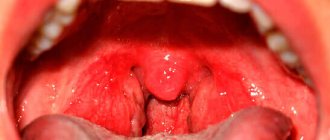
Having fallen ill with acute tonsillitis, many people do not pay due attention to it and are treated at home. However, tonsillitis, which is the medical name for the inflammatory process in the tonsil area, often leads to complications . One of them is the formation of tonsillitis plugs in the lacunae of organs, which are difficult to treat. Sometimes the most radical measure is applied to them - surgical removal.
A little about tonsils: anatomy
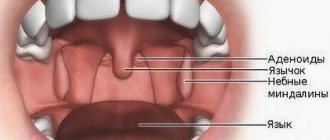
The tonsils (tonsils) consist of lymphoid tissue and are dotted with deep winding canals called lacunae. The latter turn into large crypts that permeate the entire organ. The glands are located in the nasopharynx and oral cavity, that is, right in the path of respiratory infections. Hence their main function is to protect the body from penetration of harmful agents.
Both the lacunae and the crypts of the tonsils have a large area, so everything that penetrates them from the outside is in contact with the lymphoid tissue for a long time, which stimulates the production of antibodies. In healthy people, the glands independently clear themselves of leukocytes, dead microbes and desquamated epithelial cells. This entire mass is released into the oral cavity, swallowed with saliva and destroyed in the gastric juice.
Tonsillitis plugs: what they look like and why they form
If particularly dangerous bacteria, for example, class A staphylococci, penetrate into the lacunae, an inflammatory process will develop in the tonsils, called tonsillitis or tonsillitis in medicine. The production of active substances by leukocytes to transmit impulses between cells will provoke dilation of blood vessels, thereby improving blood supply to the tonsils.
Photo: tonsillitis plug
Due to the expansion, the vascular wall will become more permeable, which will facilitate the flow of more leukocytes to the site of inflammation that fight infection. The release of the liquid part of the blood from the vessels will lead to swelling of the gland tissue.
Against the background of all these phenomena, the cleansing of lacunae will be disrupted - leukocytes, desquamated epithelium and dead microorganisms will accumulate in them and form pus. Since the process is stagnant, very soon the mass will become denser; such formations are called caseous plugs on the tonsils. If the pathology is not treated, pus will continue to form, and the inflammation will move deeper into the organ, provoking its destruction .
According to this scenario, an acute process develops. The disease becomes chronic under the influence of many factors. The fundamental one is the prolonged presence of infection, when the inflammation does not completely subside, and the remaining microbes are in the lacunae, provoking the release of leukocytes.
The absence of clinical manifestations of the disease contributes to its long-term course in a latent form. Blood cells and desquamated epithelium surround pathogenic particles, and from them plugs are formed on the tonsils, which can accumulate salts and harden.
Usually the formations have a white or yellowish tint, however, there are also gray, brown or red ones: the color depends on the substance predominant in them. The size varies from millimeters to centimeters.
Why traffic jams occur: background and etiology
The cause of tonsil plugs is inflammation in the throat area. It is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms against the background of decreased immunity, the development of caries, adenoids or chronic rhinitis. The most common culprits are group A streptococci, staphylococci, Candida fungi, adenoviruses, herpes virus, diphtheria bacillus, pneumococci and Coxsackie virus.
Most often, plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils indicate the occurrence of chronic tonsillitis, which occurs due to:
A sore throat that has not been completely cured. Self-medication or interruption of antibiotic therapy contributes to the establishment of pathogens in the organ. When the immune system is weakened, they actively multiply, and the pathology worsens.- Development of caries, periodontitis, periodontal disease and other infectious diseases in the oral cavity. The presence of a constant source of pathogens provokes inflammation in the tonsils.
- Frequent inhalation of air through the mouth. Hyperplasia of the nasal septum, their curvature and other reasons why nasal breathing is difficult.
According to WHO, chronic and acute tonsillitis are the second most common among all diseases. First place was awarded to caries.
Other reasons that lead to the formation of purulent plugs on the tonsils include:
- ecological problems;
- smoking;
- allergic reactions;
- structural features of the tonsils;
- immunodeficiency;
- hereditary predisposition.
Since during the inflammatory process in the area of focus there is intense movement of blood flow and lymph, infectious agents can spread throughout the body and contribute to its intoxication. This process leads to drowsiness, weakness, and absent-mindedness. And also to the exacerbation of chronic diseases or the emergence of new ones, for example, pneumonia, heart valve prolapse, rheumatism of the joints.
