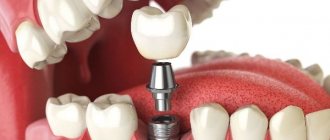
What does it mean when they say that the hood on a wisdom tooth is inflamed? Let's figure it out.
Wisdom teeth are popularly called chewing teeth (large molars) located on the edge. They usually appear at the age of 16-36 years. A person may have four wisdom teeth in total, but dental practice is faced with situations where only 1 or 2 outer molars erupt. At the same time, the rest continue to grow under the gum, being under a strong slope or in a supine position. In some cases, the rudiments of eights are completely absent in patients. When wisdom teeth do not emerge before age 35, a person should undergo an X-ray examination to rule out possible abnormalities.
Eruption is always a painful process, which is accompanied by inflammation of the hood of the wisdom tooth. This is due to the complex interweaving of the root system. With severe inflammation, accompanied by the accumulation of exudative fluid, hyperemia, abscesses extending into the deep layers of soft tissue, the patient is diagnosed with pericoronitis. This pathological condition is typical for the process of eruption of figure eights, but this does not mean that therapy for such a condition is not required. An advanced form of pericoronitis can develop into inflammation of the deep layers of the mucosa, which has a destructive form.
Possible causes of pericoronitis development
Pericoronitis is a very painful process, so it is very important to determine the causes that cause severe inflammation during the eruption of the trailing teeth. When an x-ray shows an anatomically incorrect position of a tooth or the presence of intertwined roots, the doctor refers the patient to a consultation with a dental surgeon, who will determine the need for gum excision and subsequent extraction of the tooth before it begins to erupt.
The appearance of extreme molars may be accompanied by the development of complications associated with other reasons. Knowledge of the factors contributing to the occurrence of inflammation of the wisdom tooth hood will allow for timely prevention of this pathology.
Brief description of the problem
This can happen between the ages of eighteen and twenty-five, which is why the tooth is called wise. In the dental world he is known as the third painter. But why is the hood so common among all owners of third painters?
The fact is that by the time the tooth grows, the oral cavity has already fully formed and there is no room for new inhabitants. For us, lack of space in the mouth is not a reason to stop growing. The tooth will easily find another way for its appearance. It can grow into both the gum and the surrounding bone tissue, which can cause unbearable aching pain that will definitely force you to see a dentist.
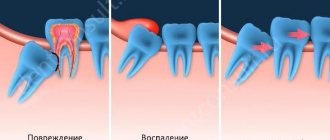
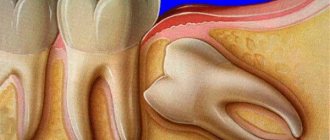
Scheme of hood formation
But, most often, the formation of a hood over the wisdom tooth occurs. This occurs if the tooth grows slightly in the wrong direction, without disturbing the hard tissue or integrity of its environment. When the sage cuts through one part of the gum and comes into the world, leaving part of the gum on his other half, this is your hood.
There are cases when nothing interferes with the further growth of the tooth and everything goes away on its own. However, in practice this happens quite rarely and this restraining part of the gum brings a lot of inconvenience. First of all, it swells, thereby inflaming the hood of the wisdom tooth.
Inflammation of the wisdom tooth hood is not a surprising occurrence. This occurs in every fifth person due to the fact that teething for many people results in a very difficult process. Most often, this occurs in the lower jaw, since it is there that the predisposition to abnormal growth takes a leading position.
Growth of wisdom teeth at different ages
The small portion of gum that accumulates on top of the crown of a growing tooth is called the wisdom tooth hood, and if the gum becomes inflamed, dentists diagnose it as pericoronitis.
Inflammation of the hood over the wisdom tooth occurs because an infection accumulates between the “sage” and the mucous membrane, which, as a result of the accumulation, leads to the inflammatory process. At first, the hood is not able to cause any discomfort in a person, but they appear after just a few days.
Inflammation of the hood due to infection
Thickening gums
In about a tenth of all patients, the tissues located at the site of wisdom tooth growth have thickened walls, which prevents tooth eruption. In this case, a person experiences severe pain, often accompanied by a rise in temperature, headache, and deterioration in general well-being. Some patients with thickened gum walls experience decreased hearing and pain in the ears and eye sockets. If tooth eruption does not occur for a long time, the lymph nodes located under the jaw begin to become inflamed.
For what other reasons does the hood on a wisdom tooth become inflamed?
