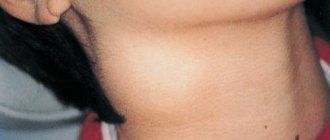
Enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear are a protective reaction of the body that occurs in response to oncological and infectious processes in the body, namely in the ear, oral cavity and nasopharynx. Lymph nodes not only enlarge, but also become painful. The skin becomes hyperemic and severe swelling appears. In this case, we can talk about postauricular lymphadenitis or a local form of lymphadenopathy.
Features of the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system of the human body is a network of ducts and vascular structures that are designed to circulate lymph (intercellular fluid). The protective function is due to the production of antibodies and lymphocytes. Normally, the nodes are no more than 0.5-5.0 cm in size. They are washed by intercellular fluid, which comes from internal organs and structures located nearby.
The postauricular lymph nodes are located along the temporal bone, in the area of the ear vein. In the absence of pathological processes in the body, they cannot be palpated and visually determined. A person has 4 protective capsules in this area. If there is an increase in size, then we are talking about an inflammatory process in regional organs or tissues. The parotid lymph nodes, including the preauricular lymph node, clear intercellular fluid from the area of the temporal and parietal parts of the head. They have a direct connection with the structures of the neck and the salivary glands.
Diagram of the lymph glands in the ear area: 1) preauricular; 2) behind the ear; 3) parotid
Lymphatic structures are a kind of filter, which is designed to destroy and remove foreign bodies and microorganisms from the body. If there is circulation of foreign agents in the blood, then active production of lymphocytes occurs in the area of the nodes. This causes them to increase in size and become quite painful.
Inflammation of the lymph node behind the ear can occur at any age. Please note that only preschool children are predisposed to lymphadenitis. This is due to the fact that their immune system is immature. The internal capsules are practically not compacted and have no partitions, which leads to the fact that even a small amount of pathogenic or foreign microorganisms or structures leads to their enlargement.
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes - causes and treatment, symptoms
The submandibular lymph nodes can become inflamed at any age. Timely and comprehensive treatment of this pathology will ensure a quick recovery. This article describes the symptoms, etiology, diagnosis, treatment methods, complications and prevention of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes.
What kind of disease is this
One of the most common forms of lymphadenitis is inflammation and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes. Often, such a pathological process in the lymph nodes is associated with the reaction of the immune system to the presence of infectious invasion near the lymph nodes.
In medical practice, there are three main stages of this pathology:
- Initial.
- Average.
- Purulent.
Important! The presence of purulent exudate in the lymph nodes is a manifestation of a serious complication, the resolution of which requires extremely urgent surgical intervention.
Inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes is an alarming symptom that indicates the development of a pathological process in the body, from the slightest inflammation to serious diseases.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, inflammation can be felt by palpation.
The initial stage of development of lymphadenitis of the cervical lymph nodes is hidden and does not show any signs.
As the disease progresses, the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw enlarge, become dense and painful on palpation. This means that the disease is becoming acute.
Characteristic symptoms of this condition are the presence of:
- Periodic shooting pain signals in the area of the cervical lymph nodes.
- Hyperemia of the skin at the location of the lymph nodes, which becomes burgundy in color as the pathology progresses.
- Swelling and swelling in the lower jaw area.
- Local hyperthermia of the body.
- Severe pain when swallowing and turning the head.
- Asomnia, deterioration of health.
Attention! Symptoms of lymphadenitis of the cervical lymph nodes are identical to inflammation of the salivary glands, phlegmon, tumor and abscess. Therefore, if you show the slightest signs of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, you should immediately seek qualified medical help.
