Fights, accidents and falls from heights lead to multiple tooth fractures. It is quite difficult to break the lateral or lower teeth, but the upper incisors are often damaged. In childhood, injuries are increased, and dental disorders account for a very large percentage. If we are talking about baby teeth, then we manage to get by with minimal losses. The situation is more complicated with permanent teeth. Gum disease leads to increased dental trauma. To identify the cause of dental problems, you should know your medical history and provoking factors.
Tooth fracture
A tooth fracture is a tooth injury in which it breaks in the area of the crown or root.
Depending on the location of the fracture, the tooth can be preserved, restored, or removed to avoid the formation of a focus of inflammation with subsequent tissue destruction. Incisors are more susceptible to such injuries due to their location. When a tooth is fractured, its mobility can be observed, and the person experiences sharp, severe pain. It is often accompanied by incomplete dislocation.
Traumatic dental damage most often occurs in childhood. But if the loss of a baby tooth does not have long-term consequences, then injury to a permanent one can become a serious problem.
The cause of injury can be not only a fall from a height, a fight or an accident. You can also break a tooth while eating if you encounter something too hard. Unhealthy gums can also contribute to fractures.
Bleeding from the socket after tooth extraction
Often, after tooth extraction, bleeding occurs from the socket (hemostasis), which occurs due to rupture of ligaments and capillaries (blood vessels). The complication may appear immediately, or maybe after a few days. Hemostasis can be stopped using a gauze pad, which the doctor places on the bleeding area for 15-20 minutes. During this period, a clot forms in the socket, after which the bleeding usually stops. If this does not happen, then stopping is done in other ways: by suturing with catgut, using hemostatic paste (sponge), applying fibrin film, or using special preparations in the socket.
Recommendations after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the patient is allowed to go home if there is no bleeding from the socket. The doctor gives the patient the necessary recommendations, which must be strictly followed. If these rules are followed correctly, bleeding can be avoided.
- At least three hours should pass from the moment of tooth extraction to the first meal.
- It is strongly recommended not to smoke within three to five hours after tooth extraction.
- On the day of surgery, avoid physical activity and lifting heavy objects.
- Also, on the day of removal, you should not eat hot food, steam or take a hot bath.
- When brushing your teeth, be especially careful on the side where the tooth was removed.
- Do not take medications that contain aspirin (this drug thins the blood).
- The next day after surgery, carefully rinse your mouth with a warm, weak solution of potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine or furatsilin. This cannot be done on the day of removal.
- To speed up healing, you can carefully rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile and sage), and also lightly lubricate it with sea buckthorn oil.
- Do not touch the wound with your fingers (even your tongue), stay as far away from drafts as possible.
It often happens that bleeding from the socket appears several days after the operation. There may be several reasons for this: a complex removal procedure, accidental injury, poor blood clotting, a jump in blood pressure, problems with a herbal clot, as well as failure to follow the rules recommended by the doctor.
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
If bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth occurs far from the clinic, then you can stop the bleeding at home yourself. To do this, you need to use the following method: make a thick tampon from a sterile medical bandage, moisten it slightly (preferably with lukewarm boiled water), then carefully apply it to the bleeding area and close your teeth. The tampon should not be too large, otherwise it will put too much pressure on the blood vessels. Then take a quiet position, sitting or lying down, and try to relax while continuing to close your teeth.
You can also replace the tampon with a bag of black tea - thanks to the tannins included in the composition, the blood stops faster. But if these methods do not help, then it is possible that a large vessel is damaged. Then you can try this method: mix one spoon of salicylic acid solution with two spoons of peach oil and seven spoons of beeswax. Heat the mixture to a boil, cool, pipette and drop into the well. The mixture will harden and turn into a protective film that will stop the bleeding. It is better to place a cotton swab on top of the resulting film.
If this method does not help, and the bleeding does not stop, contact a specialist immediately! Otherwise, everything can end in blood loss and even life-threatening.