Removing the hood
This is a fairly simple operation, which, with the current level of medicine, will not cause concern even in a child. The bottom line is that with local anesthesia, which is quite sufficient, excision (removal) of the mucous membrane covering the erupting tooth is performed. Thus, the place where microbes multiplied completely disappears. The procedure is low-traumatic, so children, adults, and teenagers who find themselves in similar conditions will no longer worry that something might become inflamed again.
Read also: If the gums near the tooth are swollen, what to do?
It is also worth talking about the stages of removing this dental problem. Never spare yourself for treatment, especially when it comes to dentistry. Is the hood over your wisdom tooth inflamed? Without hesitation, agree to all the recommendations of your doctor, because you already know all the possible consequences. How the operation will take place:
- you will be numbed with local anesthesia;
- after the pain has subsided, the dental surgeon will excise the swollen formation that binds the tooth - he will do this with a scalpel and surgical scissors;
- after excision, the wound must be washed with disinfectants and stop the bleeding;
- after neutralization, applies the necessary medications to the wound;
- At this point, the operation is completed and the person is scheduled for a second examination.
After this procedure, you will definitely be prescribed various medications, both healing and painkillers. Such as mouth rinses or, in some individual cases, antibiotics may be prescribed. After such treatment at home, this inflammatory process will be completely completed.
Complications of treatment
However, there are situations when the hood was removed from a wisdom tooth, but this did not lead to any result.
These are exceptions in which it is necessary to significantly change treatment tactics. In such cases, a decision is made to completely remove the problematic “sage” and forever get rid of even the slightest possibility of a return.
Is the hood inflamed for the second time? The tooth itself will have to be removed.
If the operation does not bring any results, then it must be repeated free of charge. But again, this happens very rarely, because an experienced dentist can determine in advance the likelihood of the problem returning. If this happens, the decision will be made to remove the tooth during the first operation. It is better to experience these unpleasant sensations once than to tell your friends again and again in the future that you have had the hood removed from your wisdom tooth again.
Thick plaque of bacterial origin on the gums
If hygiene standards and oral care are neglected, the likelihood of a patient developing pericoronitis increases several times. When a tooth erupts, the gums lift and then rupture. Microbes and bacteria located on it are able to penetrate damaged areas and provoke severe inflammation.
A photo of a wisdom tooth hood is presented.
This form of pericoronitis is characterized by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- The gums in the area where the wisdom tooth is erupting become very swollen and swollen.
- Any load on the affected area causes high-intensity pain. Moreover, the pain affects not only the molar area, but also the entire jaw.
- The temperature rises to 38.5 degrees Celsius.
In the absence of timely therapeutic measures, the pathological process can transform into a purulent-infectious one, which is dangerous because blood infection can occur.
hood on a child's tooth
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the gum hood.
Will your wisdom teeth not come through? Does it hurt to swallow? Are your gums swollen? See a doctor immediately! You may have pericoronitis!
Everyone knows that when young children cut their baby teeth, it can be quite painful. But cutting through molars can also cause discomfort. Moreover, teething can lead to inflammation in the gums. In dentistry, such inflammation of the gums is called pericoronitis.
Pericoronitis, when the gums become inflamed
As a tooth grows, it must emerge from the soft tissue of the gums, in other words, cut through them. As a rule, this is a painful process, but most often the discomfort goes away very quickly. But sometimes tooth eruption can occur not just with discomfort, but also with complications. This complication is inflammation of the gum tissue surrounding the erupting tooth, which is called pericoronitis.
Most often, the danger of gum inflammation occurs when wisdom teeth erupt. Pericoronitis occurs especially often during the eruption of wisdom teeth located on the lower jaw.
Causes of pericoronitis
The direct cause of the development of the inflammatory process of the gums is the normal microflora of the oral cavity. As the tooth grows, part of it remains covered by the mucous membrane of the gum, which in this case is called the hood. A kind of pocket appears between the hood and the tooth. Food particles get there, thus creating favorable conditions for the development of bacteria. Then the bacteria that usually live in the mouth without causing us any discomfort begin to multiply too much and cause inflammation of the gums.
Symptoms of pericoronitis
If your wisdom tooth is growing, your gums are swollen, there is an unpleasant odor from the tooth, and there is pain, you probably have a mild form of pericoronitis. But pericoronitis can also be quite acute. As inflammation increases, symptoms worsen.
Symptoms of pericoronitis include:
- pain in the area of the erupting tooth
- pain when swallowing and when trying to open your mouth
- pain radiating to the ear, temple, jaw
- bad breath
- swelling of the gums
- the appearance of purulent fluid when pressing on the gum hood.
With pericoronitis, you may also feel a general malaise, the temperature may rise, and the lymph nodes on the neck in the areas adjacent to the jaw may become enlarged.
