Why does increased salivation occur during pregnancy?
The main cause of drooling during pregnancy is hormonal changes in the body, which result in changes in the salivary glands and ducts, as well as the central nervous system.
This leads to increased activity of the oral epithelium and increased secretion of saliva. The exact etiology of the appearance of ptyalism during gestation is not known, but it has been found that most often this phenomenon occurs in the first weeks after conception against the background of nausea and vomiting. When gagging occurs, a woman tries to swallow saliva as little as possible, which is why it accumulates in the mouth and begins to actively separate. Other known causes of increased salivation during pregnancy include the following factors:
- Toxicosis. This is a common phenomenon that occurs in the first trimester of gestation. Before gagging begins, profuse salivation occurs. Most often this occurs when a pregnant woman has hyperemesis. The problem disappears after toxicosis passes.
- Heartburn. After conception, many women experience heartburn, in which the environment in the stomach becomes acidic. This condition leads to irritation of the walls of the esophagus, as a result of which the body gives a signal for increased synthesis of saliva, which is an alkaline environment that neutralizes stomach acid.
- Increased appetite. Appetite often increases during pregnancy, and taste preferences change. Many women complain of a constant feeling of hunger, which is accompanied by excessive salivation.
- Smoking. If the expectant mother was unable to get rid of the bad habit, then she will constantly be haunted by drooling. Moreover, ptyalism can occur even if someone smokes nearby.
Sometimes a similar problem occurs due to the use of certain medications, intoxication of the body, diseases of the oral cavity and other health problems.
If a woman has been observing increased salivation for several days, then she should not try to eliminate this problem on her own. You need to go to the doctor immediately. The way he will determine the potential causes of this condition. Most likely, before prescribing any medications, he will recommend:
- You need to stop smoking if you have such a habit. It is smoking that has a deadly effect on the unborn baby and most often provokes increased salivation.
- Try to rinse your mouth frequently to reduce bacteria that may cause vomiting. It is bacteria that cause the development of specific microflora in the mouth, which provokes strong salivation. To eliminate this unpleasant feeling, try to brush your teeth more often.
- Homeopathy. For excessive salivation, pulsatilla is used. However, during pregnancy it can only be used after a doctor’s prescription, especially in the early stages of expecting a baby.
- Drink plenty of warm water. An ordinary person needs to drink 1.5-2 liters a day so that the body can function normally, but a pregnant woman needs to drink more if the kidneys are functioning normally. When there is a lack of fluid in the digestive system, stagnation occurs, which is the cause of many pathologies. Expectant mothers need to carry water with them, but not sparkling water! Consume it in small sips.
Causes of ptyalism
Increased salivation is one of the adverse reactions to changes in hormone levels in the body. It has been scientifically proven that estrogen acts on the epithelium of the oral cavity, causing the secretion of salivary fluid.
The reasons for the appearance of excessive drooling in the early stages of gestation have not been precisely established, but several other factors can affect the likelihood of the symptom occurring:
- Heartburn. This phenomenon worries almost all pregnant women. As a result of reflux, stomach acid rises up the esophagus, which leads to irritation and a sore, burning sensation. An alkaline environment, i.e. saliva, helps neutralize acid. The self-regulation mechanism is activated, the salivary glands perceive signals from the receptors of the esophagus and produce more fluid. When swallowing saliva, the acid is partially neutralized, which brings the woman a feeling of relief.
- Changes in stomach acidity. Due to the effects of acid, the walls of the stomach are irritated, and in response to this, the glands secrete more saliva, which brings acidity back to normal.
- Taste preferences. Often, from the first weeks of expecting a baby, the expectant mother becomes addicted to sour or salty foods. Due to constant irritation, the salivary glands produce more fluid.
