The principle of laser operation in dentistry
A laser is a device that emits a continuous or pulsed light stream in a narrow range. This therapy has properties that help in the fight against many pathologies of the oral cavity:
- thermal;
- mechanical;
- energy;
- photochemical.
In dentistry, various types of laser systems with the same operating principle are used. The beam of the device is focused on the source of the problem area, which ensures precise impact on the affected area. The effect of the procedure is explained by tissue changes at the molecular level:
- microscopic water particles are absorbed by radiation;
- particles boil and evaporate from the damaged areas;
- pathological changes in tissues are destroyed and destroyed.
The principle of operation of the laser depends on the nature of the lesion that is eliminated by radiation:
- When treating inflammatory processes of the gums, the beam is directed to the place of formation of pathogenic microflora. The focus is destroyed, as a result of which harmful bacteria die.
- When treating chronic pathologies, the beam evaporates fluid particles from dead tissue and removes them without affecting undamaged areas.
After laser treatment of gums, there is no pain. The rehabilitation period proceeds without complications. The area treated with the device heals quickly and painlessly.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
When contacting the clinic, the patient must be sure that therapy will be carried out only by an experienced and qualified doctor. Indications for the procedure are given by the attending dentist, who in most cases performs it independently. Among the common situations, patients who have a history of the following diagnoses are sent for laser dental treatment:
- Caries – the affected surface is removed non-contactly by a beam. The damaged tissue evaporates, and the tooth acquires a rough surface, which is subsequently polished. An erbium laser is often used for treatment, which independently recognizes areas of caries.
- Stomatitis - when the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is inflamed, the areas where ulcers have formed are visible with the apparatus. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms die, and no trace of treatment remains on the gums.
- Gingivitis – strengthening of soft tissues using laser method, as well as removal of hardened plaque and professional hygiene.
- Fungal infections of the oral cavity - the device removes unwanted tumors without leaving scars.
- Bacterial diseases of the gums and teeth - in this case, a diode laser is used, which disinfects the oral cavity and eliminates the consequences of exposure to harmful bacteria.
In addition to the listed treatment options, indications for using this technique include whitening tooth enamel, grinding and correcting chipped teeth and gum lines. Laser treatment for periodontal disease has worked well.
Since the disease is characterized by detachment of the tooth from the gum and the formation of a periodontal pocket, the light beam passes into the resulting cavity. By cleaning out all pus is removed from the hole, and the tissues gradually heal and regenerate.
There are some contraindications for laser treatment. Most often, patients with the following health problems are prohibited:
- diabetes mellitus with complications;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- severely increased or decreased blood pressure;
- tumor neoplasms;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- damage mucosa .
Before agreeing to laser dental therapy, you should consult your specialist about the presence of the listed diseases. If this technique is not suitable, then other methods of dental treatment are prescribed.
Indications for laser treatment
Treatment of the oral cavity with this method is indicated for the development of inflammatory gum diseases - gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, as well as neoplasms of an inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature. Laser therapy allows you to get rid of plaque and plaque.
| Periodontitis | Coagulation and disinfection of tissues in the periodontium occurs. Removal is carried out at different levels of the periodontal pocket, thanks to the presence of a depth indicator. |
| Gingivitis | Using a laser, the surface of the gums is cleansed of bacteria. The procedure has a disinfecting effect and prevents the spread of pathology. |
| Periodontal disease | The doctor cleans the gum pockets from epithelium and infected granulation tissue. |
| Laser teeth cleaning | Used as a preventative measure to prevent gum disease. |
| Removal of benign tumors | Painless removal of the tumor using a targeted effect that penetrates into the depths of the tumor. |
| Removal of granulomas and fistulas | The laser is used as an auxiliary action to sterilize the root canal after opening the tooth. |
| Cyst removal | The device has a drying effect on the walls of the cyst, cleans the channels of necrotic tissue and microorganisms. |
Benefits of laser gummy smile correction
Increasing the height of exposed teeth through orthodontic treatment, in particular the installation of braces, takes time - on average it takes 2-3 months. Changing the shape of the upper lip with Botox or correcting the frenulum causes a lot of discomfort and only masks the aesthetic problem. Compared to all known correction methods, laser technology has a number of advantages:
- carried out without anesthesia for 20-30 minutes;
- does not cause pain or discomfort;
- does not require lengthy preparation and rehabilitation;
- stimulates tissue regeneration and healing;
- helps to achieve a visible effect.
