What is Chlorhexidine and its action
Chlorhexidine is a very popular drug known to many people, since its scope of application is quite wide. Its main purpose is to remove pathogenic microorganisms of various categories.
Most often, Chlorhexidine is used to treat all kinds of wounds and abrasions, as well as to disinfect the doctor’s hands before examination or surgical procedures.
Can Chlorhexidine be used to treat open wounds? If previously brilliant green and iodine were most often used to treat abrasions, today Chlorhexidine is in first place among many pharmaceutical products, gradually replacing even hydrogen peroxide. The drug has no contraindications, does not cause adverse reactions, and is used not only for the treatment of injuries, but also in the treatment of certain diseases.
Chlorhexidine for wound treatment perfectly destroys microorganisms of various groups , including gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, Trichomonas vaginalis, protozoa, as well as most viruses, including the herpes virus. The drug is powerless only against Koch's bacillus, which is the causative agent of tuberculosis.
At the same time, an important advantage of the product is the absence of a resistant reaction to it in microorganisms, that is, the bacteria being destroyed do not get used to it, do not mutate, do not adapt, but simply die. Therefore, the effectiveness of the drug remains throughout the entire treatment, regardless of how often treatments are carried out.
Is chlorhexidine poisoning possible and how to avoid it?
Chlorhexidine poisoning is not very common due to the fact that most of it is used in small doses and in low concentrations.
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic substance widely used in dental, gynecological, ENT, and other practices.
However, this is a drug, which means it has certain contraindications and side effects, and must be used strictly according to the instructions.
The medicine has different release forms
In this article we will talk about the properties of chlorhexidine, and also get acquainted with the methods of its use and the symptoms of poisoning with this substance. In addition, we will learn how to help with chlorhexidine poisoning.
Characteristics of the drug and its properties
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic with pronounced bactericidal properties, successfully used in medicine for more than 50 years. Has an active effect against protozoa, herpes and bacteria.
The substance can be released in the form:
- externally applied solution – 0.05% or 20%;
- gel;
- ointments;
- spray;
- candles.
The solutions are packaged in glass or polymer bottles with a volume of 100 ml or 500 ml. This is very convenient, since the polymer bottles are equipped with a cap, and in case of wounds or cuts outside the home, you can wash your hands with the drug directly from the bottle.
Chlorhexidine is used as:
- care after surgery;
- treatment of ulcers and burns;
- treatment of wounds, cracks and abrasions of the skin and mucous membranes;
- combating fungal and bacterial infections of the skin and mucous membranes;
- prophylactic agent in obstetrics and gynecology, urology;
- prevention of STDs;
- skin disinfectants;
- preparation for the treatment of dentures;
- substances for sanitation before diagnosis and treatment;
- means for sterilizing medical instruments;
- disinfectant for thermometers and surfaces;
- a preparation for treating the surgeon’s hands, the surgical field and the patient’s skin;
- means for the production of glycerin, alcohol or aqueous concentrates.
You can even gargle with the solution if you have a cold.
Thus, we see that chlorhexidine is widely used in obstetrics and gynecology, urology, dentistry, in the practice of otolaryngology and in surgical operations.
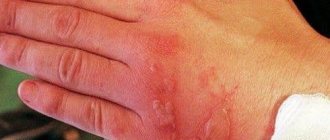
Symptoms of chlorhexidine poisoning occur when the substance enters the body
Use of the drug and signs of poisoning
The drug is used in different ways, however, despite its high safety, the likelihood of poisoning occurs only when gargling or gargling. This most often occurs when chlorhexidine is accidentally ingested.
As a result, the following symptoms may occur:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- discomfort in the stomach;
- a feeling of “tearing” in the throat - a consequence of a burn to the mucous membrane;
- temperature increase to 37-38 C;
- headache;
- feeling of lethargy and chills;
- increased sweating.
The effect of chlorhexidine on the body is strictly individual. In some cases, short-term loss of consciousness or increased excitability is possible; quite rarely, poisoning is accompanied by diarrhea.
Important! The drug is contraindicated for use in case of individual intolerance, as well as for dermatitis.
In dental and ENT practice, solutions with a concentration of 0.02% or 0.05% are most often used. It is recommended to rinse after eating, after brushing your teeth.
