an alkaline environment.
Sometimes hypersalivation occurs due to the same factors as in ordinary adults. In this kind of situation, pregnant women are advised to inform their doctor about this in order to rule out obvious causes of the problem.
Causes
There are many reasons that can cause hypersalivation.
Excessive salivation is a direct indicator of health problems. In addition, drooling flows profusely when it acts as a reaction to certain irritants, or as a consequence of an inflammatory process in the organs (more details in the article: what to do if a child drools profusely at 2 months?). Excessive salivation may be a sign of infection in the body or a symptom of a neurological disease.
In adults - men and women
Among the main causes of excessive drooling in adult men and women are:
- Acute inflammation in the oral cavity. For example, stomatitis, gingivitis or tonsillitis. Increased salivation is a protective reaction to irritation of the mucous membrane. Pathogenic bacteria, settling on it, enter the salivary canals and cause inflammation and swelling of the salivary glands (we recommend reading: signs and treatment of inflammation of the salivary gland).
- Gastrointestinal pathologies. These include gastritis, cholecystitis, stomach ulcers, liver or pancreas dysfunction. The fundamental factor of hypersalivation in case of disruption of the digestive system is increased stomach acidity.
- Central nervous system disease, constant stress or mental disorders. In this situation, the muscles involved in swallowing are weakened. As a result, there is a regular accumulation of saliva in the oral cavity.
- Intoxication of the body. This could be food poisoning, alcohol or medication. Age does not matter in this case.
- Thyroid dysfunction. It leads to hormonal imbalance and disruption of hormone production. Diabetes mellitus, being an endocrine disease, like various tumors, also sometimes causes excessive salivation.
- A side effect from taking certain medications. These include nitrazepam, pilocarpine, muscarine, physostigmine and lithium.
- Worms. In the presence of worms or other parasites, increased production of saliva continues even after eating.
- Vascular diseases.
- Smoking. Due to the constant irritation of the oral mucosa by nicotine, a large production of secretion occurs.
- Menopause. During this period, most women face a similar problem.
Why do children drool?
As for children, up to one year of age, increased drooling is the norm. The main reason for high salivation is unconditioned reflexes. Another natural reason is associated with the eruption of the first milk teeth. Both factors do not require treatment. Also, increased salivation can serve as a protective reaction of the child’s body. Bacteria are removed along with saliva.
However, there are a number of more serious reasons why a child collects a high amount of drool in his mouth:
READ ALSO: Why does saliva in your mouth become salty and cause an unpleasant taste?
- Helminthiasis. Small children are more often susceptible to helminth infestations, as they put foreign objects into their mouths and bite their nails.
- False hypersalivation. It occurs in infants due to impaired swallowing, which is caused by paralysis or inflammation in the pharynx. Saliva production remains normal.
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Viral diseases.
In older children, the problem may be related to psychological processes. With the development of higher nervous activity, children are subject to sharp emotional experiences, which contributes to the copious secretion of saliva.
During pregnancy
Most often, hypersalivation occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, as a consequence of toxicosis and frequent vomiting. Trying to stop an attack of vomiting at an early stage, pregnant women involuntarily reduce the frequency of swallowing, which leads to a feeling of excess saliva. The salivary glands work normally.
The second possible cause of increased salivation during pregnancy is called heartburn. The secretion of saliva softens the acid. Another significant factor in impaired salivation during pregnancy is increased sensitivity to all medications.
READ ALSO: causes and treatment of foamy saliva in the mouth
Severe nocturnal hypersalivation
During sleep, as is known, the work of the glands responsible for the production of saliva slows down somewhat. However, it also happens that the secret begins to be produced before the person finally wakes up. All this entails spontaneous drainage of liquid from the mouth of a sleeping person.
If such cases are rare, then there is no reason to worry. However, regular recurrence of this problem requires consultation with a specialist.
Doctors note that in some cases, during sleep, the body loses control over reflexes. This also leads to increased salivation.
Hypersalivation can occur due to certain diseases that cause nasal congestion (ARVI, influenza). As a rule, increased salivation disappears after the final disappearance of the main cause - difficulty breathing.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostics in this case involves the following steps:
- Collecting a complete medical history (when the primary symptoms appeared, the presence of concomitant diseases, etc.).
- Life activity analysis. The thing is that the hereditary factor often plays a primary role in the occurrence of such a pathology as increased salivation. The causes in adults often lie in the abuse of bad habits (for example, smoking).
- A detailed examination of the oral cavity for ulcers or other lesions of the mucous membrane.
- Enzymatic analysis of saliva itself.
- Additional examination by a dentist, psychiatrist and neurologist to identify possible indirect causes.
What should the treatment be?
We can talk about prescribing therapy only after the final identification of the cause that led to the development of hypersalivation. First of all, you need to seek advice from a therapist. After examination and medical history, he will be able to recommend a specialist.
Depending on the root cause, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. In this case, it is not the hypersalivation itself that is eliminated, but the main factor that provoked its development. This may be dental, neurological or gastroenterological treatment.
How to get rid of increased salivation? In particularly critical situations, as a rule, specific therapy is prescribed that acts directly on salivation itself, namely:
- Taking anticholinergic drugs (Riabal, Scopolamine, Platifillin). These drugs suppress excessive saliva secretion.
- Removal of glands (this method often entails disruption of the functioning of the facial nerves).
- For neurological disorders, facial massage and exercise therapy are prescribed.
- Radiation therapy.
- Cryotherapy (cold treatment).
- To block excessive saliva production for a period of time (up to one year), Botox injections are performed.
In addition to all of the above medications, homeopathic options are often used. However, they are prescribed only after consultation with a doctor.
Treatment
After the examination, the doctor will determine the optimal treatment regimen for you. Don't try to do this yourself!
The development of a treatment regimen for hypersalivation largely depends on the provoking factors. The main therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of excessive salivation. The following methods are used to combat symptoms.
- Exercise therapy and facial massage are prescribed for neuralgia.
- Cryotherapy is a cold treatment that stimulates swallowing reflexes.
- Special anticholinergic agents that reduce the degree of salivary secretion (Scopolamine, Tifen, Metacin, Riabal, Spasmolitin, Tropin, etc.).
- Carrying out the irradiation procedure.
- Injections whose active drugs reduce saliva production.
- Removal of glands.
Traditional treatment can be supplemented with home recipes, which involve repeated mouth rinsing with infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants (chamomile, calendula, oak bark, etc.).
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the main problem. To suppress excessive salivation, various means are used:
- special medications (only in emergency cases);
- cryotherapy;
- facial massage and gymnastics;
- sanitation of the oral cavity.
Useful tips
If the diagnostic examination does not reveal any significant abnormalities, you can try to use the recommendations below.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude all spicy, fatty and salty foods from the diet, as they provoke irritation of the oral mucosa. The thing is that many people complain of increased salivation after eating. These kinds of restrictions can help solve this problem.
It is extremely important to stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages. As a preventive measure, you can rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile or oak bark. These agents act as an antiseptic and prevent the development of this pathology.