What to do if the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed
Before treating an inflamed lymph node under the jaw, the first step is to determine where the source of pathology is located - on the right or left in the neck area.
This can be done using the classic palpation method at home. The pathogenic tubercle will not only protrude against the background of other tissues, but will also be very painful when touched. The skin in the affected area first turns red and then acquires a bluish tint. If such symptoms occur, you should consult your doctor.
The recommendations are as follows:
- The inflamed lymph node under the jaw increases in size, the gums are very painful, and movement is limited. This indicates the course of the pathological process and helps differentiate the diagnosis. Self-medication is dangerous to health, since the problem can only worsen.
- If the inflammation of the lymph node under the jaw is minor, no special treatment is required. It is indicated to eliminate the underlying ailment, and the symptoms of lymphadenitis will disappear on their own. Alternatively, it could be a relapse of tonsillitis, otitis, flux, laryngitis, tonsillitis, alveolitis.
- If lymphadenitis is caused by active pathogenic flora, mandatory antibacterial therapy is required. When purulent masses appear, surgical intervention is indispensable. In the latter case, local anesthesia or general anesthesia is first used to remove adenophlegmon.
- The basic principles that ensure effective treatment of submandibular lymph nodes are the implementation of conservative methods, examination, bed rest, and the use of alternative medicine methods. In the latter case, we are talking about auxiliary treatment.
If the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed, the pathogenic infection can enter the blood and spread throughout the body.
To avoid mass infection, the complex treatment regimen for lymphadenitis must include antibiotics. The general condition returns to normal within 5-7 days if you strictly follow medical recommendations.
The following medications with antibacterial action have proven themselves well:
- Sumamed. This is a representative of the macrolide group, which acts at the cellular level. The tablets are recommended to be taken before or after meals, with plenty of water. It is recommended to take 1-2 pills for 3-5 days until the normal state stabilizes.
- Amoxicillin. This is a semi-synthetic penicillin for oral or subcutaneous administration. The remission period occurs after 5-7 days if you take 1 tablet three times a day.
- Biseptol. This is a sulfonamide drug in the form of yellow pills with a pronounced antibacterial effect. If the lymph node under the jaw has become swollen, for successful treatment it is recommended to take 1 tablet in the morning and evening for a week.
Pain during difficult removal
A complex extraction is an operation during which the doctor had to cut the gum, remove the tooth piece by piece, remove the unerupted eighth molar, and drill out the bone tissue.
In such cases, pain after wisdom tooth removal is inevitable, and its intensity depends on the degree of trauma of the operation, the speed of healing of the postoperative wound and the individual pain threshold.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Coughing spasms that take away a child’s breath
After complex removal of the “eight”, the patient may experience pain for a week, sometimes lasting up to ten days.
The fact that the healing process is successful is indicated by a decrease in the intensity of pain over time.
If you observe an increase in pain, it is constantly aching or throbbing, too painful, and practically does not disappear after taking analgesics, then you should contact your dentist.
Pain after tooth extraction
After the removal of the eighth molar, dental patients may experience various symptoms. Pain often occurs after wisdom tooth removal.
The gums become inflamed, the adjacent cheek swells, there may be discomfort when swallowing food, pain when opening the mouth, etc.
Such symptoms may be typical postoperative manifestations that spontaneously disappear within a few days, or they may be signs of the development of various complications.
Main reasons for development
The submandibular form of lymphadenitis develops when an inflammatory process appears in the teeth. This often occurs due to the removal of wisdom teeth. The reasons may include the following:
- Tonsillitis.
- Pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
- Stomatitis and otitis.
- Periodontitis and periodontal disease.
- Purulent sore throat and sinusitis.
- Inflammation under the crowns.
Read also: Is it possible to apply cold after tooth extraction?
A lymphatic inflammatory process may appear in response to an infection that enters the blood. It is possible that a pathological process may develop in response to injury to soft tissues and filter capsules.
A huge role in the development of inflammation under the chin is played by a decrease in the body’s protective functions. The immune defense is disrupted in response to diseases such as lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, serum sickness, etc. Quite often, the inflammatory process is provoked by the causative agent of Koch's tuberculosis, streptococcus, staphylococcus and syphilis. Lymph nodes can enlarge in childhood, during the eruption of baby teeth.
