Inflammation, increase
Very often, the cause of a sore throat can be inflamed tonsils. In medical practice, cases have become more frequent when damage was caused to only one side of the tonsils. Read how to vacuum rinse your tonsils.
The tonsils may not necessarily be affected on both sides. There are cases of inflammation of the tonsil on only one side.
What does it mean
Before you begin treatment of a unilateral inflammatory process, it is necessary to understand the reason why it arose. Most often, the pathological process occurs due to sore throat. In this case, something appears on the affected area. This is a purulent plaque. At the same time, there is a rise in temperature to 38 degrees and. Often tonsillitis leads to the development of symptoms of intoxication.
What should you do if the tonsil is inflamed on one side?
The development of the disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, the appearance of which is caused by an inflamed tonsil.
It includes a deterioration in a person’s general condition with an increase in body temperature, loss of appetite, aching joints and muscles, and sore throat, which can be very intense and usually worsens during swallowing.
When examining the throat, you can identify an enlarged tonsil on one side, which is swollen, and on the surface may contain yellow-green purulent deposits. With follicular angina, pustules are detected.
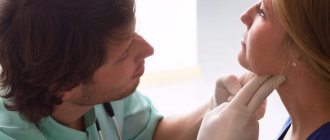
If clinical symptoms indicating an inflammatory process appear, you should consult an ENT doctor or an infectious disease specialist. He will prescribe an additional examination to determine the cause of the disease. This is necessary to select the most adequate treatment.
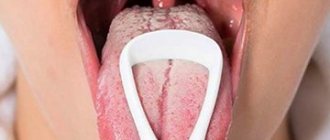
White plaque on the tonsil on one side
When a person’s throat is pink and there is no plaque, this is considered normal. But there are situations when, during an illness, plaque begins to form on the mucous membrane. It cannot be called a separate disease. This may indicate severe inflammation that requires immediate treatment.
What does white plaque mean, it hurts to swallow, one tonsil has enlarged and turned red
The presence of a white coating on one tonsil indicates that there is an infection in the body. There can be many reasons for the development of a pathological process, including:
- Often, a white coating on one tonsil can be seen in schoolchildren and preschool children. This occurs due to hypothermia, drinking cold drinks or non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. In addition, the baby could use cutlery that was infected.
- Formation of plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils. As a result, purulent mucus secretions form on the tonsils, which leads to the development of the inflammatory process.
Traffic jams in the tonsils appear due to the proliferation of harmful microbes.
As a rule, white plaque concentrated on one tonsil does not lead to a rise in temperature. The reason is that this is the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process or simply an individual characteristic of the body.
Treatment in children and adults if one tonsil is swollen/swollen/inflamed and plaque appears
Treatment can be prescribed only after a diagnosis has been made and the doctor has been able to determine the cause of the white plaque on one tonsil. In this case, he can prescribe both pharmacy and folk remedies. The main thing is that the prescribed therapy not only eliminates the unpleasant symptom, but also becomes a reliable barrier to complications.
Inflammation of the tonsils can be eliminated if you add a gargle to the drug prescribed by your doctor. For these purposes, it is worth using infusions of herbs such as chamomile, St. John's wort, and calendula. You can buy furatsilin at the pharmacy. For 200 ml of water there are 2 tablets of furatsilin. Rinse 4 times a day.
To stop the inflammatory process, you can use honey.
At the same time, make sure that it is natural.
Onions, garlic, and lemon will be useful in treatment. But people who suffer from allergies should refrain from such treatment. |
Tonsil hypertrophy is more common in children than in adults. Children aged 5 to 10 years are most susceptible to developing this pathology. This problem is not an independent diagnosis; it only indicates a disruption in the normal functioning of the body. Therefore, when treating enlarged tonsils in a child, it is necessary to first identify and eliminate the cause that caused the deviation. This helps to quickly get rid of the disease or at least alleviate the condition of the little patient. Why enlarged tonsils appear, how to treat them and avoid complications remains an urgent question.
Treatment of inflammation of the tonsils on one side
Despite the fact that the palatine tonsils are paired organs, the inflammatory process often has a unilateral localization.
It can be caused by various causes, and therefore requires adequate treatment aimed at eliminating their effects. Therapeutic measures are always complex.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism for the development of unilateral inflammation of the tonsils is initiated after damage to the cells of the mucous membrane of the tonsil area, as well as lymphoid tissue, which occurs due to exposure to unfavorable factors.
In this case, immunocompetent cells accumulate at the site of damage, which synthesize biologically active substances (inflammatory mediators). They have a number of pathophysiological effects responsible for the pathogenesis of the inflammatory response:
- An increase in the permeability of the vascular wall, which results in the release of the liquid part of the blood into the intercellular substance, which leads to an enlargement of the tonsil and indicates that it is swollen.
- Irritation of sensory nerve endings, which causes pain.
- Stagnation of blood in the structures of the microcirculatory bed.
With continued damage to lymphoid tissue cells caused by infection, a purulent process develops. A corresponding plaque appears on one tonsil, consisting of dead bacteria and immunocompetent cells.
Causes
Almost always, the cause of the inflammatory process in the tonsils is an infectious process caused by various pathogenic (disease-causing) and opportunistic bacteria.
These include staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, which cause several variants of the inflammatory process:
- Catarrhal sore throat - inflammation occurs with swelling, but without purulent plaque.
- Follicular tonsillitis is a severe course of inflammation, characterized by the accumulation of pus in the follicles of the tonsils.
- Lacunar tonsillitis is a one-sided process in which purulent plaque appears in the lacunae of the tonsils.
- Simanovsky-Vincent's tonsillitis - pathology is characterized by the appearance of plaque and ulcers. The peculiarity of the pathology is that it occurs without fever or intoxication of the body.
Inflammatory changes in the tonsils can be the result of the spread of a pathological process with tonsillitis (inflammation of the larynx), pharyngitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx), as well as a sign of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection).
Regardless of the cause, the right tonsil becomes inflamed somewhat more often than the left.
Finding out the cause of the inflammation of the tonsil on one side is a very important measure, allowing one to determine adequate treatment.
What should you do if the tonsil is inflamed on one side?
The development of the disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, the appearance of which is caused by an inflamed tonsil.
It includes a deterioration in a person’s general condition with an increase in body temperature, loss of appetite, aching joints and muscles, and sore throat, which can be very intense and usually worsens during swallowing.
When examining the throat, you can identify an enlarged tonsil on one side, which is swollen, and on the surface may contain yellow-green purulent deposits. With follicular angina, pustules are detected.
