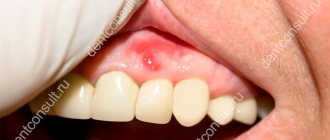
Content
- Salivary gland cyst - what is it?
- Reasons for education
- Symptoms and signs
- Salivary gland cyst in a child
- Classification
- Parotid cyst
- Submandibular salivary gland cyst
- Sublingual salivary gland cyst
- Minor salivary gland cysts
- Diagnostic methods and specific symptoms
- Puncture
- Treatment
- Surgery
- How a cyst is removed during surgery
- What to do after deletion
- Treatment without surgery
- Relapses and how to avoid them
Causes and symptoms of neoplasm
Dental surgeons often say that infections or salivary stones can contribute to the occurrence. In appearance, it is soft to the touch, painless, round and transparent. If treatment is not started in time, it may become denser. There are several types:
- true,
- post-traumatic.
They can often form on the cheeks, lips and soft palate. Treatment of salivary gland cysts with traditional methods is most effective at the initial stage. Such formations are very rare in small glands. Large ones are most often affected.
INTERESTING fact: Douching for ovarian and cervical cysts
The parotid deserves special attention. It is the largest and if it becomes inflamed, it causes a lot of problems. there is an increase in size and even a change in the shape of a person’s face. It happens that even during intrauterine development a congenital cyst can appear. It can be detected due to unpleasant sensations. Frequent symptoms:
- skin redness,
- swelling,
- restriction when opening the mouth.
Treatment of parotid gland cysts with folk remedies is quite common. It is treatable, but it takes a long time. The concentration of beneficial substances is not so high as to instantly remove the formation, but the effect is not so aggressive. It can be diagnosed by performing an ultrasound examination. If it is found, a puncture may be required to reveal the nature of the contents.
What is a salivary gland cyst
Salivary gland cysts are mobile formations that are benign in nature. They are formed from fibrous tissue and externally appear as bubbles of varying diameters filled with clear or cloudy yellow liquid.
The formation of cysts occurs painlessly and unnoticed by the patient. Patients of any gender and age are susceptible to the disease. However, cysts occur especially often in children and young people under 30-35 years of age. Favorite places for cysts to localize are the soft palate, mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips.
Salivary gland cyst (ranula): symptoms, treatment, features of the retention form
A salivary gland cyst is usually understood as a cavitary single-chamber or multi-chamber formation with a colorless liquid inside. It is localized in the maxillofacial area of the oral cavity.
The cystic capsule is a fibrous membrane, which is internally covered with granulation tissue or squamous epithelium. The increase in size of the cyst is associated with the leakage of blood through the walls of the capillaries or the gradual accumulation of salivary secretion in the cavity.
This formation is considered a rare disease, which is often diagnosed in patients before the age of thirty. Treatment of pathology is within the competence of the maxillofacial surgeon.
Symptoms
Each type of salivary gland cyst has its own distinctive features.
Small gland cyst
The tumor often forms in the area of the corners of the mouth, on the inner surface of the lower lip. The buccal mucosa may also be affected.
The location of cystic formations of this type is associated with the risk of regular injury to soft tissues while chewing food or talking.
This benign tumor is small in size and round in shape. Its development is accompanied by an increase in diameter up to two centimeters.
Typically, a minor salivary gland cyst does not cause any negative symptoms in a person. Pain can be caused by inflammatory processes, injuries, touching with hands or tongue, or while eating. Such formations do not cause external signs (for example, changes in the shape of the face).
Upon examination, the cyst has a clear demarcation from the mucous membrane, is mobile and elastic. There are frequent cases when spontaneous rupture of the capsule occurs and the contents leak into the oral cavity.
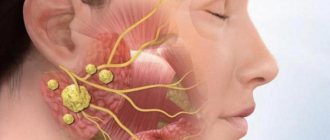
Parotid cyst
The main sign of the development of this neoplasm is a rounded swelling in the ear area on one side, which leads to asymmetry of the facial oval. There is no pain upon palpation, the skin of the face does not change its color or structure.
In case of inflammation of the cyst, an abscess develops. In such a situation, redness of the skin is observed, pain occurs in the problem area, and restrictions occur when opening the mouth. The patient feels weak and the body temperature rises.
