2394
The appearance of various wounds, cysts, growths and tumors on the oral mucosa is a fairly common phenomenon in dental practice, which most often occurs due to mechanical damage to the gum tissue.
When extracting a tooth and not carefully following the recommendations of the attending physician during the rehabilitation period, various complications associated with damage to bone and soft tissue may occur. One of them is the development of jaw exostosis.
General overview
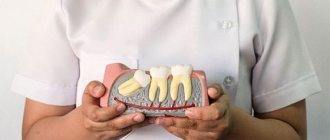
A jaw exostosis (often referred to as an “osteophyte”) is a fragment of hardened cartilage tissue protruding from the surface of the jaw. It has branches of a tortuous configuration.
It is a consequence of dental amputation and a number of other mechanical factors. When the amount is small, it does not cause physical discomfort.
As a rule, the main zone of localization of growths is the median palatal suture and the alveolar - its oral side in the area of the lower premolar organs.
All chewing reflexes in the presence of this pathology are completely preserved. Mucous soft tissues are also in a normal state.
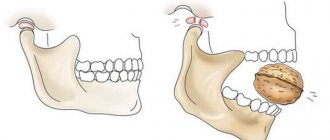
As the protrusions grow, the mucous membrane becomes thin and is constantly injured by sharp areas of the destroyed tooth. The mouth is no longer so easy to open, and when you press on the inflamed area, pain of varying degrees of intensity occurs.
Causes of exostosis in the mouth
The main reason is the removal of a dental unit and the peculiarities of restoring the edges of the socket. With complex removal, the risk of disruption of the recovery stages increases; the edges of the socket are not smoothed, but lead to compaction and the formation of bone spikes.
Other reasons are:
- Injuries of the jaw bones of any complexity.
- Previous operations on the jaw.
- Difficult tooth extraction.
- Implantation of jaw fragments before prosthetics.
An important role in the formation of jaw osteophytes is played by heredity, diseases associated with impaired binding of calcium and phosphorus, and organ failure with severe metabolic disorders.
The following factors can contribute to the development of pathology:
- Infections and inflammations leading to bone destruction (fistulas, fluxes, sepsis and others).
- Anomalies in the development of bones and teeth of any nature.
- Endocrine disorders and diseases.
- Cystic processes.
- Complicated dental history.
In the absence of contributing factors, the process of formation of exostoses can be started
with an additional gum incision and drainage.
Exostoses of the jaw can occur after tooth extraction surgery. The absence of a stage of smoothing the edges of the socket during traumatic extirpation leads to the formation of bone protrusions-spikes. Osteophytes can also be caused by injuries, incorrectly juxtaposed damaged fragments of the jaw, or old fractures. In the peripheral form of osteoma, osteophytes of osteogenic dysplastic origin appear along the edge of the jaw.
As a rule, small jaw exostoses do not cause any complaints. Bone growths can be identified when determining the degree of bone atrophy and assessing the level of compliance of the mucous membrane at the preparatory stage before prosthetics. Most often, exostoses of the jaw are localized in the area of the median palatal suture, as well as on the oral side of the alveolar process in the projection of the lower premolars. The opening of the mouth in patients with exostosis of the jaw is free and complete. The mucosa above the osteophytes is pale pink, without visible pathological changes, mobile.
As the bony protrusions increase, the mucous membrane becomes thinner, as a result of which the risk of injury to it by the base of the prosthesis or the sharp edges of the destroyed walls of the teeth increases. On palpation, exostoses of the jaw are dense formations with a bumpy or smooth surface, not fused with the surrounding soft tissues. Located in the area of the articular process, exostosis of the jaw causes pain. In this case, there is a restriction when opening the mouth, a displacement of the mental part to the healthy side, and a violation of occlusion. Regional lymph nodes are not palpable. The general condition of patients with exostosis of the jaw is not impaired.
There are two reasons why exostoses appear:
- consequences of removing a complex tooth, displacement of bone tissue that could not heal properly;
- individual structure of teeth and jaw.
The danger of growths on the gums is due to their strong pressure on adjacent teeth or on the bone itself. Pathology does not make it possible to install implants and wear them painlessly.
Often, gingival exostosis (ICD 10) is a problem identified during the installation of dentures in dentistry. The problem can be eliminated exclusively through surgery. If the bone growth is not removed, this anomaly can develop into a tumor. In turn, exostoses do not in any way complicate the functioning of the jaw or teeth, and do not affect the health of the oral cavity.
