The appearance of primary teeth in a child is a natural mechanism that makes it possible to switch from breast milk or artificial feeding to eating solid food.
These teeth are also needed so that the jaw apparatus of children develops anatomically correctly, and they also provide a constant chewing load for the formation and strengthening of the facial muscles.
The time comes and the need for baby teeth disappears. At the age of 6-7 years, the process of replacing them with permanent ones begins. However, temporary teeth require good hygienic care and treatment when dental diseases occur.
How many baby teeth do children have?
The eruption of primary teeth begins in infancy; their appearance has its own patterns and sequence.
Almost simultaneously, teeth appear on the right and left sides of the jaw. The upper incisors, molars and canines erupt later than the lower ones.
Therefore, the formation of baby teeth goes through two main stages:
- orthognathic bite (2 months - 3.5 years), which appears due to slower growth of the lower jaw, when the teeth are located very tightly and their wear is not visible;
- direct bite (3.5-6 years), with the development of signs of tooth wear and the appearance of physiological gaps between them.
As a result, in the late period the formation of primary teeth is completed. a 7-8 year old child should have .
Usually there are ten of them on the upper and lower jaws, that is, two incisors and molars, and one canine on each side, and a total of 20.
Teething order
At what age the first baby teeth begin to appear depends on the baby’s health status and his individual characteristics.
There is an average pattern of teething in a child with satisfactory health and normal physical development.
It was compiled based on many years of scientific experience and practical observation of the development of baby teeth in children:
Timing of teething
Upper jaw
Usually the central incisors appear first at 7-12 months of life, then the lateral ones at 8-12 months. Canines and molars can come out in the second and third years of a child’s life. The first in the period from 14 to 22 months, the second in 25-35 months.
Lower jaw
At 5-9 months you can see the eruption of central teeth through the gums, at 8-15 months. they are joined by the lateral incisors. Then comes the formation of canines (15-20 months) and molars (21-33 months).
Development of the dental apparatus
The digestive system is of central importance in human life, as well as in other creatures. Therefore, organs that belong to the digestive system are formed very early in the process of embryonic development. Already at 3-4 weeks of development, the embryo has an intestinal tube and the rudiment of a mouth, which interests us primarily. At the same time, the development of the dentition begins, the formation of the primary occlusion and the rudiments of permanent teeth.
Milk and permanent teeth are inextricably linked, because until the child grows his first permanent teeth, that is, until he is 6-7 years old, they will be replaced by temporary teeth. By the time of birth, they are well developed and ready to erupt in the near future, but the first ones - not earlier than 10-11 months.
The eruption of chewing organs is probably one of the central events in the life of the baby and his parents, because this process is associated with stress for the child. Parents are also very worried, trying to ease the fate of their baby, but what to do if the due date has come, but the teeth have not erupted?
First, let's define what a “deadline” is in this case. A child’s first teeth appear at 6-8 months of life, although it is possible that they may appear later. Therefore, do not worry if there is a slight delay. The lower jaw will be filled first, followed by the upper jaw. This is necessary for the child to develop a correct bite, that is, the teeth are positioned correctly in relation to each other. You will learn more about the sequence of teething in this table:
Read also: Baby's teeth at 3 months
Each organism is individual, but there are cases in which parents should pay attention to how their child’s teeth develop:
- delay in teething for more than several months, for example up to a year;
- early dental development;
- the order of eruption at 10 or 11 months is disrupted;
- tooth missing or out of shape at 10 or 11 months;
- The dentition appeared even before the baby was born.
Changing baby teeth
The time at which primary teeth fall out also depends on how correctly children develop physically and whether they have serious abnormalities or illnesses.
In weakened children, teeth erupt, fall out and are replaced with molars later than in completely healthy ones.
In dentistry, an approximate scheme for the loss of baby teeth has been developed:
Upper jaw
- incisors: central - 6-7 years, lateral - 7-10;
- fangs - 10-12;
- molars - 10-12.
Lower jaw
- incisors: central - 5-7 years, lateral - 6-9;
- fangs - 9-12;
- molars - 9-12.
Thus, the period when primary teeth begin to fall out in children varies from 5 to 6 years, and they completely disappear no later than by the age of 12. Their change to permanent ones occurs gradually over a long time and continues also in adolescence and adulthood. Molars begin to erupt in place of milk teeth after a few months.
The change of teeth roughly corresponds to the pattern of eruption of temporary canines, incisors and molars. Dentists have also noticed the fact that in girls, all the processes of growth and replacement of baby teeth with molars proceed faster than in boys of the same age.
Impaired teething
Baby teeth are important for the development of a child and one cannot underestimate how much a child needs them at 10, 11 months, and a year. They allow him to eat adult food, develop and
grow correctly. The development of the facial segment directly depends on how well the chewing apparatus is developed in the child’s mouth.
Eruption disorders are considered to be pathologies, which include the absence of teeth at a late age, incorrect eruption sequence, and underdevelopment during their emergence from under the gums.
To better understand what happens in a child's body and how certain factors can affect the chewing organs, it is best to first look at how teeth erupt and where they come from.
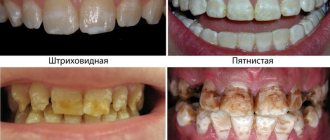
Baby tooth caries
Is it necessary to treat baby teeth if they disappear naturally sooner or later - absolutely. After all, their earlier loss can cause improper formation of the jaw and impaired diction.