Tonsils are inflamed: causes
The main causes of tonsil inflammation lie in infectious diseases caused by viruses or bacteria.
Tonsils are inflamed photo
These microorganisms enter the nasopharynx or oral cavity through the most common airborne route and can linger on the surface of the mucous membrane, affecting it.
The most common reasons why these organs become inflamed are:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- adenoviruses;
- herpes virus;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- mycoplasma, etc.
And although representatives of pathogenic microflora are always present in the surrounding air in greater or lesser quantities, a person may not always get sick.
This is facilitated by a combination of circumstances,
such as contact with an infectious agent and a decrease in natural defenses, which may be due to:
- severe hypothermia;
- recent illness or exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- low quality nutrition, which can hardly be called balanced and sufficiently covers the need for vitamins and minerals;
- damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- stress.
Source: nasmorkam.net Depending on which of the tonsils is affected by a particular microorganism, they are distinguished:
1
Sore throat is an acute inflammatory process in the tonsils, which can occur with varying degrees of intensity. Therefore, catarrhal, follicular and lacunae tonsillitis are distinguished.
For the first, only slight tissue swelling, low temperature and mild pain are typical. In the second case, the signs are pronounced, and a white coating is visible on the surface of the mucous membrane of the organs.
With lacunar angina, there is an accumulation of pus in special physiological recesses of the tonsils - lacunae, which is accompanied by the appearance of bad breath.
2
Chronic tonsillitis is a disease that is usually a consequence of the lack of timely and complete treatment of sore throat. It is characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbations, which are accompanied by the formation of white plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils and mildly manifested symptoms.
3
Adenoiditis is inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil. The pathology is characterized by snoring, discomfort in the throat, mucus running down the back wall of the nasopharynx and a long, persistent course, with regular exacerbations.
Associated symptoms
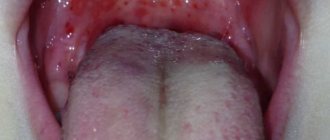
Caseous plugs in the throat against the background of lacunar tonsillitis do not pose a great danger. They are usually accompanied by soreness and bad breath, which occurs due to the decomposition of food residues and components of formations under the influence of hydrogen sulfide. Sometimes patients feel the presence of a foreign body, but only if the caseoses are large.
Photo: caseous plugs in the tonsils against the background of lacunar tonsillitis
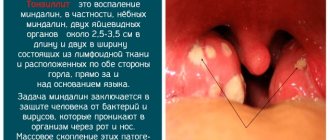
Severe symptoms develop if plugs of pus form in the throat against the background of follicular, phlegmonous tonsillitis or chronic tonsillitis. The person will be disturbed by:
- pain when swallowing food;
- increased body temperature;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the tonsils;
- soreness;
- intoxication.
Photo: purulent plugs in the tonsils against the background of chronic tonsillitis
As a result of such pathologies, connective tissue can grow, which leads to a change in the normal appearance of the oropharynx. Another possible complication is displacement of the tonsils in the opposite direction .
Caseoses are easily recognized by the white cheesy coating covering the tonsils. Since the stones are located deep in the cavity of the lacunae, the patient himself cannot see them, only external manifestations are available to him.
Symptoms
Acute inflammation of the tonsils is manifested by sore throat, sore throat, swelling and redness of the tonsils, intoxication - chills, fever, pain in muscles and joints. Inflamed tonsils become covered with purulent plaque. The lymph nodes located under the jaw become inflamed and painful.
Inflammation of the tonsils
- Catarrhal form is a superficial lesion of the palatine tonsils, manifested by persistent low-grade fever, sore throat, hyperemia, swelling of the tonsils and the mucous membrane around them. Pain in the throat is insignificant or completely absent.
- With follicular inflammation, fever and intense pain in the throat appear, radiating to the ears. On the surface of the tonsils, pustules are found - yellow-white follicles the size of a pinhead. The pharyngoscopic picture of follicular tonsillitis resembles a starry sky. Patients suffer from severe intoxication, chills, pain in the lower back and limbs, general weakness, and lack of appetite. The lymph nodes become swollen and tender to the touch. Children develop diarrhea and vomiting, and consciousness is impaired.