Video about exostosis
If you have developed exostosis of the jaw, treatment comes down to the only correct method - its elimination. During surgery, all excess bone or cartilage protrusions are removed and the surface of the oral cavity is smoothed. As a rule, general anesthesia is not required for the procedure. Local enough so that the patient does not feel the slightest discomfort.
There may be several reasons why exostosis may form on the gum, tooth surface or palate:
- Individual characteristics in the structure of the jaw;
- Heredity;
- Consequences of injuries, bruises and falls.
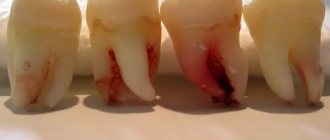
Sometimes exostosis appears after tooth extraction - the photos clearly demonstrate the clinical picture: the bone tissue on the surface of the alveoli does not smooth out, thereby provoking the growth of the tumor.
Removal of osteochondral exostoses is not always a mandatory measure. However, it still has a number of indications.
- Large size of bone growths and excessive rate of their increase.
- Discomfort and pain due to the pressure of formations on the jaw.
- Formation of cosmetic defects.
- Planned prosthetics.
Causes
In dental practice, the disease is classified as hereditary. Finding its manifestation even in infancy, exostosis rapidly progresses in adolescence.
If at this stage the formation is not too large, does not provoke jaw displacement and does not interfere with the patient, radical treatment is not prescribed.
Very often, as the body matures, the growth spontaneously resolves.
Other reasons causing the development of pathology may be:
- Inflammatory processes of an infectious nature , destroying the structural integrity of tissues and accelerating their partial atrophy.
These include syphilis in the chronic stage of its course, fluxes and fistulas, in the inner part of which purulent accumulations are observed, which over time turn into cystic formations. - Mechanical impact – injuries to the facial apparatus caused by negligence can cause displacement of the jaw and fragmentary destruction of its bone tissue.
- Deviations in the structure of individual segments of the dentition - their incorrect growth or angle of inclination causes curvature of the gum bone and forms nodular hardening.
- Disruption of the endocrine system – provokes hormonal imbalance and causes a failure of metabolic processes responsible for the qualitative composition of tissues.
Losing strength, they become vulnerable to external negative influences, self-destruct, and contribute to the appearance of focal formations.
In this case, the main reason for the development of exostosis is difficult removal.
Caused by incorrect actions of the doctor or the clinical picture, an amputated tooth often brings problems to the patient in the form of improper bone fusion or the presence of bone protrusions, which, as the wound heals, become overgrown with moving soft tissues.
Causes of development of alveolar process atrophy and degree of deformation.
Read here about indications and contraindications for tooth replantation.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/gemisektsiya-chto-eto.html all the most important things about hemisection of the tooth root.
What is exostosis?
For many patients, this pathology is better known as “bone spike.”
This is a growth on the jaw, which is formed from a cartilaginous base in the periodontal tissues. Gradually increasing in size, it appears under the mucous membrane in the form of a round lump or sharp peak. It is classified according to the type of osteophyte; it practically does not degenerate into malignant tumors. Exostosis on the gums refers to a special type of growths, the nature of the formation of which is still being actively studied by doctors. In the oral cavity, it most often appears near the base of the canines or front incisors, on the rounded part of the jaw. One or more smooth bumps are located on the outside near the inside of the lip, preventing the tongue from moving easily and making it difficult to pronounce sounds. If pathology is detected in the mouth, dentists recommend visiting an osteopath or orthopedist, because such problems often arise in several areas of the body at once.
In dentistry, exostoses (osteophytes) are associated with bone or osteochondral growths. Protrusions can form on the surface of the jaw, often on the roof of the mouth. They branch and have a tortuous configuration. Many factors provoke the development of this disease, but more often the growth appears as a result of an injury.
For a number of reasons, bone tissue begins to grow in a separate area of the jaw row. Externally, the growth resembles a cone, thorn or mushroom. Hardened cartilage tissue can damage the mucous membranes covering it, causing painful sores to appear on the gums or palate.
In the upper jaw row, neoplasms often appear in the area of the molars, both on the internal and external sides. Exostosis in the lower jaw develops mainly at the base of the incisors and canines. Usually the neoplasm is benign, although in medical practice there have been cases of its transformation into a malignant tumor.
Why does exostosis appear on the gums?
A bone spur on the jaw can appear at any age. Adolescents and elderly patients, middle-aged men and women equally often present with this defect. Sometimes such a lump is found in children during the period when baby teeth are replaced by molars. Doctors divide all causes of formation into two types: congenital and acquired. It has been proven that exostosis on the gums has a genetic predisposition, like other bone diseases.