Causes of occurrence in adults
| Name | Description |
| Pathologies of infectious etiology | Inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes begin due to infection of organs located near the cervical lymph nodes. After entering the body, pathogens change the structure of human cells. In this case, the body’s protective reaction to them is an increase in the size of the lymph nodes. |
| Immune pathologies | Associated with dysfunction of the protective system, which is the root cause of the development of pathologies such as AIDS, leukemia, systemic lupus erythematosus, joint damage and HIV infection. |
| Tumors | They provoke lymphadenitis regardless of the location. A significant number of cancer cells are located in the lymph, which entails metastasis in the lymph nodes. With this pathology, the nodes do not enlarge and do not hurt. |
| Dental diseases (abscess, gumboil, alveolitis) | Many pathologies associated with inflammation or accumulation of purulent exudate are characterized by enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. |
| Toxoplasmosis | It is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma, which affects the lymph nodes in the body. |
The etiology of the development of lymphadenitis of the submandibular lymph nodes is very important, as it plays an important role in the treatment of pathology. Inflammation of the lymph nodes is only a symptom of a disease that requires treatment first.
Features of pathology in pediatrics
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes in a child
Characteristic symptoms of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes in a child are a pronounced deterioration in health, rapid hyperthermia, and signs of intoxication.
If the slightest symptom of lymphadenitis appears in a child, you should immediately seek medical help, due to the high likelihood of developing swelling. Self-medication in this situation is strictly prohibited , as it can significantly worsen the child’s condition and even lead to death.
The main reasons for the development of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes in children are:
- Cat scratches.
- Cold pathologies.
- Infectious diseases, especially of the respiratory system, head, throat, eyes, ENT organs and dental pathologies.
Treatment of pathology is based on the correct establishment of etiology. The therapeutic course is prescribed only after a full diagnosis, taking into account the necessary complex to eliminate the underlying pathology that caused the growth of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Diagnostics
You can determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the submandibular lymph nodes yourself. But an accurate diagnosis can only be established by an otolaryngologist.
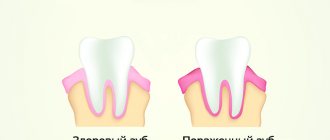
Self-diagnosis is carried out through palpation. Normal nodes:
- Elastic.
- They have a dense structure.
- They do not cause pain.
- They move easily under your finger when palpating.
- The size of the lymph node should not exceed 1 cm, and in most cases, in the absence of pathological processes, the nodes cannot be palpated at all.
Reference! If a self-examination reveals changes in the shape, structure and size of the submandibular lymph node, you should urgently visit a doctor.
Ultrasound of submandibular lymph nodes
Specialized diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis includes several studies:
- Visual inspection
- Palpation
- Ultrasonography
- Clinical tests of urine and blood
- Blood chemistry
- X-ray examination
- Histological examination of lymph node tissue
If necessary, the otolaryngologist may prescribe an additional examination by a dentist, infectious disease specialist, pulmonologist, oncologist, or hematologist. This will allow you to quickly differentiate inflammation and make the correct diagnosis as soon as possible.
Treatment
At the initial stage, you can get by with drug treatment.
The key to successful therapy is the correct identification of the cause that provoked inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes. Depending on the stage of development of the pathology and its etiology, you can do the following:
- Drug therapy. Based on the diagnostic results, the following may be prescribed as prescribed by a doctor:
- Antibacterial drugs: ampicillin, amoxiclav, ceftriaxone, sumamed and amoxicillin. Their use is effective in the presence of purulent exudate in the glands, infections whose pathogens are bacteria, and in the prevention of complications. Their choice is determined by the clinical picture of health and the age category of the patient, as well as the stage of development of the pathology.
- Antiviral agents: Kagocel, rimantadine, anaferon. Prescribed for viral etiology. Under their influence, the process of bacterial reproduction is suspended and the process of producing its own interferon is stimulated.
- Antitumor: aromazine, thioguanine, methotrexate. Block the development of cancer cells.
- Immunosuppressors: tacrolimus, cyclosporine A. Prescribed for autoimmune pathologies, which makes it possible to artificially suspend the activity of the immune system.
- Also, as an auxiliary therapy, gargling with antiseptic solutions , among which Burov's solution is the most popular. As an additional treatment, local drugs are used in the form of ointments: troxevasin, heparin, Veshnevsky.