Types of fracture
First of all, fractures differ in direction:
- Vertical. Most often, the fracture reaches the deep parts of the tooth, so it must be removed;
- Transverse. A tooth can break across in any part;
- Oblique. The fault runs at an angle;
- Splintered. In this case, there are several fractures, they can intersect with each other.
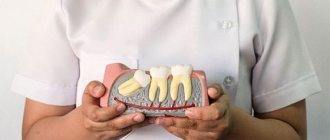
There are several types of cracks based on their location
- Violation of the integrity of the crown enamel. This type is dangerous due to the high risk of infection in the wound;
- Root fracture in the cervical area;
- Fracture of the crown exposing the cavity (complete);
- Fracture of the crown without exposing the cavity (invisible);
- Fracture of the root down to the dentin and cementum.
In most cases, the root breaks. In this case, for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to undergo radiography. On the lower incisors, such injuries occur less frequently; usually they are left with an incomplete fracture - a break or crack.
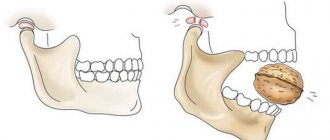
In severe cases, the injury is accompanied by subluxation. In this case, the tooth visually looks smaller and protrudes at an unnatural angle. Sometimes subluxation is accompanied by impaction of the root into the jaw bone. In this case, the victim experiences acute, persistent pain. In this case, the most surgical intervention by a specialist in maxillofacial surgery is necessary, but even under such circumstances there is a possibility of saving the tooth.
Trauma code according to ICD 10:
- The general code is S02.5.
- Small enamel fractures are classified in subgroup S02.50.
- The designation for multiple fractures is S02.57.
- Fracture of the crown and root of the tooth - S02.54.
- Tooth dislocation - S03.22.
Causes
Infection of the dental cavity can occur for the following reasons:
- Damage to the walls of the recess. Careless handling by a specialist leads to microtrauma. Remains of bone tissue enter the wound, causing infection.
- Failure to follow the dentist's recommendations. Blood clots are removed with solid food and constant rinsing.
- The slow transition of blood from a liquid state to a clot. The blood in the cavity coagulates, forming a protective layer. If the patient has problems with its clotting, the wound will not be protected.
- Weakened immunity. This condition increases the risk of developing inflammation. The immune system of a healthy patient easily copes with harmful bacteria. Therefore, surgery cannot be performed if a person is sick.
- Infection through instruments. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter an open wound from the outside.
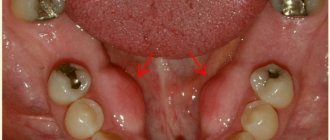
Alveolitis in an advanced stage (photo)
The risk of developing an infection is higher in people who have the following problems:
More often, inflammation of the cavity occurs in elderly patients and people with HIV infection and diseases of the endocrine system.
Causes
Possible causes of such injury are divided into acute and chronic. This division is necessary because it directly affects the overall treatment plan.
Acute form
All causes of the acute form are based on excessive mechanical stress on the tooth:
- A sharp blow during a fall, during an accident, a fight and similar situations;
- Sharp biting of hard objects (bones in meat, seeds in fruit);
- Using the jaws as a tool (trying to bite through or break a hard object);
- Incompetent work of the dentist: accidental injury during the treatment of an adjacent tooth, removal of the brace system, unjustified deepening and widening of the dental canals during the treatment of pulpitis.
Symptoms (signs)
Clinical picture • Clinical manifestations reflect increasing respiratory failure. According to the rate of increase in symptoms, acute, chronic and intermittent courses are distinguished • Complaints of inspiratory or mixed shortness of breath, dry cough. Chills and cough with sputum appear with bacterial superinfection (complication). Often fatigue, general malaise, aching chest pain, aggravated by deep inspiration, later - weight loss • Physical examination in the early stages may be uninformative •• In 40% of patients, body temperature rises to subfebrile and febrile, the peak increase occurs in the middle of the day •• With progression, tachypnea, tachycardia, cyanosis, deformation of the fingers in the form of “drumsticks” occur (with a long course of the disease) •• On inspiration, crepitus of the “cellophane cod” type is heard (usually in the basal parts of the lungs), in the later stages - sclerosiphonia (rough crepitus, reminiscent of the sound of a balsa wood plug rubbing) •• Signs of right ventricular failure appear.
