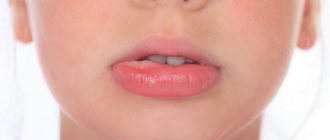
Reasons why the roof of your mouth may hurt
The upper part of the oral cavity, covered with mucous membrane, is divided into 2 parts - the hard and soft palate. The hard part is the bone wall that separates the oral and nasal cavities. It begins just behind the front teeth and smoothly transitions into the soft fold of mucous membrane near the base of the tongue that separates the oral cavity from the pharynx.
To find out why the roof of your mouth hurts, you should consult a dentist, since there are many prerequisites leading to the appearance of such symptoms. Below are just a few of them:
- People eat hot and hard foods every day, which can burn or scratch areas of the roof of the mouth, both near the front teeth and closer to the throat. And in addition, many people forget about basic hygiene rules, as a result of which harmful microorganisms develop in the oral cavity - and the mucous membrane covering it becomes inflamed. It should be remembered that even a small wound is susceptible to infection.
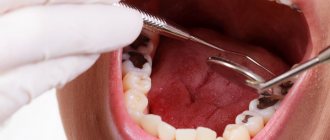
The photo shows an inflamed sky
The cause of pain in the palate and the appearance of a white coating on it can be a fungal infection. The most common causative agent of oral inflammation is Candida fungus, which can affect not only the inside of the mouth, but also the lips. Candidiasis or fungal stomatitis often occurs in girls and infants.
- The palate can become inflamed when the herpes virus is activated. This disease manifests itself not only externally (on and around the lips), but also inside the mouth. Patients feel itching in the affected area, and sometimes their body temperature rises.
- With the development of tonsillitis, a sharp enlargement of the tonsils is observed, accompanied by their redness. Sometimes with this disease, the upper palate becomes inflamed and swollen, turning a bright red hue.
- Don’t forget about one of the most common diseases of children and adults – caries. It usually affects only the teeth, but the infection can spread to the surrounding soft tissue.
- Inflammation of the palatal tissues may indicate the formation of a benign tumor, so it is important to constantly monitor your condition.
- If the soft tissues of the tongue and palate on top are swollen and covered with whitish spots, it is worth checking for the presence of leukoplakia. This disease develops in those who often eat hot food, come into contact with chemicals, as well as in people with improperly installed dentures or chipped teeth.
- The cause of inflammation of the palate is often the passage of procedures using galvanic current - when installing braces, crowns, and during some types of dental treatment.
- Redness, swelling and irritation of the gums and other soft tissues inside the mouth in adults can be caused by smoking and drinking alcohol.
Signs of inflammation of the palate in the mouth are varied and depend on the cause of its development, so self-diagnosis in this case is difficult. That is why it is necessary to contact a specialist with this problem as quickly as possible to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment.
Sometimes areas of the soft palate closer to the throat swell due to allergies to medications. If pain is felt while taking medication, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor. If the soft tissue swells too quickly, an antihistamine should be taken.
Functions of the sky
The palate is a mucous membrane-covered bony structure formed by specific processes of the two halves of the upper jaw. Its main purpose is considered to be to separate the mouth from the nose. The sky performs the following functions:
- the penetration of saliva and food into the area responsible for breathing and recognizing aromas is prevented;
- serves for continuous movement of inhaled and exhaled air;
- necessary for the separate participation of the mouth and nose in the formation of sound.
In addition to the fixed bony part of the palate, there is also a soft part. It is a duplicate of the mucous membrane, which moves up and down with a special muscle: with its contraction, the soft palate rises, and when relaxed, it falls.
During a calm state, the soft palate hangs down, allowing the air stream to pass easily. But during swallowing, with tension and blocking access from behind, from the side of the nasopharynx, it hermetically separates two large cranial strips from each other, protecting the nasal cavity from the penetration of food.
The main signs of inflammation of the palate
Some symptoms of inflammation can reveal its nature. The color of inflamed tissue can tell a lot. Redness accompanied by enlarged tonsils indicates the presence of tonsillitis. Bubbles filled with clear exudate indicate herpes. Red ulcers covered with a white cheesy coating indicate a fungal infection.
Infectious diseases are almost always accompanied by unpleasant sensations - the palate hurts, swells, bleeds and burns when swallowing. Often, not only the palatine bridge on top swells, but also the tongue, which leads to increased salivation and problems with swallowing. As a result, irritation of the larynx and throat may begin, in which a burning sensation is felt, ulcers appear, pain and swelling occur. It becomes extremely painful to swallow food. Sometimes the gums begin to bleed, and in rare situations the body temperature rises.
What does the sky look like during inflammation in the photo?
Why did the sky turn yellow?
The palate area, like all areas of the skin and mucous membranes on and inside the head, has an abundant blood supply due to a dense network of capillaries.
The palate owes its normal color to the color of the blood flowing through them: in hard ones it is pale pink, in soft ones it is also pink, but of a more saturated dark tone. When inflamed, the color may become flaming crimson or bluish with a purplish tint. If the palate turns red and the throat hurts, this is considered normal, but the palate should not be yellow. For what reason does its color change?
The first thing that comes to mind is smoking. Indeed, the resins contained in tobacco and released when it burns stain the oral mucosa, giving it various shades of yellow and cause the formation of plaque on the palate.
Treatment options for inflammation and pain in the palate
Some causes of inflammation of the palate are quite dangerous, so treatment should begin immediately after diagnosis. Treatment tactics depend on why the mucous membrane lining the upper part of the oral cavity is inflamed.
