When pregnancy occurs, women are of the opinion that it is better not to take any medications, or they try to take a minimum of medications. But no one is immune from situations in which it is necessary to take painkillers, even during pregnancy.
Many may say that pain during pregnancy can be tolerated so as not to further endanger the baby. To this I can object that enduring pain for a long time is dangerous for both the mother and the fetus.
What should a pregnant woman know about pain?
Prolonged pain creates a stressful situation for a woman. When pain occurs, the body produces stress hormones. But since a pregnant mother and her child are practically a single organism, stress is inevitably transferred to the child.
Stress hormones have a stimulating effect on muscles, including (and especially) the muscles of the uterus. As a result, a pregnant woman with chronic pain may experience miscarriage or premature birth.
This is one side of the coin. On the other hand, it is unacceptable to relieve pain simply by taking painkillers and not consulting a doctor.
Pain is the body's signal that something is wrong. This signal must be perceived in time by a person in order to find the true cause of this symptom. By directly influencing the cause, we can count on relief from pain and recovery.
Moreover, taking painkillers can mask and blur the clinical picture of many diseases, for example, acute appendicitis. As a result, time may be lost during which the woman could have received help and prevented the disease from progressing.
In other words, you need to be smart about taking any medications. That is, there is no need to self-medicate, and you can take painkillers without a doctor’s recommendation only when it is not possible to see a doctor here and now. For example, if you wait a long time for an ambulance on a weekend or holiday. Or if there is no way to contact for acute pain when your teeth hurt.
Causes and types of hemorrhoids in pregnant women
40% of women expecting a child face the problem of hemorrhoids. The main reason is an incorrect, sedentary lifestyle, lack of sports and bad habits before pregnancy. The mother's body is not ready for increased stress. Muscle tissue and blood vessels are in such poor condition that they are unable to withstand the pressure of an ever-growing uterus. It puts more and more pressure on the pelvic and abdominal organs, including the intestines. Blood stagnation occurs, hemorrhoids enlarge
Under the influence of hormonal changes, digestion is disrupted, problems with bowel movements and prolonged constipation begin, which also provokes the disease.
In addition, risk factors include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- obesity or overweight;
- age of the pregnant woman;
- low amount of fiber, vitamins, minerals in the diet, the presence of spicy and salty foods;
- lack of physical activity.
Childbirth, especially long and difficult ones, contractions and pushing, pressure on the perineal area at this moment also aggravate hemorrhoids. The load on the vessels and veins increases, they swell and rupture. This explains the presence of hemorrhoids after childbirth, bleeding and loss of cones.
The situation gets especially worse in the last trimester.
Hemorrhoids in women during pregnancy and after childbirth can be of 3 types.
- In acute form. Painful signs increase rapidly, especially in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters.
- Sluggish, chronic. Characteristic of the 1st trimester, symptoms appear infrequently and mildly. At a later stage it usually becomes acute.
- In a complicated form. It is considered the most dangerous, fraught with the appearance of pus. The main signs are the appearance of cracks in the anal area, bleeding, and prolapse of nodes.
You can’t treat yourself, but you shouldn’t endure pain either. The sooner you start treatment, the easier the birth and postpartum period will be.
Situations in which painkillers may be needed
Toothache, earache, headache, nagging pain in the abdomen, pain in the lower back and joints, pain during sprains, bruises and fractures, burns, as well as acute appendicitis, renal colic - this is an incomplete list of possible causes of pain in pregnant women.
Useful: How to sleep properly during pregnancy: in the early and late stages
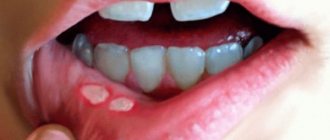
Toothache is a topic that is especially relevant for expectant mothers, since during pregnancy the female body experiences a lack of calcium and phosphorus.
Nature arranges everything in such a way that the child can be guaranteed to receive all the microelements and vitamins he needs. The baby will still take everything he is entitled to, even at the expense of the mother’s body reserves. Therefore, the destruction of dental tissue and the addition of caries during pregnancy are not uncommon for women.
Ideally, of course, you need to sanitize your oral cavity before planning a pregnancy. But even this step, unfortunately, does not provide one hundred percent protection against painful dental problems for the expectant mother.
Why can your stomach hurt during pregnancy?
Abdominal pain signals unwanted processes occurring in the digestive area.
During pregnancy, existing diseases worsen, and new ones appear. Sometimes discomfort is associated with hormonal changes. The most common causes of abdominal pain in pregnant women:
- stomach ulcer;
- gastritis;
- influence of hormones;
- physiological changes;
- stress;
- indigestion;
- binge eating.