Symptoms
A tooth fracture is not always obvious. You can recognize the problem in time and consult a doctor based on the following symptoms:
- The main symptom is acute or aching pain, which can subside only in the absence of the slightest impact on the painful area;
- The enamel changes color to pinkish due to internal bleeding;
- At the site of the injury, the gums and adjacent soft tissues swell;
- The gums bleed when exposed to it - for example, when pressing or while eating;
- The tooth itself may wobble even when moving the tongue or simply opening the mouth, and looks displaced;
- A person has difficulty speaking, it is difficult for him to open and close his mouth;
- When a fracture is located under an artificial crown, chewing is impossible and an unpleasant odor occurs;
- With a comminuted fracture, the soft tissue surrounding the tooth is injured.
The injury itself does not cause serious harm to health, but requires surgical intervention by qualified specialists. In addition to continuous pain and the inability to eat normally, there is a serious risk of complications. The maxillofacial apparatus is located close to the brain, so any uncontrolled progressive inflammation can have extremely negative consequences.
Prevention
Dental injuries can be prevented by following safety rules when playing sports and avoiding falls and blows to the face. If necessary, dental guards should be used to protect the row from destruction in the event of a direct impact. Sports injuries with irreversible consequences are rare if you properly prepare for the training process.
Planned sanitation twice a year will allow you to identify dental disorders and stop this or that disease in a timely manner. Carious cavities are subject to treatment; in case of weakening of the enamel, special pastes and vitamins are prescribed for oral administration.
There is no special prevention for dental fractures. The patient’s task is to pay attention to strengthening hard tissues in the body, which is achieved through proper nutrition and taking calcium with vitamin D3.
Complications and consequences
When a child’s baby tooth is injured, there are almost no complications, since the inflammation is easily eliminated with the help of medication. For adults, things are different.
First of all, an attempt to postpone a visit to the doctor can provoke complications. This is often caused by “tolerable” pain and discomfort, which gives the impression that the damage is insignificant.
In the case of a complete fracture of the crown, the patient has to restore hard tissue, and this is accompanied by incision of the gums. Thus, the likelihood of infection entering the wound and its development increases sharply.
Trauma provokes the appearance of purulent inflammation, various gum diseases, phlegmon with rapidly progressing periostitis. These factors, in turn, lead to the loosening of several teeth or even a whole row.
Also considered serious complications are: root displacement and/or damage, periosteal injury.
If a tooth is preserved after a fracture, it should be taken into account that its integrity is compromised and it cannot withstand full loads. If this fact is ignored, the injury will recur and recovery may no longer be possible.
Statistics and reasons
According to statistics, tooth extraction with a complication in the form of bleeding is observed in 0.25% of cases. Moreover, about 70% of them are caused by local factors, i.e., the condition of the tissues surrounding the hole.
The rest are caused by systemic disorders in the body. Local factors causing complications include:
- injury, crushing or rupture of soft tissues;
- damage to the interradicular septum or alveoli;
- cessation of the action of adrenaline , which is part of the anesthetic drug (the vasoconstriction it causes goes away after about 2 hours, and then the opposite effect appears - significant dilation, which can lead to complications);
- inflammation in the area of the extracted tooth;
- purulent melting of intradental thrombus due to the development of alveolitis;
- damage to blood vessels located abnormally close to extracted teeth;
- erosive vascular tumor (hemangioma), not opened at the time of tooth extraction;
- violation by the patient of the integrity of the blood clot in the socket.
Of all the above reasons, damage to periodontal tissues most often leads to pathology.
Systemic factors causing alveolar bleeding:
- Hypertension.
