The lymphatic system is called the white river of life because it is the regulatory system of the entire body. Recent research from the Institute of Clinical Lymphology in Novosibirsk has confirmed that 83% of toxins are located in the intercellular space. If the inflow and outflow of intercellular fluid is disrupted, a pathological process occurs - inflammation of the lymph nodes, caused by stagnant metabolic processes in the cells.
The role of lymph nodes in the human body
According to research from the Institute of Lymphology, the main functions of the lymphatic system are the delivery of hormones and nutrients to cells and detoxification of intercellular fluid : the components of the lymph nodes neutralize harmful toxins. That's why doctors advise drinking more water and recommend physical activity.
The lymphatic system is designed to keep toxic substances out of the blood and protect cells. Lymph is a type of connective tissue, permeated with capillaries, vessels and is a liquid. It moves to the lymph nodes, removing contaminants from the human body through the mucous membranes. The lymph nodes themselves contain phagocytes that destroy foreign agents.
The most extensive clusters of lymph nodes on the human body are located:
- Under the knees.
- In the groin.
- In the abdominal cavity.
- Armpits.
- In the neck area.
- In the nasopharynx area.
- Near the larynx, trachea and bronchi.
Why are lymph nodes needed?
An integral part of the vascular system of our body is the lymphatic system. It consists of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and the fluid flowing through them - lymph.
Lymph is formed in all organs and tissues by transferring part of the interstitial fluid and blood plasma, as well as proteins, into the lymphatic capillaries. The latter form large vessels that collect lymph from different parts of the body and return it to the systemic circulation.
Along the lymphatic vessels there are lymph nodes, which are accumulations of lymphoid tissue covered with a capsule. Protective blood cells - lymphocytes - are formed in these nodes. Their task is to recognize foreign organisms and direct other protective cells to eliminate them.
Thus, lymph enters the lymph node through the vessel and, passing through its sinuses, is cleared of foreign bodies and microorganisms. That is, the lymph node becomes, as it were, a barrier to the infection - it does not allow it to spread further throughout the body.
What does enlarged lymph nodes on the human body mean?
Enlarged lymph nodes under the knees are a clear sign of arthritis. An infectious disease occurs due to blockage of the lymphatic drainage by fungi and various viral infections that develop at the level of the lymph nodes. Their swelling indicates that inflammation has begun, which leads to swelling and redness of the skin in the knee area.
When the nodes in the groin area become painful, we can talk about inflammation, which is caused by chlamydia infection, herpes virus, Candida fungus or gonorrhea. The lymphatic system is cleansed through the mucous membranes of the body, so the main symptom of this type of infection is an unpleasant-smelling discharge. To combat the disease, antibiotics, antifungals, and ointments are used.
The largest concentration of lymphoid glands in the human body is located in the abdominal cavity. The intestines are lined with small villi, which both absorb useful substances and remove unnecessary substances through the lymph. Usually, by analyzing stool, the doctor determines the condition of the intestines: if there is a lot of mucus in it, the organ is inflamed.
The axillary lymph nodes also often become inflamed. If you know how their operating principle works, you won’t want to use deodorants that block the lymphatic ducts. Physiological sweating, thought out by nature itself, is blocked by deodorants for a day or two, and all toxic substances remain inside the person. This often explains the frequent occurrence of malignant tumors in the area of the female mammary glands.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of submandibular lymphadenitis. Preventive measures consist of preventing the development of causes that cause inflammation of the lymph nodes.
During periods of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, it is recommended to refrain from visiting crowded places. Regular visits to the dentist will eliminate the threat of developing lymphadenitis of the cervical lymph nodes associated with caries.
If we consider autoimmune diseases that contribute to the development of submandibular lymphadenitis, then there is no prevention.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
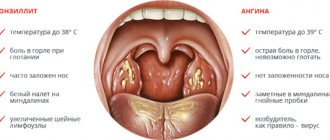
Enlarged cervical lymph nodes may indicate a cold or viruses entering the respiratory tract. Due to inflammatory processes such as sinusitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis, cervical lymphadenitis can develop - inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck. Signs of the disease are headache, weakness, difficulty swallowing, limited turning and tilting of the head. The patient's condition is aggravated by high temperature - up to 40 °C.
