What to do when your cheek hurts
If the cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, the patient may think that the symptom will disappear on its own and as quickly as it appeared.
But such a misconception is at least dangerous, since the causes of redness and swelling of tissues can not only cause complications, but also lead to death. If the cheek is swollen, it means that there is an inflammatory process in the body. The reasons that lead to it are divided into several groups:
- associated with problems in the oral cavity;
- swelling after treatment or tooth extraction;
- pathologies of internal organs and systems.
It is necessary to talk about each group of problems in more detail.
If the skin on the cheek is swollen, but the pain does not begin in the tooth area (especially in the absence of an open carious process), one of the following dental problems can be suspected.
Let's list the common causes of pain.
Dental pathologies
Pain syndrome spreading to the cheek area is in many cases caused by dental pathologies:
- Inflammation of the tooth root. It occurs as a result of complications of pulpitis, caries, characterized by a long course, and poor-quality root canal therapy.
- Periodontal disease, accompanied by a deterioration in the stability of teeth, bleeding gums, increased vulnerability to infections, and extensive swelling that cannot be eliminated with medications.
- Pericoronitis. If the eruption of the eighth teeth (“wisdom”) proceeds with difficulty, the formation of “mucous hoods” occurs in which food debris accumulates, inflammation, swelling, and hematoma formation occur. A partially erupted tooth in contact with the cheek provokes injury.
- Gingivitis, accompanied by bleeding gums. Risk factors are non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene, poor-quality fastening of the crown.
- Phlegmon or abscess. It develops when the cheek or gum cavity fills with pus.
Pain and swelling of the cheek that appears after a dental appointment is provoked by:
- Allergy to filling material. To eliminate symptoms, refilling with hypoallergenic materials is performed.
- Incomplete removal of the nerve. If appropriate therapeutic measures are not taken, the prerequisites for losing the entire tooth appear.
- Removal of a dental unit. Depending on the complexity of removal, tissue swelling is observed over a fairly long period of time. It is recommended to temporarily avoid hot, irritating foods, alcohol, and avoid touching the inflamed area until the problem is resolved.
- Gum incisions made to ensure drainage of infiltrate. It takes a lot of time for the incisions to heal, during which discomfort appears.
Pain in the cheek also occurs with progressive neurology, accumulation of fluid in the body, infectious exacerbations, cystic, tumor processes, complications of sinusitis, mumps, and other infectious diseases.
Symptoms of neurological ailments are complemented by pain in the throat, trigeminal nerve area, and ear congestion. Infectious diseases caused by the activity of harmful microbes are treated with antibacterial therapy. An enlarging cyst requires surgical removal.
Ernest syndrome develops due to damage to the stylomandibular ligament. Unpleasant sensations spread to the facial and cervical areas. Temporal tendonitis manifests itself as discomfort and pain in the cheek, teeth, and cervical region.
In case of tumor diseases (benign, cancer), developing as a result of prolonged inflammation or injury, the cheek or gums swell. Painful sensations accompany sinusitis.
Consequences of injuries
The most common causes of traumatic pathology are mechanical damage, burns (chemical, thermal), and negative consequences of insect bites.
To eliminate the consequences of injury, in which the integrity of the bones is disrupted and swelling increases, cold compresses are used. An increase in swelling is a reason to visit a traumatologist.
If a pain syndrome is detected, contacting a doctor becomes the only method of eliminating the problem.
After a dental examination, if necessary, an x-ray diagnosis is prescribed, based on the results of which the causes of pain are identified. Diagnostic measures are supplemented by consultation with a neurologist, otolaryngologist, and other specialized specialists.
If there are signs of bacterial infection, Amoxiclav, Biseptol, Lincomycin, and other types of antibiotics are used.
The drugs Nimesil, Ketorol, Ketanov, Ibuprofen, and other painkillers and anti-inflammatory complexes, the list of which is agreed upon with a medical specialist, help reduce the intensity of pain and relieve swelling.
"Erius", "Tavegil", "Diazolin", "Suprastin", and other antihistamines are prescribed for allergies.
