Tooth extraction for overcrowding
This is the most common reason. Crowding can be caused by a discrepancy between the size of the jaw and the size of the teeth, or incorrect replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. For example, when several milk teeth fall out ahead of schedule and permanent ones are displaced in their place, becoming an obstacle to the eruption of other teeth, which should be located in this place subsequently. As a result, the erupting teeth do not have enough space in the jaw. Incorrect positioning of tooth buds also leads to disruption of teeth eruption and subsequent crowding of teeth.
There are several ways to get space for closely spaced teeth:
- expand the dentition;
- “tilt” the front teeth forward;
- separate individual teeth;
- move the lateral teeth back;
- remove part of the teeth.
In order to make the right decision, the doctor analyzes the inclination of the front teeth using x-rays and photographs. Using a special telex-ray image, assess the inclination of the teeth in degrees; three-dimensional computed tomogram - determine the presence of bone tissue near the roots of the front teeth and determine the possibility of teeth tilting forward.
Assessing the bone tissue outside the lateral teeth allows you to decide whether it is possible to resort to expanding the dentition. Also, preliminary diagnostics allows you to determine the condition of the gum tissue and predict the results of treatment.
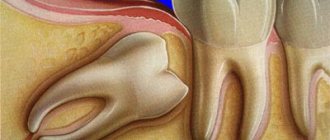
Distalization of posterior teeth, or moving posterior teeth backwards, is more often performed in adolescents. This is due to the fact that achieving a stable position is quite difficult - several years after removing braces, the teeth may return to their original position. Performing distalization involves removing wisdom teeth or missing them.
Grinding or separation is advisable when it is necessary to obtain 4–6 mm in the dentition. In other cases, the doctor suggests removal. It is also practiced when the above methods are impossible.
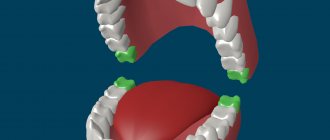
Tooth extraction makes it possible to obtain the maximum amount of space in the dentition. Basically, the fourth or fifth teeth are subject to removal - this allows you to get up to 8 mm of space on each side. Removal may not be carried out on both sides - if the amount of crowding varies significantly.
Deciding which tooth should be removed is important taking into account several parameters:
- Amount of crowding. The larger it is, the more advisable it is to remove a tooth located close to the front ones; this will allow uneven teeth to “stand up” correctly. Often fourth teeth are removed. Removing further teeth carries the risk that the back teeth will want to take up the empty space.
- Condition of teeth. All other things being equal, those teeth that are in the worst condition are subject to removal.
- Size, shape of teeth, jaw dimensions.
- The bite is correct or has defects.
Tooth extraction
Typically, the tooth extraction procedure is carried out in the first half of the day. The patient is advised to eat three hours before surgery. First, the dentist interviews the patient and examines his medical history. The patient also needs to take an x-ray of the problem teeth so that the doctor has complete information about the number of roots they have and their location. If the patient has inflammation that needs to be stopped, then in this case the dentist determines the treatment tactics on an individual basis. Before proceeding with tooth extraction, the specialist determines the method of pain relief suitable for the patient and selects anesthetics for him. In this case, both local and general anesthesia can be used. Typically, during tooth extraction, dental forceps or elevators are used, with which the dentist rocks the tooth back and forth or rotates it around an axis until the periodontal ligament is sufficiently destroyed and the supporting alveolar bone is compacted and expanded, causing the tooth to be loose enough to be removed. . If the tooth is in a normal position and access to it, the doctor uses the usual method of removing it, which consists of the following steps:
- separation of the circular ligament from the tooth;
- forceps delivery. To do this, the doctor selects an instrument of a certain group, which is designed to remove a specific type of teeth or jaw;
- advancement of the cheeks of the forceps, their closure and fixation;
- rotation (rotation of the tooth around an axis) or luxation (rocking of the tooth) to break the periodontal ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket;
- traction of the tooth, or rather its extraction from the alveoli;
- sewing up the hole with thread.
