Definition of curettage
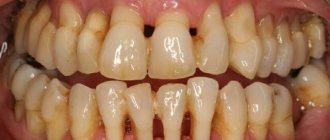
This procedure is used to eliminate gum disease. The method is very effective and here's why. Between the edge of the gum and the cervical area there is a depression (it has another dental name - periodontal pocket), into which food safely falls. Food debris often accumulates in your pocket.
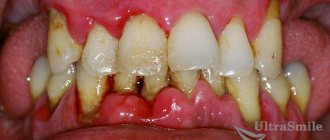
Residues of food are difficult to clean out with a brush; painful microflora continues to develop rapidly. Various types of deposits form inside and reach the surface where the tooth emerges from the gums. As a result, tartar is formed, which is quite firmly connected to the tooth enamel and is embedded in the space between the gums.
Significant changes begin to occur in the bone tissue itself: dentin atrophies, the root becomes cemented, and everything is overgrown with granulation tissue. In the place where the bone tissue has collapsed, a gum pocket appears.
Bacteria begin to multiply very actively in this pocket. As a result, the dangerous disease periodontal disease begins. An even more dangerous complication is periodontitis. The teeth become loose and fall out at the very last stage. This disease takes a very long time to cure. Unfortunately, the prognosis for recovery is not always positive. If the disease is not treated in time, you can lose all your teeth.
It turns out that the curettage procedure is simply mandatory for periodontitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis and other complications.
The procedure is shown to people:
- with inflammation of the gums;
- with a pocket larger than 3 mm;
- with large deposits of plaque;
- with a high degree of tartar formation.
A remark should be made right away: the professional cleaning procedure and curettage are two different things. During professional cleaning, only the outer surface of the tooth is treated. Curettage not only helps to clean teeth, but also removes all decay products from the pocket.
The curettage procedure solves many problems, namely:
- cleans the periodontal area;
- removes periodontal pockets;
- cleans granules;
- completely eliminates bleeding gums.
What is periodontal pocket curettage?
Curettage (from the French “cleansing”, “scraping”) is a medical procedure that involves excision of the gums for cleaning, and then suturing.
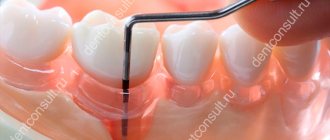
Curettage of periodontal pockets is prescribed if the depth of the pathological areas exceeds 3 mm. At this stage, ordinary hygiene procedures (brush, thread, irrigator) do not give the desired effect.
The doctor removes stones and plaque from the teeth and under the gums and treats inflamed tissue.
Types of curettage
- Open curettage. The procedure is performed in the most severe cases. This method is especially often used when pockets form in bone and soft tissues. In this case, a gum incision is always used.
- Closed curettage. The procedure is used for cosmetic whitening of the surface of the teeth or during cleaning of the oral cavity from tartar. Here they do not resort to opening the gums at all.
Closed curettage is done if:
- the patient has a mild form of periodontal disease;
- the patient has a mild form of periodontitis;
- there are no pockets in the bone tissue;
- there is a need to maintain gum density;
- there is a need to preserve the gum structure;
- the patient has a closed pocket depth of less than 5 mm.
Open curettage is done if:
- there are lesions of the interdental papillae;
- there is a severe form of periodontitis;
- there is extensive tartar on the teeth;
- the gum pocket has moved away from the tooth;
- the depth of periodontal pockets is more than 5 mm.
The curettage procedure may be postponed for a certain time. The reason for this is the inflammatory process in the oral cavity.
What is a periodontal pocket
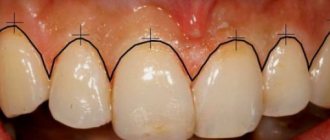
A periodontal pocket is an increased distance between the gums and teeth. Initial manifestations are amenable to therapeutic methods. If the depression is left unattended, it quickly develops to stages requiring surgical treatment.
Stages of gum pocket development:
- From 2.1 mm to 3.6 mm.
- Up to 5.1 mm.
- Up to 7 mm.
- More than 7 mm.
A small gum pocket can occur even with healthy teeth. A space with a depth of no more than 2 mm is considered normal, a physiological feature.
Tools for the procedure
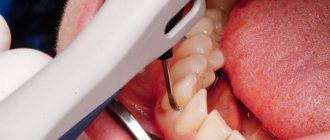
The procedure can be performed using mechanical instruments or ultrasound.
Most modern dentists prefer to use ultrasound. The procedure is distinguished by its effectiveness, speed and painlessness.
In order to cure the patient one hundred percent during ultrasound treatment, the tooth root must be polished. This method makes the tooth enamel smooth and prevents the formation of tartar.
The doctor often prescribes medications that disinfect the oral cavity and help the gums resist bacteria.