Exostosis on the gum photo
The main reasons that trigger the pathological process of proliferation of cartilage tissue in the mouth:
- advanced periodontal inflammation, which was accompanied by suppuration and decay of tooth roots;
- chronic periostitis;
- endocrine disruption;
- traumatic tooth extraction, when the specialist did not bring the edges of the socket closer together or sutured the mucous membrane;
- injuries and fractures of the jaw.
The last two reasons most often lead to violations. Damaged tissues try to grow together, and a deviation occurs: cartilage cells actively increase in an arbitrary direction. Perhaps this peculiarity is associated with the reluctance of patients to follow all recommendations for jaw immobility after a fracture and refusal to apply fixing splints to the chin. With a genetic predisposition, the defect is almost always multiple and located symmetrically.
Main symptoms of the disease
In most cases, the formation of exostosis on the gums is completely asymptomatic. Initially, a compaction appears under the mucous membrane, which grows very slowly. Upon palpation, a person does not feel discomfort. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- formation on the jaw under the mucous membranes of a hard-to-the-touch lump with a rounded top;
- there is not enough space for the tongue when chewing or speaking;
- the gums in the area of the growth lighten and become white;
- spontaneously the person begins to lisp or “whistle”;
- There is asymmetry of the face on the part of exostosis.
Exostosis on the gum photo
A bone growth on the gum does not cause pain, but often causes inflammation: the inner surface of the lip or cheek rubs against the defect when chewing, leaving a wound. Bacteria and fungi easily enter it, and suppuration begins. It is necessary to immediately consult a dentist if the lump turns red, swelling has formed around it, and a cloudy liquid with an unpleasant odor appears.
In dentistry, there are two types of exostosis on the gums: the first grows from the tissue at the site of injury, the plate in the maxillary sinus and does not affect the roots of the teeth. The second is formed from the cartilage tissue of the joint that connects the two halves of the jaw. This is a more dangerous situation, because the build-up reduces the range of motion. Patients note that they cannot fully open their mouth, chew or smile. An aching pain grows in the corners near the cheekbones, making it difficult to rest and talk.
Factors of occurrence
Pathologies that occur in the human body must have a cause. Dentists believe that this disease is hereditary and begins to manifest itself at an early age. Further, as the body grows, exostosis progresses and increases. Or it simply dissolves during life, which happens very often.
Other reasons causing the development of the disease:
- Mechanical injuries. Damage to the jaws must be treated very carefully. In case of injury, there is the possibility of displacement of bone fragments or minor destruction of hard tissue.
- Infectious inflammations. They can destroy the structure of bones and lead to their partial atrophy (chronic syphilis, fluxes, fistulas, cysts, etc.).
- Incorrect growth of segments of the dentition. A shift in the angle of inclination of the bone beams causes the development of an irregular segment shape and nodular hardening.
- Endocrine system disorders. An imbalance in the production of hormones provokes deviations in metabolic processes that are responsible for the growth and composition of bones. Losing the necessary elements, they become fragile and easily vulnerable to mechanical injuries and focal formations.
This is interesting: Is it always necessary to remove supernumerary teeth - when is the procedure justified
? The main factor is the operation to remove the tooth. Doctor errors or a difficult clinical situation can lead to the fact that after complex retraction, the bone beams do not heal correctly and a protrusion is formed.
When should you see a doctor?
Sometimes the formation of plaque on the gums means that healing is difficult. Only a specialist can distinguish a normal fibrous film from manifestations of a pathological process.
If the wound bothers you, or you are not sure about the origin of the whitish layer, go to the doctor. In any case, the film should not be touched.
Deviations from the norm may be manifested by the following symptoms:
- The swelling of the mucous membrane has spread to the cheek and does not subside for several days.
- There is a deterioration in health and an increase in temperature to 39-40 degrees.
- The feeling of discomfort does not decrease. The pain takes on an acute, throbbing character. Sometimes my head, throat, and ears begin to hurt.
- There is no blood clot in the socket. Instead, a gray substance similar to pus appears in the wound. There is a putrid odor from the mouth. At the location of the pathology, the color of the mucous membrane changes to red.
- After a tooth is pulled out, the bleeding does not stop for several days, despite all the measures taken. This abnormality may indicate a bleeding disorder or high blood pressure.
Thus, a white film may indicate the development of a pathological process, but a person without medical education will not be able to distinguish the fibrinous layer from pus. In this regard, if alarming signs appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
White gum at the site of the extracted tooth may indicate incomplete extraction of fragments. This complication occurs very rarely and is due to insufficient qualifications of the specialist. Due to the high fragility of the tooth, the doctor is unable to remove the molar or incisor completely. After a few days, the gums become inflamed and suppuration occurs.
