The presence of the sexually transmitted human papillomavirus can trigger the appearance of genital warts in the mouth and tongue, which can merge to form a single spot. Depending on the level of immunity of the body, growths may appear immediately
The human papillomavirus (HPV) can manifest itself in different forms, including papillomas in the mouth. The location where the growths appear depends on the type of papillomavirus with which the person is infected.
Improper hygiene, as well as untimely treatment of infectious diseases can lead a person to such an illness as oral papilloma. It is immediately worth noting that the disease has extremely unpleasant symptoms.
Strains that cause the growth of papillomas in the mouth are not dangerous in terms of oncogenicity. However, the presence of neoplasms can significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
Causes
The appearance of growths on different parts of the body is due to the presence of a virus in the body. HPV is considered an extremely common infection with three main routes of transmission:
- Sexual;
- Contact and household;
- Generic.
Localization of papillomas on the oral mucosa is a common phenomenon diagnosed in adults and children. This type of growth occurs mainly due to the actions of 6 and 11 strains of papillomavirus.
Transmission of these types occurs through direct contact with an infected person and usually occurs in household settings.
Among the reasons due to which the virus can appear on the oral mucosa:
- Using other people's hygiene items (towels, toothbrushes, etc.);
- Eating food from poorly processed dishes of the patient;
- Kissing an infected person;
- Unprotected oral sexual contact.
In this case, a factor predisposing to infection is damage to the oral mucosa. Even a small amount of virus particles trapped in microcracks is enough to secure HPV in the body.
The child has
Symptoms of human papillomavirus development in children are the same as in adults. However, they do not yet have the immune defense that inhibits the development of the virus. As a result, tumor growth can be very rapid and aggressive. If the child is very young, diagnosis is difficult due to the lack of complaints, and the disease can only be identified thanks to the vigilance of the parents.
Children of different ages are characterized by the development of laryngeal papillomatosis if the mother is infected with HPV.
During natural childbirth, the risk of transmitting the virus to the fetus is very high. And, as a rule, papillomavirus manifests itself in the mouth area.
It is important to understand that high-quality removal of growths is only possible under the supervision of a specialist. Independent attempts to remove papillomas can lead to trauma to the sensitive oral mucosa.
Consultation with our practicing dermatovenerologist:
Papilloma in the mouth is a small tumor resulting from the active activity of the virus of the same name. A fairly wide range of specialists are involved in solving this problem, among whom we can particularly highlight otolaryngologists, dentists, oncologists, dermatologists, virologists, and immunologists. If possible, it is better to visit each of these doctors. First, you should make an appointment with a therapist, and he will tell you which doctor to contact for papilloma in the mouth.
By type of origin
Traumatic.
Appear after injury to the oral mucosa due to mechanical or chemical influences. The peculiarity of this type of growth is that their growth usually stops after the cause is eliminated.
True
Formed due to disruption of cell functioning. Their growth and division mechanisms stop working as usual.
Typically, such growths are localized in distant areas of the cheeks, which can make self-diagnosis of the disease difficult.
Viral
This type occurs directly due to the action of the papillomavirus. After infection, it can take from several weeks to several years, so it can sometimes be difficult to determine the cause of papillomas.
Regardless of the type of growth, the patient should be tested for the presence of HPV in the body.
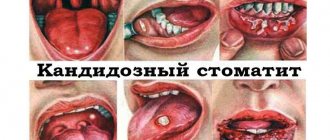
What they look like
Papillomas are a small round-shaped neoplasm with a small stalk and a wide surface.
Their size, as a rule, does not exceed 2 cm, but in advanced cases this figure may increase. The color of papilloma is usually pale pink or flesh-colored.
The mucous membrane does not change its color, but in some cases it may become paler. This occurs due to keratinization of the epithelium.
External trauma, such as biting, can cause the papilloma to change color to darker due to the hemorrhage that occurs.
When palpating the growth, the patient does not feel pain; his health is usually normal. If papillomas are constantly injured, lesions may appear on them, indicating the possibility of oncology.