- Surgical treatment. Prescribed in the presence of an abscess, oncology or complications of lymphadenitis. To eliminate it, surgical cleaning of the cavity after its removal is required. In case of a large amount of pus, after opening the abscess, a drainage is installed to ensure the outflow of the contents. After surgery, to prevent relapse and complications, a course of antibacterial therapy with certain physical procedures is prescribed. In case of oncology, nodes can be removed for additional examination or if metastases form in them.
- Traditional therapy. It can only act as an auxiliary treatment. The use of alternative remedies helps relieve acute symptoms. For these purposes, only in consultation with a doctor, the following can be used: Herbal decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs: birch, wormwood, pine needles, thyme and St. John's wort.
- Warming compresses made from rosin, gauze soaked in herbal decoctions, heated sea salt.
- Applications made from fresh dandelion juice.
- Chicory root lotions on an inflamed lymph node.
Important! The choice of therapeutic course, its type, duration and use of auxiliary means of traditional medicine is determined exclusively by the attending physician. Self-medication of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes is strictly prohibited.
Basics of therapy for submandibular lymphadenitis
Therapy should begin at the initial stage of its development and, as a rule, it consists of:
- Sanitation of the source of infection.
- Professional consultations and procedures for opening an abscess
- Sanitation of the oral cavity with Burov's liquid.
- The use of a cold compress made from anti-inflammatory drugs or drugs of natural origin.
- Conducting a course of antibacterial therapy.
- Taking multivitamin complexes.
- Carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures.
If it is necessary to carry out surgical intervention and choose the method of its implementation, the number of inflamed lymph nodes is taken into account. If one lesion is opened, a small incision is made above it and drainage is made under the capsule. If there are several inflamed nodes, the area of inflammation is opened, after which drainage is introduced into the hypodermis.
Negative consequences
Advanced inflammation
In the absence of proper therapy or the patient ignores the recommendations of a specialist, the disease can become chronic. Untreated submandibular lymphadenitis leads to serious complications that pose a danger to the health and life of the patient:
- Inflammation can involve tissues located near the lesion and provoke the development of periadenitis, adenophlegmon or abscess.
- If the infectious focus is located in the area of the respiratory system, the abscess itself may open on the affected lymph nodes, which will lead to the formation of a bronchial fistula or a fistula in the esophagus.
- An incorrectly performed operation can provoke extensive bleeding, infection in the incision area, or cancer cells extending beyond the shape of the node.
- There is also a small chance of developing lymphedema.
Timely therapy and correctly performed surgery for inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes significantly minimizes the likelihood of complications.
Precautionary measures
Do not heat or cool the affected area!
To prevent the development of a severe form of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes and the appearance of complications against its background, it is strictly prohibited:
- Self-medicate. This is due to the fact that it takes education and technology to establish the exact cause and select the appropriate treatment for the pathology. Improper treatment leads to worsening health conditions, and for some diseases, loss of time.
- Warm up inflamed lymph nodes. This provokes the spread of infection to neighboring tissues, increased swelling of the cervical-facial region, and increased intensity of pain. With oncological etiology, heating can promote the spread of affected cells through the lymph and blood.
- Cool the affected area with cold. Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes often occurs with the development of a viral infection. With this etiology, local hypothermia significantly worsens the general condition of the patient.
Prevention
A preventive measure is regular visits to the dentist.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes located under the jaw can be avoided by following a basic set of preventive measures. Among them, experts highlight:
- Timely treatment of infectious pathologies of the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract, starting from the appearance of the first symptom.
- Careful and proper oral hygiene.
- Regular visits to the dental clinic (every six months).
- The use of antiseptics in case of violation of the integrity of the oral mucosa and facial skin.
- Strengthening general immunity through hardening, playing sports, giving up bad habits, and using natural biostimulants.
- Avoiding hypothermia of the body.
- Limiting visits to crowded places during the peak incidence of acute respiratory infections.