Also, the formation of a whitish film occurs for the following reasons:
- Wound infection. The patient feels acute throbbing pain, pus appears in the socket, and the gums swell.
- Dry hole. In pathology, the blood clot does not form at all due to vascular paralysis or falls out. A gray-white or brownish film forms in the wound.
- Alveolitis (see also: how to treat alveolitis that occurs after tooth extraction?). Most often, the disease develops due to the formation of a dry socket. The patient does not consult a doctor on time, food gets into the wound, bacteria multiply, which leads to the appearance of purulent plaque.
If there is any factor that worries the patient after tooth extraction, you should consult a doctor. Gray, greenish, yellow tints of plaque are not the norm. The specialist will examine the wound, remove the fragments if necessary, perform a procedure for removing pus and prescribe treatment.
How to treat gum exostosis after tooth extraction
The only way to get rid of the growth is through surgery. The decision to remove the lump is made in case of accelerated growth of the formation, severe pain and discomfort. In addition, bone spurs prevent further orthopedic treatment. Significant facial defects caused by an enlarged growth may also be an indication for surgery.
Like any surgical intervention, removal of exostosis is not indicated for everyone. If the functioning of the endocrine system, adrenal glands is impaired, diabetes mellitus, or certain blood pathologies are present, the procedure is impossible.
Before starting the operation, the doctor must make sure that the drug used for anesthesia will not cause an allergic reaction in the patient. Most often, local anesthesia is sufficient to remove exostosis, but sometimes general anesthesia is used.
The operational process takes place in several stages:
- A painkiller is administered.
- The oral cavity is disinfected with antiseptics.
- The gum tissue is cut, opening access to the tumor.
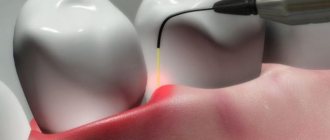
- The lump is removed. In this case, the doctor can use a chisel or a laser device.
- To smooth the relief and clean the surface from small particles, grinding of the bone tissue is carried out. The treated area must be cooled periodically to avoid overheating the bone.
- The edges of the incisions are sutured and a sterile dressing is applied.
The entire procedure takes 40-60 minutes using laser equipment. The operation using a standard instrument will take 1.5-2 hours.
In the absence of complications, 5-7 days are enough for complete recovery.
To ensure that the rehabilitation period does not drag on, you need to follow some rules:
- in the first few hours after the procedure, do not eat hard food so that the stitches do not come apart;
- do not eat too hot or too cold food;
- Avoid heavy physical activity for the first two to three days;
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages.
To avoid infection, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions. Minor swelling and pain should not be alarming; it is common after a surgical procedure. Painkillers and decongestant medications will help relieve them.
Sometimes the doctor may prescribe antibacterial agents to avoid the development of inflammation.
This is interesting: Treatment and removal of teeth with laser: pros and cons, how laser therapy is carried out
The procedure for removing exostosis usually does not cause complications. Problems can arise if you do not follow the recommendations of a specialist and ignore the rules of oral hygiene.
As a result, the stitches may come apart or severe inflammation may develop, accompanied by suppuration. In such cases, you should immediately consult a dentist to avoid more serious consequences.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to avoid the development of cartilage growth. You can only take some preventive measures to help detect the disease at an early stage.
Independent periodic examinations of the oral cavity using a mirror and palpation of gum tissue will help you notice existing defects and damage to the mucous membrane in time. Regular visits to the dentist, treatment of inflammatory processes, and maintenance of oral hygiene also contribute to the timely detection of pathology.
Is it necessary to remove the growth?
Only a doctor can give a definite answer. Since exostosis has no pronounced symptoms and does not cause discomfort at first, many patients do not pay attention to the problem. However, there are a number of factors that indicate the need to say goodbye to the bony protrusion. As soon as it starts to cause any problems, it must be removed.
Indications for removal of exostosis
- rapid growth or large size,
- pain in neighboring teeth,
- pronounced cosmetic defect (when a growth forms on the outside of the jaw),
- the danger of changes in bite, especially in a child (due to the pressure of exostosis on adjacent teeth),
- preparing the patient to wear orthopedic or orthodontic structures.
Good to know! Most often, bone protrusions on the upper jaw grow onto the outer surface, giving a negative cosmetic effect, but on the lower jaw - on the inner surface, causing discomfort when chewing and speaking.
