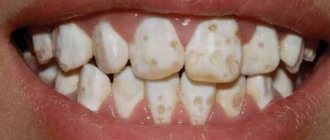
Manifestation of dental hypoplasia
Hypoplasia can be systemic or local. In the first case, the entire dentition is affected (the enamel of both milk and permanent teeth is damaged), in the second, one or more permanent teeth are damaged. Local hypoplasia is a consequence of mechanical trauma or an inflammatory process.
Clinical picture of hypoplasia:
- The appearance of white spots on the child’s teeth. Such defects are white (less often yellowish) appear on the outside of the teeth, have a clear contour, and do not cause pain.
- Underdevelopment of enamel. Grooves or depressions appear on the teeth. Pain is usually not noted, but aesthetic defects are very noticeable.
- Lack of enamel (aplasia). A rare manifestation of the disease, the most severe form. The enamel may partially or completely peel off from the teeth, exposing dentin. In such cases, a painful reaction to thermal and chemical irritants is observed.
Treatment and prevention
In this case, treatment cannot be separated from prevention, which is also a full-fledged treatment of hypoplasia. It is necessary to take care of your baby’s teeth even before birth. The surest option for preventing the onset of the disease in a baby is constant monitoring of the woman during pregnancy. Even in the absence of complaints, the expectant mother should visit the dentist every 3-4 months. It is worth remembering that not at all stages of pregnancy a pregnant woman can undergo treatment, but at all stages preventive measures can be carried out. The dentist sets the visit schedule independently, taking into account the condition of the oral cavity and the degree of progression of various diseases in the pregnant woman.
After birth, the baby should ideally be breastfed for at least a year! Subsequently, it is necessary to pay special attention to the child’s diet, which must be balanced. As the toddler grows, parents should take all measures to prevent oral injuries. The fact is that with trauma to baby teeth, as well as with advanced forms of caries, the rudiments of permanent teeth can be damaged; in the best case, enamel hypoplasia will form, in the worst case, the complete death of the permanent tooth rudiment will occur.
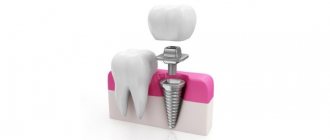
Treatment of hypoplasia can be carried out in various ways. It is possible to restore the shape of a tooth only with the help of filling materials or prosthetics, but the main goal of treatment is to eliminate the factors that contribute to the development of caries and restore the normal shape of the tooth. To do this, it is necessary to limit the contact of the damaged tooth surface with aggressive factors.
With the spotted form of hypoplasia, prosthetics are most often used, since the affected areas over time can greatly spoil the aesthetic appearance of the baby’s teeth. For the grooved form of hypoplasia, both prosthetics and filling of defects are successfully used. In primary occlusion, prosthetics are most often used, since the baby cannot sit quietly through the entire painstaking filling procedure.
In any case, the treatment method will be chosen exclusively by the doctor, based on a combination of many parameters.
My son has terrible caries. The enamel comes off in chunks from the teeth...
Today a large piece of enamel fell off my son's tooth. He and I rushed to the dentist. Verdict - caries! On all teeth. To say that I am shocked is to say nothing. I felt like I had been hit on the head. Moreover, a month ago we were examined at this clinic and they assured us that the teeth were healthy and everything was fine. They recommend plating silver. Is this effective and can it stop caries? And won't it make it worse? Are there any other modern methods? Girls, I will be very grateful to everyone who shares their experience and contacts of good clinics and dentists.
Published November 16, 2020, 11:14 pm
Treatment methods for enamel hypoplasia in children
If white spots on teeth are invisible to others, they are usually not removed. But the enamel, severely affected by the disease, ceases to protect the tooth tissue, resulting in complications - increased wear of teeth, destruction of dentin up to the loss of teeth, and the appearance of malocclusions. To prevent this, timely therapy is necessary.
Procedures for the treatment of enamel hypopalsia in children:
Bad enamel on a child’s teeth and ways to restore it
When metabolic processes in dental tissues are disrupted, poor enamel on a child’s teeth is sometimes observed. The main reason for the development of such a pathology in a baby is an infectious or viral disease suffered by a pregnant woman during the period of bearing a child, when the formation of tooth buds occurs. You should not ignore such a problem as weak tooth enamel in children. It is recommended to consult a pediatric dentist for timely treatment of baby teeth to prevent their destruction.
Features of development
Hypoplasia of dental enamel in primary teeth is a pathology that develops as a result of disruption of metabolic processes in developing chewing units. When this disease develops in a child, the condition of the tooth enamel deteriorates, it becomes thinner, cracks appear on it, and the protective layer is often exposed to carious lesions. To prevent unpleasant consequences, it is recommended to strengthen tooth enamel in children. For this purpose, various methods are used in dental practice.