Option 3
healthy-teeth.su
Lymph nodes
Every person has lymph nodes, but their presence cannot always be felt. When they start to hurt and swell, they are treated. Lymph nodes are located in different parts of the body. There are, of course, also under the jaw. You can even feel them with your fingers.
An inflamed lymph node may indicate a disease of the tooth, throat, or oral cavity. The swelling goes away after complete recovery. But there are cases when inflammation remains for a long time.
Then you should undergo a thorough examination to know the cause of swollen lymph nodes.
Wisdom tooth pulled out, now it hurts
Pain in the gum area or in the socket after tooth extraction usually begins as soon as the effect of the painkiller wears off. This is also due to tissue trauma that is inevitable during the operation.
The pain can be of varying intensity, how strong and long it will be depends on the complexity of the operation, and on the personal pain threshold, and on the individual ability of the body to recover.
In order to relieve pain, you can take an analgesic; usually the dentist recommends a medicine that can be used to relieve post-operative pain.
If the pain does not go away within a few days, but its intensity, on the contrary, increases, try to get an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible. Perhaps pain is a sign of an ongoing inflammatory process.
Bleeding started
If the surgery to remove the third molar is successful, there should be no discharge. Bleeding, especially heavy bleeding, is stopped by the dentist. The doctor puts the antiseptic medicine “Alvozhil” into the hole and gives the patient special medications.
At home, a sterile gauze swab is pressed onto the wound. Cotton wool will not work; particles of the material stick to the gum and remain in the open hole. The tampon is pressed with the teeth. The workpiece can be moistened in a solution of soda with iodine or in Chlorhexidine. Before the operation, you can buy hemostatic tablets “Vikasol” or “Ditsinon”. But the drugs must be approved by a doctor, because they are not suitable for all patients. If the bleeding does not decrease within 5–10 minutes, call an ambulance.
Treatment
When treating lymphadenitis, you must adhere to the following measures:
- Do not carry out treatment on your own before visiting a doctor.
- Visit a doctor immediately after the first symptoms appear.
- With a mild form of lymphadenitis, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease and eliminate (treat) it.
- In case of purulent inflammation of the lymph node, surgical intervention, a course of antibiotic therapy, and drug treatment are necessary.
Stages of gum treatment:
- Visits to the dentist.
- Diagnosis of the type of disease.
- Finding the cause of gum disease:
- Establish a connection between pain in the gums and in the lymph node.
- Eliminating the cause of the disease.
- Carrying out the necessary treatment and anti-inflammatory therapy.
We can conclude that if the gums hurt and the lymph node hurts, then the symptoms of pain may or may not be related to each other. When treating the disease in the oral cavity, lymphadenitis will disappear. But there are cases when the lymph nodes become inflamed and have nothing to do with the gums. Therefore, it is necessary to visit a doctor and carry out timely treatment.
bezzubov.su
Gum pain and lymph node pain: causes of unpleasant symptoms
Gum pain can affect your overall health
If your gums hurt and your lymph node hurts, these could be manifestations of various diseases of the maxillofacial area. Lymphadenitis, or inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, can occur as a result of any inflammatory processes in the facial, nasal, oral or cervical area.
The main function of the lymph nodes is to delay infection, so their increase indicates an inflammatory process in the corresponding area.
Combination of symptoms
Gingivitis - inflammation of the gums and normal gums
Pain in the gums occurs with the following dental diseases:
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Periodontitis
- Periodontal disease
- Periostitis
- Caries
- Pericoronitis
- Stomatitis
Cervical caries is a common cause of gum pain
You need to know that the symptoms of pain in the gum and lymph node may not be related to each other. For example, the gums may hurt from an incorrectly installed filling, and the lymph node from a sore throat or otitis media.
An enlarged lymph node is noticeable in the neck
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is manifested by an increase in the size of the lymph node, pain, swelling, and redness of the skin. Pain in the gums can occur with or without disruption of the integrity of the gum tissue. Rashes, canker sores, fistulas, redness, swelling and enlarged gums may appear.
With pain in the gums and lymph nodes, other symptoms may occur:
- General malaise
- Weakness
- Increased body temperature
- Toothache
- Bad breath
Causes of pain symptoms
Lymph nodes become inflamed during serious diseases of the oral cavity or diseases in the acute phase, these include:
- Periostitis is an acute serous or purulent inflammation of the periosteum that occurs when an infection spreads from a tooth and is manifested by pain, swelling, and swelling of the gums in the area of the causative tooth.
