In the structure of diseases of the ENT organs in children, a significant part is made up of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the palatine tonsils, which account for 20% of cases in the general population and up to 43% in the group of frequently ill children.
In the etiology of acute tonsillitis (angina), the main role is played by the following microorganisms: Hemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catharralis and beta-hemolytic streptococcus, the relevance of which in the development of the pathological process is still high.
Other microorganisms, such as viruses, streptococci of other groups, Neisseria, etc., are of significantly less importance.
Infection occurs by airborne droplets, the source is a sick person or, more importantly for children attending preschool institutions and schools, an asymptomatic carrier.
The clinical picture of acute tonsillitis, as a rule, is quite typical and does not cause diagnostic difficulties: there is an acute onset with a rise in body temperature from low-grade fever to severe hyperthermia, general weakness, headache, sore throat, aggravated by swallowing, enlargement and tenderness of the tonsillar lymph nodes.
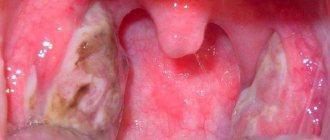
During pharyngoscopy, the picture is also typical: hyperemic and edematous tonsils, soft palate, posterior wall of the pharynx, as well as lateral columns (in Western countries the diagnosis of tonsillopharyngitis is accepted; in the lacunae of the tonsils there are inflamed purulent follicles or widespread white-yellow overlays on the tonsils (but not extending beyond the tonsils, that is, not spreading to the arches and soft palate).The plaques are loose, easily removed from the surface of the tonsils. After removing the film, the tonsil does not bleed.
Diagnosis of catarrhal tonsillitis may present some difficulties when there is no plaque on the tonsils. But this is a somewhat special case: there is currently a discussion about the legitimacy of such a diagnosis, that is, the existence of catarrhal tonsillitis as such is being questioned. In these cases, it is proposed to make a diagnosis of acute respiratory disease.
A clinical blood test determines changes typical of the inflammatory process.
Ideally, before starting therapy, a microbiological examination of a smear from the tonsils is carried out to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
Therapy for acute tonsillitis remains traditional: it is antibacterial therapy, and aminopenicillins with clavulanic acid (amoxiclav, augmentin) remain the drugs of choice.
Synthetic penicillins retain their value only in the treatment of acute tonsillitis caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Today, from the group of penicillins for oral administration, amoxicillin is the most important, surpassing other drugs in this group in its pharmacokinetic properties. Along with penicillins, cephalosporin antibiotics are used, with preference given to drugs of the first (cefadroxil) and second (cefuroxime, axetil, cefaclor) generations.
In case of intolerance to penicillins and cephalosporins, macrolides are used.
Along with systemic antibiotics, topical antiseptics are also used that have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect (hexasprey, hexoral, stopangin, tantum verde, etc.).
Irrational treatment of acute tonsillitis, in particular refusal of systemic antibiotic therapy or its unjustifiably shortened course, is one of the reasons for the chronicity of the process.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis, both in the acute stage and in the remission stage, is associated with a number of difficulties.
In particular, it is necessary to take into account that in a chronic process, as a rule, not an isolated flora is detected, but a mixed infection, which is much less amenable to antibacterial therapy. The most obvious way to treat chronic tonsillitis is surgery - bilateral tonsillectomy. In adult patients, this route is justified in any case.
But as to whether tonsils should be removed in children, and if so, at what age, expert opinions differ. This is due to the fact that the lymphopharyngeal ring performs protective functions and is an immunocompetent organ. Therefore, a significant number of pediatricians believe that if chronic tonsillitis occurs in a compensated form, it is necessary to carry out conservative treatment.
The standard complex of preventive conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis includes a set of procedures aimed at combating pathogenic microflora that is constantly located in the lacunae of the tonsils, improving the drainage of the tonsils, and correcting the body’s immunological defense. This complex includes washing the lacunae of the tonsils, lubricating the tonsils with antiseptic solutions, physiotherapeutic procedures (ultrasound in the submandibular area or laser therapy), and the use of immunomodulators. The course of treatment is carried out twice a year.
