Causes
A child’s cheek hurts for various reasons. This is often due to:
- allergies to foods or body care products;
- teething;
- a piece of food that penetrated into the gum pocket and caused suppuration;
- stomatitis;
- deep caries;
- pulpitis;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- gingivitis;
- an incompletely removed nerve in a dental unit;
- inflammation of the facial nerve or lymph node;
- injury that occurred after a blow or bite from the inside of the cheek;
- sinusitis;
- mumps;
- temporal tendinitis;
- temporomandibular joint disease;
- tumor;
- insect bite.
Any of these reasons cause inconvenience and discomfort. Therefore, it is important to contact a doctor in a timely manner, who will prescribe treatment. This way you can safely and quickly eliminate unpleasant sensations.
Why does a child's cheek hurt? It is difficult to install this on your own. But if such a symptom is present, adults need to take urgent measures to alleviate the condition.
Possible causes of a swollen cheek in a child
Unilateral or bilateral swelling of the cheek can occur as a result of various diseases.
The main conditions causing swelling include:
- dental diseases;
- jaw injuries;
- pathologies of other body systems;
- consequences of treatment.
Causes may include illnesses and other conditions.
Possible diseases
Diseases that result in a swollen cheek in a child include the following.
| Caries | In case of toothache, swelling of the gums and cheeks, the cause may be untreated caries. Such a tumor is most often one-sided and disappears when the diseased tooth is healed. |
| Acute pulpitis | Pulpitis is a consequence of untreated caries that affects the nervous tissue of the tooth. With this disease, one cheek becomes significantly larger than the other; accompanying symptoms are a putrid odor and acute toothache. |
| Periodontitis | If the cheek is enlarged and hurts on one side, the cause may be inflammation of the apex of the tooth root. It occurs due to caries or due to an incorrectly installed filling, and is accompanied by swelling, pain and discomfort while eating. |
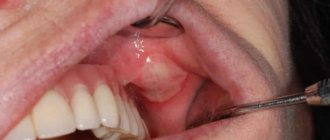
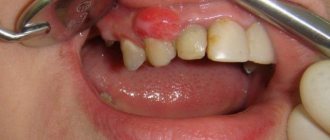
| Periostitis | Purulent inflammation in the periosteum, better known as “flux”. This disease causes redness and swelling of the gums, toothache, swelling of the cheek and a slight increase in temperature. |
| Fistula | A small growth on the gum with a purulent white tip is a symptom of a growing purulent infection and a complication of gumboil. In addition to swelling of the cheek on one side, it is accompanied by discomfort during eating and pain when touched. |
| Gum inflammation | If the cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, the cause may be gingivitis, periodontal disease and periodontitis. In the first case, the edge of the gum is affected: on the outer or inner side. The second and third diseases cause dental swelling, swelling of the gums and cheeks on the damaged side. |
| Stomatitis | The oral mucosa in children is more sensitive to infections. Stomatitis in a child can be caused by the herpes simplex virus, oral candidiasis or other infections. If inflammation of the mucous membrane is not treated in time, it leads to ulcerative defects. |
| Mumps | An infectious disease of the salivary gland, also known as mumps. In addition to swelling of both cheeks near the ear, it is accompanied by high fever and digestive disorders: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. |
| Infectious diseases of the respiratory tract | With bacterial or viral infections, fluid is retained in the body longer than expected, which is why swelling of both cheeks and other parts of the body occurs during illness. |
| Sinusitis | When the cheek swells under the eye, the cause may be inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Such tumors are accompanied by nasal congestion and difficulty breathing, but there is no pain. |
| Lymphadenitis | If the cheek is blown or the child has a cold, the lymph nodes may enlarge and swell the face on one side. Inflammation of the lymph nodes is a symptom of inflammatory diseases that disappears when the disease that caused it is cured. |
| Oral cyst | A lump in the mouth, similar to a lump, is formed as a result of the appearance of a cyst. Depending on the cause and type of cyst, it can be located inside the mouth in the corner, on the inside of the mouth, between the gum and cheek, or closer to the cheek. |
| Kidney dysfunction | Kidney problems cause severe swelling throughout the body. With this disease, not only the cheeks swell: the entire face, fingers and legs become enlarged. |
| Facial neuritis | Facial neuritis occurs due to compression of the nerve, causing swelling in the damaged area. The condition is treated with massage and acupuncture. |
Other factors
In addition to diseases, the cheek may swell due to the following conditions:
- From a blow: if a child hits his lower jaw or cheek and injures it, swelling will appear after 2-3 hours and last for several days.