All this affects a woman’s condition, both individually and in combination with other factors.
Gastritis exacerbation
Gastritis during pregnancy occurs even in those women who have not previously suffered from it. The most common reason that causes it is stress. Because it reduces the body's resistance to bacteria that cause this disease.
List of possible causes of exacerbation of gastritis during pregnancy:
- genetic predisposition;
- iron deficiency;
- deficiency of proteins and vitamins;
- overeating, incorrect menu;
- nervous shocks.
If you suspect the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the digestive system, an immediate visit to the doctor is required.
Peptic ulcer
Exacerbations of this disease occur in autumn or spring. It is provoked by changes in weather and daylight hours.
The following symptoms help to recognize pathology:
- pain after eating;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- belching;
- heartburn.
All these symptoms cause inconvenience to a woman, but do not directly affect the ability to bear and give birth to a child.
Attention! An advanced ulcer eventually transforms into gastric bleeding and perforation.
In the early stages
At the beginning of pregnancy, a woman listens carefully to her feelings.
After all, in the first trimester there is a high probability of miscarriage. This is why expectant mothers worry about the condition of the fetus. This position is correct. Pain is the first sign indicating a threat of termination of pregnancy. However, it is important to assess where the source of unpleasant sensations is located. The only cause for concern is pain in the lower abdomen. Stomach cramps are not related to pregnancy.
In the early stages, pain in the stomach is manifested by:
- stress;
- toxicosis;
- starvation;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Important! If any discomfort occurs, a pregnant woman should consult a doctor for advice and diagnosis. And also for proper treatment of the disease.
At later times
In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, the causes of discomfort in the stomach are different:
- physiological;
- food poisoning;
- infectious diseases.
Physiologically, the reasons lie in the growth and development of the child, and with it the uterus. The enlarged organ puts pressure on the stomach, the baby pushes, not sparing the mother. Therefore, in the second half of gestation, stomach pain is not a cause for alarm.
But food poisoning affects the baby’s health. Therefore, if heartburn, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea appear simultaneously with pain, you should immediately seek medical help.
Important! Infectious diseases manifest themselves as stomach pain in the last weeks of pregnancy. During this period, physiological factors cease to operate.
The first trimester is a dangerous period
In the first trimester, you always need to think again about whether it is worth taking any medications, especially painkillers. It is during this period that the risk of negative effects of drugs on the fetus is especially high, since in the first months of pregnancy the child develops rapidly, most of the vital systems and organs of the baby are formed, the development and formation of which can be negatively affected by any external factor.
Also, in the first months of pregnancy, metabolic processes occur intensively in the bodies of both the mother and the child, and the not yet fully formed placenta cannot adequately perform its barrier function. This is why most medications, including painkillers, are contraindicated in the first three months of pregnancy.
How painkillers can be dangerous for the fetus
It is important to remember that not all medications are allowed during pregnancy, and timing also plays a huge role. During pregnancy in the 1st trimester, it is, in principle, dangerous to use any painkillers, because during this period the embryo is implanted into the wall of the uterus, and all the systems and organs of the unborn baby are formed. Therefore, any external influence can disrupt this process and lead to negative consequences.
There are also some painkillers that are prohibited during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester due to the fact that they can cause changes in the amniotic fluid, which in the future can even lead to oligohydramnios.
All drugs of this type are divided into several groups:
- Group A. Medicines that do not cause any harm to either the unborn child or the mother. These include homeopathic medicines and herbs.
- Group B. Substances that are safe if the dosage and method of administration are followed correctly. This includes medications based on Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
- Group C. Drugs that partially affect the fetus. They are used in cases where the benefit outweighs the risk and these include Papaverine and Drotaverine.
- Group D. Medicines that affect fetal development and are used in extreme cases where the perceived benefit is significant. These include: Baralgin, Acetylsalicylic acid, Indomethacin, Diclofenac.
- Group X. This includes quite dangerous medications that are dangerous to take even while planning a pregnancy.
Painkillers: which ones can be taken during pregnancy and which ones are strictly prohibited?
Of the painkillers, Paracetamol is considered the safest. Its safety for pregnant women and children is confirmed by the World Health Organization. It is contraindicated for women with kidney disease, liver disease and erosive diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Paracetamol, in addition to its analgesic effect, also has an antipyretic effect. All over the world, Paracetamol is recognized as the drug of choice for fever in young children. This also indicates high confidence in the drug.
Paracetamol
A single dose of Paracetamol should not exceed 500 mg. The doctor monitoring your pregnancy will tell you the daily dose.