Contraindications for surgery
- a history of severe chronic disease (tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, connective tissue diseases, bleeding disorders, etc.),
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity,
- jaw injury under treatment or rehabilitation.
Symptoms
Since at the initial stage the pathology is almost undetectable, the disease is diagnosed mainly when visiting a dentist.
At the same time, despite some vagueness of the symptoms, the manifesting factors do exist, and the signs by which exostosis can be accurately determined become more pronounced as the size of the tubercle increases.
The main symptoms of the pathology:
- the appearance of a convex growth of unknown origin. The relief surface of mucous tissues can have a different structure, from smooth and soft to rough, and sometimes spiky;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign object in the oral cavity that interferes with the normal movement of the tongue in the oral cavity;
- pain syndrome of varying degrees and intensity;
- partial dysfunction of the lower region of the jaw apparatus - observed in cases where the formation affects articular fragments;
- change in the shade of mucous tissues . From soft pink, the color of the mucous tissues gradually changes to brighter tones;
- a state of occlusion in which the obstruction of blood capillaries and vessels is quite pronounced.
How does the process of treating bumps on gums work?
Therapeutic measures depend on what caused the lump to appear. The dentist prescribes treatment based on the diagnostic data.
Dental intervention
The dentist selects intervention tactics and performs manipulations after establishing an accurate diagnosis.
- There is no clot in the socket . The hole is cleaned of tissues and microbes, treated with an antiseptic, and if necessary, a hemostatic sponge is added. The cone is opened, cleaned, and drainage is installed inside.
- Infectious, inflammatory process . The dentist opens the lump, releases the pus, then drains it. hole. The gums are washed with an antiseptic.
- Exostosis or cartilaginous growth on the bone . An incision is made in the area of the lump, and the tumor is removed with a special surgical cutter. The dentist then applies stitches. The patient comes for a follow-up appointment after 5-7 days.
What is common to all situations is the mandatory use of antibiotics. If there is no clot in the socket or an inflammation process is observed, this is a treatment measure; in case of exostosis, this is a measure to prevent tissue infection.
Medicines
Furacilin to alleviate the condition . The drug will not reduce the lump, but will disinfect the oral cavity and reduce the inflammatory process. You can replace the product with Chlorhexidine or Betadine .
After dental surgery, the patient is prescribed ointments with an antibacterial effect. The list of popular Metrogyl Denta is a gel that contains Metronidazole and Chlorhexidine . Relieves pain, inflammation, swelling. Apply generously 3 times a day. An alternative is Levomekol . The product kills bacteria and promotes tissue restoration.
Also, after opening the lump, the dentist prescribes oral antibiotics. This could be Nimesil to relieve swelling, Diclofenac for pain relief, Diazolin, Tsiprolet . After opening the lump, the patient is advised to rinse with Malavit , a natural remedy that consists of an extract of medicinal herbs. Fights germs, eliminates pain.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes will not help get rid of the problem, but only bring short-term relief. Be sure to contact your dentist. The doctor can independently prescribe folk remedies for complex therapy and better therapeutic effect.
- Traditional solution of salt and soda . This is a popular anti-inflammatory drug. In a glass of water you need to dilute 1 tsp. components. Do not perform active rinsing; light oral baths are sufficient.
- Salt and honey . The substances soften the lump and activate the release of pus. Stir thoroughly 1 tsp. salt and 2 tsp. honey, apply to the tumor. Do not rub.
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs . Chamomile , sage and calendula will have a calming and anti-inflammatory effect . Take herbs in equal quantities, mix, take 4 tbsp. prepared collection and pour boiling water over it. Cool and make mouth baths. The temperature of the broth should be room temperature.
If a lump appears after removal, warm compresses and alcohol tinctures are prohibited. They heat and irritate the mucous membrane, which leads to worsening of the condition.
Indications and contraindications for surgery
The following clinical cases can be considered the main indications for eliminating pathology surgically:
- accelerated growth of the bone protrusion;
- patient complaints of physical discomfort and inconvenience;
- pronounced cosmetic deviations due to progression of the disease and too large a growth;
- as a preventive measure before the upcoming organ replacement procedure.
Forced contraindications to the operation are:
- adrenal dysfunction;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- blood clotting pathologies;
- diabetes mellitus in all forms and stages of manifestation.
Preparation
The success of the treatment as a whole largely depends on how well the preliminary preparation for the upcoming operation is carried out.
The first thing the doctor will do after the initial examination is to refer the patient for an X-ray examination. This is the only way to accurately make this diagnosis. Based on the results of the image, the size of the anomaly, its shape and the exact location of the anomaly will be visible.