It is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner if any problems arise with the protective layer of the dentition, since tooth enamel does not strengthen on its own and cannot regenerate on its own.
Why does the protective layer suffer?
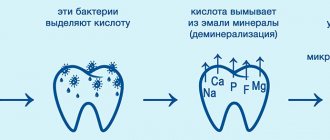
Thinning of tooth enamel occurs when metabolic processes in the body are disrupted, as a result of which the tissues of growing teeth do not receive the required amount of protein and mineral structures. This phenomenon can occur in the prenatal period, in the age category from six months to one and a half years, when mammary and permanent units are formed and mineralized.
Pathologies in the development of milk units are caused by the following factors:
- Complicated pregnancy. These include: pathologies - severe toxicosis, Rh conflict;
- diseases suffered during the period of bearing a baby - toxoplasmosis, rubella, diseases of the endocrine system, influenza, syphilis, HIV infection; The expectant mother is taking antibacterial drugs or hormonal drugs.
Chronic childhood diseases - infections, diseases of the digestive system, rickets, dysfunction in brain activity, various forms of dystrophy.
Insufficient amounts of fluoride and calcium in the body also negatively affect the condition of the protective layer of the dentition. External factors can also cause a deterioration in the condition of tooth enamel - eating a lot of sweets, sour foods, lack of proper hygiene, bad habits - biting nails, pens or pencils, as well as bruxism, in which constant friction worsens the condition of the teeth.
The pediatric dentist will tell you how to strengthen your teeth enamel after a preliminary examination and examination. It is important to establish the cause of the problem and eliminate it. Only after this the dental treatment performed will be effective.
Simple fluoridation procedure
How a child’s tooth enamel can be strengthened is determined by the doctor after an examination in each specific case. The most common procedure that strengthens the surface of chewing units is fluoridation. It is offered in many dental clinics. Fluoride is one of the most important trace elements required for proper growth and development of teeth. The fluoridation procedure involves the use of special fluorine compounds - fluorides, which reduce the solubility of enamel, reduce the degree of acid production by bacteria, and help restore the protective layer.
A qualified specialist will assess the condition of the child’s dental surface and, if necessary, decide what to do in a particular case and how to strengthen the tooth enamel. Simple fluoridation is carried out in two ways:
- The enamel on the teeth is coated with fluoride-containing varnish. The plaque is first removed, after which varnish is applied to the surface and dried under a halogen lamp. To achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to carry out this procedure immediately after the baby teeth have erupted. Repeat it once every six months.
- Using cap. The dentist makes impressions in each specific case and fills them with fluoride. After which the impression is placed on the surface of the dentition. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. To achieve maximum effect, at least 10 procedures should be performed.
Features of deep fluoridation
The most effective method of restoring enamel is the deep fluoridation procedure. This is an enhanced technique for restoring the surface of the protective layer. To carry out the deep fluoridation procedure, the dentist performs the following manipulations:
- teeth and interdental space are thoroughly cleaned of plaque and stone and dried;
- a preparation containing magnesium salt, copper and fluorides is applied, then it is dried; the enamel is treated with calcium hydroxide.
During these manipulations, the penetration of the molecules of the substances used is ensured deep into the micropores of the protective layer, thereby ensuring its effective remineralization and long-term bactericidal effect. It is recommended to carry out this procedure at least once a year (in the worst case, once every year and a half).
It is important to systematically strengthen the child’s protective layer from the beginning of the eruption of baby teeth. The fluoridation procedure is an excellent prevention of the development of caries and enamel damage.
Preventive actions
To preserve the beauty of a child’s smile, it is very important to teach him from an early age how to properly care for it. By turning to dentistry, you can strengthen and restore the surface of the tooth. And you can prevent the development of all kinds of problems with the help of proper prevention. Careful oral hygiene is important. It is recommended to use a brush with medium-hard bristles and fluoride toothpaste approved for children. Dental cleaning should be done daily, twice a day. All movements must be circular and performed for at least three minutes. Horizontal movements can injure the surface; this must be explained to the child. He must carry out cleaning procedures correctly.
An important condition for maintaining dental health is maintaining proper nutrition. The diet should be rich in foods that contain calcium and fluorine - fermented milk products, different types of nuts - almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, legumes - peas, beans, poultry (chicken, turkey), hard cheeses, oatmeal and buckwheat. cereals If necessary, take a course of multivitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor. Be sure to visit a pediatric dentist with your child at least once every six months, who will detect any developmental pathologies and, if necessary, carry out fluoridation or other types of treatment.
tvoyzubnoy.ru
How to strengthen enamel at home?
