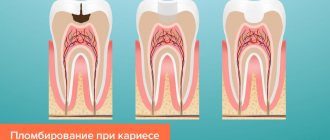
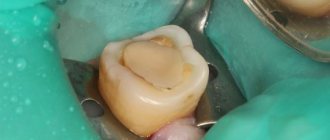
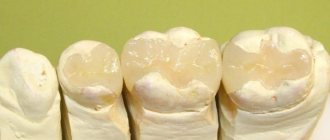
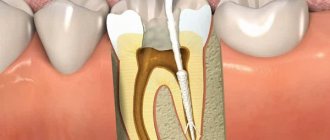
What types of fillings are there and which are the best?
Usually at the dentist's office you will be asked, “Which dental filling should you get?”
And this question is often confusing, because there are many types of fillings. In order not to get lost in this issue anymore, let’s figure out what types of dental fillings there are, what are the most reliable and the best types.
In dentistry, they are distinguished by composition and use. These can be plastic, ceramic fillings, as well as temporary and permanent.
Temporary ones are used for long-term treatment, when it is necessary to use drugs inside the cavity, and permanent ones are used for instant treatment at a time.
Dental filling is a classic of dentistry, but it is used for not very large damages; if the defect is particularly large, then an alternative to fillings is used - inlays that can cover larger sizes.
Today, clinics use several different materials to make fillings.
What types of dental fillings are there?
All dental fillings are divided into two large categories:
- permanent;
- temporary.
Permanent fillings are used after dental treatment is completely completed and it is necessary not only to restore the chewing functions of the tooth, but also its aesthetic appearance. Savings are inappropriate here - after all, such dental fillings should last for more than one year.
Temporary dental fillings are placed for a period of 3 days to several weeks. Their task is to protect the open cavity from the penetration of bacteria until the end of treatment, that is, therapeutic. Often medications are added to the filling solution to completely eradicate the infection before the final filling is completed.
Based on this, fillings made of various materials are used. This:
- ceramics;
- metal;
- plastic;
- cement and composite mortars.
Cement ones are the most affordable, they are widely used in free medicine. They are quite durable, but are prone to shrinkage, washing out with saliva and drinks, and rapid abrasion. There are a huge number of different compositions with different additives; a cement composition with fluorine is considered optimal. These are the ones that are preferred in pediatric dentistry when it is necessary to fill a baby tooth.
In this case, you don’t have to worry about durability, since the tooth will soon fall out on its own anyway. But it is necessary to protect it from secondary caries or pulpitis - fluoride guarantees this.
Metal fillings are now almost never used. They are strong and durable, but require great professionalism from the doctor when installing. In addition, they are toxic - they often contain mercury. A filling made of metal or amalgam can stain the dental tissues gray and cause an unpleasant taste and odor in the mouth. Sometimes they are used to fill teeth that are not visible to outsiders, if there is no other alternative.
Recently, white amalgam compositions have appeared. They are characterized by high strength, wear resistance and are completely non-toxic. But so far they are not widely available.
Plastic ones are suitable for temporary filling. With prolonged use, they become deformed, and a gap may form between the tooth wall and the filling itself. And this promotes the penetration and proliferation of bacteria, which often leads to repeated caries and pulpitis. This is a toxic filling material that is prone to rapid color changes.
Polymer, ceramic, glass ionomer fillings are currently the highest quality and most reliable. But they are also the most expensive. The main advantage is that they can be precisely matched in color to match the shade of tooth enamel. A person who cares about his appearance and needs filling of his front teeth cannot do without them.
Such filling materials allow you to restore a tooth with maximum accuracy, repeating its anatomical shape; they are practically invisible to others. A photopolymer filling can last up to 10 years with proper care.
Glass ionomer filling materials deserve special attention. Such a filling is not placed in one session; at the end it must be coated with a protective varnish, since it is susceptible to water and mechanical damage. But it is non-toxic, ensures ideal adhesion to dental tissues and, most importantly, prevents the development of caries due to the fluoride content in the composition.
To decide which dental fillings are best in a particular case, you need to understand what tasks they should perform.
Materials from which fillings are made
All modern materials are divided into several groups. Let's look at the types of dental fillings.
Cement (silicate and silicophosphate) fillings
This material is also able to resist the re-development of caries, however, it is very fragile and may not last very long, or can be used as a temporary option.
Although this material has outlived its best years of popularity, however, it is not forgotten in some cases, since it has a low cost and is easy to use.
Plastic
Their popularity is explained by the same factors as the previous ones - low price and quick, simple installation.
However, they have many disadvantages:
- when the material hardens, severe shrinkage occurs;
- after a while, a color change occurs;
- increased abrasion of the material;
- secondary occurrence of caries is often possible.
Such fillings are the prerogative of free medicine.
Amalgams or metals
This material includes silver and mercury, or other alloys containing the second element. It is distinguished by its hardness and service life of up to 10 years. This material is dangerous due to its mercury content and the possible harmful effects of this element on fillings. It hardens for a long time and is difficult to use; the dentist must have high professionalism in order to place a filling from such a material.
Note: When installing a product made from this material, the dentist should take into account the fact that it expands greatly during the curing process, and accordingly, a fragment of the tooth wall, which is located near the filling itself, is possible.
Their use is popular on chewing teeth, as well as under crowns, when the composite will not be visible.
Composite
What dental fillings are considered the best of the inexpensive options are composite ones. They include plastic in their composition, but their distinctive feature is quartz powder, which provides them with the desired hardness. In addition, they are distinguished by relatively good color fastness and strength. Their service life is on average 2-5 years.
Light-curing composites
This is a group of materials that require special equipment in the form of a halogen lamp, they are also known as solar curing or photopolymer. It is with its help that the lamp is given the necessary hardness. When asked which fillings are the best, we can accurately answer that these are those made of this material.
Important: However, in order for a product made from this material to be as strong, durable and aesthetic as possible, it is necessary to carry out careful grinding and polishing.