- Toxicosis. Nausea and vomiting can be provoked by any irritant, even a smell or a sharp sound, as a result of which a woman, fearing another attack of vomiting, tries to swallow saliva as little as possible. It builds up, making it seem like you're producing more saliva fluid than usual. Also, frequent vomiting can lead to the proliferation of specific microflora in the oral cavity, which provokes the production of saliva in large volumes.
Causes
During the period of bearing a baby, increased salivation of the expectant mother is often associated with a state of toxicosis. In this case, the girl may experience bouts of vomiting, heartburn and nausea.
The body of a pregnant mother is subjected to increased stress, so its immune defense is weakened. This entails a higher susceptibility of the girl to various diseases that can cause hypersalivation, in particular:
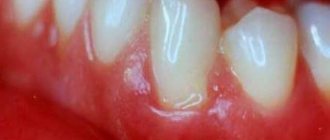
- oral cavity problems – stomatitis, gingivitis, sialadenitis;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis;
- diseases of the nervous system - strokes, brain tumors, inflammation of the facial nerve, psychosis, schizophrenia, neuroses, and so on;
- infection with worms;
- lack of vitamin PP;
- intoxication resulting from close contact with toxic substances;
- uremia – poisoning of the body due to problems with kidney function.
Hypersalivation occurs, which is characterized by a reflexive flow of saliva caused by the response of the expectant mother’s body to certain brain impulses from different organs. This situation develops most often with diseases of the uterus and nose.
In addition, the expectant mother taking certain medications can also lead to an increase in saliva production. These medications include:
- lithium salts (used in the treatment of a number of mental illnesses);
- anticonvulsants (used to prevent seizures)
- ;drugs for the treatment of glaucoma and others.
The prerequisites for siaolosis differ according to the form of the disease:
- true hypersalivation - excessive flow of saliva is explained by its increased production, which is typical for inflammation of the oral cavity and toxicosis;
- false hypersalivation - is associated not with the amount of saliva, but with the frequency of its swallowing. This occurs with problems of the pharynx and nervous system, disturbances in the functioning of the facial muscles, lesions of the lips; swallowing can bring discomfort or pain to the expectant mother. As a result, saliva is swallowed less frequently than usual. At the same time, it accumulates in the mouth in large quantities, which creates the feeling of excessive salivation.
Tips for pregnant women - how to get rid of increased salivation
The true causes of increased salivation are not yet completely clear, but very often experts associate this annoying process with significant hormonal changes that occur in the body of a pregnant woman.
Constant nausea adds fuel to the fire, in which, as you know, a person tries to swallow as little as possible, which leads to the accumulation of excess saliva in the mouth. Another common phenomenon that very often accompanies pregnancy, and which may well be one of the causes of increased salivation, is heartburn.
The problem lies in the acid-forming environment of the stomach, which, when regurgitated, irritates the esophagus and can cause an extremely unpleasant burning sensation. The acid immediately affects the salivary glands, which begin to produce large amounts of saliva.
This process may also explain increased salivation in pregnant women suffering from an increased gag reflex. In addition, many medications that women take during pregnancy can also cause increased salivation.
A very common cause is smoking. Experts who have repeatedly encountered this phenomenon in practice offer pregnant women several tips that may well help bring increased salivation under control.
1. If you suffer from constant attacks of nausea, vomiting and heartburn, then the very first step you need to take is a visit to the doctor monitoring your pregnancy. This must be done in order to try to determine the reasons that may be behind these symptoms.
2. Smoking during pregnancy is unacceptable. As a rule, even heavy smokers give up this bad habit during pregnancy, but there are those who continue to smoke.
3. If you suffer from frequent bouts of vomiting, this may cause the formation of specific microflora in the oral cavity, which in itself can provoke not only increased salivation, but also more severe bouts of vomiting.
4. Pregnant women’s love for cucumbers, as well as the constant desire to eat foods that are incompatible with each other, is the talk of the town. Meanwhile, pregnancy is a period when you need to start eating carefully balanced foods and give up foods that contain a lot of starch.