Therapy for the flux that caused the swelling involves the use of surgical methods.
Chlorhexidine rinses have a noticeable effect.
To counteract infectious agents and minimize inflammation, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system and fortify the diet.
Folk remedies
If it is not possible to receive professional medical care, you should use traditional methods of improving well-being, which do not replace full treatment, but serve as a temporary measure or an addition to the main therapy.
In the absence of signs of inflammatory processes and normal body temperature, cold compresses are used.
Relief of symptoms in diseases of the teeth and oral cavity is achieved by rinsing with antibacterial solutions: half a teaspoon of soda and salt are dissolved in one glass of warm boiled water. To enhance the effect of the product, iodine is added.
Kalanchoe helps reduce inflammation. Soak a cotton ball in the juice from the plant and place it on the surface of your cheek.
Apply lotions with aloe juice, applying pieces of leaf (with an incision to the inflamed area).
A cotton swab is moistened with propolis tincture and applied to the inner surface of the swollen cheek. Pre-kneaded dry propolis is applied to the inflamed area and held for about 30 minutes.
Rinsing with infusions of sage, calamus, nettle, and oak bark has a complex effect. The ingredients, mixed in equal proportions, are poured with water (1 liter per 50 g of mixture). After 2-3 hours of infusion, rinse the mouth (interval - several hours).
To prepare another effective remedy, 3% hydrogen peroxide is diluted with water (1 to 1). Rinse every 2 hours.
Garlic rinses involve chopping 2-3 cloves and pouring 200 ml of boiling water. The oral cavity is rinsed with a cooled solution.
In order to maintain the antiseptic, healing, antibacterial effect, one tablespoon of liquid honey is stirred in a liter of chamomile decoction and consumed warm. Also, gauze is soaked in chamomile broth and applied to the swollen area for 15 minutes without rinsing.
Swelling and pain due to an insect bite are minimized after using antihistamines and applying soda compresses to the cheek.
Pain associated with the eruption of wisdom teeth can be relieved with specialized ointments, gels with a freezing effect, and painkillers.
Regardless of the results of home treatment, it is advisable to visit a highly experienced specialist at the first opportunity. Medical intervention is extremely necessary in case of a sharp deterioration in health, fever, dizziness, headache, breathing difficulties, or rapid tumor growth.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?
Yes
No
If your cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt, you need to carefully “listen” to other processes occurring in the body; perhaps there is no toothache, but there is “tugging” and “pulling” behind the ear, gums are bleeding, or a lump has appeared on the cheek. Swelling and redness in the cheek area can be caused not only by dental problems, but also by infectious diseases, insect bites or injury.
1. Dental - even if your tooth does not hurt, your cheek most often swells due to problems with your teeth or gums: - after dental treatment. This may be caused by an ongoing inflammatory process in the root of the filled tooth. The dentist removed the nerve, cleaned the tooth cavity, put a filling, but did not “clean” the roots.
Thanks to the removal of the nerve, the patient does not feel pain in the tooth, but inflammation inside the gum causes swelling and redness of the cheek area; - often the cheek swells after tooth extraction, in this case, the dentist usually warns about this and asks the patient to be careful and try not to injure the patient region.
Inflammation that persists for several days after a complex dental operation is considered residual and goes away on its own; - the cheek may become swollen due to problems with the gums - gingivitis causes redness and swelling of the gums, swelling of the cheeks, bad breath, bleeding and is often painless.
Inflammation of the gums can be caused by improper oral care, plaque accumulation and untreated dental caries. If the patient’s cheek is swollen, and the gums look inflamed and reddened, a visit to the dentist is indispensable, since gingivitis can gradually turn into periodontitis or periodontitis;
– due to the eruption of wisdom teeth – wisdom teeth that decide to erupt after 25-30 years often cause pain in the jaw and swelling of the cheeks. In these cases, the patient feels a general malaise, severe, dull pain in the gums, the cheeks become swollen, and it becomes difficult to open the mouth and speak. What causes these symptoms and what to do with a growing wisdom tooth, only a dentist can tell you by taking an x-ray.