The cause of inflammation of the glands in the neck can be an acute respiratory staphylococcal or streptococcal infection, or infectious dental diseases. Lymph nodes can become inflamed due to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a reaction of the lymphatic system to the onset of cancer.
To determine the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes and cure the underlying disease, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination in the clinic and adhere to all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Diagnostics
Inflammation of the lymph nodes under the chin is detected quite easily - you just need to palpate and examine them. But identifying the cause of this phenomenon is carried out using a number of laboratory and hardware studies:
- General blood and urine analysis. In case of infection, the formula will be disrupted: bacterial disease - leukocytes; viral pathology - lymphocytes and monocytes.
- Blood chemistry.
- Bacterial culture of urine (if necessary).
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes.
- MRI or CT if an oncological process is suspected, as well as a puncture biopsy for cytological examination and determination of cellular composition.
If the doctor is sure that the inflammatory process of the mental lymph nodes is provoked by a cold-like disease in which there are clear symptoms (sore throat, runny nose, cough), a general blood and urine test is sufficient.
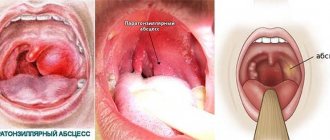
Damage to lymph nodes in the area of ENT organs
In the area of the larynx there is a ring of lymphoid tissue that protects the body from the penetration of viruses through the nose and mouth. When tonsils are removed, infectious agents do not stay in the oral cavity and penetrate deeper, leading to the development of diseases such as laryngitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
In the area of the larynx, trachea, and bronchus, lymphoid tissue grows more slowly than in the abdominal cavity. This is due to the fact that inflammation of the lymph nodes located near the ENT organs occurs due to their infection through the respiratory tract, and the immune system tries to protect the body from respiratory infections to the maximum.
Lymphadenitis in children
The lymphatic system in children under 10 years of age is not yet mature enough. Therefore, it cannot fully perform its function. Children also have a poorly developed immune system. The result is an increased susceptibility of the child’s body to infectious agents, insufficiency of the barrier-filtration function, and involvement of the lymph nodes in all pathological processes that occur in the body. All this together leads to the fact that lymphadenitis is one of the most common diseases in childhood.
Most often, childhood lymphadenitis has a nonspecific etiology and is provoked by the pathological effects of pyogenic microorganisms - streptococci or staphylococci. In this case, this is a secondary pathology that occurs against the background of a primary focus of acute or chronic purulent inflammation. But there are also cases of specific lymphadenitis - after the child has been given the vaccine against tuberculosis (BCG). Or due to tuberculosis, mononucleosis.
The main reasons for the development of lymphadenitis in children:
- Inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system, in particular the ENT organs.
- Lesions, infections of the skin, mucous membranes.
- Bacterial or viral infections (scarlet fever, diphtheria, chickenpox, measles).
- Inflammatory pathologies of tissues of the oral cavity and dentofacial system.
In this video, Dr. Komarovsky reveals in detail the topic of lymphadenitis in children. Describes normal and enlarged lymph nodes. And also about the causes and treatment of pathology.
Lymphadenitis in children has a more violent course than in older patients. And it is more difficult to tolerate and has a greater chance of causing dangerous complications. Therapy involves the prescription of antibiotics, antiallergic, and restorative drugs. And products for topical use.
If a child’s lymphadenitis has progressed to a purulent stage or if conservative treatment is ineffective, urgent hospitalization is required. The necessary surgical intervention will be performed followed by anti-inflammatory and detoxification treatment
How to treat swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes become inflamed for various reasons, so treatment should not be aimed at eliminating symptoms, but at stopping the disease that triggered its occurrence. To diagnose the underlying disease, you need to go to a medical facility.
Drug therapy
For inflammation of the lymph nodes, doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nise gels are used. Under the influence of such medications, the area of redness decreases, swelling decreases, inflammation subsides, pain stops, and body temperature normalizes.
Inflamed lymph nodes are treated with Vishnevsky ointment (balsamic liniment), ichthyol cream. Thanks to such remedies, the glands become less dense and pain is relieved. Positive dynamics are observed during treatment with hormonal drugs: Prednisolone, Dexamethasone in tablets and injections. Antiviral agents in the form of ointments and tablets (Cycloferon, Arbidol, Kagocel) and immunostimulants are often prescribed.