5. If you have read or heard that a person needs to drink large amounts of water throughout the day, then you should know that a pregnant woman should even increase her usual daily dose of fluid intake.
6. If you are unable to reduce the amount of saliva produced to a normal level, and you have to swallow it periodically, experts recommend always having hard lollipops or sugar-free chewing gum on hand.
Why does it occur
The exact cause of increased salivation during pregnancy has not been established. Some experts believe that this unpleasant condition develops due to hormonal changes in the body that occur in a pregnant woman. Others believe that the problem lies in the acid-forming environment of the stomach, which irritates the esophagus and causes an unpleasant burning sensation - heartburn. In response to it, the salivary glands begin to produce saliva in large volumes. This is how the body tries to fight stomach acid.
Often, salivation appears due to severe toxicosis in the early stages of pregnancy. Frequent bouts of vomiting can lead to the formation of specific microflora in the oral cavity, which can provoke the release of saliva in large quantities.
Increased salivation can also develop due to smoking or taking certain medications.
Some disturbances in the functioning of the body may be accompanied by increased production of saliva:
- diseases of the oral cavity and teeth;
- disruption of the salivary glands;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, damage to the pancreas);
- diabetes mellitus leading to hormonal imbalance;
- pathologies of the ENT organs (chronic tonsillitis, rhinitis);
- parasitic diseases.
Symptoms of increased salivation
Usually the main symptom of an unpleasant phenomenon is the sudden or regular release of copious amounts of saliva into the oral cavity, which leads to the desire to swallow or spit it out. Sometimes the need to spit causes nervous disorders in a person and drives him into depression.
If the patient has swallowing dysfunction, which happens with paralysis, after a stroke and for a number of other reasons, the volume of saliva may be normal. But at the same time, a person feels its increased production, although it is absent. Similar symptoms occur in people with mental disorders and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Since hypersalivation is almost always caused by health problems, it cannot do without other accompanying symptoms:
- change in taste up to its perversion;
- frequent occurrence of nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- heartburn, belching;
- abdominal pain, bloating, increased gas formation;
- pain in the esophagus, stomach;
- decreased appetite;
- lump in the throat;
- swallowing disorders;
- sometimes - low-grade fever;
- severe fatigue, weakness;
- impaired sense of smell, stuffy nose.
With regular swallowing of saliva, a person may experience loose stools, because the amount of moisture in the stool increases. In severe cases of ptyalism, saliva can flow down the cheeks and drip even during the day if the person does not control himself. Often, without sufficient care, red spots, ulcers, and wounds may appear on the face.
Correction of the condition: how to reduce salivation?
Methods of dealing with the problem depend on its cause, but if the active production of salivary fluid is associated specifically with pregnancy, and not with diseases, then it will be useful to use the following tips:
- eat often, but in small portions;
- give up starchy foods that cause a “lump in the throat” feeling;
- reduce the consumption of foods that strongly irritate the taste buds (salty, sour, etc.);
- stop chewing gum;
- eat oatmeal in the morning, which normalizes stomach acidity;
- carry mint candies with you to help stop bouts of drooling;
- brush your teeth several times a day and do not forget to use mouthwash (it can be replaced with a decoction of sage or mint);
- increase the volume of fluid consumed.
Increased production of saliva is a problem, but the expectant mother should be reassured by the fact that the secreted liquid performs a number of important functions: it neutralizes the acidity of digestive juices, moisturizes the oral cavity, contains enzymes involved in digestion and has antibacterial properties, protecting the teeth. However, if the volume of saliva is large and interferes with everyday life, there is no need to force yourself to swallow it. It is better to take napkins with you and periodically spit out the liquid.
Sources:
https://moykarapuz.com/zdorove-beremennih/povyishennoe-slyunootdelenie-pri-beremennosti.html https://www.infoniac.ru/news/Sovety-beremennym-kak-izbavit-sya-ot-povyshennogo-slyunootdeleniya.html https://vseprorebenka.ru/beremennost/zdorove-mamy/povyshennoe-slyunootdelenie-pri-beremennosti.html
Symptoms
For each woman, the first signs of pregnancy manifest themselves differently. For some it is toxicosis, for others it is a desire to eat something salty or sour, for others, no symptoms appeared at all.