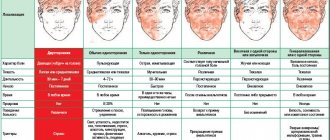
2. Infectious diseases - severe swelling of the cheek on one or both sides, increased body temperature, sore throat and general malaise can be symptoms of mumps or “mumps”. Infectious parotitis, “mumps”, “mumps” is an inflammation of the salivary glands caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
Mumps is characterized by severe enlargement of the cheek and neck area on one or both sides, increased body temperature and general malaise. Adult patients suffer from mumps quite seriously, the risk of complications increases greatly, so treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist - an infectious disease specialist or therapist.
Catarrhal stomatitis on the cheeks
- removal of a tooth;
- gum disease;
- cutting through the figure eight;
- periodontitis.
- swelling on the cheek;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity;
- violation of facial movements;
- pain in the area of pathology.
- Diseases associated with neurology, in which, in addition to changes in appearance, symptoms such as sore throat and congestion in the ears are noted. In such a situation, it is better to seek help from a neurologist.
- Swelling of the cheeks can be explained by the accumulation of a significant amount of water in the body, which can be a sign of serious problems in the functioning of certain organs.
- The development of an infectious process to eliminate which the doctor will prescribe the patient to take antibiotic drugs.
- The occurrence of a sebaceous cyst, which may require surgical intervention.
- Injuries suffered.
Associated symptoms
The symptoms that accompany cheek swelling are directly related to the main cause of the swelling. Some of the most well-known symptoms associated with swollen cheeks include:
- hives;
- a sore throat;
- toothache;
- addition of infection;
- rash;
- redness;
- seals;
- oily, itchy or dry skin;
- painful sensations;
- temperature increase;
- itching in the eyes;
- sneezing;
- labored breathing;
- paresthesia of the jaw and cheek;
- swelling of the face, tongue or lips.
Experts identify 6 types of stomatitis, each of which can develop on the inside of the cheeks. Each form has characteristic symptoms:
- Traumatic, it causes redness and inflammation of the mucous membrane, erosion and sores that bring discomfort, white plaque on the cheeks, sore throat and mouth.
- Candidiasis, also called thrush, is characterized by a curd-like coating, blisters, pain and a feeling of weakness.
- Aphthous - ulcers appear that are red in color and round in shape. Edema also appears, a gray coating under which the epithelium dies, followed by the formation of a compaction-infiltrate, rejection of necrotic tissue and healing of aphthae.
- Herpetic. This form is characterized by the formation of blisters, in the area of which there is constant itching, later they turn into ulcers and aphthae, a feeling of malaise appears, and body temperature rises.
- The allergic form manifests itself in the form of redness, ulcers and inflammation appear on the cheeks, palate and lips, the plaque is often purulent. In addition, bleeding, fever, malaise and general weakness appear, as well as symptoms inherent in the aphthous form.
- Bacterial is accompanied by a light coating (yellow or gray) or erysipelas with blisters and bleeding.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of pathologies accompanied by inflammatory processes and pain in the cheek area, it is necessary:
- Follow oral hygiene standards (use a toothbrush, floss, brush).
- Visit the dentist at least twice a year (if painful symptoms appear, immediately).
- Supplement your diet with foods that have a positive effect on the health of your gums, teeth, and oral cavity.
- Conduct timely treatment for colds and inflammatory ailments.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Refrain from uncontrolled use of medications.
A timely visit to a doctor for pain in the cheek will minimize the risk of negative consequences and complications.
Contents [Show]
Hello, dear Lesya. I would really like to know your opinion about the situation, if possible. For 10 months, since May last year, I periodically had pain on the inside of my cheek, and I felt swelling in my tongue. Several days a month, it appeared and then ceased to be felt. At that time, in May, I had 1.
At the same time, two wisdom teeth came out on one side (upper and lower), 2. they removed the nerves and put a filling on the front tooth, after which for 6 weeks there was just wild sensitivity in absolutely all teeth and gums to cold, I couldn’t even take a sip of water room temperature or eat a spoonful of yogurt from the refrigerator, during these six weeks the lips, tongue, and cheek periodically swollen.