If polishing is carried out once every six months, the color will last much longer. The most memorable feature of such materials is the mandatory use of special-purpose adhesives that can secure the raw material “tightly”.
It consists of various fillers and polymers that harden under the influence of that same blue lamp.
It has a fairly wide color palette, thanks to which you can choose any desired color and shade, as a result - as close as possible to a healthy tooth.
This material will last at least 5 years.
But such a seemingly flawless material has three main drawbacks:
- Shrinkage due to the chemical composition can be up to 5%, which reduces the quality of the installed filling. That is why it is better to use such material in small areas;
- with severe shrinkage, deformation is possible to such an extent that the thin wall of a natural tooth breaks off;
- incomplete hardening. Hardening of this material occurs only by 70%; more is impossible due to the peculiarities of using the lamp.
Glass ionomer cement
Dental fillings, which are considered the best for use in pediatric dentistry, since they contain 10-15% fluoride, which helps protect against re-infection. In addition, they are chemically bonded to the natural tooth, and therefore the likelihood of various cracks appearing is minimal. The coefficient of expansion under temperature is as close as possible to that of dental tissue, therefore minimizing the risk of the tooth cracking.
However, even this seemingly ideal material has its drawbacks. These are reduced strength indicators, both in abrasion and in bending. In addition, they do not look particularly attractive, and therefore are better used with more aesthetic fillings.
Chemically cured composites
This material was developed to replace conventional cement options. Their fundamental difference is the filler used, in this case it is porcelain. These composites can be further divided into:
- Light-curing.
- Acrylic-containing.
- On epoxy resin.
Composites that contain acrylic are highly durable and resistant, but they are also very toxic. It is often noted that after installation of fillings made from this material, a large number of pores appear. And the consequence may be the development of pulpitis or secondary caries both on this tooth and on neighboring ones.
Resin composites are more fragile, although they wear out less. They are not as toxic as their acrylic counterparts, however, they inevitably darken several years after installation.
Fillings. what are they made of?
The quality and strength of the filling depends on the material from which they are made. There are many materials for fillings. Here are some types of fillings:
- a filling made of an alloy of metal and mercury - amalgam;
- plastic seal;
- cement filling (glass ionomer);
- filling made on the basis of chemically cured composites;
- photopolymer filling, it is made from light-curing composites.
But its strength and long service life depend not only on what the filling is made of. It is necessary that during its installation all technology conditions are met. But even this is not enough for it to serve long and reliably.
All kinds of chronic diseases that the patient has, failure to maintain oral hygiene, can reduce the service life of even the highest quality filling, the highest quality material.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Sweet taste in the mouth: causes, what it means, treatment
The highest quality and most durable filling is considered to be one made from a light-curing composite. Its only “disadvantage,” perhaps, is its relatively high cost. But this is justified, since there are more advantages listed below:
- the filling is strong and flexible;
- long service life;
- external attractiveness of the filling and aesthetics. It is able to change shade depending on the lighting;
- In modern dental practice, the latest developments are used, which include the highest quality polymers - compomer fillings.
But these are general characteristics. To understand which filling suits you best not only to your taste, but also to your financial capabilities, you need to take a closer look at the main groups of fillings used in modern dentistry:
At the very beginning, we probably need to talk about a cement filling. The peak of popularity of fillings using such a filling has long passed, but it is still too early to write it off, as they say.
It is not so strong and has a rather fragile base, however, it may well prevent the development of recurrent caries. Since its service life is not very long, it is often used to install a temporary filling. In addition, it is quite easy to install and has a low price.
Plastic fillings. They are still popular with patients. However, this popularity is not explained by high quality characteristics, but rather by the same reasons that were given for cement fillings. It is quite cheap and easy to install. But she has enough shortcomings. For clarity, some of them should be cited:
- after the filling is installed in the tooth and the material begins to harden, quite significant shrinkage often occurs;
- the patient may be disappointed by the change in color of the filling. This is especially unpleasant on prominent teeth;
- the material is fragile and after a relatively short period of time the filling is worn out;
- re-development of caries is not excluded.
Taking into account all the above factors, it can be stated that dental filling with this material is used mainly in free clinics.
Amalgam or metal fillings. Fillings made from this material contain, in addition to silver, some dangerous chemical elements, such as mercury. This cannot but cause concern among patients about the possible effects of a harmful substance on the body.
However, such fillings are very durable and have a long service life. The “life” can exceed ten years. Installing such fillings requires high professionalism from the dentist; the material takes a long time to harden, and it is quite difficult to use.
You need to know: when installing a filling made from this material, the dentist must remember that the filling tends to expand during curing, so destruction of the tooth walls that are located near it is possible.
Considering these and other circumstances, this type of filling is most often installed on teeth that are invisible. These may be chewing teeth. Also on teeth during the subsequent installation of crowns.
Composite fillings. If we consider fillings from the point of view of their price and relative strength, then the most suitable option, perhaps, can be called composite. Although plastic is one of the components of these fillings, they are quite hard.
The fact is that the desired hardness is created by a special quartz powder, which is also included in the composition of the material for making fillings. In addition, they have relatively good color fastness and durability. They can serve properly for up to five years.
Light-curing composites. The installation of such fillings requires a special device so that they have the specified hardness and strength. This equipment is a halogen lamp.
Thanks to the lamp, the filling is given all the necessary qualities, which allow us to further answer the question of which filling is the best. Fillings may be called photopolymer or helium-cured.
You need to know: to give a photopolymer filling the required strength, increase service life, and also have a more aesthetic appearance, it must be ground and polished.
If the filling is polished at least once every six months, the light can last much longer. Another distinctive feature when installing these materials is the use of special adhesives.
It contains polymers and fillers, which also, with the help of a lamp, allow you to install the filling “tightly”. The set also includes a wide range of colors, which allows you to give the tooth its original appearance. A filling made from this material will last at least five years.