If these symptoms are ignored, the consequences can be very serious. Without medical intervention, pericoronitis can cause the development of periosteal abscess, phlegmon and even osteomelitis. Therefore, if symptoms characteristic of pericoronitis appear, be sure to consult a doctor.
Treatment of pericoronitis
The nature of the treatment depends on the patient’s condition and how the inflammatory process proceeds.
Often, to eliminate inflammation, the gum hood is removed and the pocket is treated with special medications. This is a simple procedure in which the gum mucosa that hangs over the tooth is excised. Thus, the place for excessive proliferation of microflora is removed and the problem is solved. The procedure is carried out after an anesthetic injection into the gum. After removing the gum hood, antiseptic baths are usually prescribed. In some cases, the doctor also recommends antibiotics.
Pericoronitis is also treated with laser therapy. In this case, the inflamed gum is exposed to an infrared ray. Laser therapy is not allowed to be used in the presence of cancer.
One of the treatment options for pericoronitis is the removal of the erupting tooth. This option is relevant for wisdom teeth.
- If it turns out that the length of the jaw is too short and there is no room for normal tooth growth. An x-ray will help identify this problem.
- When a tooth grows incorrectly, for example, towards the cheek. Then it will not take part in the chewing process, which means it does not bear a functional load.
- If there is no longer a tooth opposite, on the other jaw. In this case, the tooth will also not take part in chewing.
- If gum hood removal is inconvenient due to the structure of your oral cavity.
The fate of the erupting tooth must be decided by the doctor. He has enough knowledge to make the right decision in your situation.
Monitor the condition of your oral cavity. Avoid dental disease and gum inflammation. And timely implementation of oral hygiene procedures will help you with this.
Oral diseases.
09/13/2018 admin Comments No comments
Everyone knows that the eruption of baby teeth in children is often quite painful.
However, the eruption of molars can also cause pain. Moreover, this process may be accompanied by gum inflammation. In dentistry, this phenomenon is called pericoronitis. Growing teeth must emerge from the soft tissue of the gums, that is, cut through them. Often this gives a person painful sensations that pass quickly enough. But in some cases, when teething, not only discomfort or pain is observed, but also complications. One of them is the disease pericoronitis or inflammation of the gum hood, that is, the tissues where the teeth erupt.
As a rule, the disease pericoronitis develops during the eruption of wisdom teeth, located on the lower jaw.
The immediate cause of the inflammatory process of the gums is the normal microflora in the human oral cavity. The growing tooth is covered by a mucous membrane of the gum, which is called the hood. Between the tooth and this hood, a kind of pocket appears where food particles fall. As a result, favorable conditions arise for the growth of bacteria, which causes inflammation of the gum hood.
If the eruption of a wisdom tooth is accompanied by gum swelling, bad breath, and pain, then the diagnosis of mild pericoronitis is most likely. However, this disease can also occur in an acute form, in which inflammation of the gum hood is accompanied by:
• pain in the area of the erupting tooth;
• pain when trying to open the mouth and when swallowing;
• pain that radiates to the jaw, temple, ear;
• bad breath;
• discharge of pus from the gum hood when pressed.
In addition, pericoronitis is characterized by symptoms such as fever, general malaise, and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
In the absence of timely and competent medical care, acute inflammation of the gum hood threatens with very serious consequences: the development of a periosteal abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis. Therefore, the appearance of symptoms characteristic of pericoronitis requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
Treatment tactics depend on the course of the inflammatory process and the patient’s condition. Often, in order to eliminate inflammation, it is necessary to remove the gum hood and treat the pocket with special preparations. The procedure involves excision of the mucous membrane of the gum overhanging the tooth. Thus, the solution to the problem is to eliminate the conditions for excessive bacterial growth. Excision of the gum mucosa is carried out under local anesthesia.
After the gum hood is removed, it is necessary to take antiseptic baths, and sometimes antibiotics are required.
Laser therapy is also used to treat pericoronitis. It involves exposing the inflamed area to an infrared ray. However, this treatment method cannot be used for cancer.
In addition, with pericoronitis, an erupting tooth is often removed. This treatment option is used for the eruption of wisdom teeth. Their removal is recommended in cases where:
• the length of the jaw is too short for the normal growth of a wisdom tooth (this problem is diagnosed using an x-ray);
• incorrect tooth growth is observed (for example, towards the cheek), which will lead to the fact that the tooth will not bear a functional load, that is, it will not participate in the chewing process;
• there is already a missing wisdom tooth on the other jaw (the wisdom tooth will also not participate in the chewing process);
• removing the gum hood is inconvenient due to the structure of the oral cavity.