Then it passed, the sensitivity decreased (different clinics said that it was sealed correctly, perhaps a post-filling individual reaction, since the nerves are located very close), but the pain in the cheek remained. But since January of this year, three months, the pain has become constant throughout the day, and does not stop for a second.
In the evening there is a headache, the temperature has never risen (it has generally risen above 34.5 only a couple of times in my life), nothing bothers me during sleep, or during meals either. I wake up and it starts again, and so on every day. Neither rinses nor mouth gels help, they only make you feel sick.
Analgin tablet helps for an hour, no more. On the cheek in several places, in the middle there is like a small “nipple”, a bulge, lower, closer to the lower gum, like peas, and between them there are something like folds, as if bitten. Various dentists assumed that there could be an extra wisdom tooth or a cyst, and that the cheek was being bitten on both sides by the upper and lower wisdom teeth.
The teeth themselves, as they said, grew correctly and evenly. They sent me to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, with whom I had a consultation on Friday. He said that he really bites his cheek all the time. When I asked why I never felt the moment of biting, he replied that he felt it when he bit it once, but not when he bit it constantly and for a long time.
He advised me to remove the lower wisdom tooth. But since I have a congenital heart defect, and anesthesia is always given to me without adrenaline, he asked me to first get a certificate from the cardiologist with permission for a complex removal of the figure eight, and then make an appointment again. While I’m waiting for the cardiologist to return from vacation, I finally decided to register on the forum and write to you, I’ve been wanting to for a long time.
Please tell me, do you agree with the doctor’s recommendation? But the most interesting thing for me is that I saw the surgeon the day before yesterday, and yesterday everything exactly the same appeared on the second cheek, absolutely symmetrical to the right, and the same pain. There are no wisdom teeth on the other side, and there seemed to be nothing to bite my cheek there... Now both cheeks hurt at the same time.
Plus it became a little painful to swallow, it goes down the throat. It’s not the gums that hurt, but the cheeks. And it feels like the pain is not in the oral cavity, it’s just unpleasant that the cheek is not smooth and “interferes” with the tongue, and the pain is somewhere further... in the bone at the level of the cheeks, where the jaw connects. In general, severe pain in the jaw from 13- 14 years old, now I’m 23, that is, about ten years already.
When I was 15, I went to the dentist with a feeling of pain in all my teeth at the same time, she found nothing and said that there was something wrong with the jaw. The same thing happened again with the same symptoms and the same words from another dentist 5 years later. There is a constant desire to press hard on the jaw, after which the pain in the teeth, headaches and sleep improves immediately.
The pain begins at a point near the ear, sometimes radiating to the ears. It becomes easier if you apply Diclofenac or Troxevasin. Moreover, I have been noticing for a long time that the pain always worsens in winter, I don’t even remember in summer. Nothing crunches or clicks when you open your mouth. I also asked the surgeon about this, he said that since not all wisdom teeth are there, the formation of the jaw has not yet finished, and since it all started in adolescence, it should stop by the age of 28-29... But I doubt that this is normal process, somehow I have never heard from any of my peers about such wild pain in the jaw... Many people are cutting their wisdom teeth, their gums hurt, they complain... But the jaw? I will be very grateful for your opinion. All the best to you, success and prosperity! Evgenia
Causes of stomatitis:
- injuries to the mucous membrane of the mouth and cheeks (uneven teeth, crowns, hard food);
- allergic reaction;
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition (with a lack of certain microelements and vitamins in the body);
- stress (emotional disorders);
- infections;
- as a complication after other diseases.
Depending on the nature of the occurrence of stomatitis, the following symptoms may be observed:
- if it is fungal in nature, rashes in the form of a white coating are observed throughout the oral cavity and on the cheeks;
- with the herpetic nature of the disease, the appearance of which is provoked by the herpes simplex virus, fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, rashes in the form of ulcers in the mouth, and pain in the cheek on the inside may also occur.