We suggest you read: A healthy tooth hurts, the reasons - why does this happen and how to treat it?
However, there are also disadvantages here. There are three main ones:
- Due to the chemical composition, the filling may shrink by up to five percent. Taking this into account and in order not to reduce the quality of the filling, it is recommended to use this material in small areas;
- it is possible that with significant shrinkage, the tooth wall will break off;
- the material, due to the limited possibilities of exposure to a halogen lamp, hardens only 70 percent.
Glass ionomer cement fillings. They are popular in pediatric dentistry.
They have a chemical bond with the natural tooth; their thermal expansion is close to natural - such as in dental tissues, which makes it possible to avoid cracks or reduce them to a minimum.
In addition, these fillings contain fluoride, it is up to 15 percent - this helps to ensure that the tooth will not be re-infected.
Of course, this material is not without its drawbacks. It is relatively fragile, subject to both abrasion and bending. They are also not particularly aesthetically pleasing.
Fillings made of chemically cured composites. The reason for the development of this material was the desire to replace cement fillings. They differ in filler. This option uses porcelain. The presented composites are in turn divided into:
- resin;
- light-curing material;
- acrylic-containing.
The last group of composites from this list, containing acrylic, can be classified as durable and highly resistant fillings. However, their high toxicity is noted. Often secondary caries occurs due to the appearance of pores.
Resin composites are less toxic and less susceptible to abrasion. However, they are more fragile and have the negative tendency to darken after a few years.
How much do the products cost?
Which fillings are best to install based on their cost? It seems that the only correct answer to this question is that all good things come at a price. However, this is not so; in each specific case, one must start from specific features, and only they will dictate the future price of the filling.
However, in order to get at least a little orientation in the pricing policy, you should know that inlays cost in the range of 3000-14000 rubles, compomers from 650 to 1000 rubles, chemically cured composites from 600 to 800 rubles.
Review of the best popular dental fillings and their comparison!
Most often, before filling a tooth, the dentist asks the patient a question regarding the type of filling.
And it certainly causes confusion among most people, since today there are a large number of types of fillings. And in order not to make your choice at random, you need to know which dental fillings are better? We will also consider the cost of various filling materials.
All fillings differ in two ways:
- Their composition is ceramic, plastic, metal, etc.
- Regarding the application, the filling can be permanent or temporary. The latter are applicable when any medicine is used inside the dental cavity, while a permanent filling is focused on treatment at a time.
Dental filling is one of the main methods of caries treatment in modern dentistry. However, they are used for predominantly small defects. If the damage reaches a large size, then an inlay is used, which is an alternative to filling and is intended for large cavities.
Materials for filling teeth that are a thing of the past
Some filling materials are no longer used in modern dentistry. For example, amalgam was previously popular. Its advantages are ductility, hardness, shape retention over a long period of time, as well as resistance to mechanical stress. However, it was decided to abandon its use due to its high toxicity and completely unaesthetic appearance - it was gray in color. Another material that has become a thing of the past is gold. Probably each of us remembers how popular gold fillings were in the 90s - it was a kind of indicator of wealth. However, gold is truly a precious material for our oral cavity. It is strong, durable, does not cause allergies and even has antibacterial properties. But it’s too expensive and not at all aesthetically pleasing. Cement fillings are also practically not used today. The material, like amalgam, has a gray color and also puts increased pressure on the tooth from the inside, as a result of which it quickly collapses.
Gold fillings
What materials are used to make fillings?
As mentioned above, today there are quite a lot of materials from which fillings can be made. Depending on the material, fillings may have different technical characteristics. Silicate, silicophosphate, and cement fillings. Such materials perfectly prevent relapses of caries, but at the same time they are fragile, and therefore they do not last long, which is why in modern dentistry they are most often used as a temporary option. This material is mostly a relic of the past, but in some cases it is still used due to its cheapness and ease of use.
Types of fillings
Dental fillings can mainly be divided into two types: temporary and permanent.
Both of them perform their specific function. A temporary filling is usually installed for medicinal purposes, when it is necessary to temporarily put some medicine under it. A temporary filling often performs a diagnostic function. Permanent fillings last for years, sometimes even many years, depending on the type of material they are made from. There are currently 3 main types of fillings depending on the material:
— metal, — cement, — composite.
Cement fillings have been used continuously in dental practice for a very long time. But such fillings have a number of significant disadvantages. Their main disadvantage is their poor fit to the edges of the tooth, as a result of which the material may move away from the tooth wall. Food debris gets into the resulting gap, and secondary caries or new caries occurs along the edge of the filling.
The second type of dental fillings is metal, they are also called amalgams. Such a filling consists of an alloy of a certain metal with mercury, which is the most important and significant disadvantage, because mercury is a metal with toxic properties. Also, such fillings do not look aesthetically pleasing and have certain difficulties in installation; they harden within 2-3 hours. Due to the above, metal fillings are a thing of the past.
And perhaps the most convenient and durable material, which is often used in modern dentistry, is dental fillings made of composites. There are three types of them: fillings based on epoxy resins, acrylic-containing and light-curing ones. Just a couple of years ago, these materials were supplied to Russia from abroad, but today production has been established in St. Petersburg, Cherkassk and a number of other cities.
Plastic fillings
They are highly popular due to their ease of use and relative cheapness. But at the same time, such fillings have no less disadvantages:
- Subject to severe shrinkage after hardening.
- Characterized by high washability.
- They change color over time, which negatively affects aesthetic qualities.
- In most cases, there is a high probability of recurrent caries.
Taking into account all the above factors, such fillings cannot be considered the best modern material for the treatment of caries. However, for free medicine they are indispensable.
Ceramic inlays
This material is distinguished by its excellent strength and aesthetic component, which is similar to the enamel of a healthy tooth.
Indications for use : large cavities formed as a result of complicated caries, replacement of old fillings, root canal treatment.