Locations in the mouth
Growths can appear throughout the oral mucosa, affecting a variety of places:
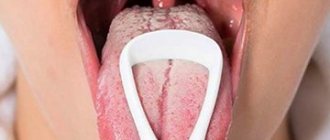
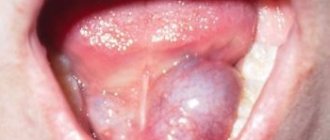
Papillomas on the tongue.
Usually it is the tongue that first suffers from the effects of the papillomavirus. Small bumps or white granularity begin to appear on it.
The growths can be either multiple and small, or single but large. In the latter case, the patient may experience not only discomfort, but also pain.
On the tongue, papillomas can appear on the tip or on the sides. Growths located under the tongue are also common. Much less often, neoplasms can be seen on the vine.
The color of the growths can vary: from pale pink to deep red.
Papillomas in the throat.
In this area, diagnosing the presence of a problem is quite difficult, since the growths do not cause pain in patients and do not interfere with the flow of food.
A distinctive feature of these neoplasms is frequent soreness and some discomfort, which is rarely paid attention to.
If the papilloma in the throat begins to enlarge, it can lead to difficulty swallowing food.
Sometimes this is reflected in the patient’s voice, which gradually becomes quieter. The neoplasm here looks like a small bump, rough to the touch. Most often it appears in the tonsil area.
Laryngeal papilloma.
The most dangerous type of growths is in the mouth area. Such papillomas interfere with breathing, as a result of which the patient may experience oxygen starvation. papillomas in the larynx of a child.
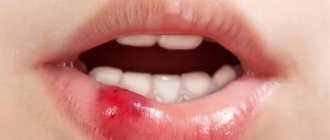
Papilloma on the lip.
The growth that appears in this area is not life-threatening, but it causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. The tumor is located in a conspicuous place, so the person experiences problems of an aesthetic nature.
In addition, a papilloma that increases in size can be injured while eating or accidentally touched by hands. What do papillomas look like under the tongue?
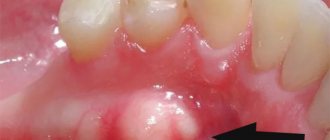
Papilloma on the gum.
This variety usually does not cause any inconvenience to the owner and can go unnoticed for a long time. However, the growth can be injured while brushing your teeth, which will lead to negative consequences in the future. What do papillomas look like on the gums?
Papilloma in the mouth on the palate
Quite often this unpleasant disease manifests itself in the oral cavity on the palate. In addition, formations can appear in the corner of the mouth, on the cheek, under the tongue, or on top of the hard palate. The formations have unpleasant symptoms. There can be several reasons for the occurrence of papillomas in the mouth, namely:
- hypothermia of the human body;
- excessive consumption of tobacco products;
- suffered from a cold such as acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections;
- on the eve of the appearance of papillomas there was excessive consumption of ethyl alcohol;
- there is a disease in the body that significantly reduces the functions of the immune system;
- the course of pregnancy in women.
The presence of some types of papillomas is difficult to diagnose independently. Therefore, if you suspect a problem, you should contact a specialized specialist.
Development mechanism and types of growths
Papilloma is a benign growth that is viral in nature. The causative agent is considered to be human papillomavirus (HPV). Once the virus enters the body, it remains there forever. How does he get inside? There are several ways to penetrate it:
contact (due to touching a carrier of the virus);- through household items;
- due to the use of personal belongings, linen, cosmetics of a virus carrier;
- due to unprotected sexual intercourse;
- through blood;
- from a mother to her child during fetal development or during the birth process.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of the virus entering the body several times are the presence of wounds, cuts, injuries on the skin and mucous membranes, as well as non-compliance with personal hygiene rules (for example, lack of the habit of washing hands after visiting public places).
The virus can remain latent for many months and even years, but in the presence of certain factors it becomes active, begins to multiply and manifests itself in the form of growths. Most often they are localized on human skin. But papillomas rarely appear on the mucous membranes and internal organs.