The fate of an erupting wisdom tooth is always decided by a doctor with sufficient experience and knowledge. The patient’s task is to monitor oral hygiene, prevent dental diseases and gum inflammation, and promptly contact a specialist if problems arise and for preventive examinations.
Tags: Pericoronitis disease or inflammation of the gum hood
Suppuration of the gums during teething in children.
Teething is a physiological process inherent in nature itself. That is why it should normally be painless and not disturb either the baby or the parents. However, due to incorrect actions of doctors, parents, and some external factors, various types of complications may arise during teething in children. One of these complications is inflammation and suppuration of the gums. Let's talk in more detail about inflammation and suppuration of the gums during teething.
What happens during teething?
Milk or permanent teeth in children erupt slowly, moving gradually to the surface of the alveolar process from the thickness of the bone. While the tooth is growing inside the bone, the baby will not feel anything, since the bone itself does not have nerve endings. But when the tooth approaches the gum, that’s when problems can begin.
Initially, small tubercles appear in place of future teeth - the top of the tooth, which is covered with a gingival hood. As teeth erupt, such tubercles will increase, and then the teeth themselves will appear.
Gingival tubercles protruding above the alveolar process are very easy to injure, and injuries of various origins are considered the main cause of the development of inflammation, and sometimes suppuration of the gums.
With the appearance of the anterior tubercles, the eruption of primary molars begins, and a little later the posterior tubercles appear. In this case, it is possible to preserve the gingival bridge on the chewing surface of the tooth.
Plaque gradually accumulates around such a bridge; food remains are also retained, and they become the cause of the formation of an inflammatory process. It also covers the gums on unerupted tubercles. The gums easily rise and bacteria can also penetrate under it, thereby provoking an inflammatory process and subsequent suppuration of the gums.
Also, babies at the age of six months grab and put into their mouths everything that comes to hand. These objects can injure the gums and cause infection.
Inflammation and suppuration during teething in children are accompanied by standard symptoms for such a case.
The gums become bright red, and this is easy to see against the background of healthy gums that cover the alveolar process. Redness is accompanied by slight swelling and pain. With proper care of the diseased gum, until the suppuration becomes pronounced, until the child has a high fever, these symptoms quickly disappear.
BELOW ARE THE BEST SPECIALISTS IN YOUR REGION
Treatment of suppuration during gum eruption in children
At a high temperature, with an obvious abscess on the gum, the help of a specialist is needed - you should immediately consult a dentist.
With minor inflammation and suppuration of the gums, the symptoms of this disease can be relieved in several simple ways.
Let your baby suck on a cooled (sterile) teether. This will help relieve pain and reduce pressure on the gums; it is best to use solid rings that do not have filler inside - they are more durable and can be easily sterilized. Massage your child's gums with a cold spoon or your finger - this will also briefly reduce the pain.
In addition, the child himself can massage his gums using a hard cracker or bread crust. You can reduce gum swelling with chilled vegetables and fruits. Well, don’t forget about the pacifier. She will massage your gums and help your teeth erupt.
If parents are afraid to give the baby cold objects or vegetables, then you can give the child cold water from a bottle or sippy cup. Older children can be given chilled puree or cool natural yogurt.
Giving babies hard pieces of bread or fruit that already have teeth should be done very carefully. As a rule, the first teeth are usually very sharp, so it will not be difficult for a child to break off a small piece of food, but the child may choke on such a piece.
It is recommended to treat the gums, instead of rinsing, with tampons soaked in medicinal decoctions (from chamomile, sage, calendula or oak bark). This helps destroy germs.
These are the most modern methods of relieving gum inflammation during teething. Traditional medicine also recommends lubricating the baby’s gums with honey during suppuration. However, this should be done very carefully, because some children develop allergies to honey.
You can rub valerian tincture directly into the gums - this will relieve swelling and pain and calm your child. In addition, valerian has a pleasant taste, which will not cause any inconvenience to your baby.
Types of pericoronitis and symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation of the wisdom tooth hood depend on its shape. Acute pericoronitis is characterized by severe pain and high intensity of the main symptoms, so diagnosing the acute course of the disease usually does not cause difficulties. Typical symptoms of acute pericoronitis are:
- The appearance of a sharp and unpleasant odor from the mouth, which intensifies after eating. However, the use of hygiene products does not eliminate it.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membranes develops, and the temperature in the eruption area rises locally.
- An acute form of pain occurs, which interferes with eating, talking, and opening the mouth.