- Such inlays are much more durable than conventional fillings made directly into the tooth. If the cavity is large, then the only correct solution is an inlay. This is due to the fact that the fillings quickly become damaged. Thanks to ceramic microinserts, it is possible to strengthen the tooth extremely well.
- Perfect aesthetics. Ceramics are characterized by translucency, which allows you to simulate the color of a healthy tooth.
- A ceramic inlay models the anatomical shape of the tooth with extreme precision. Since it is not created in the oral cavity, it is possible to achieve an ideal shape.
- Resistant to external manifestations. Even drinking coffee and smoking cannot spoil their color over time.
- Fast production. At the first visit, the cavities are processed and an impression is taken. And the very next trip to the doctor will end with the installation of ceramic inlays in the oral cavity.
- Ceramic inlays do not sag, unlike fillings (shrinkage up to 2%).
Zirconium dioxide
If tooth decay is more than 30%, then you should turn your attention to one of the new methods of microprosthetics - zirconium inlays. Such inlays will provide an excellent aesthetic appearance of the structure, as well as high strength, not inferior to metals. Pros:
- The most natural appearance, providing a magnificent aesthetic effect.
- Over time they do not darken or stain, which indicates good performance.
- Minimal risk of allergies.
- Can be used on front teeth. The zirconium inlay is not translucent and does not impart a blue tint to the future tooth.
- High wear resistance.
There is only one disadvantage - high cost.
Zirconium inlays are prescribed:
- With a completely destroyed tooth;
- For defects in the shape or location of teeth;
- As a support for bridge structures.
Metals or amalgams
Such materials contain mercury and silver. Instead of silver, any other components are possible. The material has high hardness and is durable (the filling lasts more than 10 years). However, the material is dangerous due to its mercury content. It is characterized by a very long hardening and has certain difficulties in application, and therefore requires a high level of skill from the dentist.
On a note! As this material hardens, it is susceptible to expansion, which the dentist must consider when installing it. If this feature is not taken into account, the tooth wall located next to the filling may be destroyed.
The use of such fillings is desirable in places where they will be unnoticeable, for example, on chewing teeth or under crowns.
Types of dental fillings
Depending on their purpose, fillings can be temporary or permanent. The first ones are installed for a short period of time (from 3-4 days to several weeks) if it is necessary to carry out therapy in several stages. A permanent filling is placed at the final stage of treatment and should last for several years.
Fillings are classified not only by the time of operation, but also by the materials from which they are made.
Tooth filling – “Amalgam”
An alloy of mercury, tin, silver and copper began to be used for fillings more than 100 years ago. It is characterized by plasticity and high strength after hardening. Does not change the color of tooth enamel, is resistant to abrasion, and can last up to 10 years. Due to its unaesthetic appearance, it is used when filling chewing teeth or under a crown.
Disadvantages include the presence of mercury in the composition and the presumably harmful effects of the element on the filling and surrounding tissues. The material hardens for a long time and expands during the hardening process, which can lead to tooth destruction and chipping of its thin wall. Amalgam does not prevent, but on the contrary, it can provoke the development of secondary caries.
Mineral cement fillings
They stop the further development of caries, but are quite fragile and last no longer than 2 years. Currently, they are rarely used, mainly for temporary filling. The advantages of the material include low cost and ease of installation.
Types of mineral cement fillings:
- Zinc phosphate. Powder based on magnesium, aluminum, silicon, zinc oxide, which is diluted with a solution of orthophosphoric acid during filling.
- Silicate. Releases fluoride ions that prevent the development of secondary caries. At the same time, it releases phosphoric acid, which has a toxic effect on the pulp. Therefore, to protect the pulp when installing such a filling, a special gasket is used.
- Silicophosphate. A combined material containing zinc phosphate and silicates irritates the pulp less, has higher strength and is better attached to dental tissues. Disadvantages include low strength, low aesthetic qualities, and instability to saliva.
Polymer cement fillings
They are most often used for filling baby teeth in children, installing a temporary filling or as a spacer under the polymer for medium and deep caries, for fixing pins, crowns, and dentures. Service life – up to 5 years.
There are:
- Glass ionomer. The material contains 10-15% fluoride, prevents the re-development of caries, therefore it is actively used in pediatric dentistry. Disadvantages include fairly low strength: fillings wear out over time, become cracked, chip and crumble.
- Polycarbonate. They are an alternative to mineral zinc phosphate fillings and have better adhesive properties and biological compatibility.
Plastic
Like cement, plastic fillings are easy to install and inexpensive. However, a large number of shortcomings do not allow them to be used everywhere. Plastic fillings:
- shrink when the material hardens;
- Over time they change color and are colored with pigments;
- quickly erased;
- do not prevent the re-development of caries.
Composite fillings
They are considered the best fillings in the budget price segment. Contains plastic and quartz powder to provide the desired strength. The service life of such fillings ranges from 2 to 5 years; they are quite resistant to the effects of coloring substances.
Chemically cured composites
These are materials based on acrylic or epoxy resin. Acrylic compounds are characterized by high strength, resistance to chewing and temperature loads. However, they are toxic and can provoke secondary caries and the development of pulpitis.
Materials based on epoxy resin are more fragile and darken several years after installation. But they wear out less and do not have a pronounced toxic effect.
Photopolymer fillings
Photopolymer fillings are installed using halogen lamps and special glue that firmly fixes the filling in the dental cavity. With proper grinding and polishing, they look as aesthetically pleasing as possible and last at least 5 years. Photopolymers have a fairly wide color palette, which allows you to select a filling material that is as close in shade as possible to the natural color of the teeth.
Photopolymer materials also have disadvantages:
- impossibility of installation in hard-to-reach places;
- shrinkage up to 5%, which does not allow the material to be used over large areas;
- deformation (due to severe shrinkage), which can lead to chipping of the thin tooth wall;
- incomplete curing due to the peculiarities of using the lamp.