The formations themselves form on the mucous membrane of the mouth near the auricle. Due to the deep location of the parotid salivary gland cyst, it is difficult to determine fluctuation.
Sublingual gland cyst
A ranula or sublingual retention cyst forms in the anterior part of the floor of the mouth. In its shape, this benign tumor can be oval or round. It has a blue tint and stands out significantly against the background of nearby fabrics.
As the cyst increases in size, displacement of the frenulum of the tongue and discomfort during conversation and eating are possible.
Periodically, the ranula under the tongue empties itself and then fills again with secretory fluid.
There are frequent cases of infection of the contents of the cyst with subsequent manifestation of symptoms of the inflammatory process.
Submandibular gland cyst
The growth can be located in the salivary ducts, in the lower part of the hyoid bones and in the middle of the neck. The formation upon palpation has a soft and elastic consistency. As it increases in size, swelling appears in the area of the tongue and lower part of the mouth.
After changing the shape of the face, inflammation often begins to appear. The capsule of the submandibular gland cyst has a round shape, and over time it can burst, releasing the fluid contained inside.
Ultrasound
The use of ultrasound makes it possible to establish the localization of the growth, its connection with neighboring tissues and organs, the clarity of the contours and size.
A feature of cystic formation is the ability to not transmit ultrasound rays. Thus, in the resulting image the growths will be black with clear boundaries.
CT and MRI
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are usually performed using a contrast agent. Thanks to this, the size of the cyst, location, structure and shape are accurately determined, and the presence of inflammation in the lymph nodes is determined.
Using special instruments, a puncture is made in the tissues and material is collected for further biochemical and cytological analysis. The results make it possible to determine the composition of the liquid contained in the growth.
Possible complications
If pathogenic bacteria enter the soft tissue, inflammation occurs, followed by suppuration and the development of an abscess. The patient experiences swelling of the face and neck and hyperemia of the skin. Body temperature can rise to 40 degrees. Severe pain occurs when swallowing or when opening the mouth.
Further pathological process can cause purulent melting and necrosis of the salivary gland, as well as provoke damage to nerve nodes and brain tissue.
Postoperative complications include nerve damage, which leads to impaired facial expressions, muscle function and facial paralysis. Sometimes a consequence of surgery can be the formation of a fistula at the site of the operation.
Prognosis and prevention
When a salivary gland cyst is diagnosed and adequate medical care is provided in a timely manner, the recovery process often has positive prospects. However, treatment will take quite a long time. If the patient does not respond to the presence of a growth for a long time, then over time the benign tumor can develop into cancer.
Therefore, it is easier to take measures in advance to prevent the development of such neoplasms. To do this, you should be attentive to your general health, avoid damage to soft tissues in the oral cavity, and promptly treat existing inflammations.
Experts also recommend undergoing regular preventive examinations at the dentist and professional teeth cleaning.
Source: https://onkologia.ru/dobrokachestvennyie-opuholi/polost-rta/kista-slyunnoy-zhelezy/
Causes
The main reason for the formation of a salivary gland cyst is blockage of the excretory ducts and further disruption of the outflow of saliva into the oral cavity. The constantly secreted secretion begins to accumulate in a limited space and thicken. As a result, it stretches the surrounding tissues, forming a dense capsule with liquid contents around itself.
Blockage can occur due to various etiological factors:
- sialadenitis, gingivitis;
- trauma to the mucous membrane with subsequent penetration of pathogenic agents into the wound;
- injury to the salivary gland itself (post-traumatic cyst);
- congenital anatomical features of the structure of the ducts (narrowness, the presence of “blind” branches);
- a change in the chemical composition of saliva, which causes thickening of secretions and deposition of stones in the ducts (due to hormonal disorders or taking certain medications);
- tumor growth near the salivary gland (as it grows, compression of the ducts will occur and artificial disruption of their patency).
A significant role is also played by the patient’s bad habits, poor oral hygiene, and long-term adherence to a certain diet with a predominance of protein foods.