If clinical symptoms indicating an inflammatory process appear, you should consult an ENT doctor or an infectious disease specialist. He will prescribe an additional examination to determine the cause of the disease. This is necessary to select the most adequate treatment.
Directions of treatment
After unilateral inflammation of the tonsil has been diagnosed, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes several areas of therapeutic measures:
- Etiotropic therapy.
- Pathogenetic treatment.
- Symptomatic therapy.
- Prevention.
All therapeutic measures except prevention are carried out at the same time. The duration of the main course of therapy is determined by the doctor individually.
Etiotropic treatment
The main direction of successful therapy is etiotropic treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the impact of the cause of the inflammatory reaction on one side in the tonsils. For this purpose, 2 areas of activities are used:
- Antibiotic therapy - antibiotics with a wide spectrum of activity are prescribed. The choice of drug and dosage depends on the results of a diagnostic study, with the help of which the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to modern antibiotics are established. The drug can be used in the form of tablets or injections, especially against the background of a severe inflammatory process with the formation of pus. Efficiency is determined by the disappearance of inflammatory symptoms and a decrease in the size of the affected gland. The average duration of antibiotic therapy varies from 5 to 10 days and depends on the severity of the pathological process. In adults with severe disease, parenteral forms of antibiotics are more often prescribed.
- Local use of antiseptics that lead to the death of various types of bacteria - today lozenges (Septolete, Strepsils), rinsing solutions (Furacilin Solution, Chlorophyllipt) or aerosols for treating the throat (Ingalipt) are used for this. For best effectiveness, it is recommended to combine 2 products. The throat should be treated at least 12 times a day (for example, you need to dissolve 6 tablets and gargle 6 times, and they should be alternated). The total duration of use is on average the same as antibiotic therapy.
The success of all treatment depends on the correct implementation of etiotropic therapy. Irrational use of antibiotics (“undertreated” sore throat) often causes the development of chronic tonsillitis.
Pathogenetic treatment
The main goals of pathogenetic therapy are to reduce the severity of inflammation, as well as intoxication of the body. For this purpose, drugs of several pharmacological groups and certain measures are used:
- Dietary recommendations excluding fatty fried foods, ensuring sufficient intake of vitamins and plant fiber.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help remove toxins from the body. In case of severe intoxication (follicular, lacunar tonsillitis), intravenous drip administration of solutions is used for detoxification.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketanov, Paracetamol, Nimesil) - reduce the severity of the inflammatory reaction, the intensity of pain, as well as body temperature during the development of intoxication. The duration of use of the drugs should not exceed 5 days, since almost all of them have a negative effect on the liver.
- Antihistamines are medications that reduce the risk of developing an allergic reaction, and also reduce the severity of manifestations if one occurs.
- Immunomodulators are medications or medicinal plants that help the immune system fight infectious pathogens.
Pathogenetic therapy can reduce the severity of clinical manifestations, so it closely correlates with symptomatic treatment.
Symptomatic therapy
Complex treatment necessarily includes techniques to alleviate the condition of a sick person.
In case of an inflammatory process, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and sore throat lozenges, which contain anesthetics that reduce the severity of pain, are used for this purpose.
Folk remedies
Folk advice in the form of compresses for the throat, the use of medicinal plants can be used only after agreement with the attending physician and as a supplement to drug treatment.
Independent use of such techniques without primary treatment can cause various complications, including peritonsillar abscess (the formation of a limited cavity in the connective tissue near the tonsils, filled with pus), which may require surgical intervention.
Proper treatment of tonsils makes it possible to completely get rid of the causative agents of the infectious process.
Prevention of re-development of the disease consists of performing simple measures with proper nutrition, quitting smoking, drinking alcohol, sufficient physical activity, and hardening the body.
Source: https://lorgid.ru/gorlo/simptomi-v-gorle/vospalenie-mindalini-s-odnoi-storoni
Causes of enlarged tonsils
The tonsils are lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx and mouth. They produce lymphocytes, as well as special substances that protect the body from pathogens. In addition, they are physically located in the path of inhaled air and serve as a protective barrier, preventing bacteria and viruses from entering the respiratory system.
Enlarged and not painful
When the tonsils are enlarged but do not hurt, this is a sign of chronic tonsillitis. It practically does not appear, but it cannot be launched. Preventive measures are recommended that strengthen the immune system, have a positive effect on the condition of the nasopharynx, reduce the frequency of exacerbations or completely eliminate them.
This type of throat condition requires constant monitoring by a specialist. The doctor prescribes the necessary medications and prescribes procedures that improve the condition of the little patient. With timely treatment, there is no need for surgery.
Enlarged and red
When a child has a red throat and enlarged tonsils, there is an infection in the body. It is caused by microorganisms such as staphylococci and streptococci. Similar manifestations occur with caries, sinusitis, and chronic runny nose (since the foci of infections are close to the tonsils).
The following diseases also cause redness and enlargement of the tonsils: diphtheria, mumps, scarlet fever, measles, whooping cough. All of these infections require immediate treatment. Otherwise, there is a high probability of complications developing, and in some cases there is even a threat to the baby’s life.
Diagnostics
So, what to do if a child has enlarged tonsils:
- First, you need to contact an otolaryngologist when they are not inflamed.
- Laboratory tests required:
- Analysis of the functioning of the palatine tonsils (which are enlarged in the child);
- Biochemical and general blood tests;
- General urine analysis;
- Ultrasound or lateral radiograph of the nasopharynx;
- Culture of mucus from tonsils.
After conducting a full examination and studying the test results, the specialist determines how to treat tonsil hypertrophy.
Enlargement of the tonsil on one side may be a consequence of the development of an abscess in the pharynx, phlegmon or tumor (lymphoma). If you do not experience a sore throat, you may have a chronic infection. However, an enlargement of the tonsil on only one side requires immediate examination by doctors; there is probably a need for surgery.
Enlarged lymph nodes with hypertrophy of the tonsils is also a reason to immediately contact a specialist. If the lymph nodes are enlarged, this signals the spread of a viral or bacterial infection throughout the body. To avoid possible complications, treatment begins as early as possible.
Enlarged tonsils
One of the most common causes of pain in the throat may be an inflammatory process in the tonsils, causing their swelling. It can be either unilateral or bilateral, however, today, a situation in which the tonsil becomes inflamed and swollen on only one side is much more common.
It should be noted that any inflammatory process must be treated. This also applies to inflamed tonsils. But before starting therapy, the cause of the disease should be found. This is due to the fact that if the cause is incorrectly identified, treatment does not bring the necessary results.