Our study was conducted to identify the most optimal scheme for the preventive treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
From April 2000 to June 2002, 68 children aged 7 to 12 years with a diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis, compensated form, were under our supervision. (Children under 7 years of age were excluded from the study, since contact with them was difficult and, therefore, there were limitations in carrying out the full course of complex therapy.) In 24 (35%) children, the disease occurred with exacerbations in the form of sore throats 1 time per year or 2 every three years, 6 of them had a history of peritonsillar abscesses.
All parents categorically refused surgical intervention. The remaining 44 (65%) people had a compensated non-anginal form of chronic tonsillitis. (There was no documented diagnosis of tonsillitis in the medical history.)
All children complained of increased fatigue and periodic headaches. Parents paid attention to weakness, sweating, frequent colds, and a prolonged “unmotivated” increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels.
During examination, all children showed enlargement and hardening of the submandibular lymph nodes. Soreness was noted by 11 (16%) children included in the examination 7-10 days after suffering from tonsillitis.
All children had slight hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the tonsils and the posterior pharyngeal wall. The anterior arches were significantly hyperemic and injected with vessels.
The tonsils are fused to the arches, with widened lacunae; there is pathological purulent discharge in the lacunae. 49 (72%) people had grade II tonsils and 19 (23%) people had grade III tonsils. 10 children had a purulent odor from their mouth.
All children under our supervision underwent a course of conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis 2 times a year. Every other day, they washed the lacunae of the tonsils (from 8 to 10 procedures, depending on the effectiveness). In all cases, these procedures were combined with ultrasound examination of the submandibular area.
Washings were carried out with solutions of Hexoral (10 patients), Miramistin (20 patients), Octinosept (28 patients). These drugs were chosen due to the fact that they have a wide spectrum of antimicrobial and antifungal effects, are non-toxic, are not absorbed through intact mucous membranes, have a taste acceptable to children, and are available in the form of solutions.
After the treatment, a visual effect was noted after the 5th procedure: the tonsils shrank in size, acquired a pale pink color, the lacunae remained free, and the bad breath disappeared.
In addition to the direct impact on the tonsils with antiseptic solutions and the use of physiotherapy, we included in the complex of preventive procedures homeopathic remedies that have an anti-inflammatory effect, aimed at strengthening the lymphoid tissue. In particular, tonsilotren was used, a complex drug whose action is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of inflammation, reducing hypertrophy of the palatine and nasopharyngeal tonsils, as well as regional lymph nodes by improving the drainage of lymphoid tissue and the immunomodulatory effect.
The drug was prescribed as a tablet 3 times a day (at the same time a course of lavage of the tonsil lacunae and physiotherapy began) and was taken for a long time, for 6 weeks. The drug was well tolerated. In 4 (6%) children, tonsilotren had to be discontinued on the 4th day of treatment at the request of their parents due to a slight exacerbation of tonsillitis symptoms.
Control was carried out 3 months after the start of complex therapy.
After the first course of preventive treatment, out of 64 children taking tonsilotren, 53 (83%) people did not have any complaints related to diseases of the ENT organs for 3 months. The pharyngoscopy picture remained satisfactory. 9 (14%) people suffered mild ARVI, 2 (3%) patients had ARVI with high fever and sore throat.
After 6 months (from the start of the first course), 64 people underwent preventive treatment again in full, excluding 4 children who did not take the homeopathic drug. During a follow-up examination carried out 6 months later (before the next course of preventive treatment), a satisfactory pharyngoscopy picture was noted, no pathological changes were observed in clinical blood and urine tests, and the ECG was within the age norm. During the reporting period, 59 (92%) people had virtually no complaints.
2 (3%) children suffered from ARVI, 1 child had bronchitis, 2 (3%) people suffered from follicular tonsillitis. In 1 child, tonsillitis was complicated by a peritonsillar abscess. The parents refused the operation.
During the observation period, the children received 5 courses of preventive treatment for chronic tonsillitis.
During this time, the number of children suffering from acute respiratory viral infections and other respiratory infections sharply decreased. In 62 (97%) people, sore throats did not recur. The pharyngoscopy picture remained satisfactory.
In 2 children, bilateral tonsillectomy was performed due to the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
Thus, complex preventive treatment of chronic tonsillitis with the inclusion of antiseptic solutions and homeopathic drugs (tonsilotren) in the therapeutic regimen is highly effective and allows children to preserve the tonsils as a necessary immunocompetent organ and avoid traumatic surgery.