How to carry out the procedure
First of all, the doctor examines and diagnoses the gums. Next, he treats the entire cavity with an antiseptic. In order to reduce the pain from the injection, the doctor applies a cooling gel to the surface of the gum. Then the patient is given an injection with anesthesia. Next, the doctor cleans the deposits in the gum pockets. Dental instruments are used. The gum, as mentioned above, is not cut in this case. At the very end, the roots are polished. Be sure to grind the tooth and treat the gum surface with an antiseptic. At the end, the doctor puts an ointment into the pocket itself, which restores gum tissue well. Closed curettage will take no more than 30 minutes. The duration of the procedure depends on the complexity and volume of work.
With open curettage, the gums are first diagnosed and anesthetized (as in the first case), then the gum surface is cut. This is simply necessary in order to get to the very bottom of the periodontal pocket. The incision site is the area of the interdental papillae. Next, using dental equipment, the pocket is cleaned. During the procedure, care is taken to ensure that bone tissue continues to grow. To do this, osteogenic preparations are applied to the damaged area. At the last stage, the cut gum is sutured.
Patchwork method
There is another method of curettage - patchwork. During its execution, two incisions are made. In this case, both cuts are vertical. The point of flap surgery is to expose the tooth root through a folded flap (which is formed after the incisions). With this operation, the roots are exposed and react strongly to irritants. If you expose them to temperature or other aggressive substances, the roots begin to hurt. But these feelings can be avoided. To do this, palate tissue is transplanted to the site of the cut piece. The procedure justifies its effectiveness: the pockets are cleaned and the aesthetic appearance does not deteriorate.
There are difficult cases when bone tissue transplantation is required. For this, you may need patient material or slightly different material (not living, synthetic).
Thanks to transplantation, tissue regeneration occurs. As a result, the tooth is securely fixed in the socket.
Sutures are removed approximately 1.5 weeks after dental surgery. But the damaged tissue itself takes much longer to recover. It will take several months for final recovery.
Rehabilitation period
After the curettage procedure there is a rehabilitation period. If a special bandage has been applied to the gum, then you cannot brush your teeth with it or do harmless rinsing of the mouth. In the first days, the diet must include only semi-liquid food.
After removing the bandage, you can do a quick healing procedure at home. This is usually treated with anesthetics and agents that help the wound heal faster. You should know that home care is important. Taking responsibility in this matter will help prevent re-infection in the gum socket.
After completing the curettage, you need to go to the dentist. The very first appointment is scheduled after about two months. Only after this time it becomes clear how successful the procedure was.
The issue of cost is not an unimportant aspect of treatment. The cost of curettage includes not only the doctor’s fee, but also the cost of materials. For one tooth you will have to pay about two thousand rubles.
If a doctor, a competent specialist, says that you need to have curettage, do not refuse. The disease will lead to the release of pus, severe loosening of the teeth and their loss. If there is a desire to restore them, implantation will be required. If the disease has progressed to a serious condition, then it is necessary to take action as soon as possible.
Closed
If the pocket depth is small and does not exceed the permissible norm, then the dentist can use the closed curettage method.
The difference between these two methods of dental treatment is that during closed curettage the doctor performs all manipulations blindly. That is, the pocket is cleaned without cutting the gum.
The method is less effective and in difficult cases improves the patient’s oral condition only temporarily, but the procedure is practically painless; local anesthesia can be used:
- First, a specialist uses ultrasound or dental instruments to clean all deposits.
- Next, he carefully polishes the roots of the tooth and treats everything with antibacterial agents.
- In case of severe bleeding, the doctor’s task is to stop it, but a small clot should remain in the periodontal pocket to protect the pocket from bacteria getting inside.
- Then a special bandage is applied to the gum.
In practice, the cleaning method allows you to thoroughly clean the pocket and reduce its depth. It is important that the dentist is extremely attentive and careful, since rough work can lead to complications, increase gum healing time and lead to new inflammatory processes.
The video popularly describes the closed method.
Using a vacuum
Often, when performing closed curettage, various additional techniques are used. Modern dentists successfully use vacuum curettage, which allows you to clean the pocket much more thoroughly.
During the procedure, a special vacuum device with attachments is used, with the help of which dirt is sucked out even from deep pockets.
Treatment of the problem area with disinfectants is carried out automatically.
The advantage of the method is that it stimulates tissue regeneration and improves blood circulation.
Socket curettage
After the removal procedure, cleaning of the hole is required. If this is not done, the gums will begin to bleed in the near future, the teeth will hurt greatly and a strong inflammatory process will occur.
If painful symptoms bother the patient for more than 5 days and it does not get better, it is necessary to run to the doctor. Microorganisms have formed inside the wound due to food debris or foreign objects. Sometimes fragments of bone remain that have begun to rot. Pain also occurs due to the inflamed pulp.
A diseased tooth can transmit infection to neighboring teeth, so curettage is necessary.
Curettage of the hole is done in the following sequence:
- The patient is given an application and given general anesthesia.