- Pain sensations radiate to the temple area, lower or upper jaw, and ear.
- The cervical or submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed.
- Body temperature rises.
If at this stage the patient does not seek help from a dentist and tries to cure the disease on his own, the process begins to take on a chronic form.
How long does it take for gums to heal after intervention?
Despite the fact that the actual excision of the gingival part that has grown over the tooth is a simple procedure, soft tissue is injured, which means that a certain period is required for the wounds to heal. How long the incision will hurt and heal depends on the quality of the procedure, the severity of the problem and the patient’s compliance with all recommendations.
Oral care plays an important role after the hood is cut. The more accurately you follow all the dentist’s instructions in the period after surgery, the faster all the unpleasant consequences of cutting your gums can disappear. Typically, the rehabilitation process takes several days, after which you should visit your doctor again.
Chronic pericoronitis
Chronic pericoronitis develops, as a rule, if tooth eruption occurs over a long period of time, as well as in cases where the patient self-medicates the acute form of pericoronitis, relieving pain with analgesics and avoiding a visit to the dentist.
When the hood of a wisdom tooth becomes inflamed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Unlike acute pericoronitis, chronic pericoronitis is not accompanied by intense pain - the patient can open his mouth almost painlessly, but when eating food the pain intensifies significantly. Lymph nodes with pericoronaritis in chronic form increase slightly, palpation does not cause pain. The exception is cases when the pathology develops into osteomyelitis of the jaw or periostitis.
Where does the hood come from?
As you know, a person’s first wisdom tooth appears between the ages of 18 and 25. Scientifically it is called the “third molar.”
Usually the problem arises due to the fact that at the time of the appearance of a molar, a person’s dentition is fully formed, and for this reason there is simply no room left for it on the jaw. It is this circumstance that provokes a number of complications that arise during its growth.
In particularly difficult situations, the wisdom tooth becomes impacted - in other words, it rests on soft tissue or bone and begins to destroy them. This circumstance, however, does not cause the molar to stop, and it grows either directly into the gum or into the jaw. All this provokes severe pain in the patient. Fortunately, such pathologies are relatively rare, unlike the hood.
Read also: Wisdom tooth removed, cheek swollen, what to do
The latter appears due to the fact that the tooth grows unevenly. As a result, at first only half a tooth appears from under the gums - the second part remains under the soft tissues.
If subsequently there are no other obstacles, then, most likely, the tooth will grow normally, and the person will not even suspect that he had a hood. However, most likely, the presence of unruptured soft tissue over the molar will cause an inflammatory process.
Symptoms
The chronic process is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Pus is released from under the gingival hood.
- The load on adjacent teeth increases, resulting in increased mobility and instability.
- Abscesses and abscesses appear at the site of tooth eruption.
In the absence of adequate therapy, chronic pericoronitis contributes to the development of phlegmon - purulent inflammation in an acute form that has no definite boundaries.
In addition, the inflammatory process is classified according to the form of its occurrence:
- Pericoronaritis catarrhal. It is the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process; the symptoms of this form of pathology are mild.
- Pericoronitis is purulent. It is the most dangerous form of pathology. Inflammation in this form of pericoronitis is accompanied by suppuration of the affected tissues.
- Ulcerative pericoronitis. A distinctive feature of this form is the presence of an ulcerative-necrotic process in the affected gum.
- Pericoronitis is retromolar. With this form of pathology, the purulent focus is hidden, as a result of which the normal outflow of exudate is disrupted. Because of this, pus begins to accumulate in the soft tissues, the inflammatory process penetrates deeper and deeper, affecting the periosteum and provoking the formation of an abscess.
When the hood over the wisdom tooth is inflamed, treatment should be comprehensive.
Pericoronitis: treatment
If you have inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth, the treatment most often consists of a dental surgeon removing the hood over the wisdom tooth. However, if severe purulent inflammation is observed, then complete excision of the hood is undesirable immediately, because this can lead to various inflammatory complications.
In case of severe purulent inflammation, the hood is first only dissected to facilitate the outflow of purulent discharge, and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. And the doctor will prescribe you for its complete removal after the active inflammation has subsided. Also, in some cases, the doctor may recommend immediately removing the wisdom tooth (24stoma.ru).
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth –
Removing the hood of a wisdom tooth involves excision of the overhanging mucous membrane over the erupting eighth tooth. Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth leads to the elimination of conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. This minor surgical procedure is usually less traumatic, but in some cases a large amount of gum tissue must be excised.