It is important to understand that even such cold powders as Theraflu, Coldrex, Fervex contain Paracetamol. And if they were recommended to you to relieve the symptoms of a cold, then you no longer need the additional use of Paracetamol and other analgesics. Otherwise, additional intake of painkillers may lead to an overdose.
Ibuprofen
If it is impossible to take Paracetamol, the doctor may prescribe Ibuprofen to the pregnant woman. This drug can be produced under different trade names, such as Nurofen, Ibufen.
The drug Nurofen Plus is contraindicated for pregnant women, since the drug contains additional components and a large dose of the main substance, it can have a negative effect on the fetus.
Ibuprofen is approved for use in pregnant women in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. It is prohibited to take it in the third trimester of pregnancy, as it significantly affects the amount of amniotic fluid and reduces it.
Useful: Why does pregnant women have back pain and what to do about it?
What painkillers can you take during pregnancy?
Pain itself is an alarming signal; it means that there is some kind of problem in the body. If pain bothers you during pregnancy, no matter whether it is headaches, dental pain or joint pain, you should definitely consult a doctor. He will determine the cause and select a treatment program.
But treatment is usually a long process, and there is no strength to endure the pain. It is worth paying attention to the following drugs:
- Paracetamol. This is the most popular remedy among therapists and obstetricians, used to suppress pain in pregnant women. It works in three directions at once: it dulls pain, relieves fever and eliminates inflammation. It can be taken for colds, migraines or toothache. The active components of paracetamol penetrate the placenta, which means they enter the baby’s bloodstream. But they will not cause any harm to the baby and will not affect his development. Therefore, paracetamol in the prescribed dosage can be taken during pregnancy for any pain.
- Nurofen. Its action is similar to that of paracetamol, these tablets also relieve pain, fever and inflammation. The drug in certain dosages can be taken not only by pregnant women for various pains, but also by infants, for example, during teething. But in the last trimester of pregnancy, obstetricians recommend avoiding this medicine: it can reduce the amount of amniotic fluid.
- Analgin. Many pregnant women are interested in whether they can take this remedy if the pain is very severe and paracetamol does not help. Doctors say it is possible. But: only in extreme cases and in small dosages. Chemical agents of analgin penetrate through the blood through the placenta to the fetus and, if taken for a long time, can have a negative effect on its health. In addition, analgin changes the composition of the blood: it thins it and helps reduce hemoglobin levels.
- No-shpa and riabal. These drugs are not analgesics, but antispasmodics. For some, they help eliminate headaches and toothaches, and doctors do not prohibit taking them during pregnancy. Even moreover, if the tone of the uterus is increased and there is a risk of premature onset of labor or miscarriage, gynecologists and obstetricians recommend taking no-shpu constantly. In any case, always have it with you in your purse or pocket.
All these remedies are most conveniently taken in tablets. But if for some reason tablets are not suitable - for example, with severe toxicosis - you can use a medicine with the same active substance, but in a different pharmacological form - for example, in the form of suppositories.
Analgin is contraindicated during pregnancy
Analgin is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It has already been discontinued in European countries. In our country it is used quite widely. Analgin is included in the so-called triad, or lytic mixture, which is used as an ambulance at very high temperatures, severe intoxication as a result of administration. The use of such a potent drug once during emergency care is permitted under the supervision of a physician. In other cases, you should not resort to Analgin.
Diclofenac
Diclofenac is also a potent analgesic. Pregnant women are better off using its analogue, Voltaren. Its administration to expectant mothers is possible for health reasons in the first and second trimester. In other words, it can be used only when the benefits to the health of the mother outweigh the undesirable effects of the drug on the fetus.
In the third trimester, Valtaren should not be taken, as it can further provoke weakness of labor and disrupt blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system.
Fastum-gel for pain in pregnant women
Fastum-gel is an anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drug. The active component of the drug is ketoprofen.
As a result of inhibition of local prostaglandin synthesis, the ointment prevents pain, swelling, and relieves the inflammatory process.
Indications for the use of Fastum-gel are back pain in pregnant women, injuries, muscle and joint pain.
The ointment is prescribed in the first and second trimester. However, in the last months of pregnancy, using the product may cause undesirable consequences. Therefore, after 32 weeks it is undesirable to use the drug.
To relieve back pain, pregnant women need to rub a thin layer of ointment into the skin until completely dry. You can use the ointment up to two times a day. It is important to note that if there are minor skin lesions, you should carefully rub Fastum-gel so that the product does not get into the wounds. The duration of treatment is no more than ten days.