- Wearing hats and scarves during the cold season, which protect against the development of inflammatory processes in the neck and the appearance of large lymph nodes under the jaw.
- Proper and varied nutrition, which will enrich the body with vitamins and beneficial microelements, will improve digestion, improve the gastrointestinal microflora and reduce the risk of infection of the body by pathogenic microbes.
- Treatment of caries. In its presence, a sluggish infectious process persists, which can contribute to the appearance of inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Reference! There are no special measures to prevent the development of submandibular lymphadenitis. Prevention of the disease consists of eliminating the root causes that provoke the occurrence of the disease.
The problem of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes often depends on many factors. The key to successful treatment for inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes is timely diagnosis of the pathology, which only a doctor can do. Therefore, if the slightest symptom appears, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Source: https://dentoland.com/polost-rta/vospalenie-podchelyustnyx-limfouzlov.html
Reasons for the increase
If the lymph node behind the ear is enlarged, then we are talking about the presence of some pathological disorders. In this case, the first step is to establish the cause of the changes occurring in the body and eliminate it. Only after this should the symptoms be taken into account. Otherwise, it will be possible to get rid of the manifestations only for a short period of time.
Why do the lymph nodes behind the ears become enlarged? We are talking about the course of acute or hidden pathological processes in the area of the ear, crown, back of the head, mastoid process or salivary glands. With the flow of lymph, toxins and microorganisms penetrate into the capsule area, which are the causative agents of various diseases.
Photo
When the lymph nodes behind the ear are enlarged, the causes may be related to the following factors:
- Decreased protective functions of the body.
- Pathologies of the hearing organs, such as boils, otitis, eustacheitis, etc.
- Inflammation in the nasopharynx (rhinitis, sinusitis, nasopharyngitis).
- Infections of the mouth and throat - stomatitis, caries, pharyngitis, diseases of the salivary glands.
- ARVI and colds, in which there is a severe runny nose.
- Specific diseases of an infectious nature - rubella, toxoplasmosis, mumps, etc.
Please note that the preauricular lymph nodes under the ear can also enlarge due to neurological abnormalities, in which the blood supply to the brain area increases. Lymphadenopathy can develop against the background of a fungal infection, an allergic reaction, and a malignant process in the neck or head.
Specific pathogens, opportunistic microflora, anaerobes and intracellular parasites are the etiological agents that provoke the development of the disease. Among the most common reasons why nodes enlarge are viral infections.
Lymph nodes on the face: location, functions, causes of inflammation
Lymph nodes on the face do not always have a typical location: they can be localized on the cheeks, chin, cheekbones and other areas. Most often, inflammation of the lymph nodes on different parts of the body occurs, but sometimes the lymph nodes on the face can also become inflamed, and their location may indicate the causes of lymphadenitis.
What are the lymph nodes on the face for and where are they located?
Lymph nodes (L/N) are located along the lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes of the face and neck are necessary to remove metabolic products, toxins, and create a barrier to infection.
In the facial area, several main groups of lymph nodes (glands) can be distinguished:
- superficial and deep parotid (in the projection of the parotid salivary glands on both sides);
- directly facial (buccal and mandibular lymph nodes, as well as a small number of innominate ones);
- submental (between the bellies of the digastric muscle);
- submandibular.
Strictly speaking, the last two groups of nodes (submental and submandibular) are located not on the face itself, but in the neck and under the chin. But they are also closely related to the lymph glands of the face, so they are also worth adding to this list. Lymph from all the lymph glands of the face flows through the lymphatic vessels into the cervical lymph nodes.
The location of the lymph nodes on the face depends on the degree of development of the facial muscles and subcutaneous tissue; genetic factors also play a role. Below is a schematic representation of the facial lymph system against the background of facial muscles and large blood vessels.
Facial lymph nodes can be located in the thickness of the cheek, in the cheekbone area. Closer to the angle of the lower jaw are the mandibular nodes.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes of the face
Lymphadenitis of the maxillofacial region is rarely an independent disease.
The causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes in this area can be:
- infectious diseases (colds, herpes infection, measles, purulent tonsillitis, mononucleosis, etc.);
- decreased immune response;
- various tumors and oncological diseases (including leukemia);
- hypothermia;
- traumatic injury to this area of the face;
- diseases of teeth and gums (periodontal disease, gingivitis, caries);
- introduction of pathogenic microbes from the outside (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, streptococci) from purulent-inflammatory foci on the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the facial area;
- allergic reactions.
Lymphadenitis of the facial node
Inflammation of the lymph nodes on the cheek often occurs against the background of acne, or acne. This disease is caused by special propionobacteria. In the development of the inflammatory process, the state of the immune system and hormonal system are of no small importance.
Lymphadenitis of the parotid and postauricular nodes
Inflammation of the lymph node near the ear near the cheek occurs with mumps (inflammation of the salivary parotid gland). The causes of lymphadenitis of the pre-auricular lymph nodes can be otitis media, mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid process) and some other inflammatory processes in this area.
Enlarged nodes in the lower part of the face
If inflammation affects the mental lymph nodes, it can be assumed that the cause of the disease is caries, periodontal disease and other diseases of the oral cavity. This also applies to the mandibular nodes.
Lymphadenitis of the facial area: symptoms
Inflammation of the lymph nodes on the face is manifested by redness and swelling of the skin in the corresponding area. The affected node enlarges significantly and can be very painful; when pressing on it, the pain intensifies.
If the node undergoes purulent melting, it may break through to the surface of the cheek or other area.
With a pronounced inflammatory process, the temperature often rises, the patient is bothered by weakness and headache.
Therefore, in case of any purulent processes in this localization, you should immediately contact a surgeon.
Types of lymphadenitis
The classification of lymphadenitis takes into account the nature of the course, the form of inflammation and other factors. Thus, lymphadenitis can be acute or chronic.
According to the causative factor, they distinguish:
- specific lymphadenitis (against the background of syphilitic infection, HIV infection, tuberculosis);
- nonspecific lymphadenitis (caused by staphylococci, streptococci and other common microbes, toxins).
Taking into account the nature of the exudate, there are purulent and non-purulent inflammations of the lymph nodes on the face. A photo of purulent lymphadenitis is presented below.
Diagnostics
Since damage to the lymph glands in most cases is only a manifestation of the underlying disease, for successful treatment it is necessary to determine the cause. For diagnostic purposes, the doctor examines the patient, palpates the inflamed nodes and lymphatic vessels.
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, the specialist carefully examines the oral cavity and the area of the salivary glands. To make it easier for the doctor to find out the cause of the pathology, you need to tell in detail about the symptoms and past illnesses, existing diseases.
It should be borne in mind that other diseases can occur under the guise of lymph inflammation. For example, inflammation near the ear occurs with mumps, inflammation of the cheekbone - with atheromas, deep acne and subcutaneous abscesses.
Treatment
If the lymph nodes near the ear, face or chin become inflamed, you should definitely consult a doctor. Treatment of lymphadenitis of the facial area is usually carried out by a maxillofacial surgeon.
Therapy includes the following components:
- etiological treatment (impact on the cause of the disease);
- symptomatically (reduce symptoms of lymphadenitis);
- general strengthening of the body.
Etiotropic therapy
To eliminate inflammation in the lymph nodes of the face, it is necessary to first act on the root cause. When the disease is infectious, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action are used.
If the enlargement of lymphatic vessels and nodes is associated with measles, herpes, mumps or mononucleosis, antiviral agents are used. Allergic diseases are treated with antihistamines or glucocorticosteroids (only in cases of severe allergization).
In case of mental lymphadenitis, which develops against the background of caries and periodontal disease, sanitation of diseased teeth is carried out. To treat inflamed gums, rinsing with medicinal decoctions and antiseptic solutions is prescribed.