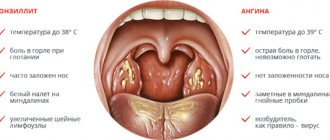
The most common cause of sore throat is acute tonsillitis or its chronic form in the acute stage. It is characterized by the appearance of a white or yellow purulent plaque; the gland may be inflamed on one side or on both sides at once. A pronounced temperature reaction occurs up to 38C, and it is very painful to swallow.
Also, the cause of such clinical manifestations may be pharyngitis, in which inflammation affects the pharynx. He does not have a very high temperature, symptoms of general intoxication and purulent plaque on the tonsils. It should be noted that inflammation on the left side may be a sign of streptococcal infection. It is easy to recognize by such signs as:
- Rash on the upper palate;
- White spots on the tonsil;
- It hurts to swallow, the pain radiates to the ear;
- Discharge of yellow mucus.
If inflammation on the left side is accompanied by pain in the ear during swallowing, and hearing begins to decrease or disappears, then most likely the inner ear was affected and otitis media developed. In this case, immediate treatment for this inflammatory process is required, since an abscess may form, which requires surgical treatment.
Sometimes the eye can become swollen and the left or right nostril may become blocked, leading to breathing problems. This is one of the signs of sinusitis on one side. This problem also requires immediate treatment, since it has a very large number of complications that are quite dangerous for human life.
Treatment of hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
Treatment of hypertrophy of the tonsils is carried out with the help of medications and folk remedies. The last resort is surgery to remove them.
Popular medications include:
- Silver nitrate (1% or 2%) – gargling helps treat inflammation;
- Tonzilotren and Tonsilgon - have an antiseptic effect, relieve swelling and inflammation, normalize the respiratory system;
- Furacilin - gargling with this remedy prevents the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
How to treat enlarged tonsils with folk remedies:
- Rinsing with decoctions and infusions of herbs (clover, coltsfoot, sage), tincture of propolis in alcohol;
- Compresses (a piece of cloth soaked in sage decoction is applied to the throat, covered with cling film, and then the neck is wrapped with a scarf);
- Kerosene - the affected areas are treated with a cotton swab dipped in it and wrung out, once a day for 10 days;
- Sugar and lemon juice – 20 g of sugar are mixed with 20 ml of lemon juice, the product is consumed three times a day.
For grade 4 hypertrophy, doctors prescribe surgery. Grade 3 also often requires this measure. In the initial stages this is not necessary. When the tonsils are enlarged in an adult patient, surgery is required in very rare cases, since the severity of the problem decreases as the body grows.
The following methods are also effective:
- Inhalations with essential oils;
- Laser application;
- Magnetotherapy.
Inflammation of the tonsils, the symptoms of which are known to almost every person, remains the most common infectious disease. About 15% of the world's population suffers from chronic tonsillitis. A sore throat with inflammation of the tonsils is quite severe: the body temperature rises, the pain syndrome is pronounced, and sometimes even the processes of breathing and swallowing are disrupted. Children especially often suffer from the activity of lymphoid tissue. Few people have not experienced doubts about the removal and treatment of adenoids and tubal palates. Let's try to understand the cause and determine the correct approach to treating inflammation.
Reasons why an inflamed tonsil on one side in an adult and a child
Very often, the cause of a sore throat can be inflamed tonsils. In medical practice, cases have become more frequent when damage was caused to only one side of the tonsils. Read how to vacuum rinse your tonsils here.
The tonsils may not necessarily be affected on both sides. There are cases of inflammation of the tonsil on only one side.
What does inflammation of the tonsils mean: what diseases cause
Before you begin treatment of a unilateral inflammatory process, it is necessary to understand the reason why it arose. Most often, the pathological process occurs due to sore throat. In this case, something white appears in the throat on the affected area. This is a purulent plaque. In this case, there is a rise in temperature to 38 degrees and a sore throat. Often tonsillitis leads to the development of symptoms of intoxication.
Structure and purpose
The pharynx is the connection between the oral cavity, nasal passages, ears, larynx and esophagus. In total, there are six tonsils along its length: two each palatine and tubal, pharyngeal and uvular. They are made up of lymphatic tissue that constantly produces lymphocytes and other cells to protect the immune system. Collectively, all the tonsils make up the pharyngeal “ring.” It does not allow harmful bacteria into the air that we breathe into the body.
The palatine tonsils are located on the right and left of the pharynx. You can see them yourself in the mirror, with your mouth wide open. Most often they take the blow, which leads to painful sore throat. Tubal tonsils are located deeper: in the area of the opening for swallowing next to the ear canals. They received this name because of the Eustachian tubes that are located nearby. The connection between the oral cavity and nasopharynx is protected by the pharyngeal tonsil. And the closing link of the pharyngeal ring is the lingual tonsil, located at the base of the tongue on the back side. The tonsils of a healthy person cope with any infection without problems, blocking its entry into the body.
Inflammation of the tonsils in adults and children primarily indicates a decrease in immunity. Lymphocytes and other cells were unable to stop the infection, and the disease began to develop. The area affected by bacteria becomes inflamed. And the tonsils react first.
Inflammation of the tonsils in the throat: causes
Soreness of the tonsils is always caused by infection. It enters the mouth and nose in different ways. Most often, the disease develops according to the following scenarios:
- Exposure to pathogenic microorganisms: streptococci, pneumococci and other similar bacteria with subsequent infection of the entire body.
- Hypothermia combined with weakness of the immune system with further development of tonsillitis.
- Infection from a patient with an infection that provokes inflammation of the tonsils. Symptoms and treatment usually coincide with the pattern occurring at the source.
- The development of the disease due to dental caries, gum inflammation, and constant runny nose.
Depending on their nature, they can be classified as viral, bacterial, fungal or herpetic in origin.
Catarrhal tonsillitis is the mildest form of inflammation of the tonsils
Damage to the surface layer of the tonsils indicates the occurrence of catarrhal tonsillitis, the causative agent of which is most often group A streptococcus. This is the initial stage of the inflammatory process, which can develop into the form of lacunar, follicular or phlegmonous tonsillitis. Adults tolerate the disease quite easily, which cannot be said about children. It is worth paying attention to the fact that catarrhal tonsillitis with a serous coating is the main symptom of scarlet fever.
The main symptoms of damage to the outer shell of the tonsils include:
- sharp pain in the throat, interfering with normal swallowing;
- low-grade fever, sometimes fever up to 40 degrees (especially in children under 3 years of age);
- intoxication of the body;
- redness of the tonsils, their swelling, lack of plaque (with diphtheria and scarlet fever, the plaque is serous);
- enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw;
- general weakness, soreness in muscles and joints;
- fever in the throat.