No specific tests are required to determine stomatitis. Treatment methods for both adults and children are identical. Diagnosis of this disease involves a doctor examining the mouth and cheeks, as well as collecting material for testing.
If your entire cheek hurts, it’s a disease of the jaw.
Separately, I would like to talk about problems such as diseases of the jaw and temporomandibular joint. There are quite a lot of them and of course they all cause pain in the cheek area.
Osteomyelitis of the jaws is a severe inflammatory process of infectious nature in the jaw bone. It is customary to distinguish between hematogenous and odontogenic osteomyelitis. The latter is more common and is caused by an infection in the periodontal pocket. The most common pathogens are staphylococci, streptococci, and anaerobic bacteria.
When the function of the temporomandibular joint is impaired, not only the entire cheek hurts, but also the temple, and even the forehead. Almost every movement of the jaw is accompanied by a characteristic click, and the mouth becomes more and more difficult to open - the mobility of the jaw is limited. This disease can occur for many reasons, in particular due to osteoarthritis of the joint, inflammation or myofascial syndrome in the masticatory muscles. Only a doctor can finally determine the cause and prescribe treatment after examining and examining the patient.
A jaw fracture is another reason why your entire cheek may hurt. A fracture is a violation of the integrity of the jaw bone as a result of trauma, for example, after a blow or other mechanical impact. A fracture may occur in the upper jaw, the lower jaw, or both jaws at the same time. As a result of the fracture, the cheek swells and severe pain is felt in the muscles.
The cause of the changes may be an infectious disease such as mumps. This pathology is characterized by inflammation of one or more salivary glands, which causes swelling.
Lymphadenitis can also provoke inflammation of the cheek. In this condition, the cervical, parotid and submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged. This can be an independent illness, triggered by an infection, but most often it occurs as a complication after illnesses in the ENT organs (reactive lymphadenitis).
A pathology such as sinusitis can also cause swelling. The inflammation usually spreads to the cheek and under the eye.
Most often, inflammation of the salivary ducts and glands occurs as a result of a pathological process on the gums. But it could also be a separate disease. The cause is stones in the ducts, various neoplasms in the system (cysts, tumors).
Swelling of the mucous membrane also occurs due to inflammation of the nerves. In this case, numbness, “lumbago”, and pain radiating to the ear may be bothersome.
In both the first and second cases, there will be clearly defined hyperemia along the nerve or salivary duct.
Osteomyelitis of the jaws is a severe inflammatory process of infectious nature in the jaw bone. It is customary to distinguish between hematogenous and odontogenic osteomyelitis. The latter is more common and is caused by an infection in the periodontal pocket. The most common pathogens are staphylococci, streptococci, and anaerobic bacteria.
When the function of the temporomandibular joint is impaired, not only the entire cheek hurts, but also the temple, and even the forehead. Almost every movement of the jaw is accompanied by a characteristic click, and the mouth becomes more and more difficult to open - the mobility of the jaw is limited. This disease can occur for many reasons, in particular due to osteoarthritis of the joint, inflammation or myofascial syndrome in the masticatory muscles. Only a doctor can finally determine the cause and prescribe treatment after examining and examining the patient.
A jaw fracture is another reason why your entire cheek may hurt. A fracture is a disruption of the integrity of the jaw bone as a result of trauma, for example, after a blow or other mechanical impact. A fracture may occur in the upper jaw, the lower jaw, or both jaws at the same time. As a result of the fracture, the cheek swells and severe pain is felt in the muscles.
Dentistry
Some of the most common dental causes are pain inside the cheek and pain in the cheek and gum.
Symptoms:
- Sharp, severe pain.
- Pain when biting.
- Painful reaction to: cold, hot, sour, sweet foods.
- The pain is pulsating.
- Swelling of the gums.
- The pain spreads to the entire oral cavity.
- Cheek swelling, redness.
Causes:
- Caries.
- Mechanical damage to the tooth, root.
- Bone disease: periodontitis, osteomyelitis.