Symptomatic treatment
For inflammation of the lymph nodes on the face and near the ears, symptomatic treatment includes the use of:
- anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and painkillers (mainly non-steroidal analgesics - Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, etc.);
- detoxification drugs.
Detoxification may be required in case of a pronounced reaction of the body, which is most often associated with an underlying disease.
The use of symptomatic remedies allows you to normalize body temperature, relieve pain and swelling in the area of lymphadenopathy. Sometimes, with the help of symptomatic therapy, it is possible to reduce the symptoms of the underlying disease, which led to the inflammatory reaction of the lymph nodes on the face.
General strengthening agents
Lymphadenopathies not only of the facial area, but also of various parts of the body are almost always associated with a weakened immune system. Therefore, immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, minerals and general tonics are often included in the treatment of the disease.
Surgical methods
With severe inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes on the face, sometimes they resort to surgical opening of the purulent focus. This is necessary to prevent complications. The operation is performed under local anesthesia with subsequent observation.
Prevention
To prevent inflammation of the facial lymph nodes, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health: treat caries in a timely manner, undergo preventive examinations at the dentist, and fight acne.
For prevention, children should be vaccinated against measles and mumps in accordance with age and the preventive vaccination schedule.
Secondary prevention consists of timely consultation with a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease appear.
Source: https://prolimfouzel.ru/stroenie_limfosistemy/limfouzly-na-lice-raspolozhenie-foto.html
Risk group
Lymphatic structures most often become enlarged in people suffering from autoimmune disorders such as HIV and AIDS. More susceptible to the development of lymphadenitis and lymphadenopathy are those people who have a genetic predisposition, and also suffer from systemic endocrine disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus.
Photo
Adults are much easier to diagnose than children. This is due to the fact that in childhood, patients may have enlarged nodes in the ear area even against the background of such minor factors as a common cold. In this case, the symptoms go away on their own within 1-2 weeks and do not require additional drug correction.
What does pain in the cervical lymph nodes indicate?
Painful sensations vary in intensity and nature. In respiratory and dental infections of moderate severity, the pain of the nodes is insignificant and is felt only upon palpation. The more serious the disease, the more painful the lymph nodes may be. By the way the lymph nodes in the neck hurt and other symptoms accompanying the pain, one can tell about the type and nature of the pathology.
- If when swallowing, moving the head, talking, the cervical lymph node on the right under the ear hurts a little and is enlarged, this may indicate unilateral otitis media or ARVI with damage to the auditory canal.
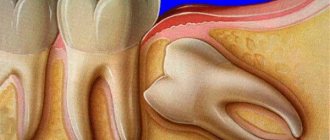
- Severe pain in the submandibular node will indicate pulpitis, caries, stomatitis, impacted or dystopic wisdom teeth.
- Pain in the supraclavicular nodes on both sides or when the left cervical lymph node is painful and inflamed indicates an infection of the upper respiratory tract, trachea or lungs.
- If the lymph node on the neck on the left, right or on both sides in the area of the angle of the lower jaw hurts, this may indicate purulent tonsillitis or inflammation of the tonsils.
Respiratory infections are a common, but not the only group of diseases that cause pain in the lymph nodes in the neck: the causes may lie in pathologies of the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis, autoimmune thyroiditis, diffuse goiter). Autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiency conditions (including HIV and AIDS) can cause pain. With malignant tumors, enlargement and pain in the lymph nodes are often observed. The focus of malignant cells can be either in the node itself (lymphosarcoma, lymphogranulomatosis, lymphocytic leukemia) or in metastases. If pain is observed in one place in the area of the carotid artery, collarbone or lower jaw (for example, the right cervical lymph node near the clavicular cavity hurts or aches), this may mean pathology in the node itself. Lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph node caused by infection through a wound or scratch. If the cervical lymph node on the back right side is painful and enlarged, especially in a child, the doctor may suspect infectious mononucleosis. Other diseases accompanied by pain in the posterior cervical nodes may be associated with the presence of cytomegalovirus, meningitis, and tuberculosis.