To protect the enamel from damage, it is recommended to follow a balanced diet (the diet should contain foods containing calcium - fermented milk products, almonds, hazelnuts, beans, peas, meat, hard cheeses, oatmeal and barley), and take vitamins with calcium.
Special toothpastes (for example, Vivax Dent, Elmex, ApaCare, Lacalut) and gels (ROCS, Amazing White Minerals) are also indicated.
Do not forget that the result of treatment depends on the professionalism of the dentist. On our website you can find a list of clinics that successfully treat this disease.
What to do if a child breaks a molar tooth
Guys often injure their chewing organs while growing up. The baby may fall at home or during sports activities. Children can accidentally knock out each other's teeth. This situation, when a child breaks a front molar, can happen on the playground at school. Parents should instruct their child in advance what to do in such a situation.
- First, rinse your mouth with cool water.
- If the bleeding is minor, there is no need to be alarmed.
- Don't worry about swollen mucous membranes. The tissues quickly heal and are restored.
Treatment of injuries to a child's front teeth should be prescribed by a dentist. It must be visited immediately after the unit is damaged. It is good if the missing fragment or the entire organ is not lost. The knocked-out rudiment should be held by the crown, and the root should be washed in water or saline solution. You need to immediately return the organ to the socket. This will increase the chances of saving the unit. When the procedure is unsuccessful, soak the rudiment in milk or water and quickly contact your dentist.
If a tooth has chipped, you should not drink hot or cold drinks. For acute pain, you should take a pain reliever. After the examination, the dentist will do everything to keep the unit alive. A fragment of an organ can be glued. When this is not possible, restoration is done using a special material - a composite, which is difficult to distinguish from natural enamel.
Remember, the sooner the child is in the clinic, the better! There is a possibility of engraftment of molars! If they are immediately delivered to the clinic, after processing the gum tissue, the doctor will insert the unit into its original place, fixing it with a specific structure. The lost crown is replaced with a removable denture.
To prevent oral injuries, buy your child a protective helmet. The mouthguard protects the chewing organs well from damage. It is made from casts in a laboratory. Parents should instill in their children a sense of caution and develop the ability to fall correctly. You need to teach your child to group, protecting his neck and head.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Gum recession: causes, treatment and elimination at the doctor and at home
Complications if you don’t see a doctor in a timely manner
If you notice that a piece of a child’s front baby tooth has broken off, you should not delay your visit to the doctor, even if there is no pain. If you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, you can provoke the development of the following diseases:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- periodontitis.
These diseases lead to destruction and loss of the incisor. An infection developing in a child’s mouth can cause the following serious diseases of internal organs:
- hearts;
- stomach;
- kidney;
- liver.
All these organs have a direct connection with the oral cavity through the circulatory and nervous system of the body.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Burning in the mouth: causes and treatment of the mucous membrane
How to keep healthy
- Before going to bed, regardless of age, children should clean their mouth.
- From the moment when the growth of the first teeth has just begun, infants need to wipe the oral cavity with a clean, damp cotton napkin after feeding.
- Before the age of two, brush your first baby teeth carefully; it is better to purchase soft toothbrushes and use plain water rather than toothpastes.
- Two-year-old children can use a minimal amount of toothpaste, fluoride-containing one is possible, but no more than a pea-sized amount.
- From 2 years of age, cleaning is carried out 2 times - after breakfast and dinner. Additionally, you can use dental floss.
- Until the child learns to brush his teeth efficiently on his own, you need to control the process.
- When teeth are replaced with molars, you need to minimize the amount of sweets, soda, and too sour fruits consumed.
- Be sure to provide your baby with his own cutlery to prevent “foreign” carious bacteria from entering the oral cavity.
- Infants should not be given sweet juices from a bottle at night, so as not to provoke “bottle” caries.
- If your child attends sports activities, you can purchase a special mouth guard to prevent your child from accidentally knocking out a tooth.
- Every six months, your child needs a dental examination.
Diagnostics
Hypoplastic damage to tooth enamel is easily recognized upon examination by a doctor. If there are still doubts about the origin of visible lesions, then differential diagnosis is carried out - a method in which diseases with similar symptoms are gradually excluded from the list until one, the most probable diagnosis remains.
Hypoplasia of tooth enamel is characterized by a combination of several signs:
- The presence of a child's history of metabolic disorders suggests a catalyst cause that triggered the development of the pathology.
- The nature of the lesions, their shape, depth and location help determine when the process of hypoplasia began.
- The symmetry of the affected teeth indicates the systemic nature of the disease.
- To distinguish hypoplastic spots from carious spots, vital staining with methylene blue can be performed. With hypoplasia, the spots do not react to the dye.
Thinning enamel is a condition that requires a very detailed examination. Only this approach will help you choose effective treatment.