We are all different. Our bodies also react differently to pregnancy. But there is an average list of the earliest signs of pregnancy before a missed period.
The clinical manifestations of ptyalism are the same regardless of the causes that caused it. A pregnant girl notices the following symptoms:
- unnaturally frequent swallowing of saliva;
- increased secretion of the salivary glands, as a result of which saliva begins to leak from the corners of the mouth;
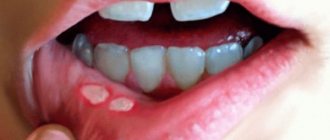
- the skin around the lips and chin becomes irritated due to constant contact with saliva;
- A pustular rash of small blisters with liquid contents appears in the area around the mouth.
Diagnosis of hypersalivation during pregnancy
When visiting a specialist, the expectant mother describes her complaints (how long they have been noted, what exactly is bothering her, what characteristic symptoms are present), and the doctor draws up a picture of the disease, analyzes the data obtained and forms an anamnesis of the patient’s illness and life. Lifestyle history involves collecting information about chronic and hereditary health problems, the presence of tumor formations, addictions, finding out the fact of taking any medications and contact with toxic substances.
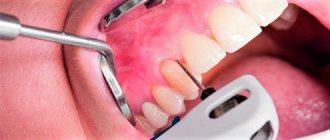
A mandatory procedure is to examine a pregnant girl. The doctor assesses the condition of the mother’s oral cavity, detects the presence of damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth and gums, as well as the skin in the chin and mouth area.
To confirm the true nature of hypersalivation, measuring the amount of saliva produced over 20 minutes is required. Normally, this figure is 1-4 ml, and with drooling it is 10 ml or more.
Symptoms of early toxicosis in pregnant women
According to various sources, early toxicosis occurs in 50-60% of pregnant women. The onset of manifestations most often develops at 5-6 weeks of gestation. The most characteristic signs are nausea, vomiting, increased salivation, a sharp change in taste and olfactory perceptions, loss of appetite, lethargy, and drowsiness. Objectively, with toxicosis in pregnant women, weight loss, hypotension, tachycardia, the appearance of acetone in the urine, an increase in azotemia and electrolyte disturbances in the blood are determined. Taking into account the severity of vomiting, several degrees of early toxicosis in pregnant women are distinguished: mild, moderate and excessive.
A mild degree of toxicosis in pregnant women (neurotic) is characterized by vomiting up to 5 times a day and a satisfactory general condition. The severity of taste and olfactory perversions, intolerance to odors, including food, are noted. Women's sleep and appetite are usually not affected. There may be a weight loss of no more than 2 kg per week, slight tachycardia (up to 90 beats per minute), hypotension (110-100/60 mm Hg). Urine and blood tests remain within normal limits.
With a moderate (toxic) degree of toxicosis in pregnant women, constant nausea is observed, the frequency of vomiting per day is up to 10 times, liquid and food are retained slightly. General health worsens, appetite decreases, sleep is disturbed. A pregnant woman can lose weight from 3 to 5 kg per week. Objectively, low-grade fever, tachycardia (90-100 beats per minute), hypotension (100-90/60-50 mm Hg), and the presence of acetone in the urine are detected.
In the most severe form of toxicosis in pregnant women - excessive, uncontrollable vomiting (dystrophic stage), severe multiple organ disorders develop. Characterized by painful vomiting up to 20 or more times a day, lack of appetite, inability to retain fluid and food in the stomach, and sleep disturbances. The woman’s condition is apathetic and myalgia may bother her. Loss of body weight progresses, reaching 7-15 kg.