- Pericoronitis is inflammation of the gums near or above the wisdom tooth. It is a complication when the eighth teeth erupt. Inflammation of the gums can be serous and purulent, acute and chronic.
- Periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium, the area of the jaw behind the root of the tooth. The disease can be acute (purulent, serous) and chronic (granulating, granulomatous, fibrous). Redness, swelling, swelling, and a fistula may occur on the gums.
- Gingivitis is inflammation of the gum tissue. A very common disease, it can occur due to mechanical, chemical or temperature injuries to the gums, as well as diseases of the oral cavity. It manifests itself as hyperemia, swelling, an increase in the size of the gums, pain and discomfort.
- Periodontitis occurs when the periodontal tissues that surround the tooth become inflamed. The disease is similar in appearance to gingivitis, but the tooth-gingival junction is destroyed and the infection penetrates deep into the tissue. Gingivitis, periodontal pockets, exposure of tooth roots, and loss of bone tissue in the interdental septa occur.
- Stomatitis is a disease that causes inflammation of the oral mucosa, including the gums. Stomatitis can be aphthous, traumatic, vesicular, allergic, aphthous, herpetic, ulcerative. The latter are the most dangerous, cause disruption to the general condition and require urgent treatment.
Non-dental diseases in which the lymph nodes become inflamed include:
- Angina
- Pharyngitis
- Sinusitis
- Tonsillitis
- Otitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Runny nose
- Tumors or neoplasms
- Trauma and infection
- Parasite infection
- Immune system disorders
- Viral diseases - mumps, herpes, measles, smallpox.
We can conclude that various diseases can provoke pain in the gums and lymph nodes. In addition, symptoms may be a sign of a serious illness or just a coincidence. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis.
Inflammation of the lymph node
Inflammation of the lymph node can cause neck pain
The lymphatic system and nodes belong to the body's immune defense system. The nodes are a kind of filter for infection and a sensor that shows the presence of inflammation.
Lymph nodes enlarge and hurt when performing their function - retaining microbes, infections, foreign cells.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs:
- Due to other diseases (most common).
- An independent disease (in the absence of diseases of other organs, lymphoma, metastases).
According to the nature of inflammation, lymphadenitis occurs:
- Serous. Symptoms will be enlarged, painful lymph node. Treatment will include searching for the underlying cause and conservative therapy.
- Purulent. It is characterized by an enlarged lymph node, severe pain, redness of the skin, increased temperature, and a disturbance in the general condition. Surgical and medical treatment is necessary.
Diagnostic search
Table 1: Diagnostic measures to identify the causes of pain in the gum and lymph node:
| Purpose of diagnosis | Ways to achieve |
| Patient Interview | Collecting anamnesis of life, illness, clarification of complaints, symptoms of diseases, how long ago symptoms appeared and the characteristics of their manifestation, determining the presence of concomitant diseases |
| Oral examination | Determining the presence of diseases of the gums, mucous membranes, teeth |
| Lymph node examination | Inspection, palpation, determination of the location and mobility of the lymph node |
| General facial examination | Determining the presence of other inflammatory processes |
| Examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx | Determining the presence of diseases of the respiratory system |
| Definition of infectious agent | Determine what is causing an enlarged lymph node |
| Consultations with other specialists if necessary | ENT specialist, dentist, ophthalmologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist. |
Differential diagnosis
Attention, to make a correct diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary. Only a doctor can conduct differential diagnosis, clinical and additional examinations, establish connections between diseases and prescribe treatment. Pain and inflammation in the lymph node is a secondary and easier to diagnose disease.