- Due to chronic trauma: the condition occurs as a result of an incorrect bite or overly sharp teeth that constantly wound the cheek from the inside.
- After insect bites: if the cheek is slightly swollen, does not hurt and is constantly itching, this is a normal reaction to the bite. If swelling and discomfort are severe, an allergy to insect bites is likely, requiring a visit to the doctor.
- Due to allergies: swelling may occur after anesthesia or after root canal filling. In the first case, the allergy soon goes away on its own; in the second, the filling needs to be replaced with a hypoallergenic one.
- After treatment of pulpitis: swelling and pain after removal of the nerve during treatment indicate incomplete completion of the operation.
- After an incision in the gum: When inflammation causes pus to form in the gum, it is removed through an incision. The gums are very sensitive, so after this procedure pain and swelling persist for several days.
- When extracting a tooth: if the extraction was difficult, or postoperative recommendations were not followed, swelling and discomfort may appear. It goes away on its own after 2-3 days.
- When the 3rd large molar erupts: the wisdom tooth breaks through painfully, especially in childhood. In addition to pain and discomfort during eating, swelling often appears.
- With prosthetics: if a child wears braces or other prostheses in the mouth, if they are installed incorrectly, swelling, malocclusion and other pathological conditions may occur.
To make sure that these reasons are safe for the child’s health, you should visit a pediatric dentist for a consultation and examination.
An insect bite can cause a swollen cheek
Diseases of teeth and gums
When examining a child's mouth, pay attention to the teeth and gums. Often their pathologies lead to pain in a given place. Black holes in the tooth enamel may be visible. Even if they are small. Caries develops deep inside, but on the surface it will be little noticeable. This process develops from dietary fibers stuck between the teeth and causing inflammation of the gingival papilla. Hard food often remains between the teeth and gums, leading to putrefactive processes.
Various dental ailments lead to both a violation of the integrity of the teeth and a change in the color of the enamel. If a child’s cheek is swollen and painful, this may be due to this particular problem. There may also be itching, bad breath, severe redness of the soft tissues. With flux, a bubble of pus is observed.
If a child has a tooth filled or removed, but pain persists for more than 2-3 days, most likely the procedure was performed incorrectly. This leads to pathologies in the gums. If a child has a sore cheek and a fever, as well as a headache, then there is a risk of periostitis. The presence of pain when swallowing food with swelling indicates inflammation of the tonsils. To prevent diseases of teeth and gums from causing pain, they must be treated in a timely manner. This way you can avoid complications.
Swelling of the cheeks and gums
Swelling of the cheeks and gums can be caused by any of the reasons mentioned.
In addition, gum problems may be associated with gingivitis, teething syndrome, herpetic stomatitis, parulis, periodontal disease, malnutrition, ill-fitting dentures, and viral or fungal infections. It is also known that pericorinitis (inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums) leads to swelling of the gums and cheeks.
We invite you to read Plaque on teeth: causes and how to get rid of it?
With this type of swelling, the affected area may be numb and painful when chewing. To reduce swelling, you can try applying a cold compress, rinsing with a saline solution, and using antifungal medications.
Injuries
When a child’s cheek hurts, it may be due to injury to the oral mucosa or teeth. If no damage is found on the external part, it is possible that the cheek was damaged from the inside by the dentition. Bruises, abrasions, and swelling are noticeable on the inside. Or the mucous membrane and gums may be scratched. Then the wounds will be noticeable. Trauma is considered a common cause of pain, especially if the child is very active.
It also happens that due to an impact, a piece of enamel breaks off and the stem of the tooth breaks. In the latter situation, the tooth may be intact, but slightly loose. These damages are detected upon inspection. You won’t be able to get rid of the problem on your own; you need the help of a dentist. If the child’s cheek not only hurts inside, but also dizziness and nausea are observed, you should urgently call an ambulance. An ambulance is also needed if there is severe bleeding in the mouth.