- Lacunar inflammation is the most severe form of pathology, characterized by the accumulation of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils. Patients complain of hoarseness or complete loss of voice. Swelling of the palatine tonsils prevents the vocal cords from closing normally, causing the voice to become hoarse.
rice. 1 – catarrhal tonsillitis, Fig. 2 – follicular tonsillitis, Fig. 3 – lacunar tonsillitis
- Fibrinous inflammation is characterized by the appearance on the surface of the tonsils of a continuous coating in the form of a white or yellow film. The disease is severe and can be complicated by brain damage.
- The phlegmonous form is caused by unilateral purulent melting of the tonsil. The pathology is manifested by fever, chills, sore throat when swallowing, salivation, bad breath, tenderness of enlarged lymph nodes and the general serious condition of the patient. The disease is complicated by the formation of a peritonsillar abscess.
Inflammation of the lingual tonsil
This pathology is quite rare, but it is very difficult. Typically, inflammation of the lingual tonsil is combined with damage to the pharyngeal or palatine tonsils. The cause of the pathology is injury caused by ingestion of rough food or careless medical manipulation.
Patients complain of pain in the mouth, which gets worse when the tongue sticks out. They have difficulty chewing, swallowing and pronouncing sounds, and have an unpleasant odor from their mouth. The tongue increases in size, which can lead to suffocation. Patients are forced to keep their mouth half open. Symptoms of intoxication are significantly expressed: fever, migraine, and enlarged lymph nodes. A purulent coating forms on the swollen tongue.
Inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil
The disease is called adenoiditis because it occurs in people with enlarged tonsils - adenoids. The pathology is manifested by fever, nasal congestion, mucus and pus. From the adenoids, the inflammatory process can spread to the auditory tube with the development of eustachitis, which is manifested by ear pain and hearing loss.
Inflammation of the tubal tonsils
Inflammation of the tubal tonsils has similar symptoms to ear pathology. Patients develop signs of intoxication, sore throat, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, and mucus or pus flows down the back of the pharynx.
Inflammation of the tonsils in a child has a more pronounced clinical picture than in adults. This is due to the imperfection of the children's immune system and its inability to cope with a huge number of microbes. Children become capricious, restless, and refuse to eat. A fever in a child can lead to seizures, and a strong cough often ends in vomiting.
Chronic inflammation of the tonsils is a source of infection in the body, gradually destroying the human immune system and disrupting the functioning of the excretory, cardiovascular, reproductive and nervous systems.
Inflammation of the tonsils in the absence of timely and adequate therapy ends in the development of complications: laryngeal edema, rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, polyarthritis, lymphadenitis, sepsis.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of tonsillitis, which is aggravated by plugs, is aimed at alleviating symptoms and destroying the pathogen. The most commonly prescribed antibacterial agents are Amoxicillin, Cephalexin, and Oxacillin. The therapeutic course is about 10 days. Sometimes the doctor recommends the use of macrolides, for example, Sumamed, Erythromycin. Such medications cannot be treated for longer than 3 days.
All antibiotics must be taken strictly according to the regimen determined by the doctor. Before use, a bacterial culture should be taken to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to the drug.
For any inflammatory process, treatment of the lesion with antiseptic agents is indicated . Inflammation of the tonsils with the formation of tonsillitis plugs can be treated with the help of drugs: Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine. Instead of solutions, antiseptics in the form of tablets and lozenges can be prescribed: Septolete, Faringosept, Strepsils.
If inflammation occurs with an increase in body temperature, antipyretic drugs are taken: Ibuprofen, Nurofen. And to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane of the tonsils - antihistamines, for example, Loratadine, Cetrin, Zyrtec.
Drug treatment
The nature of treatment depends on the causes and location of the pathological process. For viral infections, symptomatic therapy is sufficient, that is, helping to relieve the main manifestations of the malaise.
1
Medicines in the form of lollipops or sprays for sore throat (Strepsils, Orasept, Ingalipt, Decatylene, Chlorophyllipt tablets, Givalex, Tantum-Verde, Gorlospas, Septolete, Lizak, Faringosept, Lisobakt, etc.).
Medicines of this kind help eliminate pain, and some additionally have an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
2
Solutions for gargling (Givalex, Angilex, Chlorophyllipt alcohol, Furacilin or Streptocide solution, Rotokan, etc.). These medications are indispensable for the formation of plaque on the surface of the mucous membrane, since they contribute to the mechanical leaching of pus and dead cells.
3
Antipyretics (Panadol, Imet, Rapimig, Nurofen, Nise, Nimesil, Nimegesik, Efferalgan) are taken at elevated body temperatures.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are required to quickly cure the disease and eliminate the risk of complications.
A specific medicine should be selected exclusively by a doctor based on the severity of the situation and the characteristics of the person contacting him.