With the help of laser correction, you can not only remove part of the gum, but also align its position over all the teeth, achieving ideal aesthetics. A gummy smile is not a death sentence. Ben Affleck, Miley Cyrus and Cristiano Ronaldo were born with it. We will help eliminate aesthetic defects in 1 session. Give yourself the freedom to smile without embarrassment - call us and make an appointment now!
Advantages and disadvantages of laser gum treatment
Like any dental procedure, using a laser has its advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits include:
- no pain during the procedure and no need for anesthesia;
- minimal level of tissue trauma due to the targeted effect of radiation;
- no side effects;
- infection is excluded from inflammatory foci, since the procedure is carried out without contact;
- short rehabilitation period;
- no bleeding during the procedure;
- safety of therapy for children, pregnant women and the elderly.
The procedure has the only drawback - high cost.
Advantages of the technique
The use of laser is used in many areas of medicine. In dentistry, such treatment began to be used relatively recently. However, in a short period of time, the technology has found acceptance in this healing industry. All this is due to the unique properties inherent in laser radiation.
The advantages of the technique are as follows:
- lack of use of painkillers for manipulation;
- there is no need for surgical sutures, since there is a minimal level of trauma;
- there is no bleeding during the operation, or only a small amount is observed;
- there is virtually no risk of disease relapse;
- complete painlessness during the procedure and during the rehabilitation period;
- the possibility of a positive effect on all periodontal diseases;
- a minimum set of contraindications;
- there is no obvious wound area in the intervention area;
- there are possibilities for instant coagulation of vessels and overgrown periodontal tissues;
- absolute sterility of the procedure, since the operation is carried out in a non-contact manner;
- rapid regeneration and tissue restoration.
One disadvantage of the procedure is the high price. Moreover, it directly depends on the cost of the devices. Due to their high cost, many clinics are not able to provide such dental care.
Methodology of the procedure
Photodynamic therapy is carried out using 3 types of laser:
- diode (provides an effect on soft tissue);
- carbon (used for gum inflammation);
- erbium (removes dental plaque).
Laser therapy involves the presence of 4 techniques, used depending on the nature of the pathological processes of the gums:
- Deepitalization
The technique helps restore the oral mucosa and bone tissue. During exposure to radiation, the affected areas of epithelial tissue are removed. This further ensures the growth of connective tissue cells.
- Gingivectomy
The laser gum trimming method involves removing infected gum tissue and preventing the development of pathogenic microflora. The beam bloodlessly removes affected areas and is used to remove periodontal pockets.
- Laser curettage
Used to treat deep gum pockets. The treatment method consists of introducing a special guide into the periodontal cavity and eliminating pathological tissue growths.
- Ginvivoplasty is used to eliminate gum defects: receding or uneven distribution of gums in the dentition, exposure of tooth roots. Laser correction is carried out by removing gum tissue with further carbonization, which prevents the development of infections.
Each of the methods has a common preparatory stage:
- Oral hygiene is performed: plaque and tartar are removed from the teeth.
- Foci of accumulation of pathogenic bacteria are marked using a photosensitizer gel.
Next, the dentist begins to eliminate the problem using a laser.
The duration of the procedure depends on the complexity of the pathology being eliminated and varies from 15 minutes to 1 hour (for advanced forms of the disease).
How does the laser treatment procedure work?
First of all, the doctor must carry out a number of preparatory measures. To do this, perform a thorough cleaning of the oral cavity. Not only soft plaque must be removed, but also intense pigmentation, including hard dental deposits.
Treatment consists of several stages:
- Treatment with photo-sensitizer gel . It is applied to the surface of the gum, not only the affected one, but also the healthy one. This gel is based on green spirulina algae. They produce a green pigment that is minimally allergenic and completely non-toxic. The gel deeply nourishes the affected tissues. This process lasts 5-10 minutes. You can tell that the gel has been completely absorbed by the bright color of the gums in the place where there is a large accumulation of bacteria. Rinse off any remaining product with water.
- Laser processing. The stream of light comes from a special apparatus. It is designed so that the dentist can reach any periodontal area. The duration of the procedure is 2 minutes. At this time, the accumulated chlorophyll begins to break down and release oxygen. In this case, all bacteria die.
The luminous flux emanating from a laser device is undesirable for the retina. When performing the procedure, the doctor and patient must wear safety glasses.