- Hemorrhagic diathesis is a disease of various etiology, characterized by an increased tendency to hemorrhage and bleeding, which can occur not only as a result of injury, but also spontaneously.
Hemorrhagic diathesis causes disturbances in the blood coagulation system due to a lack of certain hemostatic agents.These include diseases such as hemophilia, hypoproconvertinemia (lack of proconvertin), hypofibrinogenemia (lack of fibrinogen), hypoprothrombinemia (vitamin K deficiency).
Hemorrhagic diathesis results from a low number or decreased functionality of platelets.
- Pathologies of the vascular wall - hemorrhagic vasculitis (capillary toxicosis), telangiectasia, Osler's disease.
- Scurvy and infectious diseases - scarlet fever, typhus, etc.
- Complications caused by hormonal status - hemorrhagic metropathy (cystic degeneration or reverse development of follicles), menopausal factor.
- Hepatitis, leukemia, liver cirrhosis and other diseases that reduce blood clotting.
The first place among the causes of complications among common factors is hypertension.
Reference. During the menstrual cycle, blood clotting increases, so pathology in menstruating women is not vicarious in nature, but is usually caused by significant damage to periodontal tissue
.
The video explains in more detail the causes of bleeding after tooth extraction.
First aid
The most correct decision would be to seek help from specialists as quickly as possible. However, it is not always possible to get quality help in the next few hours - for example, if a tooth was broken far from the city while traveling. In such circumstances, competent behavior of the victim and those around him can not only make him feel better, but also increase the chances of the most favorable outcome of the injury.
The essence of first aid for a tooth fracture is simple: you should not try to fix something yourself. This is too serious an injury to neglect the help of a dentist and rely only on your own strength.
The patient must remain silent and not attempt to eat so as not to disturb the damaged area. If necessary, it is allowed to take only non-narcotic analgesics. If the wound is bleeding heavily, it is recommended to apply a tampon with hydrogen peroxide.
It is necessary to take the victim to a doctor as quickly as possible, but it is also a good idea to first familiarize yourself with information about the clinic’s specialists. The help of an experienced specialist (link to our specialists), albeit with a slight time delay, may turn out to be more effective and of higher quality than the prompt assistance of an unscrupulous dentist.
Treatment methods
If the patient has signs of significant blood loss, he is hospitalized, and along with other methods of treatment, an intensive infusion is carried out - drip administration of biological fluids and drugs.
Local therapy
Methods to stop bleeding using local therapy depend on the causes of the complication.
If the hole bleeds, it is cleared of the clot, washed with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine or some other), dried with a gauze swab and a tight tamponade is made with turunda treated with iodoform or another composition for the same purpose.
Filling the hole begins from the very bottom, folding the material from edge to edge and pressing each layer tightly. If a multi-rooted tooth was removed, each hole is treated separately.
After packing, the edges of the wound are compressed and fixed with sutures. A gauze swab is placed over the gum, which the patient presses with his teeth, and the patient is observed for about 1 hour. If there is no discharge, the tampon is removed and the patient goes home. The doctor gives recommendations, the main one of which is the prohibition of taking hot drinks and food for one or two days.
If the bleeding does not stop, packing is repeated, making it more dense. A “cold” (ice pack) is applied to the cheek.
Turunda, located in the depths of the hole, is removed after 5-6 days. If you do this earlier, the complication may reoccur. But it is not recommended to leave it for a longer period, since it inhibits wound healing.
Pathology caused by rupture of the gum mucosa is eliminated by applying sutures.
If a destroyed bone septum bleeds, the problem is eliminated by squeezing the tissue with orthodontic forceps, followed by tamponade.
Sometimes you have to resort to ligation - ligation of the vessels with a thread circled around them - a ligature.
In addition to iodoform gauze, the following can be used for stopping:
- hemostatic sponges;
- statin powder;
- aminocaproic acid;
- catgut is a fibrous material produced from the intestines of small livestock;
- Kaprofer is a hemostatic drug containing ferric chloride, aminocaproic acid, sodium chloride 0.9%.