Objectively, signs of dehydration are detected: dry skin with an icteric coloration, decreased tissue turgor. Petechiae often appear on the skin, hemorrhages in the conjunctiva due to impaired coagulation and constant tension. An increase in heart rate up to 120 beats is detected. per minute, arrhythmia, hypotension (up to 80/40 mm Hg). In urine - ketonuria, albuminuria, cylindruria; oliguria or anuria develops. In the peripheral blood, the concentration of bilirubin, creatinine, and urea increases, and disturbances in water-salt and protein metabolism and acid-base balance are detected.
Ptyalism (salivation) can be an independent form of toxicosis of pregnancy or observed together with vomiting. With severe drooling, a pregnant woman can lose up to 1 liter of fluid per day, which leads to dehydration of the body, hypoproteinemia, and psychological discomfort.
Rare forms of early toxicosis in pregnant women include dermatoses, which often occur as itchy skin. Itching during pregnancy can be local (in the vulva area) or spread throughout the body. Severe and constant itching of the skin is accompanied by insomnia and irritability. To exclude other causes of skin itching, the patient should be examined for diabetes mellitus, fungal diseases, trichomoniasis, allergic diseases, and helminthic infestation. Rarely, dermatoses during pregnancy manifest themselves in the form of herpes, eczema, and impetigo herpetiformis.
Tetany in toxicosis of pregnant women develops against the background of calcium metabolism disorders. Tetany manifests itself as muscle cramps and often occurs against the background of hypoparathyroidism. Patients with early toxicosis require increased monitoring by a gynecologist during pregnancy, since they often develop preeclampsia later.
Is increased salivation a sign of pregnancy?
Increased salivation may suggest the idea of conceiving a child. Drooling is usually characteristic during the first months of pregnancy, and this condition is called ptyalism. As you know, most of the fair sex at the beginning of pregnancy suffer from toxicosis, which is a sign of hormonal imbalance.
Toxicosis of early pregnancy affects cerebral circulation. And this, in turn, leads to active production of salivary fluid. Salivation is usually accompanied by heartburn and nausea (the urge to vomit). Ptyalism does not have a negative effect on the fetus; this condition only affects the general condition of the pregnant woman.
Heartburn plays an important role in the mechanism of increased salivary fluid production. The stomach cavity contains acid. During vomiting or reflux, this acid enters the esophagus, irritating it. Irritation of the walls of the esophagus is accompanied by a burning sensation.
In the walls of the esophagus, as in other organs and systems, there are a large number of receptors. When the walls are irritated by acid, the receptor apparatus of the esophagus gives a signal to the brain, and the brain receptors transmit a signal to the salivary glands to produce saliva.
The mechanism of saliva production during heartburn is very important, because the salivary fluid has an alkaline environment and when swallowed, it neutralizes the acid of the gastric juice accumulated on the walls of the esophagus.
The reason for increased salivation in women during pregnancy may be an insufficient concentration of vitamins and microelements in the body of the expectant mother.
Hypersalivation is also a symptom of weakened immunity. In order to normalize the balance of vitamins and microelements, all pregnant women are prescribed preventive courses of vitamin complexes and special diets are prepared based on a balanced diet.
To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to spend most of the time outdoors and walk more.
If there is excessive salivation during pregnancy, the use of vitamin preparations is indicated for therapeutic purposes. It is also necessary to limit the content of acidic foods in the diet, which stimulate the formation of saliva.
The cause of increased salivation in children and adults is tobacco smoke. In adults, this can be caused by active smoking. In pregnant women and children, inhaled smoke (passive smoking) leads to increased salivation.
From the genitourinary system
Girls who constantly monitor their basal temperature and build personal charts of changes noticed that during the period of conception they experienced temperature jumps with a very high amplitude. In gynecology, this phenomenon is called implantation retraction.
Also, during pregnancy, estrogen is produced in large quantities, which, on the contrary, lowers the temperature. The combination of these two factors leads to fluctuations in basal temperature.