Tissue damage
If you complain of pain in the cheek area, it would be useful to examine it for the presence of swelling, hematoma or bruising. It is possible that the baby could damage this part of the face by hitting some surface (floor, wall corner, hard ball). If the child confirms that the pain is the result of an injury, a cold compress should be applied to the cheek. Additionally, you can give your baby an anesthetic that is appropriate for his age. An antiseptic solution should be used if there is a bleeding wound on the inside of the cheek.
Dmitry Sidorov
Orthopedic dentist
If, against the background of an injury, the baby complains of a headache, dizziness, or severe bleeding, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Infection
If a child’s cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, then the cause may be fungi, bacteria and viruses. Because of them, stomatitis appears, in which painful ulcers appear in the mouth. Soft tissues also become inflamed. The infection enters the mouth with unwashed hands, toys, and dirty dishes. Its activation occurs with seasonal weakening of the immune system or colds. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the baby’s health so that no unpleasant symptoms appear.
If there is swelling not only on the cheek, but also on the neck, and there is also dry mouth, high temperature (38-39 degrees), then there is a risk of mumps or mumps. Due to pathological infections, sinusitis may occur, which involves inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. The pain from this disease can radiate to the tissues of the cheeks, nasal congestion is observed, and by night the general malaise may intensify.
The child's cheek is swollen but the tooth does not hurt
Loving parents try to protect their baby from problems as much as possible, but, unfortunately, you can’t protect them from everything.
If a child has a swollen cheek on one side, it is important to show him to a specialist as soon as possible to make a diagnosis, and only then take any measures.
The reasons may lie in dental problems and other equally serious conditions.
Let's understand the reasons
There are many reasons for swelling and soreness of the cheek, the most common are:
- mechanical damage or bruise to the cheek;
- dental pathologies;
- fungus, infection and insect bites (these reasons are possible if the cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt);
- if the cheek is swollen and the ear hurts, then the condition is caused by an inflammatory process and infection of the ear canal, middle or inner ear, inflammation of the lymph nodes and salivary gland;
- redness of the cheek and swelling of the mucous system indicates an allergic reaction to any component: food, medicine, hygiene product, dust or pollen.
- Quincke's edema - in this case it becomes difficult for the child to breathe, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Since we are talking about a child, you should not guess the reason, but should show the baby to a specialist as soon as possible.
Dental diseases
| Caries | Signs are: tooth pain, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek (most often one-sided). Complication: decay of the dental cavity. |
| Pulpitis | In addition to swelling, there is severe pain in the tooth, and a putrid odor emanates from the mouth. During the development of pathology, the nervous dental tissue is injured. |
| Periodontitis | The cheek is bothersome and swollen on one side, the pain increases while eating. |
| Periostitis | The pathology is also called gumboil, as pus accumulates in the periosteum. Symptoms: acute pain, swelling of the cheeks and gums, increased body temperature to 37.5 |
If a child has pain and a swollen cheek, the reason may lie in other dental factors:
- Gum section . This procedure is performed if it is necessary to remove purulent accumulation. Pain and swelling will continue to bother you for a couple of days, this is explained by the sensitivity of the gums.
- Removal of a tooth . Swelling occurs when precautions are not followed or in severe cases. Everything will recover on its own on the third day.
- Prosthetics , for example, if the child has braces. Such devices can cause malocclusion and swelling.
- Treatment of pulpitis . If the nerve has not been completely removed, the child will begin to complain of pain, and after a while the cheek will become enlarged.
- Teething . If a small child complains of pain in the cheek, he has swollen gums, redness, increased salivation, and constant crying - these are symptoms of teething. The teeth themselves may appear in a few days or even a week.
Pathologies of other body systems
Redness and inflammation of the cheek do not always indicate dental problems; there are other factors and diseases that cause this condition:
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Symptoms: swelling of the cheek, especially under the eyelid, nasal congestion, breathing problems, no pain.
- Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory lesion of the lymph nodes. The cause may be a draft or a cold.
- Neoplasm in the oral cavity - a small lump forms in the mouth, which subsequently develops into a cyst.
- Improper kidney function . Such disorders are characterized by swelling of any part of the body on the face, legs, and arms.