To determine gum disease, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of possible diseases:
| Name of the disease | Definition | Accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Gingivitis | Gum inflammation | In acute form, with herpetic and aphthous lesions | Pain, swelling, redness, swelling, increased gum size | Local, etiotropic, anti-inflammatory |
| Periodontitis | Inflammation of the tooth ligament | In good shape | Pain, swelling, redness, swelling, exudate from the gums | Professional oral hygiene, anti-inflammatory therapy of gum tissue |
| Periodontal disease | Dystrophic damage to the tissues around the tooth | Rarely | Pain, discomfort, itching in the gums | General and local effects on gum tissue. |
| Periodontitis | Inflammation of the tissue behind the apex of the periodontal tooth | Rarely, in acute inflammation | Pain when biting on a tooth, pain and redness of the gums | Removal of the tooth nerve and medicinal treatment of the inflammation site. |
| Periostitis | Inflammation of the periosteum and gums | Yes | Sharp pain in the alveolar process, gums, swelling, facial asymmetry, increased temperature | Removal or treatment of a tooth, incision of the gum and periosteum. Local and general drug treatment. |
| Pericoronitis | Inflammation of the gums above or near the wisdom tooth | In purulent form | Pain in the gums and jaw in the area of the last teeth, swelling and redness of the gums | Tooth extraction or excision of the gum above the tooth, drug therapy. |
| Stomatitis | Inflammation of the mucous membrane of various etiologies | In acute form, with herpetic and aphthous lesions | The presence of lesions on the mucous membrane, gums, and tongue. Painful sensations. | Professional oral hygiene, local and general treatment with medications. |
Pain in the gums and pain in the lymph node brings discomfort
Treatment of the inflammatory process
If the lymph nodes become inflamed after wisdom tooth removal, you should definitely consult a doctor. The sooner adequate treatment is prescribed, the lower the risk of complications. After determining the type of pathogenic microorganisms and the degree of damage to the lymph nodes, the specialist decides on treatment methods.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Suppositories for teething in children: what medications can be given to relieve pain?
First, an “inspection” of the oral cavity is carried out, necrotic areas of tissue and festering blood clots in the socket, if any, are eliminated. In addition, sanitation of carious cavities or gum treatment is performed.
In all cases of submandibular lymphadenitis, antibiotics selected for the specific pathogen are prescribed. Symptomatic therapy is carried out, including painkillers and antipyretics. If there is an abscess or phlegmon, the source of inflammation is opened, followed by sanitation and drainage of the wound.
Vitamins and physiotherapeutic treatment like (UHF - ultra-high frequency therapy) contribute to faster recovery.
Alternative therapy
In order not to suffer from inflamed gums, you can use folk remedies. If the lymph node is inflamed, rinsing with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or salt may help. You can prepare infusions of medicinal herbs and take them orally, for rinsing and lotions.
Under no circumstances should you warm up the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes, even if they hurt a lot. This will only cause the filter capsules to grow more and accumulate pus. After some time, in the absence of adequate drug treatment, their breakthrough is possible. This is fraught with the spread of internal contents throughout the internal tissues of the body. In this case, the process becomes more complicated and more serious treatment measures are required.
In order to prevent the lymph nodes from becoming inflamed, it is necessary to identify the true cause of the ailment. First of all, you need to deal with the dental problem; as a rule, this will stop the inflammatory processes in the node. That is why if your gums hurt badly or there is discomfort in the area of your wisdom teeth, then you should not waste time. The sooner measures are taken, the greater the chance that complications will not develop.
Can a lymph node become inflamed due to a tooth: possible causes, symptoms and treatment of the ailment
People with dental problems often wonder whether a lymph node can become inflamed due to a tooth. Doctors have repeatedly warned that inflammatory processes in the oral cavity often lead to enlarged and painful lymph nodes. If a person experiences these symptoms, they should immediately make an appointment with a dentist. The doctor will treat the diseased tooth, after which the work of the inflamed lymph node will normalize and it will no longer cause discomfort.
Prevention
To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to consume citrus fruits
Each person can prevent the re-development of cervical lymphadenitis due to dental diseases if he follows simple tips:
- In case of lesions in the oral cavity, rinsing with saline solution is required.
- It is necessary to include ginger tea in your diet.
- You should carefully monitor your oral hygiene.
Experts recommend consuming citrus fruits, natural products and honey more often. They help strengthen the immune system and improve the functioning of the lymph nodes.
Complications after tooth extraction
Enlarged lymph nodes are not the only complication that can occur in a person some time after the removal of a problematic tooth.
Complications worry patients who, for medical reasons, were forced to get rid of their wisdom teeth.
A child and an adult may experience complications (pain occurs, the node becomes inflamed) after an operation to remove teeth that are inflamed. Most often, patients encounter the following negative consequences due to their own fault or due to a doctor’s error:
- Inflammation of tissue at the site of tooth extraction. Because of it, the patient has bad breath. He is also concerned about pain of moderate severity.