Ceramic inlays
Filling is carried out for relatively small carious lesions of the teeth. In case of a large area of damage, ceramic inlays are used instead of fillings to restore the anatomical structure of the tooth.
Advantages of ceramic filling inlays:
- hypoallergenic;
- biological compatibility;
- high strength (service life of at least 10 years);
- no shrinkage;
- resistance to saliva and food coloring (does not change color);
- aesthetics.
The only disadvantages include high cost and installation in 2 or more stages.
Composite
Perhaps, for a budget option, these dental fillings will be the best in terms of price and quality. This material contains plastic, but the high hardness of the filling is ensured due to the fact that they contain quartz powder. In addition, they are characterized by excellent color fastness and durability. They serve on average about five years.
For the front teeth, light-hardening fillings are used; for the back teeth, universal fillings are used.
Light-curing composites
These seals require the use of special adhesives that can firmly strengthen the seal. Such materials include a number of polymers and special fillers that harden under the influence of a special lamp. A very wide palette of shades allows you to choose a filling that will not stand out against the background of healthy teeth. The average service life of the material is from 5 to 7 years.
In addition to the obvious advantages, photopolymers also have several disadvantages:
- Shrinkage is up to 5%, but can slightly reduce the quality of the filling. Due to this feature, this material is most often used to fill small tooth defects.
- Severe shrinkage can cause deformation, leading to chipping of the thin wall of the tooth.
- Hardening of the material is incomplete and reaches only 70%, which is due to the characteristics of the lamp used when installing such fillings.
Light or light polymer composites
It is light composites or light-polymer fillings (simply put, “light” fillings) that are most popular today. The material, which is placed inside the tooth cavity, hardens under the influence of light from a special lamp. The shade can be perfectly matched to the color of the tooth, so fillings can be used to restore both lateral chewing and front teeth.
The advantages of the light composite are its aesthetics, minimal shrinkage, and average strength (this is a plus, since the filling will not lead to the destruction of the thin walls of the tooth and will not have a destructive effect on the opposite tooth). In addition, composite fillings can last for decades without significant shrinkage, change in shape or color.
To this day, the composition of composite fillings and the methods of their application are being improved. Accordingly, the scope of their application is expanding. Filling with a composite material can be used not only in the treatment of carious cavities, but also in the restoration of teeth - to eliminate chips, cracks between teeth and even correct their incorrect position.
Chemically cured composites
The main purpose of this material is to replace cement analogues. The difference from cement fillings lies in the filler, which in this case is porcelain. Composites can be of three types:
- Acrylic-containing.
- Light-curing.
- On epoxy resin.
Acrylic-containing composites are characterized by high durability and strength, but are toxic. It often happens that after their installation many pores appear, after which it is quite possible for both the development of secondary caries and pulpitis, and the damage can spread to neighboring teeth. Resin materials are quite fragile, but less susceptible to abrasion than the previous version. However, they are not that toxic. The main disadvantage of such materials is their darkening several years after installation.
Price
Patients often choose one filling or another based on the cost of the filling material. And many people mistakenly believe that a good filling is expensive. This is not true, as there are a number of factors that determine the final cost of treatment. If you want to get a little guidance on prices, here are some approximate data:
- The cost of tabs ranges from 3 to 14 thousand rubles.
- Compomers will cost you 600-1000 rubles.
- The price of chemically cured composites is 650-800 rubles.
When choosing a filling, you must listen to your dentist, who, after assessing the situation, will help you choose the most suitable option. Otherwise, the need for a filling may return after a short time, and as a result you will spend much more than if you initially installed a quality filling.
Watch thematic video
What is the best filling material?
Many dental clinics offer fillings using several different filling materials. Price lists (including those posted on websites) are also often replete with various commercial names of fillings: Filtek, Spectrum, Aesthetics, Charisma (Karizma), Vines (Venus), Gradia, Estelite, Herculite, Point, Tetrik, Admira, Brilliant, Enamel Plus and others. Patients are asked to make a choice, but this requires dental-level knowledge, which most people, of course, do not possess.
Popular articles on the Internet for the following queries: “which filling is better?”, “which filling material is the best?”, “which filling is better to put?” and so on. – do little to clarify the situation. Most articles (often written by anonymous authors or copywriters) discuss only classes of filling materials: cements, amalgams, glass ionomers, chemical and light-curing composites. After a detailed description of materials that went out of use several decades ago (apparently to give more volume to the text), the conclusion is made that light-curing composites are the best, and if a person has the financial means, then it is advisable to install fillings from them. Either nothing is mentioned about specific brands of heliocomposites, or it is stated that they are all approximately equally good. Or “the latest generation nanocomposites” begin to be advertised.
Main types of fillings
There are two main types of dental restorations:
- permanent - the most extensive group of materials that are used to replenish the lost structure of enamel and dentin. Such fillings provide sealing, reliable closure of the prepared cavity, and depending on the type of substance used, they can prevent static caries, protect against relapses, or have increased aesthetics, due to which the restoration on the tooth will be invisible even upon close examination;
- temporary - applied in cases where delayed treatment over several visits is required in the treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis. A filling made of temporary material protects against the penetration of microorganisms and food particles into the root canal system. Due to the fact that substances used for this purpose have the ability to crumble or dissolve over time, they are installed for a period of no more than 10-14 days.
The means used to restore the anatomy of the tooth, its functions, appearance, as well as to prevent further destruction of hard tissues, have a clear classification, which is based on differences in the composition and properties of restoration materials.
- Cements are divided into mineral and polymer. The first group includes products based on phosphoric acid: silicate, silico-phosphate and zinc phosphate. Polymers are produced containing polyacrylic or other acids of organic origin. These include polycarboxylate and glass ionomer cements.
- Plastics - can be filled (composite) or unfilled, produced on the basis of epoxy or acrylic resins.
- Composites are divided into chemical and light curing materials.