Classification
Based on location, ranulas are classified into superficial and diving. Superficial ranulae are located directly on the mucous membrane of the floor of the oral cavity, forming a characteristic protrusion under the tongue. Diving ranulas are so named because they are found deeper, hiding behind the mylohyoid muscle. This type of ranula will not be noticeable when examining the oral cavity; in patients with this pathology, a swelling under the chin can be observed, which can sometimes be confused with an enlarged lymph node.
Salivary gland cyst: symptoms
Cystic neoplasms of the salivary glands have characteristic symptoms:
- the appearance of a moving ball under the tongue, on the lip (from the inside) and in other typical places where cysts are localized;
- gradual increase in education;
- absence of any pain.
If the cyst shell is accidentally opened (for example, when chewing), the liquid contents of the vesicle are released and it sharply decreases in size. However, after a short period of time, the cyst reappears in the same place. Sometimes the tumors reach such a diameter that it becomes uncomfortable for the patient to talk (diction problems occur) or eat.
Salivary gland cyst: removal, treatment, symptoms, folk remedies
A person has several small and larger glands that secrete saliva.
In some cases, new growths appear on them, which create inconvenience and cause pain. A salivary gland cyst appears due to a blockage of the duct that removes saliva. The compaction reaches 5 cm in diameter and can cause displacement of the frenulum of the tongue. The main method of treatment is surgical removal of the formation. The tumor appears due to blockage of the duct that removes saliva.
Features of education
This is a movable seal that forms in the area of the salivary glands. It is formed from fibrous tissue and looks like a small blister filled with translucent fluid.
A seal that forms in the area of the salivary glands.
Inflammation of the salivary glands is uncommon. In most cases, patients are children, adolescents, and adults under 35 years of age. Most often, neoplasms are located in the oral cavity, covering the soft palate, mucous membranes and lips.
Causes
Thickenings occur if the outflow of secretions in the organs is impaired. Gradually, saliva accumulates in the cavity and becomes thicker. Soft tissues stretch, a capsule filled with liquid appears. The exact reason for the formation of a benign formation is unknown.
Doctors name several risk factors that provoke the development of pathology in the salivary organ:
Stomatitis increases the risk of pathology.
- inflammation of the oral cavity (stomatitis, etc.);
- trauma to the gland, after which pathogenic microorganisms entered the tissue;
- wounds of mucous membranes;
- the presence of scars that impede the proper functioning of the organ;
- a change in the composition of saliva, as a result of which the secretion becomes thicker and its removal becomes more difficult. A blockage of the duct occurs.
Some types of lumps are congenital. The ducts have their own characteristics that interfere with the correct removal of secretions.
Symptoms of salivary gland cysts
Regardless of the type of formation, the symptoms of their appearance are largely similar.
Deformation of the facial oval.
However, some characteristics can be used to distinguish one type from another. The following manifestations will be common:
It can be located under the tongue, on the inside of the lips.
- the presence of a thickening in the form of a ball. Depending on the type of cyst, it will be located under the tongue, on the inside of the lips, etc.;
- the benign tumor gradually increases in size and can deform the facial oval;
- no characteristic painful sensations;
- if the cyst has greatly increased in size, it interferes with eating and speaking.
Classification
Today there are two main classifications of seals. The first is related to the reason for their appearance. A retention cyst of the minor salivary gland or large (true) and post-traumatic (false) are distinguished. When an organ is injured, scars form, which cause blockage of the ducts.
Location of glands.
The localization of retention cysts is associated with other causes of impaired secretion outflow. Depending on the location of a benign tumor, several types are distinguished:
- cyst of small glands (located on the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate, etc.);
- parotid cyst;
- sublingual;
- submandibular
Small
Cysts appear on the mucous membrane at the bottom of the lip, sometimes on the inside of the cheeks, palate, etc. This type of tumor rarely exceeds 1 cm in diameter and grows slowly. The patient feels a rounded thickening that moves slightly when the tongue touches it.
Appear on the mucous membrane at the bottom of the lip.
The peculiarity of this variety is the absence of pain or any discomfort.
Since a small cyst rarely reaches a significant size, it practically does not bother the patient. Some people don't pay attention to it until it opens spontaneously.
In this case, the contents of the capsule flow out, but soon the cavity is filled with liquid again.