- Nerve damage. The pathology worries patients whose nerve endings were affected in the surgical area.
- Alveolitis of the socket. One of the most serious complications, which is accompanied by inflamed lymph nodes. This can cause gum damage. Pathology develops due to the removal of any teeth.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw. This is the name of a purulent process that is accompanied by inflammation of bone tissue. It is caused by infectious agents that enter the oral cavity.
Because of the wisdom tooth and others, the formation in the neck area, which is included in the lymphatic system, increases in size and hurts. If treatment for lymphadenitis is not started, it will lead to even more serious complications. Among them are:
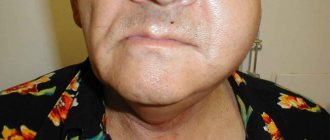
- Phlegmon. Due to pathology, the lymph nodes become enlarged. They may enlarge due to severe swelling. The pathological process actively spreads to all tissues of the neck. The node can rapidly increase in size, and the skin acquires a bluish tint. Due to phlegmon, it is difficult for a person to move the mouth.
- Inflammatory process in neighboring tissues. The active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria leads to the progression of the infection and its spread to neighboring areas. Without treatment, the disease causes tissue breakdown.
- Degeneration into a tumor. Any dentist can confirm that lymphadenitis is quite capable of leading to the development of a tumor-like neoplasm. It appears from conglomerates that tend to merge with each other.
Every person should know that the nodes of the lymphatic system can become inflamed if a wisdom tooth grows or the gums are infected. Therefore, at the first symptoms of illness, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is the only opportunity to prevent the development of complicated conditions.
Diagnostics
If the lymph node is inflamed, the doctor, after examination, will refer the patient for a comprehensive examination, which includes laboratory diagnostics (general urine and blood tests)
Any inflammatory process cannot be treated without first conducting a diagnosis. Because of this, the patient may make a mistake that will lead to a deterioration in his health.
If your gums or tooth hurt, after which a node of the lymphatic system becomes inflamed, you need to immediately go to see a doctor. With such problems, you should contact your dentist.
During the diagnosis, the doctor will find out the true cause of inflammation of the lymph node in the neck. After this, it will be possible to begin treatment of the pathological condition.
In most cases, in order to understand what to do with an inflamed lymph node, a person only needs to undergo a dental examination. Experienced specialists can make the correct diagnosis of the patient after a visual examination of the problem area.
Additional diagnostic measures help to identify concomitant diseases that also affect the condition of the lymph node:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound).
- Fluid puncture.
- General analysis of urine and blood.
The test results will show the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the body and the severity of the disease. They are also taken into account when selecting the optimal course of therapy.
Symptoms of pathology and complications
The condition when the lymph node hurts after tooth extraction develops gradually. First, the nodule increases in size and becomes denser, but retains mobility. There is deterioration in sleep, body temperature rises, neck movements are limited, and soreness of the immune gland appears on palpation.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Swelling after wisdom tooth removal, norm and deviations
As the disease progresses and untreated, the person's condition worsens:
- the node increases in size even more;
- the skin over it turns red and becomes hot to the touch;
- there are complaints of severe pain even without touching the lymph node;
- appetite worsens;
- the ability to move the jaw in full is lost;
- I'm worried about the high temperature.
Then swelling appears, which spreads to the entire neck, the skin over the lymph node acquires a purplish-bluish tint, and the pain becomes unbearable. The person's general condition is rapidly deteriorating.
If inflammation of the lymph node is not treated after removal or treatment of a wisdom tooth, unpleasant consequences in the form of phlegmon, involvement of adjacent soft tissues in the process and degeneration into a malignant neoplasm are possible.
Tips on how to temporarily relieve pain
- For the first time after removing the figure eight, eat soft food and do not eat hot food;
- the day after removing the figure eight, take an antiseptic bath, this will prevent the growth of bacteria;
- at first, try to chew on the other side where the figure eight was removed, try once again to avoid the place where the figure eight was removed;
- Sometimes dryness appears in the corners of the mouth, lubricate them with moisturizing ointment.
But remember that if your throat hurts over time, the pain does not stop even after taking painkillers, and is accompanied by bleeding, then consult a dentist as soon as possible, who will help in your particular case.