In addition, it is necessary to take a blood test to check for coagulation and the presence of pathologies that may become a contraindication. Sometimes it may be necessary to consult specialized specialists to identify diagnoses that prevent removal.
After a detailed history is collected, the specialist will select the optimal treatment regimen and, if necessary, prescribe a course of preliminary therapy.
The operation is indicated in cases where internal inflammatory or infectious processes are observed against the background of disease progression.
The presence of pathologies can complicate and sometimes completely prevent surgical intervention, which, unfortunately, remains the only way to eliminate the problem.
How is the operation performed?
How exactly is exostosis removed? This is a simple dental operation that takes on average 1-2 hours.
- administers local anesthesia (so the patient does not experience discomfort);
- cuts the gum in the place where there is exostosis;
- cuts down the growth with a drill or laser;
- polishes the surface of the bone;
- places stitches on the gum;
- if there was a hole or crack under the growth, a special implant plate is first applied to it;
- To facilitate healing, the doctor uses applications with antiseptic ointment (Solcoseryl or Levomekol).
There are two types of techniques used to perform the operation.
The choice of a specific technique depends on the location of the osteophyte:
- Removal of the palatine torus. In this case, the doctor makes a small linear incision and two releasing incisions - in front and behind. After this, the dentist peels off the mucous membrane and removes the osteophyte. Extraction can occur either once or in fragments. Next, the bone tissue is smoothed, and then interrupted sutures are applied.
- Removal of alveolar osteophytes. The execution procedure is no different from the previous technique. The main difference is in the configuration of the cut - here it has a trapezoidal shape. Otherwise, surgical treatment of maxillary and mandibular osteophytes is the same as removal of the palatine torus.
The duration of the operation lasts for a maximum of 2 hours. True, much depends on the size of the anomaly, its location and the complexity of the disease. After removing the growth, the doctor applies stitches and sometimes a special pressure bandage.
Surgical intervention
The procedure for amputating a bone protrusion is carried out in several stages:
- Administration of anesthesia - if the clinical picture is not associated with complications, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. In more complex cases, before administering anesthesia to the patient, a test for individual intolerance to the drug is performed.
- Treating the oral cavity with an antiseptic composition is necessary for complete sterility and minimizing the risk of infection of internal tissues at the time of surgery.
- Cavity incision of the gums - the surgeon uses a scalpel at a slight angle of inclination to conduct a cavity dissection of the soft tissue of the mucosa, opening access to the lesion.
- Lump amputation is carried out in two ways. Using a special tool - a chisel, or a more innovative method - using a directional laser beam.
- Grinding - bone fragments are carefully smoothed with a drill until they are given an almost even relief. This is necessary to prevent relapse. During the manipulation, cooled water should flow onto the bone.
- The final stage is the application of sutures and a sterile dressing.
On average, the duration of the operation, excluding preparatory measures, is about 40 minutes when working with laser equipment, and about 1.5–2 hours when using standard tools.
Let's find out together why a fragment may remain after tooth extraction, and what to do in such a situation.
In this publication we will talk about the stages of complex wisdom tooth removal in the lower jaw.
Follow this link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/pezohirurgiya-bez-boli.html to learn more about the benefits of using piezosurgery in dentistry.
How to prevent the formation of a growth on the jaw
Often people go to the doctor with a complaint about the appearance of a lump on the gum, which causes discomfort, interferes with chewing, and sometimes even speaking.
In dentistry, such a neoplasm is called exostosis, and modern treatment methods make it possible to get rid of it painlessly and quickly. Is this disease dangerous and who is most often susceptible to it? Let’s look at it in more detail in the article. Scientists still cannot name the exact causes of exostosis: the same factors provoke its growth in some people, but not in others. However, thousands of years of medical experience have made it possible to compile a list of provoking factors.
Causes of exostosis:
- anomaly in the structure or growth of the jaw (hereditary or acquired factor),
- jaw injuries after falls, bruises, gross surgical interventions,
- hormonal imbalance or other metabolic disorder,
- a complication after tooth extraction if the bone tissue has not healed properly,
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, including the bone.
Only a doctor can give a definite answer. Since exostosis has no pronounced symptoms and does not cause discomfort at first, many patients do not pay attention to the problem. However, there are a number of factors that indicate the need to say goodbye to the bony protrusion. As soon as it starts to cause any problems, it must be removed.
If there are indications for removal, exostosis is removed surgically. Only this way and no other way - no folk methods, lotions, rinses will help! Modern technologies make the process as painless and fast as possible.