- Compomers are hybrids of composites and GIC.
- Metal materials for restorations - amalgams, gallium alloys and pure gold for direct fillings.
Let's take a closer look at each of the groups.
Cement fillings
The most common group of dental materials used at budget appointments. Cements have the following advantages:
- high wear resistance;
- strength;
- prevention of recurrent caries due to the accumulation of fluoride from toothpastes and its gradual release;
- affordable price;
- easy to use;
- have a coefficient of thermal expansion close to that of dental tissues;
- good adhesion to dentin and enamel.
- sensitive to insufficient amount of liquid or its excess at the initial stage of hardening;
- low aesthetic properties;
- Difficulties in grinding and polishing the filling, which do not allow achieving a smooth, mirror-like surface of the restored part of the tooth.
Based on the listed qualities of cements, it is advisable to use them for restoration of molars, where resistance of the material to chewing loads is required, but aesthetic indicators are not critical.
Plastic
These fillings are also used at free therapeutic appointments in dental clinics, but they are less widespread compared to cements due to the specifics of working with them. In addition, such materials have other negative aspects.
- Low resistance to mechanical pressure.
- Tendency to abrasion.
- Toxicity and unpleasant odor when hardening.
- The fragility of restorations.
- High shrinkage rate of plastic during polymerization.
- Absorption of dyes from food and drinks.
Chemical
Chemically cured composites are a two-component self-hardening system based on a polymer matrix. They are a more modern development in comparison with classic cement materials.
Due to the fact that the matrix of the chemically cured composite consists of an organic polymer resin and an inorganic filler introduced into it, the filling products of this group have unique properties in comparison with all previous representatives.
- uniform polymerization of the material, regardless of the thickness of the layer introduced into the cavity;
- satisfactory aesthetic data;
- good wear resistance;
- ease of finishing
- affordable price.
- short working time of the material after mixing the components;
- excessive fluidity of some representatives of chemically cured composites;
- gray undertone in finished fillings due to the release of residual monomer;
- high shrinkage.
Read also: Temporary filling
Light-containing composites rightfully occupy a leading position among the entire variety of dental restorative materials, because their positive aspects are:
- no change in physical properties during the filling modeling process;
- there is no need to mix substances - photocomposites are presented as a homogeneous mass;
- the ability to combine different shades to obtain maximum resemblance to the natural color of the tooth;
- polymerization using a special lamp at the moment when the doctor needs it;
- waste-free use - the dentist takes as much material as he needs.
But, like any preparations for dental restoration, light composites have a number of negative qualities:
- long time for placing a filling due to the need for layer-by-layer application of the substance, no more than 2 mm thick, otherwise complete curing will not occur;
- high price;
- the light of the lamps used is harmful to the retina of the eye, for this reason it is necessary to work in protective glasses.
The materials are used for all types of dental restorations, as they have good strength, are well polished, are available in a wide palette of shades, and using a composite, you can create the natural anatomy of the tooth, taking into account the location of the cusps and fissures, which significantly increases the aesthetics of the fillings.
Amalgam
Metal fillings were widespread during the Soviet era, and in Western European countries they are widely used at budget receptions to this day. And this is not surprising, because thanks to the presence of silver, the material has a caries-static effect, kills microorganisms, and is also the most durable of all the types of teeth filling products presented.
However, amalgams have limited use for several reasons.
- The mercury contained in the composition is toxic to the body.
- Dark gray color looks unattractive.
- There is no adhesion to the walls of the carious cavity.
- Stains dentin.
It is advisable to use such fillings only to restore extensive defects in chewing teeth.
Ceramic
Dental products made of porcelain are primary hard structures used to restore the integrity of the lost tooth structure. The most popular are ceramic inlays, which are not inferior to enamel in terms of resistance to mechanical stress. In addition, ceramics have high aesthetic values.
All designs made from this material have the following disadvantages:
- fragility;
- lack of adhesion to the tooth;
- it is necessary to use cements for fixation;
- high cost.
Compomer
Compomers are hybrid materials that, according to manufacturers, should have the positive qualities of light-curing composites and glass ionomer cements. Due to this, they have a high degree of similarity in appearance to hard tissues, are very durable, and resistant to chewing pressure. However, as the clinical experience of dentists shows, compomers:
- less aesthetically pleasing, durable and less polishable compared to photo composites;
- have less biocompatibility, worse caries-static effect and unsatisfactory adhesion.
For these reasons, the materials of the presented group have a limited scope.
Video: about dental fillings and types of filling material.
Types of dental fillings and their comparison
Often patients are not even interested in what kind of filling the doctor puts in. This is a big mistake. A significant number of various dental materials allow you to make a choice in favor of price-quality ratio. However, it is easy to get confused in a large number of tools.
It is necessary to at least approximately know what a particular material is. After all, their classification is based precisely on durability, strength and aesthetic qualities. It is usually believed that if the cost of the work is higher, then the filling is of better quality. However, high-quality materials today can be used at a free reception.
Types of dental fillings
Dental fillings can be temporary or permanent. Temporary fillings are installed for a short period during treatment to protect the pulp (for example, during multi-stage treatment of deep caries) or to retain a medicinal substance in the tooth. Such fillings are made from lightweight, quickly hardening compounds that can be easily removed at the end of treatment. Permanent fillings are designed to restore the function of a damaged tooth. They are installed to last for many years and are made using durable, wear-resistant materials that can withstand natural chewing stress, while being non-toxic and not damaging the edges of the crown. If fillings are installed on the front teeth or premolars, the aesthetic characteristics of the material are also taken into account - compliance with the natural shade and texture of the tooth.
Currently, fillings made from the following types of materials are used in dentistry:
- metal (amalgam);
- cement;
- self-curing composites;
- composite light-polymer;
- glass ionomer;
- combined.