In case of mild mechanical or thermal damage to the palatal tissues, you can rinse your mouth with a solution of soda and salt or tinctures and decoctions of herbs: chamomile, sage, oak bark. To relieve pain caused by a person burning the oral mucosa while tasting a dish, it is enough to rinse your mouth with cold water or a soda-salt solution.
If the palate is quite inflamed, you should resort to the use of local anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications. To quickly remove pain and itching, you should supplement traditional drug therapy, and also eliminate the risk of infection in small scratches and sores.
To get rid of inflammation of the palate, you should treat not only the symptoms, but also the disease that provoked its appearance. For example, if you have a sore throat, you need to take antibiotics; the therapeutic course can last 1–2 weeks. Fungal diseases are treated only with antifungal drugs in the form of ointments, sprays and gels. Viral - antiviral. All infectious pathologies indicate a weakened immune system, and therefore require a therapeutic course to strengthen it.
If the palate is inflamed due to dental caries or pulpitis, treatment by a dentist will be required. A person will not be able to get rid of the disease until his teeth are treated, since caries is a constant source of infection in the mouth.
Essential medicines
Wounds and ulcers formed due to inflammation of the upper palate should be treated with antiseptics, for example, Rotokan, Chlorhexidine or Furacilin. The following drugs fight fungal inflammation:
If the roof of your mouth hurts too much, you can make warm infusions for rinsing with chamomile, propolis, eucalyptus or oak bark at home. But it is better to purchase an anesthetic in the form of a spray at the pharmacy: Hexoral, Lidocaine Asept or Benzocaine. Dental gels such as Cholisal, Lidochlor, Kamistad have mild analgesic properties. Their main function is to relieve inflammation, and their secondary function is anesthesia.
Read also: My first freestyle wrestling coach
If inflammation of the palate, accompanied by swelling, is caused by viral agents, antiviral medicinal sprays Miramistin, Lugol, as well as Acyclovir ointment are suitable. If the palatal tissues are swollen due to viral stomatitis, you can use folk recipes for medicines that can be easily prepared at home. The main ingredients in them are sea buckthorn and rosehip oils, propolis tincture.
Prevention of infectious lesions of the upper palate
It is easier to prevent inflammation of the palate than to cure its advanced stage. To do this you need to do the following:
- Limit the intake of solid foods - crackers, caramel, chips, lollipops, cookies. They can accidentally scratch the oral mucosa.
- Wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly. By consuming dirty foods, you can introduce infection into wounds and scratches on the oral mucosa, which can lead to the development of inflammation.
- Eliminate excessively cold and hot foods from your diet so that they do not burn the soft tissues in your mouth. This rule must be followed if the palate is already inflamed.
- Stop drinking sweet soda, as it irritates the oral mucosa. Strong alcohol has the same effect.
- Brush your teeth regularly. Brushing your teeth twice a day will not only protect against caries, but also prevent bleeding gums and the appearance of swelling near the uvula. You should also rinse your mouth after every meal, especially if your palate is already swollen.
- Constantly strengthen your immune system. You need to exercise, eat natural foods, plan your diet wisely, ensure regular good sleep and monitor the replenishment of vitamins and microelements.
- Treat your teeth regularly. To make your teeth strong, it is not enough to brush them daily and eat right. In addition, you should visit the dentist 2 times a year to undergo preventive examinations, remove tartar and plaque, and promptly treat caries and gingivitis (gum inflammation).
- Consult a doctor for any symptoms of dental diseases and pathologies of the ENT organs: if the throat turns red, the tonsils become swollen, signs of inflammation begin to be felt, wounds, ulcers and swelling appear in the mouth, and pain occurs in the palate.
- Monitor the condition of children's teeth. This rule applies to parents. It is worth explaining to your child that you should not put your hands or dirty objects in your mouth. Explain why exactly you shouldn’t do this.
Every person should take care of their oral health. Maintaining immunity, proper nutrition, good hygiene and timely visits to the dentist will help completely eliminate the risk of developing diseases of the palate and the appearance of pain in this area. If the inflammatory process has already begun, you should urgently consult a doctor and follow all his treatment recommendations.
When performing daily hygiene procedures for cleaning the oral cavity, you should carefully examine the mucous membrane of the palate and tongue.
Identified red spots, plaque and yellowness indicate problems that have arisen in the body. It is easier to prevent the development of any disease if you seek help from a doctor as early as possible.
Palate cancer: symptoms, photos, first signs at the initial stage, treatment and prognosis
Palate cancer is a rare malignant neoplasm that occurs in the oral cavity.
As a rule, it is not recognized as a primary pathology, but becomes a consequence of metastasis of tumors that arise in the head and neck area. The risk group includes men over forty years of age.
The disease rarely affects women. Bad habits, especially smoking, significantly increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
The palate is the structure that separates the oral cavity, nasal cavity and nasopharynx. Anatomically it contains two sections: hard and soft. The hard part is represented by bone, forms the arch and participates in the formation of the walls of cavities. The soft palate is called the velum palate and consists of connective tissue and muscles.
Classification of oncological pathology of the palate
Depending on the location of the tumor, two types are distinguished: cancer of the hard palate, in which the pathological process affects bone structures; and cancer of the soft palate, affecting the mucous and muscular part of the vault. The cancerous growth appears as either a nodule or an ulceration.