Classification of the disease
Enlargement of the ear lymph node can occur in different ways. Experts identify the following types of pathological process:
- Catarrhal. In this case, there is no suppuration, severe pain appears, and no external changes in the skin are observed.
- Purulent. Accompanied by an increase in body temperature, sharp pain, symptoms of intoxication of the body, hyperemia and swelling. The lymph node in this case greatly increases in size.
- Hemorrhagic. The cavity of the node is saturated with blood content, which is associated with capillary dysfunction. This form of the disease is typical mainly for such serious cases as anthrax and plague.
A chronic inflammatory process occurs only when lymphadenopathy continues for 1-2 months and the patient does not receive the necessary treatment. If the contents of the lymph node penetrate into the soft tissues that are located next to it, then we are talking about adenophlegmon. In this case, it is impossible to determine clear boundaries of the infiltrate. The lymph node quickly reaches enormous sizes, and general manifestations of intoxication of the body appear.
Traditional methods
Of course, you can resort to folk advice for treating the disease.
But you need to remember that inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is a serious disease and therefore you should consult a doctor for any symptom:
- Non-traditional methods include treatment with onions. To do this, you need to take a medium-sized onion and fry it in the oven for about 10 minutes. Then, peel it and apply it to the sore spot for half an hour.
- An excellent solution to this problem is rosin, fry in a frying pan and add laundry soap, mix everything until a thick porridge forms and apply to the neck for 15 minutes.
- Lubricate your throat twice a day with fir oil.
- Make alcohol adjustments.
- Take equal parts of onion and garlic, turn everything into a paste, fry a little in olive oil, let cool to room temperature and apply to the throat three times a day, for one month, until complete recovery.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the causes of the mucous membrane in the mouth peeling off
Clinical manifestations
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory reaction that develops against the background of destruction of the lymph nodes. If a similar reaction occurs behind the ear, then the following symptoms occur:
- Swelling. Behind the ears, the skin is thin and taut because it contains hard structures such as the skull bones and tendons. The swelling is limited on almost all sides, so the capsule itself stretches and increases in size quite strongly.
- Hyperemia. In the area of the inflammatory process, dilation of blood vessels occurs, which is fraught with stagnation of arterial blood. Externally, this process is expressed by redness of the skin.
- Increase in local temperature. Excessive blood flow caused by active cellular processes leads to a feeling of heat in the area of inflammation.
- Pain syndrome. When nerve endings are compressed in the area of tendons and skin, a pain syndrome appears. In this case, there is an active release of biologically active substances released by collapsing cellular structures. In this case, the pain is bursting and throbbing. After the acute period passes, the pain syndrome is clearly noticeable only upon palpation.
Due to dysfunction of the parotid lymph nodes, lymph is retained in the soft tissues of the head. Externally, this manifests itself in the form of edema and puffiness.
Drug therapy
On the one hand, inflammation of the lymphatic structures is a consequence of infectious diseases. First, the doctor takes measures to eliminate the underlying cause of lymphadenitis or lymphadenopathy. For this purpose, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which is carried out using broad-spectrum drugs: sulfonamides or cephalosporins.
The following are prescribed as additional agents that relieve symptoms and normalize the immune response:
- Antihistamines. Designed to relieve the inflammatory reaction and eliminate chronic inflammation. The drugs reduce swelling, relieve pain, and reduce the severity of hyperemia.
- Vitamin complexes. Necessary for restoring the body's protective functions. It is imperative to normalize vitamin C levels.
- Immunomodulators. Means whose effectiveness is aimed at normalizing the body’s immune response. Can only be used after a doctor's prescription.
After the causes have been eliminated or during the main treatment, physiotherapy is carried out in order to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and eliminate the likelihood of complications. Among the most effective procedures, electrophoresis and helium-neon laser irradiation should be highlighted.