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth is performed by a dental surgeon under local anesthesia. The procedure is completely painless if you see a good specialist, if the anesthesia is administered correctly and a good anesthetic is used, and not something like novocaine. Pain will appear only after anesthesia has passed (after 30 minutes), so it is worth taking an analgesic even before the pain appears.
- Hood removal: price for 2020 in an economy class clinic in Moscow, a similar service costs about 2,500 rubles. In the regions, the cost of the procedure may be 2 times lower. By the way, in the clinic at your place of residence (if you have an insurance policy and a passport), you should undergo this intervention completely free of charge.
Stages of excision of the hood –
- Conducting local anesthesia,
- Using a scalpel and surgical scissors (less commonly, a surgical laser), the dental surgeon excises the gum overhanging the tooth.
- Treating the wound with antiseptics.
- An iodoform turunda is usually placed in place of the excised hood.
- The doctor gives recommendations and schedules a re-examination.
Removing a wisdom tooth hood: video
Please note that both hood excision operations are performed with a surgical laser and not with a scalpel. Using a laser avoids bleeding, swelling and severe pain. In Russian dental clinics, lasers are practically not used (due to their absence), and only a few clinics can boast of their presence.
After the intervention, the following are prescribed:
- Antiseptic baths with chlorhexidine solution 0.05% (3-4 times a day);
- Antibiotics are not prescribed in every case;
- for pain - good tablet analgesics.
Usually this is enough for you to completely forget what wisdom tooth pericoronitis is after 4-5 days.
However, if the doctor performed the operation traumatically, the pain may last for 7-10 days. If you want to remove inflammation as quickly as possible, then after antiseptic rinses, you can additionally apply CholisalGel to the hood 2 times a day in the morning and evening (it has a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect). Remember that if you put gauze soaked in iodoform on the wound surface, you need to remove it yourself no later than the next day. Then it itself will become a breeding ground for infection. After you take out this turunda, it may cover a little. Then it is advisable to treat the wound with a gauze swab soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide.
Important: in some cases, the hood may form again, in which case either a repeat operation may be required, or the issue of tooth extraction will be decided. Often these teeth are in an incorrect position. An experienced doctor can quickly determine the chances of the eighth tooth taking the correct position using an x-ray and external examination of the tooth.
In what cases is it better to immediately remove a tooth with a hood -
If your gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed, the most radical treatment method will be the removal of the 8th tooth, above which the ill-fated hood appears.
This will solve the problem permanently, but you must be prepared for the fact that the eighth teeth may have curved roots (this can be checked by taking a photo) and then removal may be difficult. Situations where deletion is the best solution to the problem -
- Firstly , when the lower jaw is insufficiently long, which means there is not enough space for the eruption of a wisdom tooth. Removal in this case will prevent the remaining teeth from being displaced by the erupting tooth, and will prevent the development of crowding of teeth in the anterior part of the lower jaw.
- Secondly , if the 8th tooth has a strong inclination towards the cheek or the seventh tooth, then it will still have to be removed sooner or later, because it will injure either the buccal mucosa or the root of the 7th tooth, respectively.
For more information about the difficult eruption of wisdom teeth, read the article: → “Features of the growth and eruption of eighth teeth”
Treatment of pericoronitis
Dentists consider surgical intervention to be the only adequate way to treat pericoronitis in acute or chronic form. Only 2% of uncomplicated pathology can be treated by using anti-inflammatory ointments, gels and other agents. That is why experts do not recommend wasting time and effort trying to cure the pathology at home.
Taking into account the anatomical location of the tooth and the severity of the pathology, the doctor chooses one of two surgical treatment methods - extraction of the figure eight and its root system or excision of the gum hood over the wisdom tooth. The first technique is used only in extreme cases, since surgical intervention can provoke various complications, and the recovery period takes up to six months. In some cases, the operation to extract the figure eight from the bone alveolus is performed under general anesthesia in a maxillofacial surgical hospital, which significantly increases the load on the heart muscle and other important human organs.
Operation stages
A dental surgeon cuts off the hood over the wisdom tooth in a hospital setting, taking into account all indications for treatment, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient (age, presence of concomitant diseases and allergic reactions). Is hood removal painful? There are no painful sensations during treatment, since an anesthetic drug is injected under the mucous membrane. Removing the hood is divided into several stages, both preparatory and immediate:
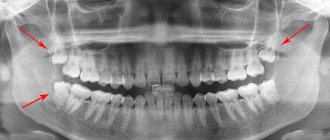
- Radiography.
Analysis of the x-ray will help determine the location of the wisdom tooth in the periodontal socket, identify caries and its complications, and also examine the area affected by infection.
- Anesthesia.