- Formation of a protective film . It is formed immediately after treatment with a laser beam. Photocoagulation film protects against the penetration of pathogenic microflora through the wound surface.
The duration of the procedure depends on the disease that can be treated, the severity of its course and the volume of affected tissue.
If we consider a severe case of a pathological process, then therapy will last 45-60 minutes. To obtain maximum effect, one procedure is enough.
The maximum course of treatment will be 3 manipulations. Apply once a week. To consolidate the effect obtained, repeat the therapy after six months.
Laser treatment is a very expensive method
Cost of laser gum treatment
The cost of using the photodynamic method depends on:
- severity of the disease;
- coverage of the treated surface;
- type of manipulation performed.
The cost of the service will also depend on the region: prices in Moscow exceed the pricing policy of other remote regions. The average price for the procedure is:
- from 600 rub. for antiseptic treatment of 1 gum pocket;
- from 1000 rub. for closed curettage of 1 periodontal pocket;
- 1500-2500 rub. for open curettage of 1 periodontal pocket;
- 3000 for gingivoplasty of 1 tooth;
- 3000 for gingivectomy of 1 tooth.
Laser treatment after tooth extraction
Laser therapy is widely used in dentistry, including for healing the hole after tooth extraction, by stimulating cellular regeneration, reducing pain, and activating the immune system. However, dentists do not agree on whether this technique should be used after tooth extraction. Therefore, the researchers analyzed scientific articles about the results of laser therapy after tooth extraction.
The review included studies in human and animal models examining the effect of laser therapy on socket healing after tooth extraction. Overall, the results showed a positive effect of the therapy.
“According to the results of the work, laser therapy promotes faster healing of the hole. However, the lack of research is that the effect of different types of laser with specific settings was considered,” says study author Carmen Elena Jacques Lemes, a lecturer in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Federal University of Pelotas in Brazil.
Healing of the alveolar socket after tooth extraction is a long and complex process. Previous studies suggested that laser therapy promotes healing speed, while the procedure does not cause discomfort to the patient. It can act as an adjuvant therapy after tooth extraction for patients with immunodeficiency, for example, those with HIV or diabetes.
Despite the fact that laser is widely used for various dental procedures, not all doctors practice the use of this method for healing the alveolar socket. To evaluate the effectiveness of the method, the study authors conducted a large-scale review of scientific papers on this topic, including those in English, Spanish and Portuguese. The review included studies that included at least one laser treatment group and one control group. Studies in both animal and human models were considered.
As a result, 16 studies were selected - 8 conducted on animals, 8 on patients. A meta-analysis could not be performed because the studies used different types of lasers with different settings.
Among the clinical studies involving patients, 6 were split-type and 2 were parallel studies. In total, 461 patients took part in them, and more than 480 dental extractions were performed. In 7 studies, the study group included patients without immunodeficiency; in 1 study, HIV patients were included. 7 studies examined the healing processes of the alveolar socket after molar extraction in people under the age of 65; 1 study included patients aged 12 to 18 years.
In 6 studies, the choice of treatment method was carried out using random sampling. Low-level laser therapy was used for therapy using hydrogen fluoride, helium-neon, gallium-aluminum-arsenide and diode lasers. Therapy lasted from 1 day to 6 months.
Based on the results of 4 studies, it was shown that therapy with hydrogen fluoride, diode and gallium-aluminum-arsenide lasers contributed to better healing of the hole. The remaining 4 studies showed that therapy with gallium-aluminum-arsenide and helium-neon lasers does not affect the rate of healing of the sockets.
As for studies on animal models: 6 studies examined the effect of laser therapy on the healing of sockets in healthy rats, 2 studies involved animals with diabetes mellitus or animals after radiation therapy. The effects of carbon dioxide, gallium-aluminum-arsenide, helium-neon, high-frequency pulsed diode lasers and yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) lasers were considered. The total number of participants was 269 animals, which underwent a total of 326 tooth extractions, mainly molars. One study looked at using high-level laser therapy immediately after extraction to increase blood clotting to prevent clot loss.
The review periods for the study ranged from 6 hours to 21 days. Based on the results of the work, it turned out that laser therapy helps accelerate the healing of the hole after tooth extraction. Only 1 study showed the ineffectiveness of the helium-neon laser for this purpose. In general, the use of carbon dioxide, gallium aluminum arsenide, YAG and high-level diode lasers contributed to faster alveolar socket healing and bone regeneration in participants in the study group compared to the control group.