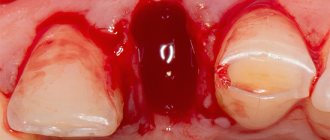
When removing complex multi-rooted teeth, a drill is sometimes used to cut the roots and extract them in parts. After the process is completed, the hole is inspected and the edges of the wound are compressed in order to reduce its size. Then a gauze pad is inserted for about 20 minutes. At this moment, a blood clot should form in the hole, which helps speed up healing and protects the wound from infections. Typically, the tooth extraction procedure lasts about 90 minutes. If there is no access to the tooth or its incorrect location, removal is carried out surgically. In the gum above the tooth, the doctor makes a crescent-shaped incision in the mucous membrane down to the bone, which faces its convexity towards the crown of the tooth. Then the gum flap is turned away and the root is hollowed out using a special instrument (osteotomome). After which the dentist returns the gum flap to its place and applies sutures. The patient can be sent home immediately, but only after the doctor is sure that there is no bleeding or formation of a blood clot in the socket. The specialist also gives all recommendations for wound care in the postoperative period.
Tooth extraction for malocclusions
Distal and mesial occlusion are in many cases indications for tooth extraction. The relative position of the jaws is assessed using teleradiograms, making plaster models, and photographs. In some cases, a computed tomography scan of the jaws is performed.
With a moderately pronounced distal bite, removal of teeth in the upper jaw helps to reduce the size of the upper dentition, which brings it into line with the lower one. The presence of crowding of the teeth of the upper jaw is an additional indication for extraction (removal).
With mesial occlusion, removal of teeth on the lower jaw also compensates for the discrepancy in size.
How is tooth extraction performed?
This procedure is a minor operation. But there's nothing wrong with that. All actions are carried out under anesthesia. Our dentists use a variety of medications. The desired tooth is removed using special tools. Our doctors work carefully and try to perform the operation quite comfortably, preserving the jaw for subsequent implantation. If the patient wishes, the implant can be installed immediately (in the vacant space). If there is no such need, then sutures are placed on this area. Our center also performs simultaneous removal of the rudiments or the four wisdom teeth themselves. We have a talented maxillofacial surgeon Ruben Araikovich Khachatryan.
Removal for asymmetry of dentition
Asymmetry occurs for several reasons:
- premature removal or loss of milk teeth - eruption of permanent teeth “out of place”;
- asymmetrical removal of permanent teeth - in this case, the remaining teeth are displaced due to the resulting free space.
The result of tooth displacement is a violation of the midline - the line of contact of the two central incisors. It should correspond to the midline of the face or the center of the lip. A displacement of more than 3 mm is noticeable not only to a professional, but also to an ordinary person. This situation requires the removal of a tooth on the side opposite to the direction of displacement.
Tooth extraction procedure
Before removing a tooth, the dental surgeon evaluates the indications and contraindications for removing a particular tooth. To do this, a targeted X-ray or OPTG (panoramic image) is taken - in this case, all teeth are visible in the image at the same time. The degree of complexity of the operation is assessed.
Anesthesia
Before administering a painkiller, your doctor will ask if you have ever had an allergy to painkillers. Currently, our clinic uses very thin needles and special syringes to administer the anesthetic, which allow the drug to be administered very slowly. In addition, our dental surgeon uses a special anesthetic gel, which simply lubricates the gums, after which the patient does not feel the injection of the needle or the injection of the drug at all. So there is no need to be afraid of tooth extraction and pain relief.
Competent tooth extraction
The tooth is held in a special place for it - the socket - with the help of periodontal ligaments.
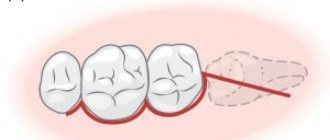
Therefore, before removing a tooth, you need to expand the hole in which this tooth “sits”. To do this, the dentist grabs the tooth with special forceps and loosens it back and forth. In this way, it is possible to separate the tooth to be removed from the periodontal ligaments that secure it. Once the tooth is loosened and there is no longer anything holding it in the hole, it is easily removed from it. In some cases, the tooth may “settle” too firmly in the socket, or it may have roots of a complex shape, which does not allow the tooth to be sufficiently loosened and the socket to widen. In such cases, the tooth is cut into fragments, and each piece is removed separately.