Another classification is based on the source of tumor growth:
- Cylinder. The source of atypical cells is glandular tissue. This histological type of tumor is characterized by intensive growth and rapid formation of metastases.
- Adenocarcinoma. The tumor is of epithelial origin. It can occur with cancer of any part of the palate.
- Squamous cell carcinoma. It occurs in practice more often than other types. Cancer cells form in mucous tissue.
Medical professionals use the TNM classification. T (tumor) – characterizes the degree of damage to organ tissue by a tumor. It is divided into subtypes Tis, T1-T4, where Tis is pre-invasive cancer.
- T1 – the size of the tumor does not exceed two centimeters.
- T2 is a formation measuring two to four centimeters.
- T3 – stage with a tumor larger than four centimeters.
- T4 – cancer grows into nearby tissues.
N (nodus) reflects damage to the lymph nodes. Classified by degrees from N0 to N3, when the lymph nodes are not affected, affected on one side, on both sides and fused with surrounding tissues, respectively.
The last characteristic is the presence of metastases, M (metastasis). Grade M0 is allocated when there are no metastases, and grade M if metastatic lesions are detected.
Causes of palate cancer
The reasons are varied, but one common feature is damage to the oral mucosa. In the first place is damage to the cells of the oral mucosa due to the toxic effects of nicotine, alcoholic beverages and narcotic drugs.
Over a long period of time, carcinogenic substances come into contact with healthy structures. Constant exposure eventually leads to cell damage and inflammation. High risk of malignant pathology.
Regarding smoking, this applies not only to active smokers, but also to passive ones.
Certain dietary habits can lead to the development of cancer. Eating excessively hot, spicy and sour foods is irritating and disrupts the cell structure due to temperature effects.
Cancer can develop due to a lack of vitamin A in the human body. Mechanical injuries take their toll.
For example, damage from a fork while eating, incorrect installation of dentures, wearing braces.
Human papillomavirus predisposes to the development of cancer. This virus has a tropism for squamous epithelium, so it can multiply in the oral cavity.
It has been proven that there is a connection between infection with the papilloma virus and the occurrence of cancer. The same applies to leukoplakia. This disease is precancerous, like papillomatosis.
Hereditary predisposition is of great importance. It is important to find out cases of the disease from relatives.
Symptoms of the disease
The initial stage of palate cancer has no symptoms. Therefore, diagnosis is difficult. Pathology can be suspected by a dentist during an examination or by a patient when the tumor is palpated with the tongue in the form of a lump or ridge. At this stage, you should urgently consult a doctor, since treatment at this stage will be highly effective.
As the dense area increases, the clinical picture of the disease unfolds. Weight decreases, increased fatigue appears, which was absent before or was less pronounced. As the tumor grows into nearby tissues, the patient feels pain that spreads to the temporal region and ear.
There is discomfort when chewing food, and then you can feel bad breath and an unpleasant aftertaste. Patients notice a symptom that is a change in speech. The mouth seems to be filled with something, words seem to be pronounced more slowly and less clearly, dialogue with the interlocutor causes discomfort.
A nasal voice appears.
The late stage is characterized by the appearance of specific symptoms that speak in favor of palate cancer. The first signs a person feels are:
- The mucous membrane is edematous.
- Numbness of the oral mucosa, followed by pain.
- Voice changes, hoarseness and roughness.
- In the area of the changed cancer cells, white spots appear, which later turn red.
- Bleeding without an established cause from the structures of the oral cavity.
Stages of development of palate cancer
In medicine, there are traditionally four stages of development of oncological pathology:
- Stage 1. The tumor is located within the hard or soft palate. Limited to the mucous and submucous membranes. Regional lymph nodes are not affected, there are no metastases. At this stage there are no clinical manifestations of cancer.
- Stage 2. The cancer also does not extend beyond the hard or soft palate. The compaction grows and reaches four centimeters. This allows the dentist or the patient to notice the pathology.
- Stage 3. The oncological neoplasm begins to grow into neighboring tissues. Regional lymph nodes are involved in the process, there are no metastases yet. The symptoms are pronounced.
- Stage 4. The tumor reaches an impressive size and affects nearby organs. The patient's condition is serious. Distant metastatic foci are detected. Progresses rapidly.
Diagnosis of palate cancer
If a malignant process of the palate is suspected, a visual examination is first performed. Then laboratory and instrumental research methods to confirm or refute the diagnosis. The results are assessed by an oncologist.
- Blood test - the content of leukocytes and hemoglobin is assessed to identify processes of inflammation and anemia.
- Test for tumor markers - specific antibodies that confirm the presence of oncological degeneration of cells.
- X-ray of the jaw - allows you to determine the exact location of the tumor, contours and extent.
- Radioisotope study - allows you to study the internal structure of the tumor.
- Taking a biopsy of the tumor and lymph nodes, followed by cytological examination. Confirms the presence of atypical cancer cells.
Treatment of the disease
The success of treatment directly depends on the time when the patient sought help: the sooner, the better. The quality of therapy depends on the experience of the surgeon and the individual characteristics of the body. The final choice of treatment method is based on the stage of the disease, the extent of the process and the presence of distant metastases.
Radiation therapy
X-rays are used to inhibit the division of cancer cells and stop their progression. It is used as the main method of treatment when cancer is detected in the early stages. In the latter case, complete remission is possible. In later stages, it is used as an additional therapy to surgical treatment, both before surgery in terms of preparation and after it.