Operation stages:
- the doctor prepares the area for intervention: treats the oral cavity with a disinfectant solution, administers local anesthesia,
- the gum in the area of the growth is incised so that the doctor can gain direct access to the bone,
- then the process of sawing off the osteophyte with a drill or laser and leveling the bone surface occurs,
- if the clinical situation requires it, the doctor applies a special preparation - the so-called artificial bone, which ensures rapid restoration of natural,
- Then the gum is sutured, the seam is treated with an antiseptic drug.
Since the reasons for the formation of osteophytes are different for each person, preventive measures are very conditional. For example, if exostosis appears as a result of a jaw injury, which often happens in athletes (especially those involved in martial arts), then prevention will consist of avoiding re-injury.
If the cause of the appearance of a bony protrusion is hormonal imbalances or inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, then you need to monitor your health and prevent the occurrence of these negative factors.
If the occurrence of osteophyte is genetically determined, then it is difficult to prevent the development of a regrowth; you just need to come to the dentist for an examination every six months in order to identify a new formation in time.
Jaw exostoses (osteophytes) are pathological bone processes on the alveolar arch or jaw bones, resembling spines, tuberous protrusions, and a tumor in appearance.
For a long time, exostoses do not manifest themselves in any way and do not cause discomfort when chewing or talking, so bone tumors are diagnosed by chance.
- Frequent localization is the upper jaw on the side of the inner surface of the cheek near the alveolar process (location of the wisdom tooth).
- When localized on the lower jaw, exostoses are diagnosed on the side of premolars, and sometimes incisors, canines, and molars.
- There is exostosis in the area of the median palatal suture - such growths are detected in newborns; as they grow older, the tumors increase in size.
In most cases, the formation and initial development of a bone tumor occurs without symptoms.
- Palpation of tubercles or bumps in submucosal structures.
- Foreign body sensation: you can feel the lump with your tongue.
- Change in the shade of mucous membranes in the pathological focus.
- Changes in bite and mobility of the lower jaw.
In severe cases - for example, with multiple or advanced exostoses - there is asymmetry of the face, disturbances in occlusion and bite, and tooth loss due to loosening of the root.
Treatment of bone growths on the jawbone cannot be conservative; drug therapy is exclusively symptomatic in nature - for example, in case of infections, stomatitis, aphthous ulcers.
Surgery is prescribed only for special indications; usually, with a small tumor volume, wait-and-see tactics are limited.
- Rapid growth of neoplasms.
- The size of the changed bone is too large.
- Soreness.
- Impaired tooth mobility.
- Changes in facial features, asymmetry, malocclusion.
- The emergence of chronic oral diseases.
- The need to install orthopedic structures.
- Preparation for prosthetics.
If exostoses grow through the maxillary bones, a pronounced cosmetic defect occurs. Localization of the growth on the lower jaw leads to disruption of occlusion (incomplete closure of the jaw), the chewing process, affects speech, and salivation.
- Severe chronic diseases (pathologies of the heart, kidneys, liver, blood).
- Active phase of tuberculosis.
- Diabetes.
- Acute infectious and inflammatory disease of the oral cavity.
- The rehabilitation period after a jaw bone injury.
The operation is not performed during pregnancy, lactation, or acute sinusitis.
First, the main obstructing factor is stopped, after which surgical intervention is resorted to.
Removal is carried out only after assessing the potential risks and expected benefits for the patient.
A consultation with an anesthesiologist is required. So, if the exostosis has an accessible localization, you can limit yourself to local anesthesia. If bone growth requires complex surgical intervention, then general anesthesia is required.
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Fixation of the jaw with special clamps.
- Antiseptic treatment.
- Making a cavity incision, exposing the exostosis.
- Removal of bone tissue using a laser beam or surgical chisel.
- Grinding sharp ends, applying antibacterial composition.
- Suturing the wound surface with self-absorbing threads.
- Final antiseptic treatment, application of a sterile bandage.
The duration of the operation varies, depending on the complexity, within 40-90 minutes.
The intervention is carried out in surgical hospitals, after removal a control X-ray is taken.
Exostoses, as a rule, do not hurt or cause discomfort. Most often they form in children under the age of 20 during the formation of the skeleton and bone tissue, however, pathology also occurs in adults.
It is necessary to remove bone growths for several reasons:
- violation of aesthetics: exostoses look like white balls on the gums, which are noticeable when smiling,
- growths often increase in size,
- possible transition to a malignant form,
- if it is necessary to install implants or prostheses, exostoses will become an obstacle to the procedure, since the prostheses will injure the growths, and the implants simply cannot be fixed due to a violation of the quality of the bone tissue.