By the way, a basal temperature above 37 degrees, which remains stable for several days, is a sign of pregnancy. This number will remain on the thermometer until the placenta is formed and begins to function.
Vika, Kharkov
I didn't take a pregnancy test at all. One day I just started feeling really sick. My cycle is precise, so when my period didn’t appear, I wasn’t surprised. I already knew that I would soon become a mother.
The nausea was very strong, toxicosis did not let me go for a long time. In the first 2-3 months of pregnancy, I lost a lot of weight. Still would! Everything I ate came right back out. So when my belly started to appear, I looked like I had just eaten a big meal.
The process of fertilization and attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus is accompanied by slight bleeding. It is also called implantation. This is brown discharge like a spot or in the form of a few droplets (like before menstruation).
This is the earliest sign of a developing pregnancy. Approximately 1-2 weeks after conception, the embryo implants into the uterine wall, which causes slight bleeding.
However, not everyone noticed brown discharge. Some women reported more yellow or pink discharge. In this case, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist to rule out termination of pregnancy (with pink discharge) or cervical erosion (with yellow discharge).
Thrush
A feeling of heaviness and fullness in the lower abdomen occurs due to redistribution of blood flow. To provide the fetus with nutrients, blood flow to the pelvic organs increases.
This is why pregnant women literally feel their uterus, a feeling of “fullness” and heaviness appears. Intuitively, this is recognized as the birth of a new life.
Maria, St. Petersburg
Among the “obligatory” signs of pregnancy were nausea, dizziness, often running to the toilet... But the surest sign was darkening of the areolas. During my first pregnancy, nausea began three days before the delay. And the second time everything was fine.
This is also a consequence of increased blood flow to the pelvic organs. The amount of urination varies from woman to woman. On average, this is 1 time per hour. Some pregnant women said that trips to the toilet continued even at night.
However, this condition is temporary, it goes away immediately after the hormonal levels normalize. Sometimes the urge is similar to the symptoms of cystitis.
Diagnosis of increased salivation
Regarding the problem that has arisen, you need to consult with various specialists who will determine the source of the phenomenon: therapist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, dentist, neurologist.
The problem of hypersalivation can be diagnosed by the following methods:
- collecting anamnesis when talking with the patient - the doctor finds out all the details regarding the onset of active saliva production, accompanying symptoms and complaints;
- examination to check the act of swallowing and the condition of the oral cavity;
- examination of the salivary glands - the volume of saliva produced in 20 minutes is determined. If the number exceeds 10 ml, then this indicates a problem.
How to deal with increased salivation during pregnancy
Salivation during early pregnancy, despite the seemingly insignificant nature of the problem, can cause many unpleasant moments. After all, it is difficult for a future mother to explain to outside witnesses of her suffering that a new hormonal background is to blame. And this problem noticeably worsens my well-being.
Therefore, you need to fight it:
- Increase the number of meals per day, but reduce portions. This will help neutralize toxicosis.
- Do not get carried away with sour, spicy and salty foods, as well as foods with a lot of starch. The latter provoke the presence of a lump in the throat and nausea.
- Don't forget to drink water, taking small sips and taking your time.
- Do not eat foods that are opposite to each other at the same time. Start the day with oatmeal, which helps normalize stomach acidity, cope with heartburn and toxicosis.
- Snack on dried fruits, non-acidic candies (mints are best) or stop the salivation attack with a small sip of water.
- Brush your teeth more often and use various mouth rinses and herbal infusions. Of the latter, sage, mint, and yarrow are suitable.
- Do not force yourself to swallow saliva at all costs if this is problematic. It is better to keep paper napkins in your purse and place a towel on your pillow at night.
- Stop chewing gum and smoking.
Considering the possibility of exacerbation of diseases during pregnancy, it would be good to get rid of pathologies that could theoretically cause excessive salivation before pregnancy.