Before administering an anesthetic injection, the injection site is treated with an anesthetic (0.05% chlorhexidine solution, Miramistin). After disinfecting the mucous membrane, the dentist performs conduction anesthesia, which reduces the sensitivity of 2-3 adjacent teeth and soft tissues. After the anesthesia has taken effect, it is allowed to cut the gums.
- Gum incision.
The surgeon cuts the gum crosswise using a surgical scalpel or laser.
- Washing the wound and removing pus.
After opening, the incised wound is treated with distilled water, an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine, and also a weak solution of sodium chloride. The accumulated pus is removed with a curettage spoon, after which dental drainage is installed.
- Application of a therapeutic pad.
To protect the postoperative wound from infections, as well as accelerate the regeneration of soft tissues, a therapeutic pad soaked in iodine and other wound-healing components is applied.
After removing the hood, the dentist schedules a follow-up visit for dynamic monitoring of the wound surface. Your doctor will tell you how much it will hurt if you cut the gum above the wisdom tooth. Usually the gums grow together by 10 days after surgery. Prolonged non-healing of a postoperative wound, as well as the appearance of exudate, indicate the development of complications.
Indications for wisdom tooth extraction
Wisdom tooth extraction is carried out only when there are strict indications:
- The patient has a specific anatomical structure of the jaw (for example, the jaw arch is too narrow, and there is no space in the dentition for tooth eruption).
- Pathological disorders during the formation of tooth primordia in the embryonic period.
- Abnormal location of the figure eight, its roots, abnormal tooth growth.
- Lack of effect, recurrence of pathology after the hood on the wisdom tooth was cut off.
- Formation of a new gingival hood (quite rare, only in 5% of cases).
Both surgical methods for excision of the wisdom tooth hood require careful preparation and effective pain relief. Upon completion of the surgical intervention, the patient is prescribed a special regimen that involves minimizing the load on the area that was damaged. It is also recommended to use various medications aimed at preventing possible complications.
What else do you need to know
As was said, the operation itself to excise the hood is simple and quick. But the tricky thing is that wisdom teeth really take a very long time to cut. And sometimes excision has to be done again and again. And every time this means pain, inflammation, accumulation of pus.
In advanced cases, when peritonitis causes the formation of phlegmon, a much more complex operation will be required to remove pus from the soft tissues and long-term treatment in a hospital setting.
Therefore, if the hood has formed again, doctors strongly recommend not to suffer - removing the wisdom tooth will be the best solution if there are no direct contraindications to this procedure.
It is important to know:
Drug treatment after surgery
After surgical removal of a wisdom tooth or excision of a gingival hood, a patient must be prescribed drug therapy. One of its components is antibacterial drugs. Most often, antibiotic medications with a wide spectrum of action are used, which are active against most anaerobic and aerobic pathogens. The most effective drugs are:
- "Hemomycin." The patient is prescribed a single dose of one tablet per day, the course duration is about 5 days.
- "Amoxicillin." One tablet is recommended to be taken three times a day. Therapy takes up to 10 days.
- "Zinnat". One tablet is prescribed twice a day; therapy lasts up to 10 days.
- "Metronidazole". Take one tablet twice or three times for 10 days.
- "Tsiprolet". Take one tablet twice or three times a day for a week.
- "Ciprofloxacin." Use one tablet three times a day. Therapy usually takes 10 days.
Treatment methods for pericoronitis
Pericoronitis can be treated in several ways.
- Wisdom tooth removal. This is the most radical and most common way to quickly and permanently get rid of gum inflammation. Unfortunately, in most cases, wisdom teeth are cut incorrectly and do not represent any physiological value for their owner. On the contrary, with its roots, a wisdom tooth can injure the roots of other teeth, nerve fibers and capillaries, and with its upper crown - the oral mucosa. Therefore, if the x-ray shows that the tooth is problematic, especially if a hood has formed over it and pericoronitis develops, removal is carried out under local anesthesia. Further treatment is determined by the doctor depending on the situation.
- Excision of the hood on a wisdom tooth. The operation is quick but painful, so it is performed only under local anesthesia. First, the doctor makes one or two injections into the gums. Then, with a scalpel, the interfering part of the mucous membrane is excised. The pus is removed and the wound is washed with an antiseptic solution. To stop bleeding and disinfect the gums, the gums are covered with turundas and tampons with iodine or Vishnevsky ointment. If the incision is deep and larger, the dental surgeon may apply several stitches. The patient continues further treatment independently at home.