After tooth extraction, the hole is sutured so that the restoration process is quick and safe.
Observation
Tooth extraction is the most important, but not the last stage of treatment. After the surgeon completes the tooth extraction procedure, he will give you recommendations on how to behave in the next 24 hours after removal. As a rule, the doctor can invite you after tooth extraction for an examination a few days later at a time convenient for you to monitor the healing process.
Features of orthodontic treatment after tooth extraction or loss
If a side tooth is lost, the problem is solved in one of two main ways:
- prosthetics - replacing a lost tooth with an artificial one;
- closing the resulting space by displacing the remaining teeth (performed using a brace system).
Of course, orthodontic movement to the site of an extracted tooth is extremely rarely practiced independently. Often, this approach allows you to solve several problems at once - aligning the dentition, normalizing the bite.
Removal of wisdom teeth during orthodontic treatment
Removal of the “eight” can be carried out for preventive purposes - to avoid crowding during their eruption. But the doctor makes this decision for other reasons:
- The “eight” is affected by caries, severe destruction.
- Wisdom tooth root cyst.
- Figure-of-eight pressure on the adjacent tooth, promoting destruction.
- Pericoronitis, etc.
In orthodontic terms, wisdom teeth can interfere with distalization - moving the side teeth back, but such a need arises quite rarely. Therefore, it can be argued that the main reasons for removing wisdom teeth are of a general dental nature.
Prices for removal of wisdom teeth in Moscow
| Name | Cost, rub. |
| Primary appointment with a dentist or surgeon 1. Examination 2. Consultation 3. Documentation | 440,00 |
| Repeated appointment with a dentist-surgeon | — |
| Removal of an impacted, dystopic tooth 1. Application and injection anesthesia (according to indications) 2. Formation of a mucoperiosteal flap 3. Formation of access to the tooth 4. Complex tooth extraction 5. Hemostasis 6. Bandaging 7. Suture application 8. Suture removal 9. Repeated observation 10 .Price does not include x-ray | 9900,00 |
Delayed deletion
Making the decision to have a tooth removed is not an easy task. There are no strict standards and regulations - each person has individual characteristics of the structure of the dental system and health in general. It all depends on the experience, professionalism and knowledge of the doctor performing orthodontic treatment.
There is a list of factors whose influence is difficult to predict. They can affect the progress of the treatment process and force a change in plan. Each time, to make the right decision, the doctor evaluates and takes into account the effect of these factors - if there is a possibility of their possible influence on the correction of the position of the teeth, a “therapeutic diagnosis” takes place. This means that if there is doubt about the need for removal, treatment is started without the last one, and after the first stage the specialist evaluates the situation again. This minimizes the risk of making bad decisions. Orthodontic treatment without tooth extraction can also lead to desired results.
Why should you not be afraid of tooth extraction during orthodontic treatment?
Common concerns of patients when it is necessary to remove healthy teeth are the following:
- Fear of the procedure - fear of pain or discomfort. In most cases, the anxiety is not justified - the use of modern anesthetics relieves discomfort.
- Anxiety about the aesthetics of a smile - fear of a defect in the dentition. If teeth are removed for the purpose of implementing an orthodontic solution, there will be no gaps left at all - neighboring teeth will be located in the place of the removed tooth. Until the end of orthodontic treatment, the resulting gap can be effectively masked using special onlays.
- Worry about chewing function. A healthy tooth is, of course, of great value, but do not forget that if it interferes with the creation of a correct bite, then the entire dentition will function poorly. Bite defects lead to disturbances in chewing function, increased wear of certain groups of teeth and other consequences. In many cases, it makes more sense to remove one healthy tooth and keep the rest.