How does papilloma appear on the lip? This happens quite rarely, since the oral mucosa is covered with multilayered epithelium, which is constantly renewed, which protects it from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. However, if there are wounds or microcracks on the lips, the virus is able to penetrate inside the cell and provoke the proliferation of cylindrical cells. As a result, epithelial cells grow, appearing in the form of growths. They are localized:
- on the inside of the lip;
- on the outer part of the lips (papilloma can occur in the area of the lower or upper lip);
- in the corners of the lips;
- inside the mouth.
Papillomas in the lip area are of the following types:
- Reactive. They tend to progress due to constant irritation.
- Neoplastic. These are rashes in the form of nodules. There are numerous. Often they tend to merge, forming a large growth in the lip area.
If papilloma does appear on the mucous membrane, then there is a danger of its transformation into a malignant neoplasm.
This is due to the fact that as the epithelium grows, atypical cell division occurs. In addition, with any injury to the papilloma on the lip, access is opened for the penetration of bacteria that provoke cancer.
For some signs, it is necessary to urgently seek help from a specialist to avoid the formation of a malignant tumor.
Among them:
- the appearance of discomfort or pain in the lip area;
- taste of blood in the mouth;
- bleeding from a growth on the lip;
- proliferation of papilloma (especially its legs);
- change in color, nature of formation.
The appearance of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes causes a lot of trouble because they are a cosmetic defect. In addition, a benign formation can transform into a malignant tumor.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease begins with collecting anamnesis and external examination of the oral mucosa. Based on this, a preliminary diagnosis can be made, which must later be confirmed using a special study.
If the nature of the growth is viral, strains of papillomavirus will be detected in the patient’s body. Their presence can be checked using PCR diagnostics, aimed at determining the strain and viral load on the body.
In some cases, a histological examination is prescribed to determine the good quality of the material taken.
Which doctor should I contact?
When suspicious formations appear in the mouth, it is often not known who to turn to for help. In most cases, people with oral problems go to an ENT specialist. After the examination, the specialist will refer you for the necessary examinations and, after making a diagnosis, prescribe a course of treatment. In controversial cases, a consultation with other specialists – a dermatologist, venereologist and others – may be prescribed. If you experience the slightest discomfort, you should consult a doctor. The sooner therapy is carried out, the greater the likelihood of avoiding relapses and complications. It is important to regularly conduct self-examination and examination of children who, due to their age, can contract the infection through unwashed objects, toys, and dirty hands.
Removal
Removing papillomas in the mouth area requires special delicacy. Traditional removal methods, cryodestruction and electrocoagulation, are not recommended for such growths, as they can injure the mucous membrane and affect healthy tissue.
The best option is laser removal, which can be performed anywhere the papillomas are located.
Dental laser for removing papillomas in the oral cavity
This also applies to laryngeal tumors, which are considered quite difficult to remove. The area of action of the laser beam is very limited, due to which local destruction of growths is carried out.
This method is considered safe and the most progressive to date. Before the operation, anesthesia is first administered so as not to cause great discomfort to the patient.
In severe cases, surgical methods can be used. Such operations are typical for large papillomas that cause significant pain to the patient.
They can merge into associations, which makes them difficult to remove with targeted techniques.
Removal of papilloma in the oral cavity
As a rule, removal of warts in the oral cavity is carried out using the radio wave method or using a laser. These two methods are the most effective, safe and painless (in some cases, local painkillers may be used). The essence of laser cauterization of papilloma is the impact of narrowly directed beams of a certain frequency, which leads to destruction and necrosis of pathologically altered tissues. Radio wave removal of warts involves cutting off the papilloma at its base, which allows the removed material to be sent for further histological examination.
The advantages of laser and radio wave treatment of papilloma include:
- Efficiency of the procedure;
- No postoperative scars;
- Minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Possibility of removing warts of any size and location;
- No postoperative complications (bacterial contamination, spread of infection, bleeding).
There are also other destructive methods to combat warts in the mouth. These include:
- Cryodestruction (cauterization of papilloma with liquid nitrogen);
- Electrocoagulation (excision of warts with electric current);
- Cauterization of growths with chemicals;
- Surgical excision of papilloma using a scalpel.
However, due to the special sensitivity and increased humidity of the oral mucosa, the listed methods will be less effective and safe.