Surgery
The pathological tumor and a small part of healthy nearby tissue are removed. In the early stages, they try to avoid surgery. This is a mutilating intervention, and after it there will be a defect on the face.
If it is not possible to not perform the operation, then it is performed in several stages: first the main therapeutic stage, then the reconstructive stage. Sometimes it is enough to establish dental processes, but in severe cases a bone and skin flap transplant is required.
The bones of the ribs, upper and lower limbs are used to form the lower jaw. Modern medicine has special implants that can replace the removed bone.
Chemotherapy
The patient takes cytostatic drugs that act on cancer cells and destroy them. Chemotherapy drugs are available in the form of tablets and in the form of a system for intravenous drip administration. Chemotherapy is difficult for patients to tolerate, with severe side effects such as nausea, vomiting, pain and hair loss.
Rehabilitation after treatment
One of the main functions of the oral cavity is participation in the formation of sounds and speech, respectively. Operations on the palate involving adjacent tissues are extremely traumatic and are accompanied by loss of speech production function.
In this case, on the fifth day after the operation, a speech therapist is invited to work with the patient. The work involves performing various exercises, the goal is to strengthen the facial muscles.
If the mandibular bone is preserved, the patient relearns its movement.
As progress develops, articulatory gymnastics exercises are introduced. Their goal is to restore the functioning of the language. This helps to restore speech function and normalize the swallowing process, which is also disrupted after surgery.
Complications
Palate cancer is a dangerous disease. The head and neck are supplied with blood extremely well, so all pathological processes spread in the shortest possible time. Nearby are vital organs - the brain, respiratory tract, large blood vessels (branches of the external and internal carotid arteries), and nerve trunks. When these structures are involved, the prognosis becomes unfavorable.
Once the tumor ulcerates, there is a high risk of secondary infection and microorganisms entering the blood. In conditions of reduced immunity, a septic condition will occur, characterized by multiple organ failure.
When cancer grows into blood vessels, life-threatening massive bleeding is possible. An increase in the size of the tumor threatens to form a mechanical obstruction to the passage of air into the lungs, in which case asphyxia will develop.
Probability of disease recurrence
After intensive therapy, the patient is discharged home. He must be observed by an oncologist on an outpatient basis for a year. It is recommended to visit a doctor for a preventive examination every three months. This will allow you to recognize the symptoms of relapse in time and carry out treatment again.
In case of relapse, a cancerous tumor arises either in the same place or in other organs. Distant metastases are difficult to diagnose if the cancer cells are dormant in the organ they entered through the blood or lymphatic system. The period of remission in this case can be long.
Survival prognosis
A favorable prognosis for cancer of the palate will be if cancer is detected in the early stages and treatment is promptly initiated. For example, at stage 1 cancer, the five-year survival rate is eighty percent.
In the second stage, the percentage of survivors after five years drops to fifty percent. At the third stage, survival does not exceed a quarter of cases of the disease.
When the fourth stage is detected, the prognosis is unfavorable - only five percent of cases.
Disease prevention
The only method of prevention is maintaining a correct lifestyle. Considering that ninety percent of those sick were smokers, you need to quit smoking first. Then give up other bad habits. If you can’t completely eliminate alcoholic drinks from your life, then at least try to minimize their consumption.
The next point is nutrition. The diet should be balanced. It is recommended to eat more fruits and vegetables, greens. Since vitamin A is important, you can get tested for its concentration in the blood and take supplements.
Here you should be extremely careful: you must consult a doctor, since an overdose of vitamin A has a toxic effect on the body and causes night blindness.
Food should be above room temperature, but in no case scalding. Minimize your consumption of spicy foods.
Periodically you need to visit the dentist for a preventive examination. If you notice bad breath or a strange aftertaste, it is better not to delay a visit to a specialist. The recommended frequency of inspections is once every six months.
Source: https://onko.guru/organ/rak-nyoba.html
Causes
The palate area, like other areas of the skin and mucous membranes, is characterized by a strong blood supply, which is due to the presence of a dense network of capillaries.
The normal color formed on the surface indicates the absence of an inflammatory process in the body and other serious disorders. A change in the color of the palate is a manifestation of the symptoms of the disease, which is determined after the study.
The reasons that provoke the formation of yellowness can be found in the table:
| Reasons for the formation of yellow plaque on the palate | ||
| Reason name | Description | Additional symptoms |
| Liver diseases | The most common liver diseases, recognized by the yellowness of the palate, are: jaundice, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis and syphilis. When an organ is damaged, disruptions in the functioning of all systems and metabolic processes occur: protein, carbohydrate, fat, pigment, etc. Depending on the disease, the corners of the palate and the boundaries between soft and hard tissue (with cholecystitis, bile stones) or the entire surface of the mucous membrane turn yellow. (for hepatitis). |
|
| Pancreas problems | The organ regulates energy exchange and biochemical processes occurring in the human body. If there are problems with the pancreas, one of the main signs appears - the soft palate acquires a bronze tone. If malfunctions occur in the biliary system, the color is combined with pronounced jaundice. |
|
| Intestinal inflammation (large/small) | Yellowness on the upper palate with intestinal dysfunction appears due to the morphofunctional unity of the oral mucosa and the gastrointestinal tract. The color of the palate changes to yellowish both in individual zones and over its entire surface. The neglect of the disease is reflected in the intensity and structure of plaque. |
|
| Kidney failure | The main provocateurs of renal failure: urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus, pyelonephritis, neoplasms, lipid metabolism disorders. As a result of a failure of metabolic and biochemical processes, yellowness appears on the hard palate. Additional symptoms help determine whether the kidneys are involved in the problem. |
|
| Cholesterol and fat metabolism disorders | Cholesterol metabolism disorders are accompanied by a change in the color of the soft palate from pink to yellow. At the same time, gray lumpy spots are clearly visible on the surface of the mucosa. Failures in fat metabolism are recognized by a pale icteric coating on the palate. The main provocateurs of metabolic disorders are: tuberculosis, diabetes, oncology. |
|
| Smoking | The color of the palate changes under the influence of resins, which are included in tobacco in high concentrations. A bad habit provokes disruption of blood circulation and biochemical processes in tissues associated with disruption of metabolic and other processes. The mucous membrane loses its pink color and becomes yellow. |
|
Diagram of the oral cavity
What diseases can we talk about?