Orthopedic indications for tooth germ removal
Why do our orthodontists insist on complex extractions of teeth that are still in their infancy? This decision of the specialist is determined by certain features of the patient’s orthodontic condition:
- crowding of teeth (removal of the tooth germ as a preventive measure for crowding);
- before installing braces (to eliminate the risk of tooth displacement during treatment);
- the need to prevent relapse after orthodontic treatment;
- in cases where the rudiments are supernumerary teeth;
- the presence of a rudimentary dental tubercle that threatens to distort the normal position of full teeth;
- situations where the appearance of a new tooth can cause a defect in an even dentition.
In our work, we often encounter the need to remove tooth germs in order to reduce the time of orthodontic treatment, which often requires additional space in the dental arch. In some cases, excessive expansion of the dentition is undesirable, which negatively affects the maxillofacial parameters. These considerations may also be a sufficient basis for the removal of individual teeth in their infancy.
How is tooth extraction performed during orthodontic treatment?
Tooth extraction during orthodontic treatment is carried out similarly to conventional extraction performed for general dental reasons. The procedure is accompanied by mandatory local anesthesia. In rare cases, the issue of anesthesia is resolved - it is necessary when a large number of teeth need to be removed or there is an allergic reaction to local anesthetics. If the patient is afraid of the intervention, the doctor may suggest sedation or other methods to promote relaxation.
In many cases, tooth extraction precedes the installation of braces. It is worth noting that the procedures are not carried out in one visit to the doctor. After tooth extraction, a certain time must pass - this is necessary for tissue healing. As a rule, one week is enough, but this issue is resolved taking into account individual characteristics, the patient’s age, the condition of the dental system, the ability to regenerate and other issues.
Stages of wisdom tooth resection (removal):
- anesthesia - injection anesthesia;
- opening access to the bud - peeling or incision of the gum;
- extraction of a dental unit using universal forceps, an elevator;
- treatment of the gum surface with an antiseptic - cleaning, rinsing the socket;
- suturing and bandaging.
The procedure for resection of wisdom teeth buds takes no more than 30-40 minutes. Its duration depends on the number of units removed at a time, their depth, size and position. Advances in modern medicine make it possible to perform such an operation absolutely painlessly.
Methods of pain relief - general anesthesia or local anesthesia
General anesthesia for children during dental treatment is used in cases where all 4 rudiments are removed at the same time. If resection of units is carried out one rudiment at a time, local anesthesia is used. General anesthesia has a negative effect on the entire body as a whole, but helps solve the problems of patients with panic fear of the dentist. Sometimes such anesthesia is the only way to provide dental care. But in all other cases, it is better to give preference to local anesthesia, selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the child. Important. A contraindication to wisdom teeth removal is the absence of adjacent units. In the future, such molars can be used as a support for prosthetics.
Possible complications
Complications after surgical removal of buds are extremely rare and most often arise due to accidental infection of the open socket. Finding himself in such a situation, the patient complains of pain and bad breath. The gums become inflamed and the temperature rises. To prevent complications, you must strictly observe hygiene and the prescriptions prescribed by your doctor. Important. In the first 5-7 days after resection, the patient may feel aching pain. This is fine. Every day it will decrease. If this does not happen, complications should be ruled out by visiting a dentist.
Contraindications to tooth extraction
Even when an optimal treatment plan for malocclusion is drawn up, which involves tooth extraction, this procedure may be postponed or even contraindicated. As a rule, we are talking about general somatic, endocrine, cardiovascular diseases, and blood clotting pathologies. The specialist will also postpone the procedure in case of exacerbation of chronic diseases, elevated body temperature, or pregnancy of the patient.
Dentists strive to save every patient’s tooth, but some cases require taking care of the bite and overall aesthetics of the smile, at the cost of one or more teeth. If the orthodontist has proposed such a solution, it is important to rely on the professionalism of the specialist - the result of treatment will be a beautiful and healthy smile.