Inflammation of the tonsils in a child with catarrhal tonsillitis is accompanied by severe pain in the throat and leads to rapid loss of fluid. The general condition is weak and requires a gentle daily regimen. It also happens that children suffer from sore throat easily. Adults do not experience severe illness and quickly restore health.
Causes of tonsil inflammation on one side
An inflamed tonsil indicates the development of a sore throat.
If a person has an inflamed tonsil on only one side, this may indicate that this condition is caused by a complication of various inflammatory and infectious diseases, or is a consequence of the effects of streptococci, staphylococci or fungi on the loose surface of the tonsil with a significant decrease in immunity.
The main causes of unilateral inflammation of the tonsil may be the following diseases and conditions:
- Tonsillitis.
- Laryngitis.
- Pharyngitis.
- Acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI).
A sharp drop in immunity caused by hypothermia, exposure to rain, wet shoes, and the entry of various pathogens into the body upon contact with a sick person.
An inflamed tonsil not only causes severe discomfort to a sick person, prevents him from working and causes severe pain, but also threatens with various negative consequences.
This is not such a simple and easy disease as is commonly thought. Inflammation of the tonsils requires a full examination and diagnosis, since the basis of treatment is antibiotics, and they must be selected for a specific pathogen and used strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Self-medication for such diseases can cause the disease to become chronic or develop various complications.
You can learn more about how and how to treat a sore throat from the video:
If in the initial stages, when the tonsil is inflamed, treatment is incorrect, untimely, or the person does not receive treatment at all, the disease can cause complications in other organs. Most often, this condition is complicated by the chronic course of tonsillitis, which in turn has a negative impact on the functioning of the heart, kidneys, lungs and reproductive system. A constant source of infection in the body can cause the development of rheumatism, inflammation of the middle ear, affect the condition of the teeth and provoke diseases such as sinusitis and sinusitis.
Signs of intensification and development of infection are a sharp increase in body temperature, an increase in symptoms of intoxication, severe weakness, the appearance of other foci of inflammation, runny nose, cough, and increased sore throat.
Treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis
Even mild inflammation of the tonsils in a child is often accompanied by a serious condition: high fever, weakness, sharp pain in the throat. If you notice the first symptoms, you should definitely call a doctor, because sore throat is a concomitant symptom of many infectious diseases (diphtheria, scarlet fever). After examination by a doctor, the best tactic will be strict adherence to all instructions in order to eliminate inflammation of the tonsils and symptoms. Treatment for a child is usually based on penicillin antibiotics, bed rest and vitamin therapy. Additionally, you can use rinses made from decoctions of chamomile, celandine, and other medicinal herbs. It is necessary to ensure that the baby drinks a sufficient amount of warm liquid.
Treatment in adults is carried out depending on general well-being and clinical picture. But for a faster and more effective recovery, antibiotics are prescribed. Various sprays, antibacterial plates for resorption, and rinsing relieve inflammation. To prevent the development of complications, it is recommended to observe until the body is completely restored.
Symptoms of inflammation
The signs of unilateral tonsillitis are quite clear. At the initial stage, the inflamed tonsil turns red, the process is accompanied by a sore throat, pain when swallowing, talking and coughing.
Then the swelling of the affected tonsil increases, one tonsil becomes larger than the other, and this causes significant difficulties in swallowing, sometimes so pronounced that the patient is forced to eat in small portions.
In some diseases, a plaque appears on the surface of the tonsil, which has a specific appearance, depending on the causative agent of the disease and is a diagnostic sign. With fungal infections, there is almost always plaque on the tonsils - milky white in color, with a curdled consistency (which is why candidiasis is called thrush).
With unilateral tonsillitis, the left tonsil may become inflamed more often than the right one. The mucous membrane around the affected lymphoid formation becomes red and inflamed, the process extends to the healthy paired tonsil.
Fever, cough and other cold symptoms do not always accompany tonsillitis. High body temperature is a less dangerous diagnostic sign than normal. An inflammatory process at normal temperatures is a sign of a weak immune response to infection.
Severe forms of damage to the palatine tonsils
If superficial inflammation is poorly treated, the disease progresses to deeper parts of the tonsils: lacunae. A white coating or even individual purulent follicles forms. Sore throat becomes severe, requiring high-quality treatment. There are lacunar and follicular types of the disease. They differ in characteristic signs, and sometimes occur on different sides of the pharynx at the same time.
Purulent inflammation of the tonsils causes rapid proliferation and vital activity of cocci. The disease is accompanied by:
- dry mouth and constant thirst;
- cough, sore throat;
- severe pain that radiates to the ear when swallowing;
- the formation of follicles (yellow-dirty “grains”) with pus inside;
- general weakness, high fever;
- constipation in adults, vomiting or diarrhea in children.
The condition is dangerous due to complications for the heart and kidneys. That is why it is extremely important to be treated correctly and not neglect the regimen. Lacunar tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, the symptoms of which, the treatment of which are very similar to the follicular type of the disease. A distinctive feature is the formation of a white coating and a sharp sore throat that occurs suddenly. During the day, a person may not feel any discomfort, but in the evening all the signs of a sore throat will be evident. There are often cases when the follicular type developed on one of the palatine tonsils, and the lacunar type on the other.
Compresses
Compresses, despite the fact that they are a very old method of treating inflammatory diseases of the throat, effectively eliminate the symptoms of these pathologies. They can be used only if there is no purulent process, and the body temperature rises slightly or is normal. They should not be done if the neck is very swollen on one side or both. The most effective remedies for them are potatoes, honey, and vinegar lotions can combat high temperatures, provided they are changed frequently.
Treatment methods for follicular and lacunar tonsillitis
Purulent inflammation of the tonsils is very dangerous for both adults and children. Treatment should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor. There are two methods: medication and surgery. Of course, the main therapy can be supplemented with folk remedies to reduce inflammation of the tonsils and symptoms. What antibiotic treatment is used? Typically, the use of a wide range of medications is provided: penicillin series, Erythromycin, Sumamed. In case of viral infection, antiviral drugs are used. Prescriptions should only be carried out by a doctor, taking into account the nature of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body. In addition to antibiotics, the following are prescribed:
- follicular rinsing with antiseptic solutions;
- suction of pus with a vacuum;
- local injections;
- treatment of tonsils with an oil solution that promotes healing;
- physiotherapy;
- vitamins and immunostimulants.