Literature
Belov B.S. A-streptococcal tonsillitis: clinical significance, issues of antibacterial therapy // Attending Physician.
2002. No. 1-2. WITH.
24-28. Karaulov A.V., Sokurenko S.
I., Barmotin G.V. Principles of immunoprophylaxis and immunotherapy of recurrent respiratory diseases // MMA im.
I. M. Sechenov, clinic of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation.
M., 1999. Lazarev V.N.
Adaptive reactions and their correction in chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract: Abstract of thesis. dis. ...
doc. honey. Sci.
M., 1995. Lopatin A. S.
Treatment of acute and chronic pharyngitis // RMJ. 2001. T.
9. No. 16-17. Dagnelie C.
F. Sore Throat in General Practice. A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Study.
Thesis. Rotterdam, 1994. Rice D.
H. Microbiology. In: Donald P.
J., Gluckman JL, Rice DH
Editors. The Sinuses. New York: Raven Press.
1995. pp. 57-64.
At the beginning of an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis or in the postoperative period (after tonsillectomy), it makes sense to use topical antiseptics to accelerate the relief of inflammatory and pain symptoms in the oral cavity. In particular, the drug faringosept, which has a pronounced antiseptic effect and is available in the form of lozenges, has proven itself well. This ensures convenience and painlessness of its use, which is especially important in the postoperative period.
Enlarged, inflamed and loose tonsils (what this means will be described below) are quite common, especially in young children. This can be detected at a doctor's appointment, as well as during an independent home examination.
What it is?
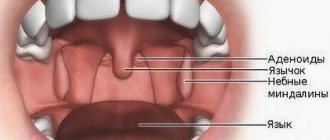
We are talking about specific nasopharyngeal and palatine tonsils located in the nasopharynx. They are small-sized accumulations of lymphoid tissue. Their functionality in the human body has not been fully studied. But one thing is known: tonsils are designed to protect against viruses and bacteria.
They are a kind of barrier to pathogenic microbes that try to enter the body through airborne droplets. The second name for the palatine tonsils is tonsils. Thanks to them, the infection cannot go further and seriously damage the airways.
A disease in which the tonsils become inflamed is tonsillitis. We’ll figure out how to treat loose tonsils in this article.
Description of the symptoms of the disease
Chronic tonsillitis is popularly called loose tonsils, or loose throat.
This is not a medical term, it is an indicator of the inflammatory process in this organ.
When lymphoid tissue grows, the appearance of a loose throat is created. Also, this tissue is often covered with follicles, causing the throat to begin to resemble a sponge. This is what enlarged, loose tonsils look like.
Functions of the tonsils
The main function of lymphoid tissue is protective, therefore, when an infection occurs, its increased growth occurs, which creates the so-called loose throat.
This is how the body starts the mechanism of protection and fight against pathogenic microorganisms. Loose tonsils indicate infection.
The tonsils themselves become inflamed and can no longer perform a protective function. They themselves are the source of inflammation. At this time, the body is most susceptible to various serious diseases.
Removing tonsils is most often impractical; this is now done in rare cases, since it is undesirable to deprive a person of the first barrier to infection. Doctors decide to perform an operation to remove tonsils only when the harm to the body from their inflammation is very great, that is, greater than the possible benefit from their functioning. Therefore, if loose tonsils form in a child, treatment should be timely.
Cleaning loose tonsils
The presence of loose tonsils is often accompanied by the formation of purulent plugs in their lacunae, which can be easily seen as white dots on the tonsils.
Many people do the cleansing themselves at home, by pressing on the tonsils with a hard object, causing hard accumulations of pus to come out.
But this method cannot be recommended: firstly, a person cannot completely clean the tonsils, and secondly, it can damage the tonsils, causing the tissue to become scarred.
In the hospital, cleaning is carried out using special tools and devices:
- a syringe with an antiseptic and a special nozzle that allows you to enter the lacunae and wash out the pus without damaging the tonsils;
- ultrasound;
- vacuum device.
As a rule, a course of 5-10 sessions is enough to thoroughly and safely clean the tonsils and eliminate the infection. If 2-3 such courses are not enough, and the pathology constantly recurs, the doctor will recommend the patient a tonsillectomy.