- Postoperative complications.
- Damage to gum tissue.
Contact your dentist immediately. The doctor will determine the stage of the disease. If necessary, he will order laboratory tests and examination by other specialists. Conservative dental therapy, surgery, and medication are expected.
ENT diseases
There is pain in the cheek, but the tooth does not hurt, perhaps this is a symptom of a pathology of the ear, nose or throat. These diseases have accompanied us since childhood and are closely related to the environment. They are mostly inflammatory in nature.
Symptoms:
- Deterioration of hearing and smell.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Pain radiating to different parts of the face.
- Labored breathing.
- Purulent, bloody discharge from the nasal cavity.
- Earache.
- Discharge from the ear.
- Increased body temperature.
- Dizziness.
- Vomit.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CLSbFzAMbZw
Causes:
- Sinusitis.
- Otitis.
- Sinusitis.
- Foreign body in the ear, nose.
- Injuries.
- Polyps.
- Past viral infections.
The main task is to prevent complications and transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
The following are used in treatment:
- Therapeutic methods: taking medications, physiotherapy.
- Surgical intervention.
Neuritis
Peripheral nerve inflammation:
- facial,
- occipital,
- intercostal,
- limbs.
Manifested along its location by pain, impaired mobility, loss of sensitivity. Damage to several nerves is called polyneuritis.
Severe pain in the cheek, swelling, can be caused by neuritis of the facial nerve.
Symptoms:
- Numbness.
- Paresthesia (tingling).
- Paralysis.
- Partial decrease in mobility in the affected muscles.
- Edema.
- Cyanosis.
- Trophic ulcers.
Causes:
- Infection: brucellosis, measles, influenza, herpes, diphtheria, malaria.
- Injury.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Poisoning with toxic substances: alcohol, mercury, lead, arsenic.
- Diabetes.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Hypothermia.
Treatment is primarily aimed at identifying the cause that provoked the neuritis. Includes:
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Antiviral drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Vasodilators.
- Biogenic stimulants.
- Decongestant therapy.
- B vitamins.
- Physiotherapy.
- Surgery.
Neuralgia
Nerve damage. It is characterized by pain in the area where the affected nerve passes. It differs from neuritis in that there is no loss of sensitivity and mobility.
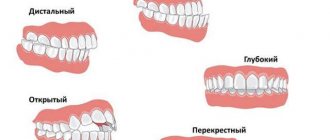
The cheek and jaw hurt when opening the mouth, there are no ulcerative lesions or hyperemia, a possible cause is neuralgia.
Symptoms:
- Throbbing pain radiating to: temple, ear, jaw, back of the head, forearm.
- Sensitivity to temperature changes.
- Ear congestion.
- Pain at the root of the tongue.
- Impaired taste, salivation.
- Pain in the throat and soft palate.
- Swallowing reflex disorder.
- Painful tic.
- Severe shooting pain, reminiscent of an electric shock.
- Increased pain when: chewing food, washing, talking.
- Pain in the submandibular and sublingual area.
Damage to: glossopharyngeal nerve, submandibular and sublingual nodes, trigeminal nerve, ear node.
It is necessary to contact a neurologist. The doctor, after carrying out diagnostic measures, will determine the stage of the disease and prescribe outpatient treatment or hospitalization. Medications prescribed to treat affected nerves have significant side effects and are prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment may also include surgery.
Pathological proliferation of tissue cells. Divided into benign and malignant formations. Precancerous conditions represent a separate group.
Tumors of various etiologies can cause pain in the cheek.
Symptoms:
- Dense nodules, roughness of the skin.
- Plaques, ulcers.
- Pain.
- Inflammation.
- Bright color.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Warty, scarred, uneven surface of the lesions.
- Perforating ulcers.
- Local compactions of adipose tissue.
Causes:
- Atheroma.
- Lipoma.
- Dermatofibroma.
- Melanoma.
- Senile keratoma.
- Epithelioma.
The danger of being affected by skin tumors sometimes lies in the slow progression of the disease with minor sensations.