Note! It is not for nothing that the instructions state the importance of rinsing after eating. In case of accidental ingestion of the drug on a “full” stomach, the organ is already covered with food and the solution will not get inside. As a result, the solution reacts with food, and not with the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, and its concentration in the body decreases.
For one rinse, about 15-20 ml of solution is used, the duration of the procedure is on average 30 seconds. After rinsing for 15-20 minutes, you should not eat food or any liquids, or perform any manipulations in the oral cavity.
Providing assistance in case of poisoning
When providing assistance, there is one unspoken rule - do not panic. Panic can somewhat blur the true symptoms of poisoning. Typically, chlorhexidine poisoning does not require a doctor, as there are no life-threatening symptoms. However, if your health does not improve, it is still better to seek specialized help.
It is better if the victim is examined by a doctor
When using chlorhexidine orally, the first minutes are extremely important. Basic actions in case of poisoning include:
- Gastric lavage - drinking large amounts of water and artificially inducing vomiting. The annotation for the drug says that when it enters the body, the kidneys excrete it in an amount of 1%. Some people noticed that with every 0.5 liter of water consumed, the concentration of chlorhexidine in the body decreased noticeably. However, there are situations in which it is impossible to induce vomiting, for example, in case of diseases of the teeth and gums, when the likelihood of getting an infection or getting an acid burn is critical.
- Drink activated carbon. Fortunately, it can be found in any first aid kit, and if it is not available, the price of the drug in the pharmacy does not exceed 10 rubles per plate.
- The use of other medications, in particular sorbents and antacids, is allowed, but only in consultation with the doctor.
It is worth noting that there are no significant differences in providing assistance to children or pregnant women, but first aid control must be especially careful.
In addition, children under 6 years of age and women during pregnancy and lactation are at risk when the likelihood of side effects increases.
From the photos and videos in this article, we learned about the likelihood of chlorhexidine poisoning and the symptoms of this condition, as well as methods for providing the necessary assistance to those who have been poisoned.
Source: https://Toksikolog.com/etiologiya/lekarstva/hlorgeksidinom-otravlenie-104
Indications for use
Indications for use of the drug include:
- Carrying out disinfection of wounds of various types, including those on mucous membranes.
- Use as part of complex therapy in the treatment of various fungal infections.
- Preventive treatments to prevent STDs.
- Treatment of oral diseases such as gingivitis, periodontitis and stomatitis.
When treating wounds, cuts, abrasions and other injuries, the solution is applied directly to the surface of the skin and injury without the use of gauze pads or cotton swabs (discs). To carry out the treatment, simply pour the composition onto the damage after preliminary cleaning.
It is important to remember that when treating skin and soft tissue injuries, bleeding should be stopped before filling the wound with Chlorhexidine, since the drug does not have a hemostatic effect.
To disinfect injured areas, a solution of concentration from 0.05 to 0.1% is used. The same solution (in the same concentration) can be used to carefully treat the surface of burns, including chemical and thermal ones. In this case, the solution will work not only as an antiseptic, but also as a means of cooling the surface, as well as washing away chemicals from the skin and the site of damage that led to the burn.
Chlorhexidine is often used for dressings instead of hydrogen peroxide. Wounds, including purulent ones, are washed with the solution, the hands of medical personnel are treated, and bandages that have dried to the wounds are watered for painless and careful removal.
Chlorhexidine is the best antiseptic for eyebrow care.
We are probably all accustomed to the fact that alcohol must be present in a skin disinfectant.
ATTENTION! It is not allowed to use alcohol-containing substances when caring for eyebrows after permanent makeup.
According to reviews from many cosmetologists, as well as women who have had eyebrow tattoos, chlorhexidine is the best antimicrobial drug recommended for the care of skin subject to tattooing. The antiseptic is active against many types of bacteria. Accelerates the regeneration of skin cells even during burns. It must be remembered that it is incompatible with the use of soap. The drug is 30 times cheaper than Miramistin. Avoid contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes. For the first three days, it is recommended to treat eyebrows with chlorhexidine every 2 hours.
Wound treatment with Chlorhexidine
The main purpose of the drug is precisely the antiseptic treatment of various surfaces, not only healthy skin, but also wounds of almost any origin.