If problems with the oral cavity of a local nature are more often manifested by redness, with a sore throat and other symptoms on the mucous membrane, then pathologies of the internal systems often look different. Let's describe the most common situations:
- The pancreas may change the color of the mucous membrane to bronze. If yellow color is added to it, it indicates problems with the adrenal glands. This symptom is usually found in patients with Addison's disease. Only the soft part of the palate acquires a characteristic color.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract often lead to yellowing of the oral mucosa. This is due to the fact that with pathologies of these organs, salt deposition, acid secretion, and chronic inflammatory processes occur, manifested by constipation. As a result, the tissues in the mouth, skin and other body systems react. Often a yellow sky is an indicator of problems with the intestines, stomach, pancreas, etc.
- The work of the liver and pathologies in its functioning are most often reflected in the condition and shade of the mucous membrane and skin. In this case, one can judge the nature of the disease by visible changes. For example, if the line in the middle of the palate turns yellow, as well as the corners near the soft part on the sides, then this indicates cholecystitis or gallstones. Cirrhosis appears as yellow spots, and viral hepatitis completely colors the mucous membrane in a bright shade.
- Kidney problems, for example, renal failure, threaten not only tissue swelling, but also general intoxication of the body. If this system does not cope with the release of waste, this leads to the accumulation of uric acid, heavy metal salts, poisons and toxins. As a result, the biochemistry of the blood is disrupted and the color of tissues, including the mucous membrane of the palate, changes. In this case, inflammatory processes of the periodontium, bleeding gums are often observed, the patient feels a bitter taste and dry mouth.
- Failures in cholesterol metabolism appear as grayish or yellowish spots. They appear lumpy and cover the soft surface, occasionally affecting the hard palate.
- As a result of diseases such as tuberculosis or diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism is disrupted. This causes the mucous membrane to turn pale. The presence of neoplasms and oncology may look the same way.
- Syphilis, HIV and other dangerous infections lead to disruptions in the functioning of all internal organs, which is also manifested by yellowing of the oral mucosa.
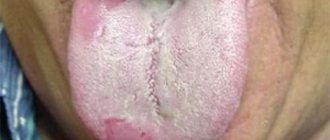
Yellow palate in the mouth of an adult
If the sky has turned yellow, you should see a dentist. During the examination, the specialist will determine whether the yellowness of the mucous membrane is a sign of any disease, or indicates a lack of proper oral hygiene.
The patient’s attitude towards bad habits is also taken into account. Yellowness with a pronounced network of veins is often formed as a result of regular smoking.
When conducting diagnostics, the patient's age is taken into account. In people over 50 years of age, the appearance of yellow plaque on the palate is considered a physiological process, so serious health problems are not always detected.
Read also: What to drink orange liqueur with
The child has
A yellowed sky appears not only in adults, but also in children. In addition to dental problems, this sign may indicate other diseases, so the child should be shown to a gastroenterologist, ENT specialist, pediatrician, infectious disease specialist, or hepatologist.
Often, young patients with this symptom are diagnosed with thrush. If there is any doubt in determining the problem, it is recommended to undergo a full examination, including donating blood to check bilirubin levels.
Diagnostics
The initial examination should be entrusted to the dentist; problems with the oral cavity are within his competence. The specialist studies not only the oral mucosa, but also the condition of the gums, teeth and the gaps between them.
This is where signs of thrush or stomatitis may appear. Based on the visual examination, the doctor outlines the following stages of diagnosis.
Changed color of the palate may be an independent condition or indicate the development of other diseases.
To clarify the diagnosis, the dentist refers the patient to the following specialists:
Diagnostics also includes laboratory tests of biological samples: blood, urine, feces.
If an allergy is suspected, the patient is referred to undergo:
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI;
- x-ray.
The doctor examines the oral cavity
Carrying out diagnostics
When a person notices that the shade of his mucous membrane or palate has changed, he should definitely consult a doctor. Initially, patients visit a dentist or therapist in this case. And when, after an examination, the doctor decides that a consultation with another specialist is needed, he can refer you to an otolaryngologist, nephrologist, gastroenterologist, oncologist, allergist, urologist, etc.
To establish a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, it is not enough just to see the condition of the oral cavity. Most often additional procedures are performed:
- blood, urine, stool tests;
- allergy tests;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI or CT;
- radiography.