Loose tonsils in a child can only be cleaned in a clinical setting. The sensations during cleaning are quite unpleasant, so the child may jerk at the wrong moment, causing injury.
An experienced otolaryngologist will be able to prevent the risk of such injury by performing cleaning as quickly, painlessly, and correctly as possible.
Main features
As already mentioned, the tonsils become loose due to inflammation.
But this is not a disease. Therefore, there are no specific symptoms, there may only be accompanying signs. So, the inflammatory process in the tonsils is characterized by:
Bad breath. Why does it appear? The fact is that food is retained in small quantities on enlarged and loose tonsils.
Then it decomposes, hence the unpleasant smell. Constant gargling is recommended to disinfect and flush out decomposed food particles. Otherwise, the inflammatory process will spread to the larynx and the person will get laryngitis.
Sore throat. These unpleasant sensations most often appear when swallowing, they are provoked by the inflammatory process. Increased body temperature. But it does not necessarily rise to too high levels.
Sometimes it is within normal limits, sometimes it is low-grade. A sharp increase in temperature indicates the development of a sore throat. Headache. Headache is caused by swelling of the mucous membrane, difficulty breathing, general weakness of the body. Weakness, lethargy. Due to infection, the body becomes weakened. With severe nasal congestion, breathing may be difficult, then the person eats poorly and sleeps little.
This leads to lethargy, fatigue, and weakness. Children are often capricious. Enlarged lymph nodes. When lymphoid tissue grows, enlargement and inflammation occur in the nearby lymph nodes. If you palpate, they can be better palpated, become much larger in size and painful. They have a special appearance. If you look into a person’s healthy throat, you can see tonsils with a smooth, even and pinkish surface.
And if you examine an inflamed throat with loose tonsils, you will notice that the throat has become red and the surface of the larynx has become uneven. The tonsils become covered with red or yellowish bumps; these are places of suppuration. They are covered with a white-yellow coating.
All of these symptoms that relate to loose tonsils do not have to occur at the same time. As a rule, one or two are enough to understand that inflammation has begun.
If there is a suspicion of tonsil disease, body temperature has risen, a sore throat appears when swallowing, and plaque has been noticed, you should consult a doctor for help as soon as possible. He will prescribe immediate treatment.
Physiological manifestations
Loose tonsils are only a conclusion from an external examination of the oral cavity, and not a diagnosis. And the manifestations of this pathology can be different. Of particular concern are:
- Change in bad breath. Due to the presence of grooves in loose tonsils, a factor of food retention in the lacunae appears. The food begins to decompose and emits a putrid odor that spreads throughout the entire oral cavity. To avoid laryngitis, you need to gargle.
- Pain. It has a pulling character, not sharp. Sharply intensifies when swallowing.
- Temperature. This symptom does not affect everyone. If it rises sharply to high numbers, a sore throat can be suspected.
- Headache. Also an optional symptom, it develops due to impaired breathing, poor blood supply to the brain and weakening of the body by infection.
- Weakness. The body directs all its forces to fight the infection, the child quickly gets tired. And if nasal breathing is impaired, it is difficult for children to even eat and sleep, which provokes moodiness, fatigue and apathy.
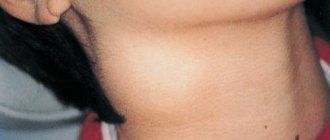
- Lymphadenitis. This is what doctors call enlarged lymph nodes. In response to the infection, other lymph nodes in the immediate vicinity of the throat begin to work. They are very easy to palpate.
- Pathological appearance of the tonsils. In the absence of pathology, a smooth pink wall is observed. When infected, redness and looseness of the tonsils, a white or yellow coating, and bumps from the mucous membrane appear, which then become purulent plugs.
For what reasons can loose tonsils occur?
This condition, in which the tonsils become loose, is not life-threatening. Therefore, panic should be stopped.
But this at the same time indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the body. If, apart from a loose throat, no other signs of illness are detected, then you need to take the medications prescribed by your doctor and gargle. This is done if loose tonsils constantly torment a person.
The special mechanism of the tonsils’ response to infection is the main factor in their looseness. When pathogenic microorganisms enter the throat by airborne droplets, increased production of lymphocytes occurs. Their active production causes redness of the throat, loose tonsils, inflammation of the palate and larynx.