Expert opinion
Vasilyev Alexander Alexandrovich Implant surgeon Experience 7 years “Exostoses do not always have external manifestations - often they can only be detected on photographs when diagnosing other diseases. However, the examination uses an x-ray - a targeted image of one tooth. Or, more effectively, an orthopantomogram. It allows us to examine the condition of the jaw bone and tooth roots along the entire row, because growths are often formed in multiple quantities.”
We suggest you read: How long does pain go away after tooth extraction?
Rehabilitation
If everything went without complications, the rehabilitation period is about 5 days. This time is enough for the wound to heal and the bone tissue to return to its normal position.
The operation to remove exostosis is classified as simple surgical interventions.
However, for patients with poor physical health or serious chronic diseases, the doctor may prescribe a control course of antibiotics to consolidate the positive result and eliminate inflammation of the internal tissues.
To protect the stitches, during the first hours after the procedure, you should eat only soft foods, bringing them to the consistency of puree.
Important:
- Avoid temperature changes in the oral cavity, do not touch the affected area with your hands or tongue.
- In the first two days, limit physical activity, rest more, and do not play sports.
- Completely eliminate alcohol and smoking - these habits inhibit the natural processes of cellular tissue regeneration, preventing their rapid healing.
A slight increase in general body temperature during the first 24 hours is considered normal.
Why does exostosis appear after tooth extraction?
To date, scientists have not been able to establish the exact causes of gum exostosis. Predisposing factors for the development of the disease include:
- injuries received as a result of mechanical impact, for example, after a poorly performed tooth extraction operation;
- inflammatory processes;
- heredity;
- endocrine disorders.
The tumor begins to form as a result of excess tissue growth. This process usually starts after surgery, a crack or a fracture.
The most common cause of exostosis is tooth extraction. If during the operation the surgeon violates the tooth extraction technique, the periodontal tissue may become displaced or deformed. A doctor's mistake leads to the formation of a protrusion on the jaw.
After a poorly performed operation, patients begin to feel a tumor in their mouth. It is easy to detect if you run your tongue along the damaged area of the mucosa.
Sometimes a protrusion after tooth extraction appears not due to the doctor’s fault, but due to hypercalcemia. Excess calcium in the body causes it to settle on the bones. This mineral is found in large quantities in dairy products, eggs and hard water.
Possible complications
The specificity of the disease is that almost all complications arise due to the negligence of the patients themselves.
Failure to comply with doctor’s recommendations, ignoring the rules of personal oral hygiene at the rehabilitation stage, neglect of diet can provoke:
- partial or complete divergence of postoperative sutures - this may be caused by excessive mechanical stress on the affected area or consumption of fairly hard foods;
- inflammatory manifestations - swelling of the tissues surrounding the wound occurs. Later, purulent accumulations are observed at this place. The main reason is poor wound care and poor hygiene.
Prevention
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely exclude the occurrence of the disease due to the reasons that provoke its formation.
However, the patient is quite capable of somewhat reducing the likelihood of developing pathological processes, as well as identifying the disease at an early stage of its course.
The basic rule is self-diagnosis. Regular examination of the oral cavity will allow you to notice the slightest external anomalies in time.
To do this you will need a mirror and good lighting. With clean hands, you should gently but thoroughly palpate the jaw rows, gums, surrounding soft mucous tissue, palatal area and floor.
Not only the presence of seals and growths, but also unpleasant sensations when pressing should be of concern.
If you manage to notice something, consult a doctor immediately. Treating a disease at the stage of its formation is much easier, faster and cheaper.
Price
The cost of the operation is determined by the region, the status of the medical institution, the qualifications of the specialist, as well as the complexity of the clinical situation and the chosen method of manipulation.
On average across the country, the cost of exostosis removal varies from 2,200 to 3,000 rubles.
This amount does not include:
- consultation with a doctor – from 400 rubles;
- cost of anesthesia – from 300;
- price of antibiotics and other drugs.
Reviews
It is important for patients who are faced with a similar problem in practice to understand that they should not ignore the situation. Exostosis can be easily eliminated in the early stages; the main thing is to diagnose it in a timely manner.
If you are interested in the problem discussed in the article, the causes of its occurrence and ways to eliminate the pathology, you can leave your comment in the appropriate section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: operations in dentistry, tooth extraction exostosis
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
What is bite height and how important is its correct determination?
Next article
Simpl Swiss implants are the best solution to dental problems