Only with a fully collected medical history and the results of laboratory and instrumental studies can we talk about what exactly was the root cause that caused disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems. And only by eliminating the main factor can we expect that the condition of the mucous membrane will be restored.
Treatment
The results of the patient's studies indicate a problem existing in the body.
A specialist with a narrow profile will be able to prescribe treatment: nephrologist, gastroenterologist, urologist.
If signs of a systemic disease are detected (syphilis, rheumatism, HIV, etc.), a referral is given to the hospital of a specialized medical institution.
When oncology is detected, a treatment regimen is developed jointly with other specialists: a surgeon, oncologist, neurologist, ophthalmologist, etc.
Diagnosing a local viral infection on the oral mucosa involves prescribing antiseptics and antibiotics to suppress the inflammatory process and destroy the pathogen. The same drugs are used to treat periodontitis, gingivitis and in cases where it is necessary to prevent ulcerative-necrotic complications.
Whatever treatment method is chosen, the doctor also prescribes oral hygiene procedures:
- professional cleaning;
- selection of products for daily hygiene of the dentition and oral mucosa;
- regular rinsing with an antiseptic solution.
An equally important step is strengthening the body’s protective functions. For these purposes, regular intake of vitamin complexes is suitable, which promptly replenish the deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals.
Traditional methods
In folk medicine, mainly components of plant origin are used, which have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and other effects.
To remove yellow plaque from the palate, local treatment with various infusions and internal use of infusions and products to strengthen the body's protective functions are recommended.
Eg:
- infusions and teas from marshmallow root, St. John's wort, licorice, and chamomile provide an excellent antiseptic effect;
- rinsing the mouth with a decoction of sage, calendula, and yarrow has an antibacterial effect;
- consuming bee products and citrus fruits strengthens the immune system.
The traditional medicine methods used must complement the general principles of treatment recommended by the doctor, but in no case should they contradict official requirements.
It is also worth considering that infusions, decoctions and teas have an enhancing effect of traditional therapy, but they cannot replace drugs and procedures.
Preventive measures
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to periodically undergo dental examinations.
This will help identify the disease at an early stage and begin a course of treatment in a timely manner, thereby preventing the development of complications.
It is also necessary to carry out daily oral hygiene procedures to remove food debris and remove plaque from the mucous membrane.
The main defense of any person is, first of all, immunity. To strengthen it, you should maintain physical fitness, radically review your diet, and enrich the body with valuable minerals and vitamins.
The following recommendations are also preventive measures:
- You should not overuse spicy, salty foods, or foods with a hard structure;
- after eating, you need to rinse your mouth with a special balm or at least clean water;
- If you experience unpleasant sensations in your mouth, rinse for several days using decoctions of propolis, chamomile, oak bark or sage.
Quitting bad habits, in particular smoking, can prevent the formation of yellow plaque on the palate.
Prevention
Thorough professional and daily home oral hygiene is an important measure to prevent any dental problems. Strengthening the immune system, a balanced diet, and proper nutrition will help avoid any diseases of the digestive tract and excretory system.
It is not always possible to prevent and avoid any diseases. But if you adhere to general medical recommendations, you will be able to significantly reduce the risks of pathologies.
To do this you need:
- regularly clean your teeth and tongue, perform hygiene procedures twice a day, morning and evening;
- after each meal, it is advisable to rinse the mouth with warm, clean water or special decoctions;
- avoid spicy and salty, as well as excessively hard or hot foods, so as not to injure the mucous membranes;
- Visit your dentist every 6 months for preventive examinations and professional cleanings;
- monitor your health, increase your immunity, eat right, and strengthen yourself;
- In case of any ailments, consult a doctor promptly;
- If you have an allergic reaction, try to avoid allergens as much as possible;
- give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
What color is the palate of a healthy person and what does it look like?
The human palate is located in the upper part of the oral cavity, which consists of two lobes: soft and hard. The hard palate is located closer to the dentition, and the soft palate is in the tonsil area.
Their structure is formed from sensitive tissues covered with a mucous membrane, which explains their tendency to immediately respond to various stimuli.
The mucous membrane of a healthy palate looks like this: it has an even color of a soft pink tone, no veins are visible on the surface. If any changes are detected, you should consult a specialist for advice.
After examining the oral mucosa and studying the characteristic signs, the doctor will give recommendations for additional examination. Based on the test results, an accurate diagnosis is made and an individual treatment regimen is developed.
You should not ignore the appointments, because a change in the color of the palate indicates that irreversible processes have begun in the biochemistry of tissues.
Inflammatory and infectious pathologies of the throat, gums, dental diseases, mechanical damage to the mucous membrane - all these are reasons that can provoke inflammation of the palate (palatinitis). As a result, pain occurs, the timbre of the voice is disrupted, and the pitch of the sound changes. The goal of treatment is to eliminate provoking factors and prevent serious complications with the help of medications and traditional recipes.
Inflammation on the palate
Causes of inflammation of the palate
Components of the palate:
- hard palate or upper palate - bone tissue, has an arched shape;
- soft or lower - consists of the mucous membrane.
The main function of the organ is to prevent food from entering the nasal passage from the mouth. Additional responsibilities include participation in articulation through superficial receptors that are associated with the larynx.
The functioning of the palate can be affected by an inflammatory process that affects mucous tissues due to exposure to external irritants or dysfunction of internal organs.