Sublingual
This type of lump occurs in the sublingual area, in the area of the major salivary gland. A benign tumor of a characteristic round or oval shape appears under the root of the tongue. You can distinguish a cyst by its color. It has a bluish tint, reminiscent of translucent veins.
A benign tumor of a characteristic round or oval shape appears under the root of the tongue.
Sublingual neoplasm contributes to the development of complications.
As the cyst grows, it puts pressure on the frenulum of the tongue, causing it to shift. Because of this, the patient cannot eat or speak normally.
When the capsule spontaneously opens, the unpleasant symptoms subside for a while, but as the cavity fills with saliva, the signs become more pronounced.
Submandibular
One side of the face may be different from the other.
The submandibular salivary gland cyst is located in the lower jaw. The thickening is ball-shaped, soft. When pressed, you feel that the capsule is filled with liquid contents.
If a benign tumor spreads to the sublingual area, it can provoke deformities of the oval of the face. As the formation increases in size, the contour becomes less clear, one side of the face may differ from the other.
Parotid
The next type is a parotid salivary gland cyst. It has certain features and symptoms:
- the parotid cyst in most cases is located only on one side (on the mucous membranes in the area of the right or left ear);
- a round neoplasm forms on the soft tissues;
- as the compaction increases in size, the contour of the face is deformed;
- a soft capsule filled with liquid contents is palpable inside.
A soft capsule filled with liquid contents is palpated.
In the absence of infection, a parotid cyst does not cause any inconvenience or discomfort to a person. The condition of the skin does not change, there is no pain. However, many people experience negative emotions due to changes in facial contour.
If an infection is added to the pathology, in addition to the main symptoms, temperature and swelling of the soft tissues appear, a feeling of neck tightness, and pain occurs. The patient cannot open his mouth normally.
Diagnostics
At the initial examination, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis based on the identified symptoms. The pathology of the salivary glands has its own characteristic signs, some of which are difficult to confuse with something else. However, to clarify the diagnosis, in any case, additional tests and laboratory examinations are prescribed.
This will allow us to identify the type of tumor, and will also be needed to determine the size of the benign tumor and to prescribe subsequent treatment. To make a final diagnosis, the attending physician sends the patient for the following studies:
An ultrasound will help determine the size of the lump and its exact location.
- An x-ray of the salivary gland and its ducts allows you to see whether the secretion is disturbed;
- Ultrasound examination will help clarify the size of the seal and its exact location;
- in some cases, a computed tomography scan (instead of an x-ray) is prescribed;
- MRI;
- blood chemistry;
- a puncture is performed to select material, which is sent for analysis to the laboratory. This will exclude the presence of a malignant tumor.
Treatment
Salivary gland cysts are not treated using conservative methods. The only effective way to avoid relapses is surgical removal of the capsule along with its contents. Most often, the gland itself is cut out at the same time.
The operation is performed through the mouth or through an open approach using an incision.
Depending on the location, the operation is performed through the mouth or through an open approach. Local anesthesia is used. After completion of the procedure and the end of the recovery period, a small cosmetic seam is formed, which is practically invisible.
Surgical methods
Surgery will prevent relapse and reduce the risk of complications.
During the operation, the capsule of the cyst is opened and the internal tissues are scraped out. Then the tumor is completely removed along with the gland. This will prevent relapse and reduce the risk of complications.
After surgery, the attending physician selects a rehabilitation course. Physiotherapy is prescribed and medications are prescribed. Antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. are used.
If the cysts are small (usually nodules that form on small glands), they are removed using a laser. The contents are burned out with a directed beam, and the remains of the capsule grow together with the mucous membrane.
Folk remedies
Doctors never tire of repeating to patients who have encountered a salivary organ cyst that it cannot be cured using traditional methods.
If you postpone a visit to a specialist, you may encounter serious complications. At the same time, timely surgical intervention will avoid facial deformation and other unpleasant symptoms.
Mumiyo is diluted in water and then rinsed in the mouth.
Traditional medicine recipes can be used after surgery to safely treat the oral cavity and reduce the concentration of pathogens.