- Facial neuritis . Swelling of the cheek occurs due to nerve pressure. Acupuncture and facial massage are used for therapeutic therapy.
All diseases require immediate medical intervention and timely treatment!
Injuries
Injuries, bruises of the jaw and cheek are of two types:
The first type includes damage due to biting the mucous membrane or careless use of a dental instrument. A hematoma, swelling and pain forms at the site of injury.
Infectious lesions
If a child has pain inside the cheek, we may be talking about the following infectious diseases:
- One of the common infectious diseases is mumps , in medicine it is called mumps. The entire nervous system and salivary glands become infected. The pathology is mainly characteristic of boys and subsequently causes infertility.
- a growth with a purulent infection has formed on the inside of the cheek , it is a fistula. The cause of development is advanced flux or infection.
- Thrush damages the oral mucosa, causing stomatitis. The provocateurs of thrush are: herpes virus, dirt, unwashed foods.
What to do, how to help the baby
If a child has one cheek larger than the other, you should first show the baby to a pediatrician or dentist to find out the exact reason. Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor will tell you what to do to alleviate the baby’s condition.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited. There are several methods of therapy:
The drug Miramistin is prescribed as a medicine for rinsing the mouth. A solution based on iodine and salt has a similar effect.
If the inflammation is advanced, antibiotics are prescribed, the dosage and the drug is prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the age of the child.
Antibacterial gels and painkillers are used to treat dental pathologies.
In folk medicine, it is recommended to make rinses based on potassium permanganate, chamomile, baking soda and sage. A product based on propolis is considered effective. You can buy ready-made propolis tincture at the pharmacy; it acts as a strong anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent.
So, if your baby’s cheek is swollen, don’t panic. Show your child to a specialist and immediately begin to act in accordance with his recommendations.
What to do if your cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt
A cheek tumor can be caused by various reasons, some of which are life-threatening. Therefore, such a symptom cannot be ignored, especially if no problems with teeth are observed.
Moreover, you should not devote a lot of time to self-medication, as this can provoke more serious health problems.
articles:
Reasons for this symptomatology
A cheek tumor without toothache most often implies the presence of an inflammatory process . There are many reasons for the appearance of edema and they are all divided into:
- consequences after dental treatment ;
- consequences associated with oral diseases ;
- consequences of other diseases .
Teething
If a child's cheek hurts on the inside, this may be a confirmation of teething. During this process, swelling of the gums appears, and maybe fever. Through the translucent gingival tissue, whitish dental units and bluish hematomas can be seen breaking through to the top, which appears during teething. Children become capricious, sleep poorly and refuse to eat.
Painful sensations appear when sharp fangs or molars with a wide chewing surface grow. Pain in the cheeks sometimes occurs in older children, especially during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars. This phenomenon occurs in almost all children. Parents need to monitor the child’s condition, and if unpleasant symptoms appear, seek help from a doctor.
Other diseases
Possible non-dental causes of swelling:
- Allergic reactions. They are typically associated with taking new foods, medications, or using atypical hygiene products. Often, local hyperreactivity of the body develops in response to insect bites. A rapid increase in the volume of not only the cheek area, but also the child’s neck indicates Quincke’s edema, which requires emergency medical attention.
- Lymphadenitis. An increase in size of the lymph nodes is a reaction to inflammation in nearby organs or a systemic disease of a bacterial or viral nature. Diseases such as tuberculosis, infectious mononucleosis and diphtheria can cause lymphadenopathy.
- Inflammation of the salivary glands due to mumps or other causes.
- Sinusitis. The pathology has a similar clinical sign, which is most often characterized by bilateral spread.
- Neuritis of the facial nerve. The picture of the disease is so specific that any pediatrician should immediately suspect it and send the child to a neurologist. In this condition, the affected half of the face hurts.
- Cellulitis of the cervical tissue. Occurs rarely - in extremely advanced cases. It is characterized by a severe course and requires urgent treatment in a hospital setting.
- Traumatic injuries to the cheek. On the inside, the cause may be a tooth or its fragment, on the outside – a blow with a blunt object without violating the integrity of the skin.