Metal fillings are the simplest and cheapest option. Amalgam contains metals such as silver, copper, zinc and tin. This combination provides the filling with all the necessary characteristics - copper gives it strength, silver increases resistance to corrosion and has an aseptic effect, zinc gives it plasticity, and tin accelerates hardening. Such fillings are strong, durable, abrasion resistant and inexpensive. However, they also have a lot of disadvantages - high thermal conductivity, severe shrinkage during hardening, low level of adhesion (adhesion) to the crown, as well as the risk of poisoning if the production technology of the filling composition is violated.
In addition, they are contraindicated for people who already have metal structures in their mouths - in order to avoid the accumulation of galvanic currents in the oral cavity, the so-called galvanism. Therefore, today such fillings are not very popular and are being actively replaced by other materials.
Cement fillings are still popular today. They are made from a special dental cement that is non-toxic, flexible and easy to harden. Such fillings are inexpensive, their installation is simple and quick, and if necessary, they can be easily removed. However, the advantages of cement fillings also have a downside: light and brittle cement is not very durable, wears out quickly and has poor adhesiveness.
Self-curing composite fillings are made from special composite materials (consisting of more than one component) that contain silicon compounds. Thanks to this, fillings made from such materials have high strength, are resistant to abrasion, but during hardening they shrink significantly, and in addition, they are quite toxic.
Light-curing composite fillings are made from silica and are a more modern version of composite fillings that are more durable and less toxic. Such materials harden only when exposed to special visible blue light, which allows the doctor to adjust the shape as accurately as possible. Today this is the most modern type of filling. However, it also has disadvantages: a certain degree of shrinkage (although much less than that of self-curing composites), as well as incomplete curing - only 70% of the material hardens under the light of a blue lamp.
Glass ionomer fillings are another new development in the field of dentistry. They are made from glass ionomer cement, a plastic, non-toxic material that bonds well to tooth tissue. Glass ionomer cement is actively used in pediatric dentistry due to its high (up to 15%) fluoride content, which prevents the re-development of caries. At the same time, it is very fragile, wears out quickly, and also poorly imitates the natural color of the tooth, which is why the filling does not look very aesthetically pleasing.
Also in modern dentistry, combined fillings are used, combining several types of the listed materials.
What fillings are installed for free?
Typically, such procedures are carried out under the mandatory minimum medical care of the population or under insurance medicine. Of course, the quality of these materials differs greatly from those used as paid services. But until some time these same means were used everywhere, since there were no more modern ones. Mostly, cement fillings are installed free of charge. Silicate and silicophosphate dental cements are used. After such treatment, caries relapse often occurs; these cements have too weak adhesion. They are quite dangerous when placed in a deep carious cavity, as they are capable of releasing toxic substances.
Silicate cements are placed on the front teeth. They are more consistent in color with natural fabrics, have a certain transparency and are well processed. Silicophosphate materials are designed to close cavities in chewing teeth.
What materials are used for such filling?
Let's consider all the options for filling materials that are used in Clarimed dentistry. They have proven to be the best in terms of price-quality ratio and help solve almost any problem with chewing teeth.
Glass ionomer cement (GIC). This is a modern cement material that is often used to install permanent fillings on the chewing surface. It hardens well in a humid environment, so it is also used to treat the most problematic types of caries, for example, those below the gum level. The material creates intermolecular bonds with enamel and dentin, therefore it holds well and does not require additional sites for strengthening. During the polymerization process, the cement material practically does not shrink, releases fluoride ions into the tooth tissue and adheres perfectly to the edge of enamel and dentin due to thermal expansion.
Light-curing composite "Filtek". A light-curing nanocomposite material that has received medals in various dental competitions at the international level for several years in a row. It lends itself well to modeling, is aesthetic, elastic and very durable after hardening. Suitable for any carious cavities, retains its properties for a long time and is minimally susceptible to abrasion.
Liquid-flowing light-curing composite FLOW. Ideal for filling small carious cavities on chewing teeth. The material is aesthetic, well modeled, and durable.
Liquid-flowing light-curing composite Estelite. The highest award in the field of dental restoration, a kind of dental Oscar, according to the popular American magazine The Dental Advisor, was awarded to this Japanese filling material from 2010 to 2020.
Estelite is suitable for all types of carious cavities, gives minimal shrinkage when cured and has 20 shades that will completely restore the aesthetics of any tooth. This is the most wear-resistant material presented, it has minimal abrasion, and it is possible to restore both front and side teeth; cutting and chewing surfaces. The Japanese composition releases fluoride ions, therefore reducing the risk of recurrent caries. In addition, the composite is characterized by deep adhesion to dentin, resulting in a monolithic structure without a marginal gap.
If the filling is placed correctly on the chewing surface, then it is practically indistinguishable from a real tooth.
Types of fillings
They can be conditionally divided according to the material of manufacture and purpose. So, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
Temporary fillings
They are used as a filling at intermediate stages of dental treatment. For example, during the treatment of apical periodontitis, when it is necessary to check the sealing. They are also irreplaceable in the treatment of pulpitis using the devital method, when a medicinal substance is placed under the pad.
This material can be easily removed if necessary. It has low strength but sufficient adhesion to temporarily cover the problem area. Its composition is absolutely harmless if swallowed by the patient.
Cement fillings
This type of filling has been used for quite a long time, but today it has not lost its relevance. There are three types of materials used:
- Silicate . They contain special glass and phosphoric acids. After polymerization, silicates are capable of releasing fluorine to a certain extent. Therefore, they are quite relevant for acute caries. However, they are not used in primary occlusion due to the fairly large release of orthophosphoric acid. Weak enamel can become saturated with this substance and a chemical burn of the pulp will occur.
- Phosphate . These are low-quality products that dentists are gradually abandoning. For a long time they were used as insulating pads in the treatment of uncomplicated caries. Until now, phosphate cements are used under the crown during dental prosthetics.