It is necessary to pay attention to childhood inflammation of the tonsils. Komarovsky distinguishes symptoms and treatment from the adult course of the disease. According to a famous pediatrician, the use of antibiotics is a mandatory requirement, otherwise tonsillitis cannot be cured. In addition, most rheumatic diseases and heart defects develop precisely because of the activity of cocci during angina. Penicillin series are considered the safest and are recommended even for newborn children. Additionally, it is necessary to provide the child with plenty of warm drinks and food in the form of soft purees and cereals.
White plaque
Normally, the human throat is pale pink in color, and there are no plaques on it. However, with various pathologies, the tonsils can become covered with a film or purulent rashes. Sometimes plaque can develop without disease, but it cannot be called normal. It may indicate an inflammatory process, which means it needs to be treated. There are many reasons that can provoke such phenomena:
- A person could get a sore throat, and pustules begin to form in the lacunae. At this time, mucous formations form on the tonsils, which, together with bacteria, form a bright purulent process, while pain when swallowing can radiate deep into the chest.
- The throat can become inflamed due to severe hypothermia. Most often, this can be observed among elementary school students, which is due to the fact that they do not always like to dress for the weather. Also, a similar situation can occur when personal hygiene rules are violated.
Usually, when a white coating occurs on one of the tonsils, it does not cause a sharp rise in temperature. This is due only to the onset of inflammatory changes or to the individual characteristics of the body.
Phlegmonous inflammation of the tonsils: symptoms, treatment, photos
Phlegmonous tonsillitis - or purulent acute inflammation of the tissue near the tonsils - is a common complication of tonsillitis. It usually occurs 1-2 days after inflammation of the tonsils. Phlegmonous It rarely develops on both palatine tonsils. It is characterized by acute pain when swallowing, high fever, weakness, and increased salivation. The affected tonsil increases in size and moves to the center of the larynx with retraction downwards.
Delayed treatment can provoke the occurrence of an abscess, which confirms the diagnosis - “phlegmonous inflammation of the tonsils.” Symptoms and antibiotic treatment are similar to the previous case. The main rule: you need to start taking medications as soon as possible. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics (penicillin series, Erythromycin, Sumamed), as well as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunostimulants. In the first days of treatment, the patient must remain in bed. When an abscess forms, it is opened surgically. Then they are washed and, if necessary, the tonsils are removed to avoid complicated conditions.
Why inflammation of the tonsil develops on only one side and how to treat it
The tonsils, or more precisely the ring of the tonsils, are the natural anatomical protection of the respiratory and digestive canal.
They are located at the junction of the oral cavity and the pharynx and retain all pathogenic microbial flora, that is, they act as a kind of filter. Most often we are talking about bilateral inflammation of the tonsils, which is called “tonsillitis” or “tonsillitis”.
Inflammation of the tonsil on one side is much less common than bilateral inflammation, but requires much more skill from the doctor and attentiveness of the patient.
Possible reasons
If the tonsil (gland) is affected only on one side, the patient should not attempt self-medication. Conventional home remedies are usually ineffective, and as morphological changes progress, the patient's condition only worsens.
Among the possible causes of unilateral inflammation of the tonsils, the most likely are:
- paratonsillitis;
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- dental diseases;
- Plaut-Simanovsky-Viensant's angina;
- syphilitic atypical chancre;
- anginal form of tularemia infection.
In each of the above cases, treatment will differ significantly. You need the help of a qualified specialist - an otolaryngologist or an infectious disease specialist.
Peritonsillitis
This name is given to the inflammatory process that develops in the fatty tissue surrounding the tonsil.
Peritonsillitis develops as a result of insufficiently effective or incomplete treatment of ordinary bacterial tonsillitis, general weakness of the patient (state of immunodeficiency, systemic metabolic disorders, alcohol abuse, smoking, repeated hypothermia).
As a rule, its clinical signs appear 1-2 days after the onset of normal inflammation of the tonsils. Bilateral paratonsillitis is observed extremely rarely; unilateral paratonsillitis is more often diagnosed. In the worst case, a peritonsillar abscess is formed from the inflamed area of tissue.
The following symptoms are characteristic of paratonsillitis.
- Deterioration of general condition (very high temperature with tremendous chills).
- Significant sore throat that radiates to the neck and ear, worsens when opening the mouth and swallowing.
- With severe swelling, there is a deviation of the head in the direction of the lesion and the inability to open the mouth (trismus), increased salivation.
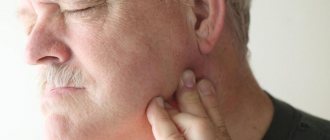
- Painful enlargement of the lymph nodes on the affected side.
- An unpleasant (putrid) odor may emanate from the patient's mouth.
Upon examination, there is a significant enlargement of the tonsil on one side, a peculiar overhang of the velum (soft palate) on the affected side, bright hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane.
Depending on the stage of the inflammatory process, several variants of paratonsillitis are distinguished.
- Edema is rare and is characterized only by swelling of the tissues and a significant enlargement of the tonsil and palate.
- Infiltrative – the most typical, characterized by a typical mixing of organs in the healthy direction.
- Peritonsillar abscess is the extreme and worst stage of the process, in which an abscess of various sizes forms near the tonsil.
Diagnosis of paratonsillitis usually does not cause significant difficulties for a specialist. It is somewhat more difficult to determine the stage of the process, which is of great importance for subsequent therapy.
Treatment for paratonsillitis only (without an abscess) includes:
- antibacterial therapy with a drug with a wide spectrum of effects;
- rinsing with an antiseptic to reduce swelling;
- systemic antipyretics (if necessary);
- multivitamins and desensitizing agents.
In the event that a peritonsillar abscess has already formed, only surgical intervention is required - opening the abscess. After this, the tissues are washed to prevent recurrent abscess formation.
Retropharyngeal abscess
It is formed as a result of the same mechanisms as a peritonsillar abscess, but inflammation covers the tissue located behind the pharynx (hence the name). This complication is most typical for children in the first 5 years of life. The following symptoms are characteristic of a retropharyngeal abscess.
- Severe pain, even worse when swallowing.
- Choking and even leakage of food through the nose due to insufficient mobility of the soft palate.
- Difficulty in nasal breathing (without discharge from the nasal passages).
- Severe general intoxication syndrome.
Treatment of retropharyngeal abscess is only surgical. It is necessary to open the abscess as quickly as possible so that the infection does not spread to adjacent tissues. After autopsy, broad-spectrum antibiotics and local antiseptics are prescribed.
Plaut-Simanovsky-Viensant's angina
Its causative agent is a symbiosis of two microbial agents: fusobacteria and spirochetes. This disease develops in weakened patients and those who have chronic diseases of the dentition and oral cavity.