- Neoplasms of nearby tissues and anatomical structures.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Metrogyl Gel - official instructions for use, analogues, price, availability in pharmacies
Severe pain
Pain can be both moderate and severe. In any case, it causes inconvenience, so it is better to get rid of it as soon as possible. If the pain is severe, it may be due to:
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- temporal tendinitis;
- Ernst syndrome.
When the buccal nerve is inflamed, there is loss of movement of the painful cheek. Much depends on the children and parents themselves. It is important to spend time on hygiene and follow preventive measures.
When visiting a doctor, he first examines the oral cavity. The specialist also asks about complaints and symptoms. Depending on the problem, a referral to a specific specialist may be provided.
Why do my cheeks swell?
Reasons why a child's cheek swells include:
- bad teeth;
- temporomandibular joint disease;
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- flux;
- allergy;
- sinusitis;
- lymphadenitis;
- neuritis;
- phlegmon.
We suggest you read: Severe sore throat and ear without fever
This is not a complete list of possible causes. To establish an accurate diagnosis of edema in a child, you should contact the clinic. You may need to undergo testing. But only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment.
Help
When a child’s cheek hurts, what should you do? If you have not yet been examined by a doctor, without a diagnosis and prescription of therapy, assistance must be carried out carefully. We must not allow the pathology to worsen. And for this it is prohibited:
- unauthorized use of antibiotics and other drugs that are sold in pharmacies only with medical prescriptions;
- perform warming up using lamps and warm compresses;
- give your child sweets and solid foods;
- feed cold or hot foods, give sweet, sour, fizzy drinks.
First aid can be performed using pharmaceutical drugs and traditional methods. They will improve the child’s condition, but then you still need to visit a doctor.
Treatment of cheek swelling
What to do if a child’s cheek is swollen? This question arises for every parent who is faced with a similar phenomenon. First of all, if the baby can already speak, then you need to try to find out whether he has damaged the oral cavity in any way. If the child is very small, it is better to immediately contact a pediatrician or pediatric dentist.
Self-medication is not recommended, as this can lead to serious complications. In simple cases, you can use some medications or traditional methods of treatment.
Medication
The first step is to rinse your mouth with Miramistin (Chlorhexidine) or an iodine-saline solution. They will help quickly relieve inflammation and remove swelling. If the inflammation is severe, then antibiotics are prescribed, taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen, as well as the age of the patient.
To eliminate swelling, doctors can prescribe drugs from the following drug groups:
- anesthetics,
- antihistamines,
- antibiotics,
- analgesics,
- NSAIDs.
You cannot select medications for a child. For the treatment of dental diseases, painkillers and antibacterial ointments are prescribed. It is forbidden to place hot compresses on a swollen cheek, as this provokes the progression of inflammation.
Home methods
With the permission of the doctor, alternative medicine can be used in addition to the main treatment. Propolis tincture is considered an effective and safe remedy, which relieves inflammation and also disinfects the wound.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth with it several times a day, after dissolving it in warm water at the rate of 5 drops of tincture per glass of water. To relieve swelling, you can apply a cold object wrapped in a soft, loose fabric to your face for 10-15 minutes.
It is allowed to rinse your mouth with soda-salt, manganese or herbal solution. Herbal compresses and sage tea help.
Medicines
If a child’s cheek hurts on the inside, then painkillers with ibuprofen (Ibuprofen, Nurofen), paracetamol (Calpol, Panadol), which can also relieve fever during teething, help.
Older children (from 12 years old) are given medications with nimesulide (“Nimesil”, “Nimegesic”). The use of “adult” painkillers (“Analgin”, “Ketanov”) is permitted from the age of 14. But you still need to read the instructions for the medications. And it should be borne in mind that giving a child painkillers without consulting a doctor for more than 3 days is considered dangerous.
During the treatment of wounds in the mouth, ulcers, and inflammations, gels, ointments, and oils are used that have an antiseptic effect and stimulate recovery. These are Acyclovir, Cholisal, Karotolin. Sprays are used - “Ingalipt”, “Miramistin”, as well as balms and solutions intended for rinsing - “Rotokan”, “Vinilin”, “Chlorhexidine”. But it must be borne in mind that these are only temporary measures that cannot replace professional help. Even if it seems that the disease has subsided, you still need to consult a doctor.