- Treatment with medications. Excision of the hood does not mean that pericoronitis has already been cured. It is imperative to properly care for the wound at home after surgery. First of all, you must take baths and rinses every day with a special antiseptic solution. Most often, the doctor recommends chlorhexidine or Givalex. If these drugs are not suitable for health reasons - for example, during pregnancy or individual intolerance to the active component - you can use a solution of soda and salt or sage decoction for rinsing. In case of suppuration and extensive abscess, antibiotics are prescribed - they must be taken in full course. Antimicrobial drugs suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, accelerate wound healing and prevent re-infection and inflammation.
Removing a wisdom tooth or just excision of the hood over it - after the operation it still becomes very painful when the anesthetic wears off. Therefore, you definitely need to stock up on a good painkiller. As the practice of doctors shows and is confirmed by reviews of experienced patients, ketans best relieve pain.
Inflammation of the wisdom tooth hood
The use of oral medications should be combined with the use of local agents. Quite often, dentists recommend rinsing and mouth baths using antiseptics such as Miramistin, Hexoral, and Chlorhexidine. Sometimes the use of anti-inflammatory gels containing soothing components, antibacterial substances and antiseptics is prescribed. Some of them contain lidocaine, which helps reduce the intensity of pain after removing the figure eight.
If the hood over the wisdom tooth is inflamed, taking into account the indications, the patient may be prescribed the following gel preparations with a local type of effect: Dentinox, Metrogyl Denta, Asepta, Kamistad, Cholisal.
It is important to consider that any medications after surgery can only be used on the recommendation of the dentist, and the combination of local drugs and oral medications is allowed only in some cases. With uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs, dysbiosis of the oral cavity may develop, which reduces the protective functions of the mucous membranes and increases the risk of complications.
Preparing for surgery
If the doctor has diagnosed pericoronitis over a wisdom tooth, he postpones surgery until the inflammation has completely disappeared. The patient is prescribed home treatment: rinses, baths, compresses using the above antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Additionally, “Dental drops” can be prescribed, which have analgesic, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and sedative effects. A cotton swab moistened with 3 drops of medicine should be applied to the damaged area 3-4 times a day for 5-10 minutes. In case of complications, the dentist prescribes antibiotics: Metronidazole, Tsiprolet, Tarivid, Amoxicillin. The dosage is selected by the doctor.
Removal of the hood over the wisdom tooth is performed under anesthesia. In most cases, local anesthesia is used, which you can read about in the article “Does it hurt to remove wisdom teeth?” When excision of the gum fold, the same methods and anesthetics are used as when pulling out the third molar.
At the request of the patient, the dentist can perform the operation by combining anesthesia with sedation - a “dream-like” state of calm achieved with a small dose of drugs that are usually used during general anesthesia. General anesthesia is also possible. In any case, it is first recommended to consult an allergist to identify a possible allergy to anesthetics.
Anesthesia can be combined with sedation
Treatment of pericoronitis with traditional methods
Pericoronitis is one of the few diseases of the oral cavity that cannot be cured by using traditional recipes. Alternative treatment for this disease has very low effectiveness; it is for this reason that dentists recommend immediately contacting a medical institution, without waiting for the development of a purulent form of pericoronitis.
Inflammation of the hood over a wisdom tooth is one of the most dangerous and serious pathologies in dental practice. If there is no treatment, pericoronitis can lead to serious consequences, among which the greatest danger is systemic blood poisoning. When the eruption of figure eights is accompanied by the appearance of primary signs of the inflammatory process, the patient should immediately contact the dental clinic. Prevention of the disease involves periodic visits to the dentist. This will make it possible to detect existing abnormalities at the earliest stages, predict the further course of the pathology, take measures to prevent the development of complications, and, if necessary, begin treatment immediately.
It is important to remember that only timely diagnosis and therapy will allow you to avoid undesirable consequences of inflammation of the wisdom tooth hood.
Pus is dangerous
An abscess, a purulent abscess, can form anywhere in a lymph node or around wisdom teeth. If it bursts, pus will leak into nearby tissues. This is fraught with the formation of oral, esophageal or bronchopulmonary fistulas - holes through which purulent fluid flows.
Cellulitis can develop - purulent-spread inflammation of the connective tissue, osteomyelitis - purulent-necrotic destruction of bone tissue. Or mediastinitis - inflammation in the middle parts of the chest cavity. Any of these diseases can lead to hospitalization and even death.
The dentist will help you avoid complications. It is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as a gum fold has formed above the wisdom tooth, without waiting for it to become inflamed. If it is not possible to urgently visit the dentist, you can begin self-treatment. This will help prevent or stop the development of pericoronitis.