If there is any suspicion of deviations from the norm, consultation with an oncologist or dermatologist is necessary.
Treatment consists of removing the affected area. Modern surgical methods are used: laser, cryodestruction, radio wave removal. In case of inoperability of the malignant process and to prevent the spread of metastases, radiation and chemotherapy are used.
Prevention
- Clinical examination.
- Visit the dentist 2 times a year.
- Complete nutrition, rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Avoiding excessive sun exposure.
- Avoiding contact with chemicals and carcinogens.
- Removal of benign formations at the initial stage of their occurrence.
- No exposure to extreme temperatures: cold, heat.
Self-treatment with folk remedies can worsen the course of the disease.
A common recommendation for home help: if you have pain in your cheek, apply a cold compress, which can cause a serious condition if you have nerve damage. The method of applying purified lard to the gum to relieve pain can cause infection of the gum tissue and the inner surface of the cheek. Thermal procedures not prescribed by a doctor can provoke a purulent-inflammatory process.
It is important to be attentive to your health. Often the patient seeks help in the later stages of the disease. Making a diagnosis in the early stages improves the prognosis for recovery and increases the effectiveness of treatment measures.
Teething
If a child's cheek hurts on the inside, this may be a confirmation of teething. During this process, swelling of the gums appears, and maybe fever. Through the translucent gingival tissue, whitish dental units and bluish hematomas can be seen breaking through to the top, which appears during teething. Children become capricious, sleep poorly and refuse to eat.
Painful sensations appear when sharp fangs or molars with a wide chewing surface grow. Pain in the cheeks sometimes occurs in older children, especially during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars. This phenomenon occurs in almost all children. Parents need to monitor the child’s condition, and if unpleasant symptoms appear, seek help from a doctor.
Caries
A common disease characterized by gradual destruction of the integrity of tooth tissue and the subsequent formation of pronounced carious cavities. With caries, sometimes the cheek inside the mouth hurts if destructive processes occur near the tooth or in the tooth itself. Pain occurs when the deep layers of the tooth are affected, when the dental nerve is exposed.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease in which there is an inflammatory process in the supporting apparatus of the teeth. If your cheek hurts during periodontitis, this may mean that processes of destruction of the structure of the alveolar process of the jaw are occurring in the corner of the upper or lower dentition.
Periodontitis develops almost asymptomatically at first, but if pain already appears, then, most likely, there is significant damage. If pain in the cheek occurs, it is better to immediately consult a specialist and find out the cause of the syndrome.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease in which there is an inflammatory process in the supporting apparatus of the teeth. If your cheek hurts during periodontitis, this may mean that processes of destruction of the structure of the alveolar process of the jaw are occurring in the corner of the upper or lower dentition.
Treatment of stomatitis
The choice of treatment method for stomatitis depends on the cause and nature of its occurrence. That is:
- for allergic stomatitis, drugs are used that neutralize the effect of allergens;
- if the disease is viral or bacterial in nature, drugs are prescribed that suppress the activity of the corresponding microorganisms.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Orthodontic toothbrushes for cleaning braces
To get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of stomatitis, when the cheek inside the mouth hurts, local corticosteroid drugs (mouth rinses), antibiotics (usually in the form of rinses), as well as anesthetic drugs that help relieve pain in the mouth and mouth are used. on the cheeks.
Swelling of the cheek
Most often, pain in the cheek is associated with teeth, but situations are also possible when the cheek is swollen, but the tooth does not hurt. The cause may be an ear disease or inflammation of the parotid gland, so you may need to consult with several specialists to determine the true cause of the swollen cheek.
It should be remembered that swelling of the cheek, even if there is no pain, is a reason to consult a doctor. Inflammatory processes in the body can develop very slowly, but when the disease is advanced, it is much more difficult to cope with its consequences.
Possible causes of the problem
Many people do not pay much attention when their left or right cheek is slightly swollen, but there is no pain. Hoping that everything will soon go away on its own without outside help, they delay going to the doctor and thereby greatly aggravate the situation. Unfortunately, in such cases, very often patients themselves initiate the pathological process and seek help only at a late stage of the disease, which requires complex and lengthy treatment.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with White dots in the throat on the tonsils: what does it mean?