If, despite all efforts, the problem does not go away over time, it is worth reminding the doctor about it again. You may need to be treated for a sore throat, gastritis, or take care of your teeth. It is available and even necessary during pregnancy.
If increased activity of the salivary glands is associated only with a new position, and ordinary measures do not help in eliminating it, the doctor will prescribe medicine or a homeopathic remedy. But you shouldn’t experiment with them yourself.
Early signs of pregnancy. Waiting for a new addition to the house. The woman also begins to salivate profusely, regardless of the dose.
Early toxicosis during pregnancy (in later stages - gestosis) occurs. The woman begins to suffer from nausea, vomiting, and salivation increases.
Is increased salivation a sign of pregnancy? Hunger during early pregnancy: why.
Based on materials from 7mam.ru
Pregnancy is a period in a woman’s life when many unusual, unpleasant and even painful symptoms may appear. One of these symptoms is increased drooling. This condition can appear simultaneously with toxicosis, and can also develop independently.
Salivation is a natural physiological process that occurs in the body of every person. Normally, approximately 2 mg of saliva is released every 10 minutes. In some pregnant women, salivation can be so strong that they lack the physical and moral strength to constantly spit out excess saliva. In addition, excessive salivation during pregnancy causes irritation of the mucous membrane of the lips, chin, corners of the mouth, and also leads to loss of fluid (1-1.5 liters per day) in the body, which causes a dangerous condition - dehydration.
conclusions
Increased salivation during pregnancy is not a dangerous phenomenon, but exhausting and unpleasant. You can defeat it if you balance your diet, give up bad habits and avoid dehydration.
We must not forget that health must be protected, so you should follow the practical recommendations of specialists and then the secretion of saliva will not bother you. Recommend this useful article to your friends on social networks, repost and leave comments. Thank you all for your attention and see you again!
Sincerely, Katherine Grimova, mother of a wonderful daughter!
After conception, the female body prepares for big changes. Actually, they have already begun, which in some women is very pronounced. Increased salivation during early pregnancy is just one of these signs. But it does not always indicate conception. After all, this also occurs in some pathological conditions.
Read in this article
Why does increased drooling occur in pregnant women?
Often, drooling in pregnant women appears due to severe toxicosis in the early stages. Frequent bouts of vomiting can lead to the formation of specific microflora in the oral cavity, which can provoke the release of saliva in large quantities.
Also, increased salivation during pregnancy can develop due to smoking or taking certain medications.
In many pregnant women, excess drooling disappears at the end of the first trimester along with toxicosis. However, in some women, this condition occurs before childbirth. There is no specific treatment. If there is severe salivation during pregnancy, then treatment with droppers in a hospital is indicated to prevent dehydration.
The following activities can help some women alleviate the condition of excessive drooling:
- rinsing the mouth with infusion of chamomile, sage, oak bark, rinse with menthol;
- spitting saliva into a cup (constant swallowing of saliva provokes nausea and vomiting);
- brushing teeth with mint paste after every meal;
- chewing sugarless gum, sucking mints;
- while resting on the bed or sleeping, you can place a thick terry towel under your cheek so that excess saliva drains into it;
- eat balanced and often, but little by little, exclude spicy, fried, salty foods, as well as foods containing starch;
- long walks in the fresh air.
Based on materials from moykarapuz.com
With the onset of an “interesting situation,” the work of the female body changes dramatically. And this is not surprising, because much is explained by hormonal changes. Often such changes affect the functioning of the digestive system. These include heartburn, the emergence of new taste preferences, and increased appetite. Such changes include increased salivation. It is called ptyalism. Sometimes this unpleasant phenomenon is accompanied by vomiting. So, let's learn about it in detail, about its causes and features.
This phenomenon causes some discomfort to the woman. But let us hasten to reassure you: ptyalism is completely safe for the unborn baby. This disorder is considered a side effect of hormonal changes in the female body. It is worth noting that the reason for the appearance of increased salivation during different periods of gestation is not precisely known. Of course, it’s unpleasant when an expectant mother spends a lot of time in the bathroom, constantly spitting out excess saliva that accumulates in her mouth.