Consequences of injury
Injuries to the oral mucosa that cause the cheek to swell can be acute or chronic. Acute injuries occur due to strong biting of the mucous membrane or damage from dental instruments. They have the appearance of a hematoma, due to which the cheek becomes larger, pain occurs, and a defect in the mucous membrane occurs.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?YesNo
If an infection gets into the wound, an ulcer may form. Chronic trauma occurs due to persistent malocclusion, dentures, or sharp teeth. Damage to the oral mucosa can occur due to eating excessively hot or spicy foods.
Teething
If a baby's cheek is swollen, the most likely cause is teething. First, symptoms appear, and after 5 days the teeth themselves begin to appear. The gum where the tooth is about to appear swells, turns red and increases in size. The swelling often extends to the cheek.
All this is accompanied by symptoms:
- lack of appetite,
- restless sleep,
- anxiety, tearfulness of the baby,
- increased salivation,
- increase in body temperature.
Swelling is normal and does not cause much discomfort to the baby.
ethnoscience
If a 5-year-old child has a sore cheek, traditional medicine can alleviate the condition. Cold compresses are considered effective, in which ice must be wrapped in a cloth and applied to the sore area. This allows you to relieve discomfort. Instead of ice, you can apply half a raw potato with the cut side to the skin.
Antiseptic rinses with a baking soda solution help. For this, 1 tsp. The product is dissolved in a glass of warm boiled water. Herbal infusions based on chamomile, calendula, green or black tea, oak bark and other herbal infusions have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects. Preparation is carried out by brewing 2-3 tbsp. l. raw materials with a liter of boiling water.
Why does a child's cheek swell? Advice for parents
By the age of 6 months, babies lose the protection they receive from their mother. Problems begin in the oral cavity caused by infection and teething. The swelling of the cheek is caused by an inflammatory reaction. It is dangerous to use “adult” measures for treatment.
Why does swelling appear in the cheek area of a child?
The reasons that cause a swelling of the cheek in a child are not always associated with dental diseases. Parents often forget about the need for oral hygiene and massage their gums incorrectly. Nursing mothers neglect regular nipple treatment.
The baby's cheek swells if he is allowed to lie on one side for a long time. An infection that gets into the mouth of a one-year-old child with dirty hands or toys causes inflammation of the mucous membrane and involves the gum tissue.
In older children, there is destruction of tooth enamel, deep damage to the internal parts of the tooth with the formation of a carious cavity, and root inflammation.
When a child's swollen cheek is not associated with dental damage
Typical diseases that accompany swelling of the cheeks in a young child are:
- Stomatitis is a consequence of contact with the mucous membrane of bacteria and viruses. Candidiasis (fungal infection) is especially difficult to tolerate. Bright spots are visible on the inner surface, painful when touched, so the child refuses to eat and cries. In advanced cases, ulcers form.
- Gingivitis occurs when the gums become inflamed due to overirritation by improperly growing teeth. Typical signs include pain when feeding, drooling, loose gums around the teeth, and swollen cheeks. Bleeding indicates increased fragility of blood vessels and hypovitaminosis.
- Diathesis - caused by hypersensitivity to food components, premature transition to artificial feeding, and violation of the diet by the nursing mother. Manifested by fever, hives on the body, redness and itching of the skin. The swelling disappears after normalization of nutrition.
- Allergy to insect bites is difficult for an infant to tolerate. Redness and swelling form at the site of the bite.
Attentive parents sometimes notice that their child’s cheek is swollen, but his teeth don’t hurt. In children over five years of age, this symptom is usually observed against the background of other infections (tonsillitis, herpes), trauma to the mucous membrane from chips or sharp objects.
- Mumps is an infectious disease that occurs with inflammation of the parotid salivary glands. In addition to significant swelling in the jaw and neck on both or one side, patients exhibit symptoms of intoxication (fever, diarrhea, weakness).
- Submandibular lymphadenitis - inflammation of regional lymph nodes is characteristic of respiratory infections (influenza, ARVI). Pain appears when swallowing and chewing. There is a painful reaction to palpation. A similar pathology occurs with sinusitis with prolonged runny nose and damage to the nasal sinuses.