Pre-medical measures
If your cheek hurts, before visiting the dentist you can take some measures to alleviate the condition:
- Apply ice, a cold compress, or a bandage to the affected area;
- Take an analgesic;
- Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day with a warm solution of antiseptic drugs, a salt solution or a decoction of herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Under no circumstances should you apply warm compresses to the painful area, as this may trigger the onset of a purulent process. You should also not take antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
To prevent cheek pain, you should practice good oral hygiene. During the cold season, it is important to keep your face warm, as hypothermia can cause sinusitis and other inflammatory diseases of the ear, nose and throat.
As already mentioned, swelling of the cheek tissue can be a sign of any, including serious, disease. Therefore, in order to avoid dangerous consequences, it is advisable to immediately contact the clinic. If it is not possible to do this immediately, you can try to help yourself to alleviate the condition before visiting a doctor.
First aid measures include:
- application with Kalanchoe juice - freshly squeezed juice can be mixed half and half with boiled water or used undiluted. A cotton ball is moistened in it, then placed behind the cheek, on the side of the swelling - this will help get rid of swelling caused by the inflammatory process;
- rinsing with a solution of salt and soda - both components have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. You need to mix them in equal proportions (0.5 teaspoon each), add to a liter of boiled water and rinse your mouth at least 3-4 times a day. To achieve an antibacterial effect, you can add a couple of drops of iodine to the solution;
- lotions with aloe juice - to make a compress, you can squeeze the juice from the leaf of a three-year-old aloe flower, wet it with a piece of cotton wool or bandage and apply it to the inside of the cheek, or simply place the leaf itself behind the swollen cheek;
- baths with a collection of anti-inflammatory herbs - you can prepare a collection of calendula, chamomile, sage and coltsfoot, take dry raw materials in equal proportions and pour boiling water. After insisting, take the decoction into your mouth and keep it there for 3-5 minutes, while you can rinse with Chlorhexidine;
- rinsing with propolis tincture - you can buy it at the pharmacy, moisten a cotton ball with it and apply it to the swollen cheek, you can also take a piece of dry propolis and dissolve it in the mouth for a long time, until completely dissolved.
You should not get carried away with self-medication, since the swelling of the tissue may decrease and the pain may go away - but this does not mean that a complete recovery has occurred, and there is no longer a need for a visit to the doctor. Problems with swollen gums and cheeks need to be addressed immediately, depending on the cause of their occurrence.
If you don’t want to make a mouthwash yourself, you can buy it at the pharmacy
If you have not been able to get rid of the tumor and pain on your own, you do not need to take painkillers and antibacterial drugs before visiting a doctor - this can blur the full clinical picture and lead to an incorrect diagnosis.
Treatment of inflammatory diseases that provoked the problem will be carried out using antibiotics, an allergic reaction requires taking antihistamines, and to relieve pain and eliminate fever, taking NSAIDs is indicated. No matter how insignificant ailment a swollen cheek (even a small one) may seem, it can be a symptom of serious illnesses, and therefore requires a serious approach from the patient.
Many people believe that teeth are the only cause of cheek inflammation. But there are many reasons for the occurrence of this disease; below we will consider them all in detail.
Causes of the inflammatory process
Inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth is most often accompanied by pain and discomfort, so it can be quickly noticed and treated. Before prescribing a course of treatment, the dentist finds out the cause of the pathology in order to eliminate not only its symptoms, but also the source of infection.
To find out why your wisdom tooth hurts and your gums are swollen, you will have to take an x-ray. Only after collecting a medical history and x-raying the painful area does the dentist begin excision of gum tissue, tooth extraction or drug treatment.
In some serious diseases, for example, a cancerous tumor in the jaw, AIDS, removing a tooth without careful preliminary preparation for the operation is dangerous for a person’s life.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Symptoms and treatment of facial neuritis: causes, medications and physiotherapy