This happens with certain diseases, decreased immune defense, and hypothermia. After a while, when treatment has already begun, the sore throat subsides, but the tonsils are still loose. In the absence of fever or purulent plaque, no additional therapy is required.
Causes
There are many reasons why tonsils become loose. The basis for their occurrence is the function of the tonsils. The tonsils are the first defenders against external infection, upon contact with which they react with inflammation, becoming loose. Therefore, an increase without looseness and plaque can be observed constantly and is not a reason for an urgent visit to an ENT specialist. Some pathogens are very fond of the localization of the tonsils, for example, streptococci always actively attack this area, causing a sore throat.
We also recommend reading Enlarged tonsils - causes, symptoms, treatment of hypertrophy
More often, this disease manifests itself in children, because their immunity is not yet familiar with many infectious agents. Therefore, the reaction to them in children is more pronounced and manifests itself differently than in adults. The etiology can be any past infection, disruption of the proper functioning of the immune system, or hypothermia. Loose tonsils are observed some time after the disease.
It should be borne in mind that these diseases are very often complicated by loose tonsils:
- Angina. It always manifests itself acutely and begins with a very high rise in body temperature. There are complaints of chills and fever, headache. Sore throat appears due to the penetration of streptococcus into the respiratory tract. Next, you may experience a nagging pain in the throat, which gets worse when swallowing, and a cough.
- Pharyngitis. This is a nonspecific inflammation of the pharynx, which can also affect the tonsil area. It manifests itself as pain in the throat, cough without sputum. When examining the oral cavity, hyperemia and mild ulceration of the mucous membrane are observed.
- ARVI. Most common among all segments of the population. Manifestations vary greatly from case to case, most often complaining of discomfort in the throat and cough. However, after this diagnosis, pharyngitis often begins.
Colds
This often happens with colds. If the following diseases occur and loose tonsils appear (the photo can be seen below), then a more serious approach to treatment is necessary:
For sore throat. The first sign of this particular throat disease is high body temperature. Manifested by fever, chills.
From about the second day my throat hurts a lot. If there are purulent rashes on the tonsils, then this is purulent tonsillitis. Often the patient cannot eat due to painful sensations when swallowing.
A manifestation of streptococcal sore throat or tonsillitis is possible, then a severe cough appears. With pharyngitis. Severe inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, as well as lymphoid tissue, begins. This is an independent disease most often, but it can also occur as a result of another disease. There is a constant sore throat, sore throat, painful dry cough.
If you carefully examine a sore throat, you can easily see redness, the presence of ulcers and pus on the mucous membrane. With ARVI. This is the most common type of infection, exacerbation begins in autumn and winter. In this case, there may not be a severe sore throat. But if treatment is not carried out, a complication will arise in the form of pharyngitis or sore throat.
Therefore, it is not recommended to start this inflammatory process. So how to treat loose tonsils? More on this later.
Tonsils: remove or keep?
The palatine tonsils, or, as ordinary people call them, tonsils, play an important role in the body. However, there are situations when they cease to perform their functions and begin to cause harm to the body.
In such cases, the question of removing the tonsils is raised.
We talked about the reasons and feasibility of surgery to remove the tonsils with Elvira Ismagilova, a pediatric otolaryngologist at the Dobrobut medical network.
The palatine tonsils are located in the pharynx, belong to the organs of the immune system and perform a protective function. They consist of lymphoid tissue and are located at the intersection of the digestive and respiratory tracts.
One of the main functions of the tonsils is to “get to know” the microbe, read information about it and transmit it to other immune organs, which produce protective proteins - antibodies that allow our body to fight it.
How to treat green snot in children?
Tonsils are an important link in our body, but only when they perform their function. However, with chronic inflammation of the tonsils (chronic tonsillitis), soft lymphoid tissue is replaced by coarser connective tissue and adhesions and scars form.
In this case, closed and semi-closed cavities are formed, filled with pathological contents (desquamated epithelium, food debris, leukocytes, dead and multiplying microbes). All this content supports the inflammatory process.
Inflammation spreads to nearby lymph nodes and causes them to enlarge.