It is important that in children with any inflammation the local lymphatic system reacts violently. Therefore, the outflow of fluid on the face is delayed and the cheeks become swollen.
When the jaw is injured, unilateral swelling and hematoma occur. Damage to small branches of the facial nerve leads to facial asymmetry. In addition to the tumor, patients are bothered by headaches, sensitivity when pressing on certain points, and dysfunction of chewing and swallowing.
Parents are not recommended to decide on their own what to do if a small child has a swollen cheek. It is necessary to see a pediatrician, check the baby for possible infections, and rule out allergies.
What dental problems cause cheek swelling?
The most common picture is that the child has a swollen cheek on one side and a toothache. Tooth damage causes intense pain if a nerve is involved.
First, doctors find darkened enamel, then destruction leads to the formation of a carious cavity with local inflammation.
If the changed tooth is not treated in a timely manner, then the involvement of neighboring tissues leads to successive changes in the form of:
- acute pulpitis - purulent melting of the inner part of the root with pulp and nerve endings, in a 5-year-old child a flux forms (swelling of the cheek due to the spread of inflammation to the gums and periosteum, lymphatic vessels), the pain becomes jerking, radiating to the ear and throat;
- periodontitis is a less pronounced pain reaction, since only part of the root is affected, but if the body localizes the infection in the form of a suppurating cyst, then the abscess manifests itself much more intensely, the face on the affected side swells until gumboil forms;
- periostitis - the process transfers to the bone tissue of the jaw, the cheek swells on one side, the disease is detected by x-ray, due to the deep location of the lesion, conservative treatment is unsuccessful, complicated by the formation of a fistulous tract into the oral cavity or gumboil.
Other causes of cheek swelling in a child 5 years of age and older
When determining what should be done if a child has a swollen cheek, the doctor must rule out the effects of previous treatment. For example, if the nerve is not completely removed and the canal filling is unsuccessful, repeated intense pain is possible. Options:
- Swelling lasts for several days after an incision is made in the gum to open the abscess. The symptom is pronounced if the doctor’s recommendations for regular rinsing of the mouth with disinfectants are not followed.
- Even with normal tooth extraction, the possibility of moderate pain and swelling for 2-3 days cannot be ruled out. In adolescents, the eruption of wisdom teeth is accompanied by pain and swelling.
- The trauma of poorly placed dentures or braces to treat malocclusion contributes to irritation and swelling.
How to remove cheek swelling
Treatment options vary depending on the cause. Diagnosis is carried out by doctors of different profiles:
pediatric dentists - will help if a child has a swollen cheek before or after dental treatment; pediatricians and infectious disease specialists - check the connection between symptoms and bacterial and viral diseases, complications of antibiotic therapy (candidiasis); neurologists - exclude persistent pain due to neuralgia; traumatologists - treat the consequences of bruises and fractures.
You may need to consult an otolaryngologist if a connection with diseases of the nasopharynx and ears is suspected.
In case of large lymph nodes, children undergo repeated blood tests and are referred to a hematology center or an oncologist.
How to help at home Children who do not know how to rinse their mouths need to gently massage their gums.
Applying cold (heating pad, compress) is carried out on the first day for 3-5 minutes 3 times at intervals of 30 minutes. From the second day, if the patient is trained in oral hygiene, rinsing with a warm decoction of herbs with a bactericidal effect is suitable:
- chamomile;
- calendula flowers;
- sage;
- plantain;
- mint;
- birch buds.
It is good to keep the decoction in your mouth for several minutes. A solution of salt and soda (1 teaspoon per glass) helps relieve pain and swelling. The number of rinses is not limited.
The same means are used for gargling, which is useful when a child has a swollen cheek on one side due to a sore throat. A compress is made from the warm leaves remaining after straining.
Pharmaceutical medicines are suitable: propolis tincture, a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
For runny nose and sinusitis, use drops and sprays to improve nasal breathing, Aquamaris to rinse the nose and remove mucus. To apply to inflamed gums, it is recommended to cut pieces of aloe or Kalanchoe leaves, divide them in half and make a compress, applying the juicy inner side to the sore spot.