Table “Causes of inflammation of the palate”
| External factors | Consuming hot foods or drinks, which can cause a burn to the mucous membrane (blue, swollen palate, bruising) |
| Negative effects of metals (braces, crowns) on a healthy oral environment | |
| The use of prostheses (friction of a foreign body on the mucous membrane over time can provoke wounds or ulcerative processes) | |
| Abuse of tobacco products | |
| Ignoring oral hygiene. If you do not brush your teeth or rinse your mouth for a long time, any mechanical damage (scratches, bruises) can allow infection to enter the body. | |
| Wounds, ulcers due to injury or an injection of anesthesia during tooth extraction (treatment). As a result, vascular spasm or ischemia occurs, which leads to a benign compaction - sialometaplasia | |
| Pathological conditions of the oral cavity | Fungal or bacterial infections, viral pathologies provoke a rash on the mucous membrane - enanthema (in a child it is expressed in the form of hyperemia of the mucous membrane, small pimples, ulcerations) |
| Development of infection in the bone tissue of the jaw (osteomyelitis) | |
| Seals of oncological etiology. Often found in adults with pathological immune disorders | |
| Damage to the joints of the jaw (upper or lower) due to the development of neurological abnormalities | |
| Upper respiratory tract infections (tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, rhinitis) | |
| Dental diseases (caries, periodontitis, stomatitis, pulpitis) | |
| Allergic manifestations to drugs | |
| Temporomandibular joint dysfunction |
Read also: How much do Marco Polo cigarettes cost in Russia
Inflammation of the palate does not occur hidden. Usually the pain is pronounced, which makes chewing food very difficult and becomes acute when swallowing. Depending on the reasons that led to this condition, there are many symptoms of the disease.
- With fungi and bacteria (often happens in children under 1 year of age due to the fact that the child puts everything in his mouth) - a white coating and small ulcerations appear on the palate. The mucous membrane burns, hurts (especially while eating), and a putrid odor appears from the mouth. In adults, infection can develop after poor-quality tooth extraction, be a consequence of dental pathologies, or result from injuries.
- In case of throat diseases (tonsillitis, sore throat), the upper palate is red, there is swelling, the mucous membrane is loose. Swallowing is accompanied by pain and tingling, and severe irritation of the mucous membrane develops.
- With malignant tumors, the patient's palate hurts inside, with aching discomfort.
- After tooth extraction, bruising and swelling are observed closer to the teeth near the gums.
- In case of liver dysfunction, there is a yellow coating on the soft and hard palate, slight swelling and redness are possible.
- When you have a cold, the upper part of the oral cavity stings, cramps, and the mucous membrane is rough.
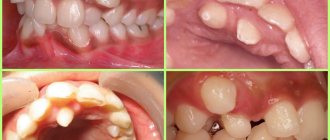
The photo shows what a healthy palate looks like and one affected by foci of inflammation.
Palate without deviations
Inflammatory process on the palate
Types of diseases that can cause pathology
Yellowness of the sky can appear due to the following ailments:
- Jaundice. It increases the concentration of the hormone bilirubin in the blood. Yellow sky is a symptom of infection with hepatitis viruses, cirrhosis of the liver, and obstruction of the biliary tract. The patient experiences nausea, vomiting, belching, and difficulty defecating. Treatment is performed after identifying the virus that caused the pigmentation changes.
- Syphilis. At stage 2, which lasts 2-5 years, symptoms of the disease appear periodically. Yellow spots usually appear in the mouth. There is a feeling of weakness and aching in the muscles. Hair loss also occurs. Unpleasant symptoms can be avoided with timely treatment. Penicillin or antibiotics are often used. We also need procedures to strengthen the immune system.
- Cholelithiasis. This is a gallstone disease that causes a yellow tint to the palate. The reason may be the filling of the gallbladder with stones formed due to the accumulation of cholesterol and salts. In this case, different methods of breaking stones are used. In advanced cases, the gallbladder must be removed through surgery.
- Cholecystitis. With it, a pronounced yellowness appears. Additional symptoms include a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea and pain in the right hypochondrium. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, means to normalize digestion, and detoxification.
The specific causes that provoke the development of cancer of the oral mucosa are unknown.
But the opinion of scientists from different countries agrees that the following factors become the trigger button:
- There are pathological processes that precede malignant formations
: infection with the papilloma virus; - addiction to smoking tobacco and drinking alcohol (when bad habits are combined, the risk of developing the disease increases);
- the male part of the population is susceptible to the disease more often than women;
- lichen on the mucous membrane;
- malnutrition, leading to a deficiency of microelements in the body;
- working in hazardous occupations;
- weakened immune system;
- consuming too hot food and drinks.
Risk factors include:
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking, chewing and sniffing tobacco);
- the presence of prosthetic structures in the oral cavity, which periodically injure the mucous membrane with sharp edges;
- work in enterprises where there is an increased concentration of toxic substances, asbestos and other chemical compounds;
- complications after complex injuries of the jaw system or tooth extraction operations.
Diagnostics
To find out the factors that provoked inflammation of the palate, the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination:
- Examination of the oral cavity by a dentist and, if necessary, an otolaryngologist.
- Laboratory research. General and biochemical blood test, scraping (for seals on the palate).
- Ultrasound, computed tomography – for immune pathologies and diseases of the digestive system.
A blood test is done to identify the causes of inflammation of the palate.
If inflammation and pain are caused by dental disorders, you need to undergo an x-ray of the jaw to rule out purulent processes in the bone tissue.