When the tonsils don't do their job
The palatine tonsils affect a number of organs and systems of the body (cardiovascular system, joints, kidneys, digestive system, etc.). Inflamed tonsils can cause complications on these organs. Diseases that arise as a complication of chronic inflammation of the tonsils are called metatonsillar.
If the ENT doctor, together with highly specialized specialists, determines the presence of such a disease, then the question is whether to preserve the tonsils or operate.
Even if it is established that the pathology of the kidneys, cardiovascular system or joints is associated with chronic inflammation of the tonsils, the otolaryngologist first of all carries out conservative, or non-surgical, treatment.
How is tonsillitis treated?
Sore throat during pregnancy: symptoms and consequences
If a diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis is established, for effective conservative treatment, a bacterial culture is first taken to determine the flora. After which the lacunae are washed.
Using a special cannula, a saline solution is injected into the tonsil cavity, with the help of which the pathological contents are washed out. This procedure is carried out when the child is healthy, as it can cause an exacerbation of the process.
In case of a pronounced inflammatory process, in addition to washing, antiseptics are used. Physiotherapy is also used: ultrasound, phonophoresis on the submandibular area or directly on the tonsil.
The complex treatment also includes sanitation of teeth and gums, treatment of sinusitis and restoration of impaired nasal breathing, compliance with home hygiene rules, balanced nutrition, adequate physical activity, and a set of hardening measures. In some cases, cryotherapy—exposure to liquid nitrogen—is used as an alternative to surgical treatment.
When is surgery impossible?
If conservative treatment does not produce positive results and does not lead to relief from metatonsillar disease (associated with inflammation of the tonsils), surgery is inevitable.
A decision is also made about surgery if exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis recur despite attempts at conservative treatment. One of the indications for surgery is recurrent peritonsillar abscess.
All of these reasons indicate that the tonsils no longer perform a protective function, but cause harm to the body.
How is the operation performed?
The operation is performed under endotracheal (general) anesthesia.
Before the operation, the child undergoes a laboratory and instrumental examination (a general and biochemical blood test is taken, an ECG is done, an examination by specialized specialists, an anesthesiologist).
Only with a general conclusion that the patient has no contraindications to surgical treatment is surgery performed. During the operation, all lymphoid tissue is removed.
Cons and negative consequences of the operation
As mentioned above, tonsils play an important role in the body, so their removal leads to negative consequences. Often such children suffer from pharyngitis, which manifests itself as a sore and dry throat. Many children also suffer from laryngitis and bronchitis. Therefore, surgery is advisable only in cases where the consequences of the operation are less than the risks of preserving the tonsils.
When is surgery still necessary?
It happens that the tonsil is not inflamed, its function is not impaired, but it is large. This phenomenon is called hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils. Large tonsils interfere with the child's ability to swallow and cause snoring during sleep. Then the question arises about trimming the tonsils, that is, reducing them in size.
Treatment methods
As already mentioned, the choice of treatment method depends entirely on what caused this pathology.
Also, the general condition of the patient plays an important role, his age, and the presence of other diseases. There is no need to self-medicate. You should definitely visit a doctor.
The specialist will prescribe special tests - you need to take a scraping from the tonsils for laboratory testing. This will help determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to antibacterial drugs. After which you can choose therapy.
Loose tonsils in a child. Treatment
Since at home it is not always possible to determine that the problem is constantly associated with the tonsils, you should consult a doctor. He determines how to treat this pathology for children.
1. With bacterial sore throat, signs of malaise appear, severe pain in the throat. Headache occurs due to intoxication of the body. It is necessary to take a swab from the throat and nose to test the microflora and determine sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Next, the specialist prescribes symptomatic treatment (to relieve pain and symptoms of malaise) and antibiotics, since it is impossible to cope with this situation without them. The course of treatment is at least 5 days. This is done to ensure that there is no possibility of relapse. Experts often recommend a penicillin series containing clavulanic acid, as it destroys the protective coating of bacteria. It is necessary to use drugs that restore and maintain the normal composition of microflora. If the child cannot or does not want to take the tablets, they must be crushed and added to the drink.
2. For diseases of a viral nature, antiviral agents are indicated in combination with symptomatic treatment. Such diseases cannot be treated with antibiotics. They not only do not help, but also gradually develop resistance in microorganisms to them.