General methods
The method of stopping alveolar bleeding caused by systemic diseases depends on their type and nature.
For loss caused by hypertension , antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
If a coagulation disorder leads to pathology , coagulants are prescribed to normalize the process of platelet adhesion. There are many such drugs; the doctor chooses a specific drug taking into account the clinical picture. The tools listed below are just a few of them.
Vikasol (synthesized analogue of vitamin K) – is involved in the synthesis of proteins that ensure coagulation. It is prescribed intramuscularly and orally.
- IM - daily dose - 30 mg, taken 2-3 times.
- Inside - in the same doses as intramuscularly.
Aminomethylbenzoic acid. Hemostatic and hemostatic drug, the action of which is based on inhibition of fibrinolysin activity.
Available in the form of tablets and solutions for intravenous and intramuscular administration, as well as in the form of a sponge for topical use, which has the ability to completely dissolve.
- IV – 5-10 ml of 1% solution or 100 mg IM.
- Orally 100-200 mg up to 4 times a day.
- Topically in sponge form.
Ambien. Contains aminomethylbenzoic acid as an active component. Used as a solution for intravenous administration.
- IV – 5-10 ml of 10 mg/ml solution.
Etamzilat. Activates thromboplastin, stimulates coagulation, normalizes platelet adhesion, and reduces vascular permeability.
- Orally, daily dose 250-500 mg in 3-4 doses.
- IM and IV - 125-250 mg/day.
Dicynone with the active substance ethamsylate.
- Orally 250 mg every 4-6 hours.
- IM and IV – 2.0 ml with isotonic solution (effect within 10-15 minutes).
Calcium chloride. Along with many other functions, calcium ions have a hemostatic effect, reduce capillary permeability, and normalize coagulation processes. Available in the form of a 5-10% solution for oral administration and intravenous administration.
- Orally – 10-15 ml.
- IV - 5-15 ml (diluted in 100-200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride).
Calcium gluconate. Pharmacological action is similar to calcium chloride. Available in tablets of 0.5 g, and in the form of a 10% solution.
- Orally 1 g 2-3 times a day.
- IM and IV - 5-10 ml.
Aminocaproic acid is a hemostatic agent, an inhibitor of fibrinolysis - the process of dissolving clots and blood clots.
- Orally up to 5 times, 2-3 g per day.
- IV – 4-5 g, diluted in 250 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride.
Ascorbic acid.
- Orally – 50-100 mg up to 2 times a day.
- IM and IV – 1-5 ml of 5-10% solution.
Diagnostics
The tooth root fracture itself is easily diagnosed by an experienced surgeon using palpation. In this case, the presence of fragments or absence of fragments, mobility and displacement are determined. But a complete treatment plan requires a more detailed examination, which, in addition to the fracture, will help identify related problems.
Stages of diagnosis for traumatic injury:
- Percussion. With its help, the condition of neighboring teeth, the presence of swelling and ruptures of soft tissues are assessed;
- Electroodontometric diagnostics. At this stage, the condition of the pulp during root fracture is determined, which is decisive in the choice of treatment;
- Radiography. The photo clearly shows the root system. Allows you to clearly determine the location of the fracture and fragments, if any.
After analyzing the overall picture based on the research results, the doctor draws up a treatment plan.
Fracture of the tooth crown without damage to the pulp
Symptoms of a tooth crown fracture (tooth enamel fracture, tooth dentin fracture).
Patients diagnosed with a tooth crown fracture without damage to the pulp (tooth enamel fracture, tooth dentin fracture) complain of:
- For short-term pain from any irritant. But the closer the fracture is to the pulp of the tooth, the more intense the pain during a fracture of the tooth crown will be;
- pain when any touch of the tooth;
A doctor in a clinic with a fracture of the crown of a tooth without damage to the pulp (fracture of tooth enamel, fracture of tooth dentin) notes:
- painful percussion;
- pain on probing.
Often, dental trauma such as a fracture of tooth enamel or a fracture of tooth dentin is accompanied by abrasions, hematomas of the lips and cheeks.