The product belongs to the group of special germicidal antibiotics, and therefore Chlorhexidine is capable of not only stopping the growth of harmful microorganisms, preventing their reproduction, but also completely destroying pathogenic elements.
If we compare the product with other drugs of the antiseptic group, we can note that Chlorhexidine has no color or any odor, which means that this antiseptic is not toxic, does not leave marks on the skin, and does not cause pain to the patient when treating wounds, which is also significant advantages.
The drug does not have a negative effect on the healing process and does not lead to the formation of pronounced scars.
Chlorhexidine is completely safe , it does not cause allergic reactions or irritation of damaged tissues, and therefore is very often used to treat fresh skin lesions and disinfect them, along with regular hydrogen peroxide.
To treat fresh scratches, abrasions, various wounds, including postoperative wounds, in order to prevent the development of infection, a solution of the drug is used in a concentration of 0.05 - 0.1%. A solution of the same concentration can also be used to treat burns, as well as wounds in the oral cavity after tooth extraction.
A one-time treatment of the wound immediately after receiving it does not exclude the possibility of secondary infection, therefore, after washing, a sterile bandage should be applied, and if it is small, it can be sealed with a bactericidal plaster.
To treat wounds, it is recommended to simply pour a small amount of the drug onto the surface, wait a little, and then carefully blot the residue with a sterile napkin. Before carrying out such treatment, it is recommended to thoroughly wash the wound and the skin around it with water and laundry soap to remove any existing contaminants.
The drug in a concentration of 0.1 - 0.2% is often used for disinfection when performing various medical procedures , for example, when removing splinters, opening calluses and small abscesses, boils, when striking wounds that have dried to the surface of bandages, bandages, and plaster. A solution of this concentration is also used to treat the hands of medical personnel.
Is it possible to treat a tattoo with chlorhexidine?
Congratulations, you got a tattoo! The master applied a compress to you and wrapped you in cling film to prevent infections. But this is only half the battle on the way to beautiful, well-done work. How carefully you take care of your tattoo is directly related to its future appearance.
So, let's figure out how to properly care for a tattoo?
The first thing to do is to remove the film (no later than 2 hours from the moment you were wrapped), wash your hands with soap and wash the tattoo with running cool water and soap, wash off all the Vaseline. Excess moisture can be blotted with a cotton pad. Then wait until the water dries and then apply D-panthenol or Bepanten+ ointment.
Tattoo healing occurs within 7-12 days. At first, the tattoo site looks swollen and red - this will go away in 5-6 hours. During the healing process, crusts will appear on the tattoo, which will gradually disappear - this is a normal healing process, there is no need to be alarmed.
For the first three to five days, adhere to one of the following care options:
- Wipe the tattoo 2-3 times a day with a cotton pad soaked in Chlorhexidine, and after drying, apply a thin layer of D-panthenol or Bepanthen+ ointment.
- Buy baby diapers at the pharmacy. Wipe the tattoo with Chlorhexidine, after drying, apply a thick layer of D-panthenol or Bepanten ointment, cover the tattoo site with a diaper using a plaster. Wear the compress for 12 hours, then remove the diaper, wipe with Chlorhexidine and leave to “breathe” for the next 12 hours, repeat again for another 48 hours.
And now - attention! During the healing period, DO NOT:
- apply a thick layer of ointment to the tattoo
- take a bath, go to the sauna, pool, swim in ponds
- engage in active physical exercise, sports
- wipe the tattoo with alcohol, hydrogen peroxide and other means not specified in the care options
- scratch, hit, rub tattoo
- tearing off scabs from a healing tattoo
- wear synthetics and wool, only natural fabrics
- sunbathing and especially visiting a solarium
Among water procedures, only short-term, non-hot showers are allowed.
Our studio guarantees you a dense coloring, tattoos made in our studio do not float, do not lose color after a year or even after three or more, since we do not use application techniques that require constant correction of the work, which means you save your time and money .
We wish you pleasant care and speedy healing!
1.WHEN SHOULD THE BANDAGE BE REMOVED?
The length of time the protective bandage is preserved depends on the nature of the tattoo (intensity of work, size and intensity of the tattoo). The average time varies from 2 to 12 hours, I will tell you the exact time after the session.
Use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy, as well as breastfeeding a baby, is not a contraindication to the use of the drug.