The following symptoms are characteristic of Simanovsky's angina:
- putrid odor from the mouth;
- an ulcer with jagged edges forms on one of the tonsils;
- the ulcer is practically painless and does not cause any particular inconvenience to the patient;
- general condition does not change, temperature is normal;
- lymph nodes may be enlarged.
Therapy is mainly done with local remedies: rinsing the tonsil area with antiseptics (hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine) or applying powdered sugar to the surface of the tonsil. Systemic antibiotic therapy is not advisable.
Syphilitic atypical chancre
Syphilitic chancre in the oral cavity forms after unconventional sexual intercourse or as a result of domestic infection. Inflammation of the right tonsil (or left) is called atypical chancre or chancre-amygdalitis.
The following symptoms are characteristic of chancre-amygdalitis:
- little changed general condition;
- there is no plaque or ulcerative defects on the surface of the tonsil;
- sore throat occurs only when swallowing;
- Upon examination, only an enlargement of one tonsil is revealed; the surrounding tissues are intact.
Diagnosis of chancre-amygdalitis can cause certain difficulties, especially if the patient does not advertise promiscuity. A positive specific Wasserman reaction and no change in general condition are the key elements of a successful diagnosis.
Therapy for chancre-amygdalitis is the same as for any other form of syphilis - with penicillin antibiotics according to a certain scheme.
Anginal form of tularemia
Tularemia is a zoonosis, meaning it is transmitted to humans from a sick animal. The source of infection in this case is about 30 species of rodents (rat, vole, nutria and others).
People who have contact with rodents are at greatest risk of infection:
- veterinarians;
- hunters;
- workers of livestock farms (industrial breeding of rodents);
- laboratory staff.
The causative agent of tularemia can also be transmitted by airborne droplets or fecal-oral routes. Typical for the anginal form of tularemia:
- general intoxication syndrome;
- unilateral damage to the lymph nodes (bubo);
- the surrounding tissues are not fused to each other;
- soreness is moderate;
- The bubo matures for several weeks, after which it spontaneously opens.
Treatment involves the use of antibiotics from the group of aminoglycosides or tetracycline. Surgical intervention is strictly contraindicated, as it can provoke the spread of tularemia infection.
Source: https://provospalenie.ru/gorla/mindaliny-s-odnoj-storony-lechenie.html
Inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil
The nasopharyngeal tonsil, popularly called adenoids, is the first line of defense during nasal breathing. At the slightest sign of disease, they increase in size. If diseases occur frequently, with an interval of less than one week, the tonsil does not have time to recover and chronic inflammation develops. Most often, adenoids enlarge in childhood, because they play a major role in protecting the body from infections. After 13-15 years, they decrease in size and practically no longer become inflamed.
Frequent runny nose provokes the growth. Inflammation should be suspected if the following signs are present:
- persistent runny nose, which is difficult to treat;
- difficulty breathing through the nose and lack of runny nose;
- frequent mouth breathing, especially at night;
- colds, the interval between which is only 1-2 weeks.
They provoke inflammation of the adenoids and infectious diseases. For example, scarlet fever, measles, whooping cough, influenza. Often, parents are not even aware of problems with the pharyngeal tonsil, which indicates poor awareness of the signs of their enlargement and proliferation. A chronic process can lead to complications from the heart, kidneys, and musculoskeletal system. Breathing is impaired, numerous tissue growths sometimes even lead to defects in the upper jaw.
Treatment of adenoiditis
Success in the fight against an inflamed pharyngeal tonsil depends on many factors: the approach to treatment, the qualifications and experience of the doctor, as well as the lack of haste. It is also worth considering that with any cold, the adenoids enlarge. And this does not always indicate the development of adenoiditis. They often return to normal after recovery. It’s another matter when the infection is not treated in a hurry, and the weakened child catches it again. The tonsil does not have time to recover and becomes inflamed again, which provokes proliferation.
There are two approaches to the treatment of adenoids: conservative and surgical. First of all, it is recommended to try all possible methods of medication:
- rinsing the nose with saline solution, herbal decoctions and special preparations;
- use of anti-inflammatory drops;
- general immunotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
If, after a long and persistent struggle, the adenoids do not decrease in size, but only grow, most likely, you will have to resort to surgical removal. It is a mistake to think that after this the child will stop getting sick at all. Yes, this is a huge source of infection. But it poses a threat only if it grows significantly and causes serious problems with nasal breathing. If there is no pharyngeal tonsil, the infection will spread throughout the body faster and find a “loophole” for its comfortable existence. Adenoiditis will be replaced by tonsillitis or otitis.
It should be remembered that removal of the adenoids is not a solution to the problem of weakened immunity and frequent colds. This is an extreme measure, which is justified only if the tonsil is significantly enlarged and there is no effect from conservative treatment. Removal is performed by an ENT surgeon using a special loop under local anesthesia. A more modern method is endoscopy, which requires general anesthesia and allows you to completely get rid of vegetative growths of the adenoids and avoid relapses.
Inflammation of the tonsils: symptoms, treatment of damage to the lingual lymphoid tissue
The lingual tonsil is located on the back of the tongue. Its tissue becomes inflamed extremely rarely. If lesions do begin, it is usually against the background of tonsillitis of a catarrhal, follicular or phlegmonous nature. Acute inflammation of the tonsils of the palate or pharynx indicates a widespread localization of the infection, which also attaches to the tongue. The clinical picture is characterized by pain when moving the tongue and its swelling, significant difficulties in chewing and swallowing, and speech impairment. The remaining symptoms coincide with the signs describing inflammation of the tonsils. The temperature is subfebrile and can rise to 39-40 degrees.
The treatment approach is based on the use of antibiotics, bed rest and restorative drugs. The lack of effect from medications is explained by individual resistance to the effects of drugs or the development of a sublingual abscess. To avoid complications, inflammation of the lingual tonsil should be treated by a qualified specialist - an ENT specialist.
Tubal tonsil damage
Tubal lymphoid tissue is located near the eustachian tube on both sides of the jaw. Inflammation of these tonsils is often attributed to ear diseases, since pain occurs precisely in this location. The following symptoms distinguish tubal lesions from otitis media:
- the primary source of pain is the throat, after which unpleasant sensations arise in one ear or two at once;
- mucous or purulent discharge flows down the back wall of the pharynx;
- the lymph nodes under the jaw are enlarged, and the parotid ones do not enlarge at all or react slightly to infection;
- intoxication of the body is observed.
As with inflammation of other tonsils, the disease is more severe in children than in adults. The condition is accompanied by high fever, often coughing, cramps, and vomiting. The approach to alleviating the patient’s condition is based on the same principles that are used to eliminate infectious inflammation of the tonsils. Treatment is based on taking a course of general antibiotics or antiviral drugs (depending on the pathogen). Additionally, it is recommended to provide the baby with warm drinks, soft and liquid food, as well as proper rest. Taking immunostimulants and vitamins will only improve the condition and speed up recovery.