Initially, the patient is prescribed drugs for topical use (Isofra, Polydexa, Rinil). If their effectiveness is low, systemic antibiotics of the penicillin group are recommended:
- Augmentin;
- Flemoxin;
- Ospamox;
- Amoxiclav;
- Amoxicillin;
- Wilprafen et al.
If there is no effect after 3-4 days of treatment, they are replaced by representatives of the tetracycline group (Tetracycline, Doxy-M, Doxycycline, Unidox Solutab, etc.) or macrolides (Sumamed, Hemomycin, Azithromycin, Azivok, Azitral, etc.).
In difficult situations, when antibiotics do not give the expected results, a bacteriological examination of a throat smear is carried out to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease
and its sensitivity to various drugs. [ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1] For bacterial infections, the above-mentioned means of symptomatic therapy and gargling are also required.
In this case, you can add a few drops of iodine and soda to the rinsing solution, which will increase its antibacterial properties.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy procedures are not aimed at removing plugs from the tonsils, but at reducing the activity of inflammation in the tissues and preventing the progression of pathology. They are not recommended for use during exacerbations.
Types of procedures:
Ultraviolet irradiation. The effectiveness of the method is due to the fact that UV rays can destroy bacteria. Course duration is 10–15 sessions. A targeted effect on the foci of tonsillitis prevents further accumulation of pus and an increase in plugs.- Laser irradiation. It has an antimicrobial effect and improves blood circulation in the affected lacunar area. During the procedure, the patient does not feel pain, it lasts no more than 5 minutes. Treatment course – 6 sessions.
- Ultrasonic aerosols. The principle of the method is to introduce medications into deep almond lacunae using an ultrasonic device. Thanks to it, medications reach the most inaccessible places, which increases the feasibility of their use.
Physiotherapeutic procedures and drug treatment help improve the condition of tonsil congestion. But complete recovery is not achieved with them. Purulent plugs may be located not on the side of the throat, but in the depths of the lacunae, so they can only be removed using mechanical or hardware cleaning.
Removing traffic jams
To get rid of tonsillitis plugs forever, they need to be removed. Typically, the procedure is carried out in one of several ways: by washing, using a special apparatus or using surgery. The last option is the most radical. It is resorted to only as a last resort: if complications of purulent tonsillitis may appear.
This condition is characterized by a significant increase in sore throat. There is an increase in temperature to 40 °C and an increase in intoxication phenomena. The neck in the affected area swells, and usually the swelling appears on one side. There is no pus or tonsillitis in the visible area.
With lacunar angina, it is possible to remove purulent plugs by mechanical cleaning. The doctor presses the outer arch of the tonsil with a spatula - and liquid pus comes out.
Washing lacunae
Doctors rinse the tonsils using a syringe with a cannula at the end. Washing out is carried out after introducing the drug into the lacuna. The procedure is carried out 5 times, usually this is enough to remove all purulent formations. But the method may be ineffective if the passages of the gaps are too tortuous and deep .
Video:
Hardware removal
Rinsing the tonsils does not always give results, since plugs can form in the depths of the lacunae. In such cases, another method of extracting almond stones is used - using the Tonsillor apparatus. After the introduction of this method into medical practice, the effectiveness of treating tonsillitis doubled and the number of operations performed to remove tonsils decreased fourfold.
The principle of operation of the device is to extract the contents of the almond canals using a vacuum. After the procedure, the organ must be washed, this is done using ultrasound and phonoresis.
The ultrasound used in the device is capable of:
- lead to the death of bacteria;
- soften stones in gaps;
- improve blood circulation at the site of the lesion;
- slow down the formation of scar tissue;
- create a high concentration of medications at the site of inflammation.
You can get rid of pus in lacunae using the hardware method in 10 sessions. To consolidate the results forever, it is recommended to repeat the procedure after 6 months. If after using the method the patient continues to complain of a sore throat, the doctor will advise rinsing the tonsils with antiseptics: Theraflu LAR, Strepsils plus.
Surgical intervention
If there are significant changes in the tonsils with a complete loss of their function, the organs are completely removed. If the processes are reversible, methods are used to partially eliminate those areas of the tonsils where white plugs have appeared.
Tonsilloliths are removed under local anesthesia. There are many techniques for performing the operation: often the method of excision with scissors or a wire loop is used, and a little less often with an infrared laser. The latter method allows both cutting and joining fabrics, and the temperature in them increases insignificantly.