The authors emphasize that the reliability of the results of studies using an animal model may have been affected by the fact that many of the experiments performed were not based on random sampling. In most studies involving patients, the distribution and results of the experiments were not masked to the assessor. Also, the benefits of using low-level lasers have only been confirmed for certain types of lasers.
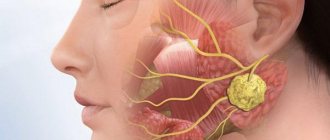
What are the clinical manifestations of a dental cyst?
In the first stages of the disease, the patient does not feel the problem at all. The only sign of pathology may be slight discomfort when pressing or a feeling reminiscent of crepitus (crunching). As the cyst grows, the following symptoms appear:
- a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth, a feeling of fullness, twitching, or fullness in the affected area;
- aching pain in the tooth or even in the entire jaw when biting, which makes differentiation difficult (typically worse at night);
- problems with the chewing process (discomfort and increased pain);
- an increase in the size of the gums on the affected side (its swelling, and with an exacerbation of infection - severe hyperemia);
- swelling of the face, in particular the cheeks on the affected side due to impaired functionality of the lymphatic system.
During the period of an acute infectious process in the area of the cyst, that is, during the development of flux, general signs of inflammation are observed: increased body temperature, headache, enlargement and soreness of the nearest lymph nodes. At such moments, the pain becomes sharp and throbbing.
Treatment of the disease
In our clinic, this disease is treated quite successfully. For this purpose, the canals are cleared of inflammation, then the canals are disinfected and hermetically sealed. After treatment of the infection inside the tooth, the tissue begins to recover and the granuloma goes away. The sooner you start treatment, the faster the restoration of the tissue around the tooth will begin, and, as a result, the lower the risk of losing the tooth. Let us add that surgical intervention in the treatment of this disease fades into the background in our country, but is still used in a number of difficult situations.
Treatment of dental cysts - basic techniques
Therapy for a dental cyst is rarely carried out in the initial stages of the development of the disease, but its accidental discovery cannot be ruled out either. All techniques can be divided into two large groups: therapeutic and surgical, with the latter being the most popular and effective. In recent years, the development of dentistry has also highlighted the treatment of dental cysts with a laser, but the effectiveness of the method is still highly doubtful. Dentists recommend not to take unnecessary risks and treat with classical methods that give guaranteed results.
Installation
The principle of using turunda is simple, you need to twist the material into a rope, then close the hole, reaching to the bottom. Cavities should not be left, and the doctor should not apply too much pressure, further injuring the tissue. If empty cavities remain after the procedure, there is a high risk of bacterial growth and inflammation.
Installation Features:
- inspection of the cavity after the intervention, the fragments must be completely removed, as they can cause inflammation and the appearance of pus;
- the turunda is tightly inserted into the hole, filling the cavity;
- The turunda is bitten to eliminate the remaining free voids.
The turunda remains in the hole for the entire time recommended by the doctor; you cannot remove the gauze yourself earlier. In case of inflammatory processes, the tampon is impregnated with medications. It is placed in the hole for one to two weeks, during which it cannot be removed. During normal removal, the gauze swab remains in the hole for no more than twenty to thirty minutes.
Attention: Turunda cannot be kept in the hole for a very long time, as it will become a source of proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Also, a tampon left for a long time prevents the formation of clots at the operation site.
After removing the gauze, you need to make sure that bleeding does not start. This situation often occurs if the patient is taking any blood-thinning medications.
There are no special contraindications to the use of turunda, however, the patient should not have allergic reactions to the iodoform used for impregnation and other materials used for treatment. The doctor must conduct a preliminary test. If there are no rashes or itching, turunda can be used to stop bleeding and protect the wound. If allergic reactions occur, other methods are used, for example, sterile bandages.
Why does granuloma occur?
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of this disease. Let's name the main ones:
- Chronic pulpitis can cause the development of granulomas.
- The root canal is not completely sealed or, conversely, the filling goes beyond the root apex can also lead to the development of this disease.
- If an instrument breaks in the root canal or in the periapical tissues, periodontitis develops as a result, which can also be granulomatous.
- If there are large periodontal pockets, infection can penetrate through them into the periapical tissues.
Regardless of the cause, you need to know that every inflammatory process in the body requires treatment, regardless of its nature and stage.