Inflammation of the tonsils is the most common disease of the ENT organs, especially in childhood. This can be explained by the function that nature has endowed them with. Forming a kind of pharyngeal ring, lymphoid tissue produces antibodies and lymphocytes that actively fight any infection that enters the body. A healthy person with a strong immune system has virtually no problems with the tonsils - they do their job perfectly and have time to recover.
But when the body weakens, which is facilitated by prolonged hypothermia, stress, poor sleep and nutrition, strong defenses are destroyed, and the tonsils cannot cope with their task. Inflammation develops. Only a correct understanding of the essence of the problem will help to avoid problems with swelling and proliferation of lymphoid formations. Remember that it is not the tonsils that are to blame, but the weakened state of the body. The first step to treating an adult or child should be a visit to an immunologist and increased attention to health.
More recently, the tonsils were treated as an extra part of the body. In case of inflammation in children, they were removed immediately, without considering it necessary to treat inflammation of the tonsils. Meanwhile, this organ, consisting of lymphoid tissue, plays an important role for the immune status of a person.
A little anatomy
The tonsils are located in the larynx, between the palatine arches at the level of the root of the tongue. Pathogenic flora, when trying to penetrate the body, is deposited in them.
Macrophages produced in their thickness begin work to destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
If the infection turns out to be stronger than the immune defense, an inflammatory process occurs, which can be stopped at the level of the upper respiratory tract.
In the absence of tonsils, pathogenic bacteria and viruses immediately pass to the bronchi and lungs, causing severe inflammatory processes.
Causes of constantly enlarged tonsils
The causes of enlarged tonsils in children and adults are most often chronic inflammatory processes caused by the presence of constant foci of infection and allergic manifestations. Pathogenic flora can settle in adenoids, in carious cavities of teeth, in the tonsils themselves.
But if in adults the main cause is infectious, then a child’s tonsils can be enlarged without an inflammatory process.
Gland hypertrophy in children can be caused by the following factors:
- asphyxia during childbirth;
- intrauterine infection;
- hereditary factors;
- developmental pathology.
Three degrees of hypertrophy can be distinguished:
- I – the gland covers 1/3 of the lumen between the arch of the palate and the midline of the pharynx;
- II – 2/3 of the lumen is closed;
- III – tonsils almost touch each other;
- II and III degrees of hypertrophy can complicate swallowing and breathing processes.
However, degrees I and II hypertrophy do not always require treatment - as the child grows older, the lymphoid tissue often decreases on its own.
How to stabilize the condition
To treat enlarged tonsils in adults, agents are used that eliminate allergic manifestations and destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
Antihistamines and eliminating contact with the allergen quickly relieve dangerous symptoms. If you have an allergy, you should not expect the condition to stabilize on its own. If the tonsils are enlarged, the immune status of the body decreases, and there is a risk of infection with pathogenic flora.
Infectious processes in which the tonsils become enlarged and inflamed are treated according to the standard regimen.
When the disease manifests itself only locally, rinsing with medical antiseptics and folk remedies is sufficient. If tonsillitis or pharyngitis occurs against a background of elevated temperature, then it is necessary to use antibiotics when sowing the bacterial flora, and in case of inflammatory processes of a viral nature - oral antiviral agents.
It is impossible to cure a sore throat without medication. It becomes chronic and “falls asleep” until favorable circumstances arise. It is not necessary that the pathogenic flora will again show its activity in the tonsils next time - it can be transported through the bloodstream to the genitourinary system, the brain and provoke an acute inflammatory process.
Treatment of enlarged tonsils in a child caused by the introduction of pathogenic bacteria is carried out in the same way as in adults.
First, the reasons for the enlargement of the tonsils are clarified, and then the targeted destruction of pathogenic microorganisms begins.
Local antibiotics have appeared in the arsenal of modern medicine. It is most advisable to administer these drugs to the treatment of adults and children, since they are absorbed into the bloodstream in a minimal dose, and side effects occur in isolated cases.
Moreover, undesirable manifestations - sore throat, frequent sneezing, the appearance of an unpleasant taste - do not require stopping the use of medications.
Therapeutic measures include bed rest - when a high temperature appears, increasing the amount of fluid drunk - preferably with anti-inflammatory and vitamin properties: chamomile tea, rose hip decoction and similar remedies.
Tonsils can grow significantly not only in children, but also in adults, causing constant inflammatory processes. If therapy with medications and folk remedies does not help, and the disease constantly recurs, then surgical intervention may be required - an operation to remove them is prescribed. Currently, they are trying to perform tonsillectomy - during this surgical intervention, the lymphoid tissue is not completely excised.
But this does not mean that the tonsils will be pulled out or excised during an acute process - first treatment is carried out, the disease is brought into remission, and only then the operation is performed.
The presence of open foci of infection during surgery is very dangerous. Pathogenic flora can spread throughout the body through the bloodstream and provoke an inflammatory process in any organ or system. Operations performed with a laser or ultrasonic scalpel do not have a negative impact on children's health.
They are performed under local anesthesia and do not depress the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. Congenital pathologies that cause hypertrophy of the tonsils in children of degree II and III often have to be treated surgically. The proliferation of lymphoid tissue can make it difficult for infants to suck and breathe, so it is excised if there are direct indications.
Causes, signs and methods of treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is an inflammatory disease in which pathological damage to the tonsils of the palate occurs. In particularly severe cases, inflammation can also affect the soft tissues of the pharynx: the tonsils of the tongue, nasopharynx and larynx. Medical specialists characterize this disease as an infectious-allergic one. Pathology has two forms: acute and chronic tonsillitis.
How does the chronic form of the disease manifest?
A chronic disease is called in cases where the area of the tonsils and pharynx becomes a regular focus for the development of the disease. Symptoms in this form are observed with a certain frequency.
This is explained by the increased sensitivity of the tonsils due to insufficient immune function.
Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis gives standard symptoms: increased body temperature, impotence, noticeable inflammation in the tonsils.
How does chronic inflammation develop?
In the chronic form, the pathological process begins directly inside one or more tonsils, affecting soft tissue. Under the influence of provocateurs of inflammation, lymphoid tissue is replaced by dense connective tissue. Hard scars and narrowing of the spaces between cells are formed.
Inflammation becomes locked in one location and forms a permanent focus of infection.