Dentists' recommendations
What to do if a child’s cheek is swollen from a bad tooth will be determined exactly by the dentist after an examination. You may need an x-ray, opening the cavity to remove pus, and filling it in a few days.
Removal of cheek swelling indicates successful elimination of the source of inflammation. You should not frighten a child with the inevitable removal of a tooth.
Conservative use of antibiotics, hypoallergenic filling materials, and physiotherapeutic procedures helps avoid surgery.
The variety of causes that cause cheek swelling in children requires immediate medical consultation. Due to postponing a visit to the dentist and relying on traditional methods, the inflammatory focus goes deeper and spreads to the periosteum.
The use of drugs according to the “adult” regimen is strictly prohibited. Subsequent complications will cause severe suffering to the child.
In case of an allergic reaction, an insect bite mark is visible on the swollen cheek
Carious cavities are formed by bacteria; dentists open them and fill them within healthy tissues.
Keep a warm compress on the cheek for 2–3 hours
Source: https://OtekoVed.ru/litso/pochemu-u-rebenka-opuhaet-shheka-sovety-roditelyam
Dentists' recommendations
Dentists may advise following simple rules to prevent cheek pain:
- Do not use hot compresses.
- Do not self-medicate.
- If your cheek is swollen, you should not disturb it. At this time, you should not eat very hot or cold foods, nuts, spicy foods, or toffees.
- You should not self-prescribe antibiotics.
You should not delay treatment, especially if a tumor appears. If it increases, then this is considered a sign of the development of a purulent process in the cheek. In the absence of professional help, the situation can only worsen.
Wisdom tooth
Typically, a wisdom tooth is an ordinary multi-rooted tooth, which often appears in adulthood. Most people experience severe pain as their wisdom teeth grow, caused by the following reasons:
- tissue rupture near this tooth;
- dental diseases (pulpitis, caries);
- development of the inflammatory process;
- destruction of a neighboring tooth;
- growth towards the cheek (the cheek near the wisdom tooth hurts).
We suggest you read: If my upper palate hurts in my mouth, what and why, reasons, what to do, what to do, how to treat
Prevention
To prevent your child from having a sore cheek, you need to take care of prevention. It is necessary to adhere to simple hygiene rules. It is important to brush your teeth regularly (as soon as you have them). At first, this is done not with a brush, but with a finger with gauze wrapped around it. It is necessary to teach your child to rinse his mouth with boiled water after each meal. From 6 years old, you can floss.
You should examine your child’s mouth at least 2 times a week. If you find food particles stuck between your teeth, they should be removed with a toothpick. The children's menu should consist of apples, carrots, and crackers. Calcium-fortified dairy products and vitamin-rich greens are also needed. This is necessary to strengthen dental tissues. The child should drink clean water, as it is the basis for the production of saliva that washes the mouth. It’s better to exclude sweets.
Do not allow your child's face and ears to become hypothermic. In very cold weather it is better not to walk. Colds in the facial nerve, colds, sinusitis, and mumps should not be allowed to occur. You should visit the dentist twice a year (even if there are no complaints).
Dental problems
If the cheek or gums on the inside are suddenly swollen, this may indicate the development of gumboil - purulent inflammation of the periosteum. This can be caused by ordinary advanced caries or serious mechanical trauma to the gums. Infections reach the tooth root and provoke the development of a purulent sac.
We suggest you read: Sensation of a lump in the tonsil, pain in the ears and lymph nodes - Question to the ENT - 03 Online
In the initial stages of the disease, only redness in the area of the problematic gum and slight swelling are observed. If flux is diagnosed in time, you can get rid of it with the help of medications. After a purulent sac appears on the gum, you will have to go to the doctor. The sac must be opened to release all the pus from the soft tissues.
Flux in a child proceeds in approximately the same way as in an adult, except that obvious purulent inflammations appear much faster.
Various injuries can trigger swelling. Even a blow to the outside of the cheek can cause the cheek inside the mouth to swell if the mucous membrane is injured by the sharp part of the teeth. Swelling caused by injury can be relieved with a cool compress.
For minor injuries, it is not necessary to see a doctor and the swelling will subside on its own. Serious wounds on the mucous membrane will require rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions. Prolonged bleeding and headaches are a signal that it is better to see a specialist.