Only after making a diagnosis can the doctor choose a special treatment that will be aimed at eliminating the source of the problem and improving the patient’s well-being.
Treatment at home
Pain and discomfort inside the oral cavity due to inflammation of the palate greatly worsens the patient’s normal life. Pharmacy medications and folk remedies as auxiliary therapy help alleviate the condition and cope with the disease.
Medicines
The main treatment depends on the original disease:
- For fungi and bacterial pathologies, it is recommended to use local preparations for rinsing the mouth and lubricating the mucous membrane - Chlorhexidine solution and gel, Rotokan, Stomatofit.
- For severe pain of various etiologies, local anesthetics are prescribed - Kalgel, Cholisal-gel.
- For purulent lesions, antibiotics are needed for oral use - Flemoxin, Sumamed.
Sumamed is an antibiotic agent
Folk remedies
If wounds in the mouth do not heal for a long time, traditional medicine will help relieve inflammation in the oral cavity and relieve pain. Effective recipes help well in complex drug therapy.
Sage decoction
Brew 1 tsp in 250 ml of boiling water. herbs, simmer over low heat for 3 minutes, cool. Rinse your mouth with the strained solution 4–6 times a day. The course of treatment is until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated.
Gargling with sage decoction will help relieve inflammation.
Oak bark decoction
Grind the raw materials and pour 2 tbsp into an enamel pan. l., pour 500 ml of boiling water. Boil in a water bath for 5-7 minutes, leave to infuse. Strain and rinse your mouth with warm broth every 2 hours.
Rinse your mouth with oak bark decoction every two hours
Raspberry leaf infusion
Finely chop raspberry leaves (2 tbsp) and pour a glass of boiling water. Rinse your mouth with the cooled liquid at least 5 times a day. For each manipulation it is necessary to prepare a glass of fresh infusion.
An infusion of raspberry leaves effectively relieves inflammation
St. John's wort tincture
Dry grass (150 g) pour 0.5 liters of vodka, leave for a week in a dark place. Take the medicine 35 drops with water. The product is also suitable for external use. Dilute 20 drops of solution in 50 ml of water and moisten a cotton pad and wipe the ulcerations on the palate.
St. John's wort tincture can be used for internal and external use
Viburnum berry decoction
Place dried berries (100 g) in boiling water (1 l) and boil for 15 minutes. Rinse your mouth with the cooled broth 3-4 times a day.
A decoction of viburnum berries is a good remedy for treating inflammation of the palate.
Chamomile and calendula infusion
Combine chamomile and calendula inflorescences in equal parts (1 tsp each). Pour two cups of boiling water over the vegetable mixture and leave to steep for 50 minutes. Thoroughly rinse your mouth and throat with herbal tea in the morning and evening.
Rinse your mouth with chamomile and calendula infusion morning and evening.
Propolis tincture
Dilute the pharmaceutical product in water at the rate of 10 drops per 200 ml of warm water. Rinse your mouth with the solution for 5–7 minutes every 2–3 hours.
To relieve inflammation on the palate, use propolis tincture
Possible complications
In most cases, inflammation of the palate is a consequence of external irritants or internal diseases.
Ignoring this condition can provoke undesirable consequences:
- destruction of bone tissue;
- tooth loss;
- purulent lesions of the gums;
- deformation of the upper part of the oral cavity;
- disturbances in voice timbre and changes in sound quality.
In severe cases, advanced stages can transform into malignant pathologies.
Ignoring palatal inflammation can lead to tooth loss
Prevention of inflammation of the palate
To avoid discomfort and pain that accompany inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, you need to follow simple rules of prevention.
- Brushing your teeth should be done in the morning and before going to bed at night.
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Avoiding very hot foods and drinks.
- Limit smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Eat a balanced diet. There are foods rich in microelements and vitamins (vegetables, fruits, fish, meat, beans and soy).
Rinse your mouth after eating
Prevention helps strengthen local immunity, establish metabolic processes in the body, maintain a healthy environment in the oral cavity and strengthen the body as a whole.
Inflammation of the upper and lower palate can be caused by dental diseases, infectious pathologies of the throat, gums, bad habits and poor oral hygiene. The disease causes severe pain and worsens a person’s quality of life, as it interferes with chewing food, speaking, and swallowing. To prevent the disease from worsening, it is important to consult a doctor on time and receive proper treatment.
Rate this article ( 2 ratings, average 5.00 out of 5)
Folk remedies
The symptom itself in the form of yellowing of the palate, tongue or mucous membrane cannot be eliminated only by improvised methods. You should definitely consult a doctor and make a diagnosis, determine what exactly caused the pathology. Self-medication in this case can be very dangerous.
But after undergoing diagnostics and choosing an effective method of therapy, you can further eliminate certain unpleasant symptoms in the oral cavity and speed up healing. For this we recommend:
- Prepare antiseptic infusions or decoctions from medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula, oak bark). After making a light solution and cooling it to a warm state, you can rinse the mouth. They are good at eliminating various pathogenic microorganisms from the surface, thereby accelerating healing.
- Beekeeping products also help a lot - honey, propolis, etc. By consuming them in small quantities, you can relieve the inflammatory process, heal wounds, ulcers, normalize blood supply, etc.
In order not to harm yourself, it is better to first consult with your doctor what folk remedies are allowed to be used in your case.
Video: three warning signs in the mouth.