Contraindications for surgical treatment of warts include the presence of cancer, acute infectious viral pathologies, exacerbation of chronic diseases and diabetes mellitus in the decompensation stage.
The most effective and appropriate method of wart surgery is selected by the doctor after an examination. In this case, the specialist takes into account the age and health status of the patient, the presence of possible contraindications and allergic reactions, as well as the location, size and number of tumors.
Treatment
The goal of any treatment is not only to get rid of unwanted growths. In addition, therapy performs such tasks as:
- Strengthening immunity;
- Reduced viral activity;
- Reducing the risk of relapse.
For this, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs, used topically, if the papillomas are located on the lips. As a rule, this is Acyclovir ointment in combination with various mouthwashes - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, etc. This helps reduce the concentration of the virus in the affected area.
Immunomodulatory therapy is necessary to correct the state of the immune system, which is responsible for naturally containing the virus.
Such drugs include Isoprinosine, Allokin-alpha, Panavir, etc.
It is important to combine drug therapy with the removal of all existing tumors. Otherwise, the treatment will give a temporary effect with a high risk of reappearance of papillomas.
Methods for treating papilloma on the inside of the cheek
A papilloma that appears on the cheek in the mouth should alert a person, although it is usually benign. Immediately after its detection, you need to contact an ENT specialist, dentist or therapist for diagnosis and effective treatment. A timely response to this growth will help to avoid malignant processes and prevent you from putting your life in danger.
Treatment of papilloma on the inside of the cheek with medications
In the photo there are preparations for papillomas on the inside of the cheek
First of all, you need to strengthen your immune system by drinking special immunostimulants . Among them, Immunal, which costs about 250 rubles, best copes with its tasks. (120 UAH). It is sold in liquid form, making it easy to use. It can be replaced by Lymphomyosot, also available in the form of drops. You can also recommend taking Echinacea purpurea, which is the most economical option. Treatment of papilloma on the buccal mucosa should be carried out for at least 2-3 weeks.
In parallel with taking immunostimulants, it is recommended to take antiviral drugs - Likopid, Kagocel or Tsitovir-3. On average, they need to be taken for 5-10 days; taking it longer is not recommended in order to avoid suppression of the intestinal microflora.
Among external agents, it is recommended to use Miramistin , which perfectly reduces the activity of bacteria, viruses and infections. They need to rinse their mouth 2-3 times a day for 2-3 minutes. It costs about 200 rubles. (90 UAH).
It has a good analogue - Chlorhexidine . Both are antiseptics, but the latter is recommended to be used 2-3 times a day. Successful treatment of papilloma on the buccal mucosa will take at least a week.
Traditional medicine for papilloma on the inside of the cheek
The most famous remedy is calendula tincture , which should be used to wipe the papilloma 3-5 times a day. To do this, you can use an ear stick or a piece of cotton wool, moistening them in the composition.
Instead, sea buckthorn oil ; it needs to be lubricated with the formation twice a day for 7-10 days.
You can also rub the cone with peeled garlic, treat it with the juice of celandine and aloe, potato and lemon.
, tincture of walnuts , prepared with the addition of 50 g of this component along with crushed green shells and the use of vodka, which is taken twice as much, is also very helpful All this is mixed and left in a jar for 2 weeks, kept in a dark place. After this time, the composition must be filtered, soak a cotton swab in it and wipe the growth. This must be repeated 3 times a day, treatment is carried out for about 2 weeks.
To combat papilloma on the oral mucosa, castor oil , which is recommended to be heated beforehand. They treat formations with an ear stick 2-3 times a day. For this to help, treatment should be carried out for at least 10 days.
It is useful to rinse your mouth with a soda solution , for the preparation of which you should add this component (2 tsp) to 200 ml of warm water and stir well. This procedure must be carried out 5 times a day for 2-3 minutes.
No less useful will be lubricating the growth with propolis , which has strong cleansing and anti-inflammatory properties.
Also, when treating papilloma on the buccal mucosa, you should pay attention to an infusion of wormwood and chamomile , of which you need to take 2 tsp per 250 ml of water. The composition must be kept covered for 2-3 hours, filtered and used to rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day. This treatment should be carried out for at least 10 days.