The rather pronounced severity of symptoms in adults and children is seriously aggravated by the fact that due to increased obstruction in the soft tissues, accumulations of pus, food debris, microorganisms, and decomposition products can form inside the almond lacunae.
The constant formation of the inflammatory process leads to the accumulation of more than three dozen types of possible pathogenic microorganisms in the soft tissues. These harmful bacteria, fungi and cocci can complicate treatment, gradually destroying the patient's body, causing subsequent infection to enter the bloodstream and damage other organs.
Causes of tonsillitis
Before deciding how to treat chronic tonsillitis, it is important for the doctor in the diagnostic process to understand what exactly was the trigger for the development of the disease. The tonsils on the roof of your mouth are part of the body's immune system.
They provide protection to the respiratory system from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, fungi, and cocci.
The tissues of the organs responsible for protection produce antigen proteins that help the human body fight harmful microorganisms.
A decrease in the level of immunity, provoked by factors of the external and internal environment, leads to the fact that over time the body cannot resist harmful effects, especially if it suffers from prolonged inflammation.
The causes of tonsillitis may be the following:
- physiological disorders of breathing through the nose or throat (polyps, adenoids, purulent inflammatory diseases, curvature of the nasal septum, advanced forms of caries);
- a sharp decrease in immunity after suffering from infectious diseases;
- genetic predisposition to the appearance of inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system;
- transition from acute to chronic form, if irrational, ineffective treatment of tonsillitis was prescribed;
The reasons for the sharp deterioration of the condition in an established form of chronic disease are called:
- smoking tobacco, leading to regular irritation of the soft tissues of the nasopharynx;
- neglect of the norms and rules of oral hygiene;
- insufficient daily fluid intake;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body;
- harmful working conditions;
- poor ecology in places of work or residence;
- high fatigue;
- neuroses, stress;
- poor nutrition.
During the course of the chronic form of tonsillitis, the symptoms and treatment for each person may differ due to similar factors, since therapy is prescribed individually, in accordance with the form and type of pathology. These data are determined by the doctor after a thorough examination.
Forms and types of chronic tonsillitis
Systematic pathological inflammation of the tonsils is classified by medical specialists according to several criteria: according to the localization of inflammation and exactly what symptoms of chronic tonsillitis are observed in a particular clinical case.
The forms of tonsillitis are distinguished according to the location of the pathological inflammatory process:
- Lacunar - the main focus of inflammation and accumulation of exudate will be observed in the lacunae of the palatine tonsils.
- Parenchymal - diagnosed when inflammation affects the follicles of the tonsils and soft lymphoid tissue.
Based on the nature of clinical manifestations, the following forms are distinguished:
- Compensated - in this type of pathology, only local forms of manifestation and development of inflammation can be present. The tonsils continue to perform a protective function and prevent the pathology from spreading through the bloodstream to other organs and tissues.
- Decompensated – a form of pathology accompanied by the formation of inflammation in other organs and cavities. In this case, systemic damage to a whole complex of vital organs may occur.
Based on exactly how the signs appear and how acute the periods of relapse are, medical specialists suggest dividing the pathology into the following types:
- Simple, regularly recurring type. Characterized by the frequent occurrence of simple sore throats.
- A simple, protracted form is a sluggish inflammatory process in the palatine tonsils.
- A simple compensated appearance - it extremely rarely bothers the patient with manifestations of tonsillitis and tonsillitis.
- Toxic-allergic type, which is divided into two subtypes:
- simple - in addition to inflammation of the palatine tonsils, allergic tonsillitis of this type is accompanied during the acute stage by signs of an autoimmune reaction and general intoxication of the body. Symptoms and signs characteristic of an allergic response are added.
- complicated - signs of allergy accompany the patient not only during exacerbation of chronic inflammation, but also during periods of remission. The patient complains of constant weakness, nasopharyngeal congestion, and headache.
Determining the type of chronic tonsillitis and how to treat it in each specific clinical case is exclusively the responsibility of a medical specialist. To do this, he will need a detailed diagnosis of the patient’s condition, careful consideration of the manifesting symptoms and consideration of factors such as the patient’s age, the presence of other chronic diseases and the severity of the pathology.
Signs of a chronic form of the disease
Symptoms can manifest themselves in different ways, depending on the form and severity of the disease:
- Simple form
(any manifestation): - a large amount of liquid pus;
- uneven surface of the tonsils, swelling;
- frequent reaction of mild sore throat to overheating or hypothermia;
- swelling of the edge of the palatine arch;
- the formation of connective tissue adhesions between the tonsils and the folds of the palate;
- regional lymphadenopathy;
- The toxic-allergic form
is simple: - a set of symptoms of a simple form;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile;
- headache, weakness, tinnitus;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- lymphadenitis;
- Toxic-allergic form
complicated: - a combination of symptoms of the two previous stages;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- nausea, vomiting, digestive problems;
- urinary dysfunction;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- rheumatic pathologies.
If chronic tonsillitis is not treated in a timely manner, complications caused by the development of inflammation and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms will lead to extremely serious conditions, from which it will be very difficult for doctors to remove the patient.
Treatment methods for tonsillitis
Treatment, therapy, methods of influence and recovery are determined by the doctor depending on the form and severity of the pathology. In decompensated forms of the disease, the degree of decompensation is also necessarily noted. To eliminate inflammation, two treatment methods are used:
- conservative therapy;
- operative surgical intervention.
With any type of therapy, before starting treatment, it is recommended to eliminate inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, get rid of caries and take care of the health of the gums. This will significantly reduce the risk of re-provoking an exacerbation of inflammation, since some pathogenic microorganisms will be destroyed.
Drug treatment
This method of influencing pathology involves the use of medications prescribed by a doctor, taken in courses in certain doses. The doctor decides how to treat tonsillitis based on the most severe symptoms of the disease.
The standard treatment regimen includes the use of drugs from the following groups:
- antibacterial drugs ( Flemoklav, Suprax, Amoxiclav, Macropen
); - antipyretic drugs ( Paracetamol, Nurofen
); - local antibacterial and antimicrobial agents ( Bioparox, Hexoral, Tantum Verde
); - immunostimulating drugs ( Ingavirin, Kagocel
); - probiotic products in capsules and drops to restore normal microflora, which can be significantly damaged during treatment with antibiotics ( Linex, Bifiform
).
To select an antibiotic, the doctor must take a smear from the damaged tonsils to determine the type of pathogenic pathogen.
Also, as an additional measure, it is recommended to regularly gargle with a warm solution of water with antiseptic agents (tincture of eucalyptus, calendula, chamomile decoction, propolis) or use special disinfectant solutions ( Gexoral, Stomatofit
).