Using the product to treat wounds is acceptable, but with caution. The drug has no toxicity and does not have a systemic effect. When treating damaged areas of skin, only a small part of the product can penetrate the bloodstream without creating a threat to the developing baby.
The drug does not cause any adverse reactions, so theoretically its use for external treatment of skin lesions cannot cause any harm to the unborn baby. Rather, on the contrary, an infection that penetrates a wound can enter the bloodstream through damaged blood vessels, and through it to other organs. The development of an infection anywhere inside the body will lead to an inflammatory process and the occurrence of diseases that will affect the development of the baby.
Therefore, the use of the drug for treating wounds during the period of bearing and feeding a baby is more than justified, but caution in use will not hurt.
Can chlorhexidine be used in dogs?
Chlorhexidine is safe for use in dogs. It can be used in the same way as many other disinfectants such as those mentioned above. Betadine . We can use it without first consulting a veterinarian, but they should be contacted if there is any doubt. This is if the wound is minor and can be treated at home. If our dog has serious injuries, they should be taken to an emergency veterinary clinic. Blood loss, infection and poor healing are some of the complications that can occur without proper treatment...
Not only is Chlorhexidine safe for dogs, but you should not bite them when using it. It acts as a barrier against bacteria, so a dog with a wound can be cleaned with chlorhexidine. It may also protect against fungal infection, although usually to a lesser extent. Depending on the concentration, chlorhexidine can have a bactericidal or bacteriostatic effect. First, the bacteria will be killed. In the latter case, it only works to limit its growth.
Is chlorhexidine safe for dogs ears?
Although chlorhexidine can be used to treat wounds on a dog's ear, we must be careful. Chlorhexidine is potentially ototoxic, meaning it can damage the ear. The outer part of the dog's ear will be fine, but if it is inserted into the ear canal, it can damage the vestibular system. This is especially true if the eardrum is already perforated. Do not inject chlorhexidine into the ear canal unless directed by your veterinarian...
Treatment of wounds in children
Children of different ages very often receive all kinds of injuries and wounds. Kids are very actively exploring a new world for them, and in the process of getting to know it, they do not do without abrasions.
Children learn to rollerblade and bicycle, play outdoor games, climb trees, swing on swings, play various sports, communicate with animals, and quite often they get various injuries that require antibacterial treatment in order to prevent the penetration of harmful microorganisms and spread infections.
Since Chlorhexidine does not have a toxic effect on the body, does not cause adverse reactions or allergic manifestations, it can also be used to treat wounds, abrasions and other skin lesions even in very young children.
How to replace Chlorhexidine when treating wounds
The most famous analogue of Chlorhexidine can be called Miramistin solution, which has the same properties and actions, has the same high efficiency and an almost similar list of indications for use.
Analogues of the drug:
- Miramistin is only a functional analogue, precisely because of its similar action, and although the main substance in these drugs is different, they can completely replace each other. The use of Miramistin, unlike Chlorhexidine, is not contraindicated for people suffering from any types of dermatitis.
- Akhdez-3000 , which has a pronounced fungicidal effect, suppressing harmful microflora in literally 30 seconds. After application to the skin or surface of wounds, the product remains effective for an hour if the injury remains open, and for at least 3 hours if a sterile bandage is applied or medical gloves are worn (when treating hands).
- Citeal is another analogue containing Chlorhexidine, along with Hexamidine and Chlorocresol. The drug belongs to the group of foaming antiseptic solutions used to treat hands and skin surfaces, as well as mucous membranes and all kinds of damage.
Which is better: Miramistin or Chlorhexidine
There is no clear answer to this question. It all depends on the person’s preferences and scope of application. Solutions are effective if used as directed. Miramistin is considered a more universal remedy , as it has a wider spectrum of action.
Chlorhexidine is most often used in the treatment of cosmetic instruments and manicure accessories. The disadvantage is considered to be the manifestation of side effects in the form of itching, dermatitis, and increased dryness. Especially if your skin is sensitive. There are no drugs similar to Miramistin. But Chlorhexidine is present in some medications. This includes:
- lidocaine throat spray;
- Anti-Angin tablets and lozenges;
- Drill lozenges
But among the analogues that can be used according to indications, there are:
- Hexoral;
- Inhalipt;
- Lugol;
- Novosept;
- Stopangin;
- Strepsils;
- Theraflu.