Excessive salivation may occur in pregnant women with hyperemesis. Severe vomiting appears in the morning and can continue until the evening with short breaks. When a woman feels sick, saliva accumulates, which causes an attack of vomiting.
Sometimes heartburn can be a catalyst for excessive salivation.
In addition to hormonal changes, the cause of ptyalism is a change in the acid-forming environment of the stomach. Its walls are more irritated by internal factors, which leads to burning sensations and excessive salivation. Stomach acid affects taste buds. They, in turn, signal the salivary glands to produce more secretions. And if, when ptyalism manifests itself, you take saliva for analysis, then, most likely, the content of acid carbonate will be several times increased. This is how the body counteracts the secreted stomach acid, which is accompanied by copious salivation.
Based on materials from beremennost.net
Treatment
In many pregnant women, this condition disappears at the end of the first trimester along with toxicosis. However, for some it can be observed until the birth itself. There is no specific treatment. If there is strong salivation during pregnancy, then treatment with droppers in a hospital is indicated to prevent dehydration.
The following activities can help some women alleviate the condition of excessive drooling:
- rinsing the mouth with infusion of chamomile, sage, oak bark, liquid with menthol;
- spitting saliva into a cup (constantly swallowing it provokes nausea and vomiting);
- brushing teeth with mint paste after every meal;
- chewing sugarless gum, sucking mints;
- while resting on the bed or sleeping, you can place a thick terry towel under your cheek so that excess saliva drains into it;
- eat balanced and often, but little by little, exclude spicy, fried, salty foods, as well as foods containing starch;
- long walks in the fresh air.
We suggest you read: When does anesthesia wear off after tooth extraction?
Increased salivation during pregnancy is a condition that, although not dangerous, can cause severe discomfort and overshadow this period. In addition, it can lead to dehydration and disruption of the acidic environment of the stomach, which is not at all good. Attentive attention to health and nutritional correction can help normalize the condition.
What can you do
The expectant mother should establish a harmonious daily routine, including adequate rest during the day and at night. If signs of hypersalivation appear, it is wise to visit a doctor as soon as possible, since this condition may indicate the development of some disease.
What does a doctor do
If drooling is caused by any disease and is a symptom of it, the doctor must identify the causative disease and begin to eliminate it.
In case of severe hypersalivation, the expectant mother may be recommended treatment in a hospital setting. General doctor's orders include:
- building a proper daily routine with proper rest and night sleep lasting at least 8 hours;
- intravenous administration of special solutions for dehydration caused by excessive salivation;
- treatment of the oral cavity with herbal infusions;
- using ointments and creams to treat rashes around the mouth.
Depending on the causative disease, the following are recommended:
- individual psychotherapy sessions;
- taking medications that affect the functioning of the nervous system;
- taking anti-worm medications;
- vitamin therapy and so on.
The expectant mother should inform the doctor in advance about the gestational age so that the prescribed treatment is effective and safe for the baby in the womb.
Causes of excessive salivation in a child
For a baby in the first year of his life, increased saliva production is not considered a problem at all - this is a natural process in the child’s body, caused by an unconditional reflex factor. An attack of temporary active production of saliva also accompanies such an important period as teething - the gums become inflamed, hurt, the child constantly tries to scratch it, etc.
Older children normally do not suffer from hypersalivation, and detection of a problem may indicate the following pathological causes:
- oral disease – stomatitis, thrush, etc.;
- dysarthria and other consequences of disruption of the nervous system;
- cerebral palsy - due to the disease, there is a lack of coordination between the oral muscles, and swallowing saliva is much more difficult. In such a situation, there is no excessive salivation; it flows from the mouth due to difficulties with swallowing function;
- perinatal brain damage;
- brain injuries as a result of bruises and blows.