- Glass ionomer . They have a chemical composition very similar to natural tooth tissue. Thanks to this they have excellent adhesion. Polymerization occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The doctor manages to completely shape the material to the anatomical shape of the tooth. Glass ionomers have some modifications that are characterized by increased strength. So they include ceramics or even metal. This property allows them to be successfully placed on chewing teeth. Glass ionomer cements have been successfully used in primary dentition. They release a large amount of fluoride, at the same time, without having a toxic effect on the pulp. A high degree of adhesion allows you to place a filling even in a humid environment. Unfortunately, they lack aesthetics. But modern dentistry is already producing glass ionomers to which photo-curing is added, which makes it possible to achieve fairly high aesthetic results.
Composite fillings
These are relatively new technologies in the treatment of complicated and uncomplicated dental caries. But in a short period of use, they have already earned the trust of many patients and dentists. This type of material also has its own subgroups, which mainly include the following:
- Acrylic oxide compounds . They are one of the first composite compounds. They have sufficient strength and abrasion resistance. However, they have more negative qualities than positive ones. The main disadvantage is high toxicity. They are categorically not recommended to be placed on non-pulpless teeth. There are cases where acrylic-containing materials had a toxic effect on neighboring healthy teeth and contributed to the development of caries. At the same time, they are successfully used in pulpless chewing teeth. The service life of the material is up to 5 years.
- Epoxy compounds . Made on the basis of epoxy resins. They are stronger than acrylic fillings, but are quite fragile. In addition, they darken after a few years. Epoxides are less toxic. When placed, they perfectly fill the cavity and are evenly distributed. Their rapid hardening can prevent the dentist from forming a filling in a timely manner. The service life of the material, like acrylic, is up to 5 years.
A product made from the materials listed above is a so-called chemical filling. That is, its hardening occurs on its own due to certain processes occurring by composition and contact with the environment. Other representatives of composites are compounds that harden only under the influence of a special lamp.
- Light-curing fillings . They are a high-quality material in terms of aesthetic and physical properties. They are successfully placed both in the chewing and in the frontal areas of the jaw. For the best contrast, match the color to the tooth tissue. The package can contain up to 12 tubes with different color markings. Polymerization occurs only from exposure to an ultraviolet lamp, and then only by 70-80%. To impart strength, the surface of the filling must be carefully ground and finely polished after hardening.
The service life of composites is from 5 to 10 years. In modern dentistry, the use of hybrid composites and nanocomposites is practiced. These compounds contain very small particles. Namely, they provide ultra-reliable adhesion to natural fabrics. This is the best option for treating chewing teeth. However, dentists tend to consider the material universal and use it in all cases.
Compomer compounds (compomers)
The first compomer fillings began to be used in the early 1990s, representing a hybrid of composites and glass ionomers. Both types of these materials have both positive and some negative properties.
Their complex composition includes benzoin and amine peroxides, monomer, various resins and polyacrylic acid. Polymerization occurs evenly, without the formation of pores, which gives the filling additional strength. This light filling is placed mainly on the fangs and incisors, that is, in the places of the least load. However, it has been practically proven that compomers are able to withstand any chewing load. An important disadvantage is the rather high price and fragility, like composite materials.
Filling materials for baby teeth
For a long time, dentists were content with only glass ionomer cements. But they did not quite meet all the requirements. Today it is proposed to carry out fillings with special children's colored materials based on composite resins. This very unusual approach has recently been used and has gained popularity among children and dentists. In addition to their color appearance, these products have a number of advantages over conventional fillings:
- They combine the properties of glass ionomers and photopolymers.
- They have high plasticity, which allows the dentist to easily work with them and achieve the best placement in the carious cavity.
- They have a high degree of adhesion to milk tissue.
- It is installed on baby teeth and is kept on them for up to 3-4 years. This is quite enough for the normal process of changing the bite to take place.
- The material is capable of accumulating fluoride from toothpaste and food during chewing.
- On bright fillings, areas of abrasion are more noticeable, which can be corrected in a timely manner.
- Affordable price.
- Psychological factor. From the first visit to the dentist, the child begins to show interest in colored fillings. Thanks to this, tension is relieved during treatment, and the habit of oral care is quickly instilled. The child is happy to visit the dentist again.
Amalgam fillings
Such fillings are also called silver fillings. This is outdated material. It is an alloy of mercury, silver, tin or copper. The filling is very hard, durable, but completely lacks aesthetic qualities. There is evidence that the material lasted in the oral cavity for more than 20 years.
The big disadvantage is the high thermal conductivity and heat capacity. In addition, there are suggestions that mercury particles may be released from the amalgam. As you know, this is a very harmful substance that can cause some mutations and cancer in the body. But this fact remains unproven and it is believed that the amount entering the body is extremely insignificant. At the moment, amalgam is practically not used.
The choice of one or another filling material remains with the patient. The doctor can only recommend which one to choose after an adequate examination and diagnosis. The patient has the right to refuse the imposed material, but he must consider the consequences of his choice. If you ask a doctor, he can always tell you about the advantages and disadvantages of a particular material, so only the dentist knows which filling is better.
Popular dental materials
Fillings are divided into permanent and temporary. A permanent one is placed when there is minor damage to the tooth crown, a temporary one is used for long-term complex treatment or diagnostics. A temporary filling is also used to protect medicinal compounds during dental treatment: a medicinal compound is placed under it.
The materials from which fillings are made are divided into several types:
- cement, silicate;
- plastic;
- metal, amalgam;
- ceramics;
- composites.
Depending on the material used, fillings are divided into several main types:
- cement;
- composite;
- compomers.
The dental industry also produces other types of fillings - plastic, metal and ceramic.
The most durable material is made from light-curing composite. Such fillings are expensive, but the high price justifies the long service life. The fillings look aesthetically pleasing and have the ability to change their shade with changes in lighting.
The most popular material is dental cement. These fillings are still in demand among patients due to their low cost, high adhesion and strength. The fillings literally stick to the surface of the crown and do not form air gaps.