Diagnosis of a tooth crown fracture without damage to the pulp (tooth enamel fracture, tooth dentin fracture).
The patient is sent for an x-ray to make sure that there is no fracture of the tooth root and to understand where the fracture line is. Pulp viability tests must be done.
Treatment of tooth crown fracture
Treatment of a fractured tooth crown should be carried out as soon as possible after the injury. Because exposed dentin is a threat to pulp damage. Treatment will consist not only of protecting dentin from the external environment, but also of forming replacement (reparative) dentin. Therefore, it is best to first place a calcium-containing pad on the bottom of the cavity and place a temporary filling. Thus, the doctor warns himself against possible complications, and after the symptoms have been eliminated and a favorable X-ray picture is available, a permanent filling can be placed.
In the next article I will try to talk in detail about complete/incomplete dislocation of a tooth, a fracture of the crown of a tooth with exposure of the pulp, a fracture of the root of a tooth, and we will touch on some features of dental trauma in childhood.
The article was written by N. Shidlovskaya specifically for the OHI-S.COM website. Please, when copying material, do not forget to provide a link to the current page.
Treatment
Any good dentist will first try to save the tooth, but with some fractures it cannot be restored. Depending on the situation, various treatment methods are used. First of all, procedures are carried out to eliminate inflammation and restoration, then the issue of aesthetic correction is resolved.
The easiest to treat is a marginal enamel fracture. The lost element is quite easy to build up. If the root has been broken, it will have to be removed. The doctor cleans out the fragments and remains of the tooth, and after healing, a prosthesis can be installed.
The main criteria that determine the treatment method:
- Direction of fracture;
- Pulp condition;
- General condition of connective tissue;
- Number and location of fragments.
Preventive measures
After tooth extraction, the patient needs to keep the cotton swab in the mouth for at least 30 minutes. And if there are problems with coagulation, then longer.
When removing the tampon, you need to check the degree of its blood saturation. It can be used to determine whether bleeding continues or not.
To avoid the destruction of a blood clot, it is advisable to refrain from eating hot food and drinks, as well as rinsing your mouth for 24 hours. In the future, when rinsing, it is advisable to use special solutions.
Rehabilitation
Unfortunately, you should not count on quick rehabilitation after treatment of a broken tooth. But it is necessary to follow all instructions and recommendations so that recovery occurs as soon as possible.
Often during the rehabilitation period the patient needs to do the following:
- Rinse your mouth with antiseptic agents;
- Keep the oral cavity as calm as possible if splinting has been performed;
- Eat exclusively liquid and pureed foods;
- Carry out daily hygiene in a gentle manner.
In the event that it is not possible to restore the full functionality of the incisor, you can resort to additional methods of protection such as a mouthguard or lining.
Differential diagnosis
Primary diagnosis for alveolar bleeding includes:
- examination of the oral cavity, external examination of the patient;
- heart rate measurement;
- blood pressure measurement.
The following questions must be asked:
- what is the general health of the patient;
- when did the complication begin?
- whether it was provoked by anything, for example, rinsing the mouth, eating food immediately after removal;
- does the patient suffer from high blood pressure;
- Do you have problems stopping in case of domestic injuries and cuts?
- Is your body temperature elevated?
- what measures were taken by the patient to stop;
- what concomitant diseases does the patient suffer from;
- What medications does he take (particular attention is paid to fibrinolytic drugs, anticoagulants, NSAIDs, oral contraceptives).
If the use of drugs that reduce blood clotting is confirmed, hospitalization is necessary.
Differential diagnosis is made in relation to systemic diseases characterized by complications:
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- arterial hypertension;
- acute leukemia;
- diabetes mellitus;
- infectious hepatitis.
Reasons for the eruption of supernumerary teeth and indications for removal.
Visit here to learn more about the benefits of laser teeth removal.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/tsel-primeneniya-turundyi-posle.html we will tell you what functions iodoform turunda performs after tooth extraction.