If you remove tonsils using a laser, the postoperative period will pass with minimal pain, without bleeding or swelling. But the method is used only for adults; it is unsafe for children under 10 years of age.
What does herpes sore throat look like?
A characteristic sign of herpes tonsillitis: the presence of blisters with red bloody fluid on the tonsils at the very beginning of the disease. If these bubbles are touched with a spatula or food, they will burst. Most often, the rashes are localized on the tonsils, palate and back of the throat.
5-7 days after the appearance of the first symptoms, the blisters open, and erosive rashes and ulcers are observed on the mucous membrane of the tonsils. Due to the dense fibrous tissue, it is impossible to open the resulting ulcers, the diameter of which ranges from 1 to 8 mm. Each ulcer is surrounded by a hyperemic cushion. In this case, the entire mucous membrane of the oropharynx turns red and swells, and salivation increases.
Herpes tonsillitis is accompanied by severe sore throat. After healing, the surface of the tonsils becomes pinkish.
Treatment of caseous plugs at home
It is unlikely that you will be able to remove tonsil plugs at home. Such manipulations are rarely successful, and there is a high risk of damaging the soft mucous membranes of the oral cavity , which can lead to inflammatory processes. However, in the treatment of chronic tonsillitis and to prevent the formation of almond stones, traditional methods are used.
To soften surface plugs, you can rinse your mouth with decoctions and solutions prepared at home. Recipe options:
Lemon juice, beetroot and honey are mixed in equal proportions and diluted with water. The mixture is kept in the mouth for more than two minutes, the recommended frequency of rinsing is 7 times a day.- A pharmaceutical collection consisting of rose hips, calamus, peony root, herb or St. John's wort, Leuzea root, wild rosemary is brewed in 250 ml of water and infused. The product can be used not only for gargling, but also for oral use.
How to treat at home? Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies can be perceived solely as a complement to drug therapy. The most effective way to relieve throat discomfort is gargling.
Here are a few recipes for the best way to gargle:
1
Sea salt solution. Take a teaspoon of salt for 200 ml of warm boiled water and thoroughly dissolve it. It is recommended to repeat the procedure up to 5 times a day.
2
Infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile flowers, calendula, string herbs). A tablespoon of the selected plant material or mixture is brewed in a mug of boiling water. It is advisable to cover the container with a lid. After the infusion has cooled to room temperature, gargle thoroughly several times a day.
3
Lemon juice solution. Squeeze 3 tablespoons of lemon juice into 200 g of warm water. The procedure is performed 2–3 times a day.
Features of treatment for children
In children, tonsil plugs appear more often than in adults. And since their immunity has not yet strengthened, antibiotic therapy and, even more so, removal of the tonsils are used only as a last resort, which complicates the treatment of tonsillitis.
The only safe and productive method is regular gargling and rinsing the tonsils . In both cases, you need to use only proven products with hypoallergenic effects.
If gentle methods are ineffective, antibacterial therapy is used. The child must remain under medical supervision throughout the course of treatment, and parents must not go beyond the scope of the treatment prescribed to them.
Functions, structure and purpose of tonsils in humans
The tonsils are one of the organs of the immune system.
Their primary task is to protect the body and especially the respiratory tract from the penetration of pathogenic microflora. By their nature, they represent lymphoid tissue, which is a source of lymphocytes - blood cells that fight various infectious agents. These organs have a loose structure, which favors the retention of microbes in them.
There are several types:
1
Palatine, which are often called tonsils. They are located between the palatine arches in special tonsillar niches.
2
Tubular, localized in the pharynx. It is impossible to see them during a normal visual examination, but the inflammatory process affects them quite rarely.
3
Pharyngeal, located at the vault of the pharynx and called adenoids. Accordingly, when inflammation affects these tonsils, adenoiditis is diagnosed.
This pathology is mainly diagnosed in preschool children, but it often becomes chronic, so sometimes the fight against it continues until adolescence.
4
Lingual, located at the root of the tongue. Its defeat, as a rule, is observed exclusively in adults and then extremely rarely.
Preventive actions
To avoid the formation of pus and purulent plugs in the tonsils, you must follow the following rules:
- Brush your teeth twice a day: morning and evening.
- Clean your mouth from food debris after every meal.
- Cure caries and other oral diseases in a timely manner.
- Get rid of pathologies of the sinuses and larynx.
- Stick to the basics of healthy eating.
- If necessary, strengthen the immune system with vitamin complexes.
- Avoid hypothermia.