Dry socket after tooth extraction
As mentioned above, after the operation a blood clot should form in the socket. It ensures rapid wound healing, protects bone and nerve endings. To prevent the clot from being washed away, it is forbidden to rinse the mouth after tooth extraction for the first or second day, and then rinsing must be done very carefully.
A dry socket increases the risk of wound infection, increases pain, and may cause an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
When a wisdom tooth is removed, the situation is complicated by the fact that when the clot is lost, the patient cannot see for himself that the socket has become dry. Therefore, he sees a doctor only when pain develops. And very often complaints that a wisdom tooth has been pulled out and now hurts are associated with the formation of a dry socket.
In such situations, the doctor places a cotton swab with a special medicine on the wound, which, instead of a blood clot, provides protection to the hole and promotes its effective healing. This medicine must be changed daily until the wound is completely healed.
Disinfecting procedures
Improper care of a fresh wound leads to complications and serious illnesses:
- alveolitis;
- stomatitis;
- hematomas;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- purulent periodontitis;
- abscesses.
The risk of complications increases due to smoking. Hot smoke dissolves the blood clot, so it may fall out prematurely. An open wound will remain, into which infections and bacteria will penetrate.
You cannot rinse your mouth, but you can make disinfectant baths. Disinfecting compositions are prepared from medicinal plants:
- chamomile;
- oak bark;
- calendula;
- eucalyptus;
- sage
Herbs not only destroy germs, but also stop inflammation. They also stimulate the regeneration of soft tissues and dull pain. Decoctions are prepared from 2–3 tbsp. l. healing raw materials and a cup of water. Plants are either steamed with boiling water or a water bath is used. Solutions for disinfecting the oral cavity are cooled to 35–36 degrees and must be filtered through gauze folded in 7–8 layers. The main thing is that there are no small particles in the infusion that could get stuck in the hole.
Antiseptics for washing the hole are prepared from baking soda. For 300 ml of chilled boiled water, 35–40 g of powder. Plus 5-6 drops of iodine or alcohol tincture of calendula. You can also use Chlorophyllipt, but it is not necessary. The soda mixture is also filtered through cheesecloth.
The third version of the antiseptic is prepared from table or iodized salt. The spice kills germs and also cauterizes the edges of a fresh wound, reducing the likelihood of bleeding. The solution should not be too concentrated, so take 25–30 g of salt per cup of liquid. Stir until the seasoning crystals are completely dissolved, and then filter so that solid particles do not injure the gums.
A patient planning to remove a wisdom tooth can purchase Miramistin or Chlorhexidine in advance. The second option is practically no different from the first, but costs two to three times less. Pharmacy antiseptics are used to disinfect the oral cavity 3–4 hours after surgery.
To prevent the solution from washing out the blood clot, you need to take the product into your mouth and slowly “pour” it onto the sore side. Hold the antiseptic for 5 to 15 minutes and then carefully spit it out. The procedure is repeated 4–5 times a day.
We suggest you read: Brushing your teeth after wisdom tooth removal
Antiseptics for washing the hole are prepared from baking soda. For 300 ml of chilled boiled water, 35–40 g of powder. Plus 5-6 drops of iodine or alcohol tincture of calendula. You can also use Chlorophyllipt, but it is not necessary. The soda mixture is also filtered through cheesecloth.
A wisdom tooth was removed and swelling developed
During the operation, trauma to the gingival tissue occurs, the integrity of the periodontium is often damaged, bone is cut out, etc. Naturally, recovery from such serious injuries cannot occur completely painlessly. That is why, after the removal of any tooth, inflammation of the gum tissue develops, and very often the cheek adjacent to the tooth swells.
If the removal was not difficult, then such phenomena disappear without a trace within two or three days; with a complex operation, the inflammation may not go away for a week, sometimes even ten days.
In order to alleviate the condition, you can apply ice compresses to the cheek, and also rinse your mouth, starting from the third day after removal, with decoctions of herbs or antiseptic solutions.
In some cases, inflammation may be caused by an allergic reaction to an anesthetic drug. This swelling also goes away quite quickly. But if the inflammation increases over time, affects neighboring tissues, and is accompanied by throbbing pain and purulent discharge, then you should consult your dentist.