3. Symptomatic treatment includes local anesthesia of the throat in the form of sprays and lozenges; rinses (soda, chamomile, chlorophyllipt); drinking plenty of water. You can only lower the temperature if it is above 38 degrees. Antiseptics are used in the form of ointments, sprays and rinses.
4.Physiotherapy
- For example, the sun device, which operates on the basis of ultraviolet rays that destroy pathogens.
- The salt cave helps saturate the mucous membranes with salts, which reduces the inflammatory process and the number of infections entering the respiratory tract.
- Vacuuming. Using a vacuum, purulent plugs from the tonsils are sucked out. Next, treatment is carried out with an antiseptic or antibiotic to remove any remaining infection.
- Laser therapy.
5.Operational method. Removal of adenoids. It does not always give a 100% effect, since these formations may appear again.
What if there is no pain?
If there is no pain when swallowing, tickling, coughing, fever, general weakness and malaise, and the tonsils are loose, regular prevention is needed. The room must be well and regularly ventilated, and a certain humidity must be maintained in the room.
The mucous membranes of the mouth and nose must be moisturized to destroy bacteria. Also, overdried shells are more susceptible to infection. It is better to visit crowded places less often, especially with a small child, this will help reduce the risk of the virus entering the body.
What will relieve inflammation?
Consider below procedures that have a beneficial effect on loose tonsils and help relieve inflammation faster:
Tonsils are treated with ultrasound, laser, magnetotherapy, herbal medicine, inhalations, and other physical procedures. They undergo a course that lasts for two weeks. The infection is destroyed, the suppuration is removed, the person recovers much faster. A new method is used for loose tonsils - vacuuming.
Now it is very popular and effective. Lymphoid tissue recovers faster after pus is pulled out from the inflamed surface using a vacuum. This helps to reduce the size of the tonsils and smooth them out. Antibacterial sprays are used to relieve inflammation.
Use only as prescribed by a doctor. Allergy sufferers need to be careful, especially those with sensitivity to honey, because almost all sprays contain propolis. The dosage should not be exceeded; if the slightest allergic reaction occurs, you should immediately stop using the drug and consult a doctor.
In cases where swelling in the tonsils does not subside for a long time, the throat constantly hurts, and sleep is difficult due to heavy breathing and oxygen deprivation, surgical removal of the tonsils is prescribed. We looked at the cases in which loose tonsils occur and what to do to treat them.
Preventive measures
Those who have a weakened immune system, experience frequent colds, and are prone to inflammatory processes in the tonsils, need special prevention. Vitamin complexes and hardening procedures can help improve health.
It also makes sense to gargle regularly. This needs to be done in courses, systematically.
Furacilin or decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, and sage are suitable for these purposes. For a whole month, I gargle with solutions every day, then take a break. After which the course must be repeated.
Your doctor should examine your tonsils regularly.
It also makes sense to wash them in the doctor's office. But, unfortunately, it is not always possible to see a doctor. You need to protect yourself from infection, because it is the cause of enlarged tonsils.
If there is an epidemic, you need to take care of yourself and try not to visit crowds of people. If a person is sick in the house, you need to protect him from other family members. Oxolinic ointment in the nose helps well during colds.
Therapy and prevention
Young children are more likely to suffer from various throat diseases than adults. If a child has a tendency to develop inflammatory processes in the tonsils, parents can take the following preventive measures:
Proper oral hygiene
- Strictly monitor oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day. Rinse your mouth with regular boiled water after each meal.
- Timely treatment of all dental problems. Carious bacteria can cause constant swelling of the tonsils.
- Home or medical rinsing of lacunae. This can be done independently by gargling with a solution of furatsilin or with an antiseptic.
- Gargling the throat with decoctions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, calendula, sage. It is recommended to alternate herbs.
Hardening
Hardening should begin gradually, preferably in the summer. Sports and physical activity play an important role in strengthening the immune system. You need to walk in the fresh air, do exercises, run, play outdoor games.
To harden your throat, it is good to gargle with cold water, but it is better to start with cool water. Contrasting rinses are perfect. You can dissolve the ice cube over time.
Teeth should be brushed thoroughly, twice a day, this will help destroy bacteria in the mouth. Then loose tonsils will not appear and treatment will not be required.
Sources:
- www.lvrach.ru
- fb.ru