Side effects are rare. Sometimes itching and burning of the skin, dermatitis, and hypersensitivity to the sun's rays are possible.
Contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- Rashes
- Bronchial asthma
- Aspirin intolerance
- Eczema
- Allergic rhinitis
It is important to remember that pregnant women should not use the ointment on their own, as this can harm the woman’s body and the fetus.
No-shpa or Papaverine
No-shpa or Papaverine are antispasmodics, that is, drugs that eliminate spasms of smooth muscles. If the pain is associated with a spasm (pulling pain in the lower abdomen with uterine tone, throbbing headache), then these drugs will cope with it. In all other cases they will be useless. As prescribed by a doctor and under his direct supervision, No-shpa can be taken regardless of the stage of pregnancy.
Headache medications you can take during pregnancy
Antispasmodics
Often the cause of pain can be a spasm of blood vessels in the brain, neck muscles or the back of the head.
In such cases, products that contain substances that relax the walls of blood vessels are effective. Due to this, the diameter of the vessels increases and blood circulation is normalized.
It is important to know that this group of drugs is effective for tension headaches.
Antispasmodics are the safest group of painkillers during pregnancy.
“No-spa” (“Drotaverine”) is a drug that helps relax smooth muscle cells. This drug affects not only the walls of blood vessels, but also the cells of the intestines, biliary system, urinary system, and uterus. It is for this reason that “No-spa” is successfully used during pregnancy with increased uterine tone.
Thanks to numerous studies, it has been revealed that this medicine does not have a negative effect on the fetus and does not cause developmental defects.
Application should be in acceptable therapeutic doses, since exceeding the dosage may lead to side effects:
- Decreased blood pressure (to the point of fainting).
- Heart rhythm disturbances (increased heart rate).
- The emergence of a tendency to constipation (due to decreased intestinal motility).
Contraindications for use are individual sensitivity to the active substance, hypotension from 90/60 mmHg. and below, tachycardia from 110 beats/min.
Combined antispasmodic analgesics, which in addition to the antispasmodic component contain another active ingredient - an analgesic, are prohibited for use during pregnancy. Such drugs include “Spazmalgon”, “Andipal”.
Medicines that lower blood pressure
One of the causes of headaches is increased blood pressure. For pregnant women, this situation is most relevant for a number of reasons:
- an increase in circulating blood volume during gestation by almost 40%;
- the development of gestosis, which is characterized by increased pressure, as well as fluid retention in the body;
- increased load on the cardiovascular system;
- exacerbation of existing chronic kidney and heart diseases.
Increased pressure is manifested by pain, most pronounced in the occipital region. There may be a feeling of heaviness in the head, flashing “spots before the eyes.”
Among the approved centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, they include (“Dopegit”) and a solution of “Magnesium sulfate” (“Magnesia”).
"Dopegit" acts on alpha-adrenergic receptors located in the brain.
It can be used during pregnancy for a number of reasons:
- There is no negative effect on fetal development.
- Adequate uteroplacental blood flow is maintained.
"Magnesia". When a pregnant woman experiences a headache associated with high blood pressure, the Magnesium sulfate solution is highly effective. In addition, it is a tocolytic (reduces the tone of the uterus), promotes the removal of fluid from the body (with edema).
This medicine is successfully used in obstetrics; it is especially necessary if a pregnant woman has gestosis, as it affects many parts of the pathogenesis.
The main route of administration is intravenous infusion, less often intramuscularly.
If necessary, tablet magnesium preparations (Magnerot, Magnelis, Magne-B6) are prescribed. Their effect appears gradually, the duration of therapy ranges from 10 to 30 days.
Preparations based on paracetamol
This group of medications can relieve pain of moderate intensity without harming the condition of the fetus.
The drug penetrates the placental barrier, but according to studies, Paracetamol does not have a toxic or teratogenic effect (does not cause developmental abnormalities) on the fetus. It should be remembered that the use of this drug should be limited.
Analogues of Paracetamol are Panadol, Efferalgan.
Aspirin is contraindicated during pregnancy
Pregnant women should generally forget about Aspirin as an analgesic and antipyretic. The drug has many side effects, and therefore the possibility of relieving pain with its help should not be considered by pregnant women at all. Aspirin is prescribed to patients with cardiovascular pathology in small doses at night as a blood thinner. It is its blood-thinning effect for a pregnant woman that can lead to irreparable consequences.
Very common and effective analgesics Nimesulide (Nise, Nimesil), Ketorolac (Ketorol, Ketonov) are contraindicated for expectant mothers.