Surgical intervention
When a lymph node is inflamed, under no circumstances should you heat the painful area, apply compresses, or undergo physiotherapy - such activities are fraught with aggravation of the nature of the inflammatory process and a deterioration in the general condition. If purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes begins, urgent surgical intervention is required.
Depending on the patient's condition, the operation can be performed under local or general anesthesia. After opening, the lymphoid glands are drained, removing tissue that has undergone necrosis. Drainage from tampons soaked in antiseptics is placed in the wound. The patient is given dressings within a week. The cleaned wound heals by secondary intention (without stitches).
The removed tissues are sent for histological examination. If the test result is positive, the patient is observed by oncologists. It should be borne in mind that inflammation of the lymph nodes can develop due to cancer of the lungs, kidneys, and stomach.
Folk remedies
For inflamed lymph nodes, traditional methods of treatment can be used, but only in tandem with conservative drug or surgical therapy. Mild forms of the disease can be cured using the following folk remedies:
- Licorice root is a remedy that stimulates the removal of mucus from the respiratory organs. Indicated for inflammation of the bronchi, lungs and colds. Licorice root accelerates the removal of fluid from the intercellular space; this fluid is sputum, which is excreted through the bronchi, which contributes to their speedy cleansing of infection and recovery. Usually the medicine is prescribed to children and people with low blood pressure.
- Red clover. It is characterized by the same properties, but is recommended for normal and high blood pressure.
- Rosehip, oats, yarrow.
- Leaves of a young blackcurrant bush, raspberry leaves.
A mild form of inflammation of the lymph nodes can be cured with the help of anti-inflammatory mixtures from several herbs: birch buds, oregano, St. John's wort, echinacea. Pour 200 ml of boiling water into a spoonful of the mixture and let it brew. This decoction is drunk within one day.
To prevent serious disturbances in the functioning of the lymphatic system, preventive procedures should be carried out, and possibly completely change your lifestyle. It is necessary to stop drinking alcohol, smoking, do exercises daily, strengthen the body, eat moderately, treat infectious diseases in a timely manner and drink more fluids.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis
If a patient has chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis, he will have the following symptoms:
- There are no special complaints, pain is insignificant or absent.
- Body temperature is normal, but can be elevated to subfebrile (37-38 degrees).
- Slight swelling of the affected lymph nodes is diagnosed.
Acute lymphadenitis is characterized by severe pain, a significant increase in the size of lymph nodes, and redness of the skin at the site of the lesion. As well as a general clinical picture of malaise - high fever, weakness, lethargy, lack of appetite, irritability, insomnia.
Purulent lymphadenitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The nature of the pain is sharp, twitching, pulsating.
- The skin over the lymph node has an intense red tint and severe swelling.
- The patient exhibits signs of intoxication - febrile body temperature (above 38 degrees), lethargy, drowsiness, lack of appetite and sleep. The skin outside the area of inflammation may acquire a pale or bluish tint and be sticky to the touch. A decrease in total body weight may begin.
If the inflammation is serous, the patient experiences dull pain. Lymph nodes enlarge and become denser. However, the skin over the lymph nodes does not change, and general signs of the presence of an inflammatory process are blurred or absent.
With cervical or submandibular lymphadenitis, specific symptoms such as difficulties with breathing, swallowing, and speech may occur
Lymphadenitis is a rather dangerous disease, especially its purulent form. It can cause serious complications, including death. Therefore, warning signs cannot be ignored. You need to urgently consult a doctor and start treatment.
How is an ultrasound done?
The procedure is carried out in a separate room, equipped with a special apparatus, monitor, couch and blinds to prevent excess light from entering the room.
The patient removes clothing and jewelry to expose the desired part of the body for the examination. Next, the patient takes the correct position, for example, puts his hands behind his head or lies down on the couch, having previously laid out a disposable or reusable diaper. The doctor will suggest this position. A special transparent, odorless gel is applied to the skin and the device, improving the glide and penetration of rays under the skin.
The doctor may ask the patient to breathe differently to improve the visibility of the lymph nodes. Typically, a similar breathing principle is used to examine internal lymph nodes.
During the ultrasound process, the doctor takes photographs of the lymph node from different angles and writes a detailed description of what he saw. A medical report is issued to the patient.
The duration of the ultrasound is ten to fifteen minutes. If a full examination of the lymphatic system is ordered, the procedure will likely take several hours. It is important to note that no pain is present during the ultrasound.