- The alveoli are freed from the blood clot.
- Using dental instruments, foreign bodies, tooth fragments and other elements are removed.
- The hole is treated with an anesthetic.
- Tampons are applied (no incision or suturing is performed during treatment).
The entire process is carried out in one procedure.
At first glance, the interventions appear to be minor. But that's not true. After surgery, it is imperative to follow the recommendations throughout the rehabilitation period.
Once you can brush your teeth, you should perform this procedure with extreme caution. To clean your teeth, you will need a tool with very soft bristles. You can purchase it in the store in advance.
Vacuum curettage
Vacuum curettage is a combined method; its technique is similar to the closed method of curettage of periodontal pockets, but together with standard curettes, hollow nozzles connected to a vacuum apparatus are used. Using a compressor, a vacuum is created in the device’s container, capable of sucking out mucus, deposits, and granulations from the space between the root and the gum. To improve visual control, the vacuum method can be performed in conjunction with gingivotomy (dissection of the gums).
Stages of the vacuum method:
- injection pain relief;
- scraping out accessible deposits from the tooth root with curettes;
- scraping granulations from the gums;
- bottom treatment with a vacuum nozzle;
- washing the cleaned area with antiseptics;
- applying a protective bandage for two days.
The vacuum method can be used in the area of 2-4 teeth in one session. As a result of the procedure, congestion is reduced, lymph and blood circulation is normalized. During the action of vacuum, microhematomas are formed, which help accelerate regeneration processes and, as a result, more rapid restoration of the periodontal junction.
Contraindications
You should not do the procedure if:
- there is gingival fibromatosis;
- there are the slightest contraindications to surgical operations;
- there are infectious processes in the oral cavity (for example, sore throat);
- have any infectious diseases (acute respiratory infections, influenza);
- there is pus in the gum;
- deep bone pockets are observed;
- the gum itself is very thin;
- the dentition has an abnormal arrangement;
- the patient's jaw is underdeveloped;
- there is a purulent tumor;
- tooth mobility is observed.
Recommendations:
- To alleviate the condition, cold compresses should be applied. Inflammatory processes slow down and disappear over time.
- If open curettage was performed, then for the first few hours you need to drink through a straw. This will prevent bleeding.
- Do not eat or drink hot food until the tissues are almost completely healed.
- Use antiseptics daily. For example, Miramistin and Chlorhexedine. They need to be used to wipe your teeth after and every meal.
Recommendations after curettage
- Eating after surgery is possible no earlier than two to three hours later;
- During the recovery period, it is extremely undesirable to touch the part of the gum on which manipulations were carried out with a toothbrush;
- It is necessary to treat the oral cavity with antiseptics several times a day;
- Gum pockets should not be probed for three weeks after the procedure.
Advantages and disadvantages of curettage
The advantages include the following:
- Closed curettage is inexpensive: 200 rubles per pocket. Open curettage of one tooth: about 2000 rubles.
- It is possible to completely restore bone tissue (osteological preparations help with this).
- Complete elimination of gum pockets and removal of painful microorganisms from them.
- Tooth mobility completely disappears after treatment. After curettage, the teeth sit more firmly in their sockets.
Disadvantages include:
- Ineffective for periodontitis.
- Closed curettage is an expensive method.
- In terms of time, open curettage lasts quite a long time (it takes 2 hours to treat seven teeth).
- The doctor who will perform the curettage procedure must have a high category and be a specialist in his field.
- If a patient encounters an inexperienced dentist, he is likely to suffer wounds and damage to the mucous membrane.
Open gum curettage
Open curettage is performed if there are pathological gum pockets deeper than 5 mm, as well as if periodontitis occurs, a disease in which deep damage to bone tissue develops with loosening of teeth. This is a full-fledged surgical operation.
Open curettage is preceded by mandatory anti-inflammatory measures, suppuration is eliminated.
Sometimes, before surgery, preliminary splinting of mobile teeth is performed.
The doctor performs open curettage of periodontal pockets in 2-3 visits, in the area of no more than 4-6 teeth at a time. First, using special graduated dental probes, the doctor measures the depth of each pathological pocket and makes a mark on the gum. Next, under local anesthesia, he makes a horizontal incision in the gum with a scalpel, removes the cut flap of the mucous membrane and gains free access to the granulations, scrapes out the exposed walls of the socket and tooth with curettes and then grinds them with cutters.
After antiseptic treatment, drugs that stimulate osteosynthesis are applied to the wound surface. Sutures are placed on the mucous membrane in each interdental space. The top of the seams is covered with a protective bandage.
In this case, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers, as well as rinses or other auxiliary procedures carried out at home.
After ten days, if healing is normal, the sutures are removed.
Good postoperative care under the supervision of a dentist will prevent the development of complications such as inflammation of the gums, suppuration of the postoperative wound, and loosening of teeth.
Complete restoration of bone tissue occurs 2-3 months after curettage.