And the development of carious processes often provokes diseases of the gums (gingivitis, cysts and periodontitis) or the oral cavity (stomatitis).
In addition, the accumulation of bacteria on the teeth can become a source of infection of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, ear, tonsils, throat and lead to the appearance of chronic sinusitis, adenoiditis, otitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis.
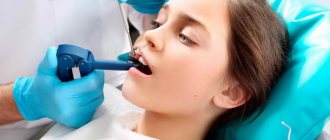
Treatment of caries of primary teeth is considered a necessary and important procedure in dentistry. Filling is carried out using the latest composite materials. To successfully conduct it, the child is distracted with games or uses mild sedation techniques.
To preserve baby teeth with superficial caries, doctors actively use a technique such as silvering . By coating the enamel with silver nitrate, dentists protect teeth from pathogenic microflora. The disadvantage of this method is the pronounced darkening of the enamel after silvering.
Modern analogues of this procedure are remotherapy methods, ICON. With them, the enamel is saturated with minerals, i.e. make it much stronger and it does not change its natural color.
Even if the teeth are completely destroyed and they are removed, doctors recommend installing special space holders in their empty place before permanent teeth appear, which avoid mixing and deformation of neighboring teeth and pathological expansion of interdental spaces.
Advanced technologies in pediatric dentistry include the use of crowns or comfortable removable dentures.
Deviations from the norm
If at the age of eight months the baby’s teeth are not yet visible, this may indicate some developmental abnormalities.
Heredity and individuality should be taken into account. True, missing teeth can sometimes be caused by other factors.
If a child’s teeth do not grow, this may be caused by the following factors:
- Rickets . This disease is typical for young children. It is associated with a lack of calcium; it, as we understand, is necessary for normal bone formation. Rickets causes retention of the baby tooth, in other words, the inability to erupt.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements . Teeth growth requires fluoride, calcium, as well as vitamins D, B, A, E. If there is a deficiency, then tooth development may be delayed.
- Edentia . We are talking about pathology, which consists in the fact that the rudiments of baby teeth are absent in the jaws. In most cases, this situation is provoked by disturbances in the development of the fetus while still inside the womb. If we refer to the observations of doctors, then we have all the evidence to talk about failures in the formation of hair and nails that accompany adentia.
Small children, as a rule, always undergo regular examination by a pediatrician and neurologist. In cases where the doctor does not find any deviations from the norm in the child’s development, there is no need to worry about missing teeth at 7, 8 or 9 months. You just need to wait. They will appear, sooner or later.
Pulpitis of a baby tooth
Pulpitis is a common pathology among children. It develops due to the fact that the hard tissues (enamel and dentin) of baby teeth are very thin, so caries quickly “corrodes” them and quickly gets into the tooth pulp.
This disease is a complication after caries or injury. As a result of pulpitis, a purulent process in soft tissues can quickly develop, a fistula may appear on the gum, and the periosteum may become inflamed.
Previously, such teeth were removed, but today there are a number of procedures to cure and preserve them:
- Conservative treatment is used in the early stages of the disease. The carious cavity is opened (drilled out) and treated with antiseptics, then a medicinal paste is placed into it and filled. This therapy is often combined with electrophoresis. In total, the result of treatment is the disappearance of inflammation and preservation of the tooth.
- Surgical treatment (used in advanced stages). Involves partial or complete removal of the pulp, sanitation of dental tissues, filling of canals and teeth.
Removal
Some people question whether baby teeth nerves The fact that they are not there is a misconception, it’s just that the roots of temporary incisors, molars and canines are shorter than those of permanent teeth.
Therefore, pain during the treatment and removal of temporary teeth is practically not felt by children. Due to the fact that the nerve is located deeper than the root system of the baby tooth, it is also possible to extract it independently in cases of good mobility.
There are a number of rules on how to pull out a baby tooth at home:
- It is important that at the time of tooth extraction the child is healthy, without signs of infection (sneezing, coughing, runny nose, general weakness);
- It is necessary to ensure that there are no pathological processes in the mouth, i.e. redness and swelling of the gums, cysts, bleeding, etc.;
- The compliance of the tooth should be significant; it should “walk” almost freely in the socket in opposite directions;
- The tooth is wrapped with gauze soaked in an alcohol solution and firmly pulled upward until it comes out; you can use a sterile thread tied in a knot around the tooth to pull it out;
- After removal, the mouth should be rinsed and carefully examined for remaining tooth particles, and sterile cotton wool should be placed in the hole and pressed with the teeth for 15-20 minutes to stop bleeding.
Important! Home removal of a baby tooth can only be done if it has good mobility. After removing it, it is necessary to ensure that the bleeding stops, the soft tissue around does not turn red or swell, and there is no pus, mucus or swelling in the hole.
If the teeth are inactive or loose only on one side, and the gums around them are inflamed, you should immediately come to see a dentist. The doctor will perform tooth extraction in safe and sterile conditions, using special surgical instruments.
The procedure can be carried out free of charge in municipal clinics or in specialized dental centers, where the price for removing one tooth is quite affordable and ranges from 500-1000 rubles .
Indications for professional removal of baby teeth are:
- a tooth completely destroyed by caries and not subject to treatment or prosthetics;
- complicated pulpitis, fistula, periodontitis;
- late resorption of the root of a temporary tooth, in the presence of signs of eruption of a permanent one.