To do this, use the following rinsing products:
- eucalyptus oil. 2 tbsp. l. The products are diluted in a glass of water and used several times a day;
- Shilajit is dissolved in warm liquid (2 tablets per glass);
- use rinses with decoctions of injuries. Brew oak bark, chamomile and other plants that provide an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Do not use products if you are prone to allergic reactions.
Preventive actions
Compliance with the following recommendations will help reduce the risk of tumors of the salivary organ:
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- regular visits to the dentist to exclude infectious lesions of the oral cavity;
- timely dental treatment;
- avoid injuries to the jaw area;
- proper nutrition (including protein foods rich in calcium, fluorine, and other microelements in the diet);
- absence of bad habits.
Surgery to remove a gland cyst is a simple procedure, after which a person recovers quickly. If surgical intervention is delayed, the lump will increase in size and over time will lead to deformation of the facial contour, displacement of the frenulum of the tongue, difficulty in eating and impaired diction.
Source: https://kistateka.ru/rotovaya-polost/slyunnoj-zhelezy
Salivary gland cyst in a child
Cysts of the salivary glands in children (including infants) arise for the same reasons as in adults, and have absolutely identical symptoms. The only thing with which complications may arise is the timely detection of formations (due to the child’s shyness, his fear of the doctor, or his inability to accurately describe the factors that bother him). Removal of a cyst in an infant should only be performed by a qualified specialist due to the high level of complexity of the operation and the risk of relapse.
Salivary gland cysts: causes, symptoms and treatment
Update date: 2019-05-14
Salivary gland cysts are pathological benign formations of fibrous tissue that look like single cavities, most often single-chamber, less often multi-chamber. The inside of the cyst is filled with white or yellow mucous fluid.
The formation of cysts is painless. People of all categories are at risk, especially people under 30 years of age. Most often, cysts form on the minor salivary glands. The large gland is also affected by pathology, but much less frequently. Cysts are located on the soft palate, inner sides of the cheeks and lips.
If left untreated, the cyst grows over time and the problem worsens. The reasons for this are complications such as leakage of fluid through the capillary walls and accumulation of secretions inside the cyst with the inability of its outflow.
Classification of salivary gland cysts
Cysts are classified according to several criteria: place of formation, location, cause of appearance.
The main classification of this type of formation is the grouping of cysts by the names of the glands that they affect. Thus, there is a cyst of the minor, sublingual, submandibular and parotid glands. Cysts of the large and small glands are very distinguishable from each other.
Experts classify these tumors based on their location, since the cyst can be located directly in the duct itself or in the parenchyma - the tissues of the entire gland.
In addition, the cyst may belong to false or true tumors. The former arise due to various types of soft tissue injuries, the latter due to the occurrence of pathologies such as salivary stones or other natural causes.
In this case, a true cyst has an epithelial lining inside, while a false cyst does not have one. If there is mucoid mucous content inside the cavity of the cyst, it is called a mucocele. What will be another variation of this education.
Such a cyst is formed because the gland has lost the ability to release secretions from it. The salivary outflow can also be blocked due to excessive thickness of the secretion, which forms a salivary stone.
In addition, cystic pathology is caused by injury or a tumor that compresses the canal and prevents the release of saliva.
As a result, the fluid stretches the glandular lobule or the salivary duct itself, and a cyst forms at the site of the pathology.
Depending on which gland it forms in, the symptoms of a salivary gland cyst can be distinguishable.
Classification of salivary gland cysts
Cysts are usually classified according to 2 criteria: depending on the location (type of affected gland) and the cause of occurrence. To systematize cystic formations that have arisen as a result of various etiological factors, the following classification has been proposed:
- retention cysts (true) - appear due to mechanical obstruction of the ducts;
- post-traumatic (false) - formed by the duct becoming overgrown with coarse scar tissue after its trauma.
Based on location, cysts are divided into:
- parotid;
- submandibular;
- sublingual.
In addition, cysts can be dermoid (consisting of the epidermis and its derivatives) and glandular (adenoma).
Parotid cyst
The formation has a spherical shape and is most often located only on one (left or right) side inside the oral cavity near the auricle. As a result, the face loses symmetry. The skin over the cyst does not change color or temperature and easily folds. A “sterile” cyst does not cause problems (except aesthetic ones).
But in the case of the addition of an infectious process and inflammation, characteristic symptoms appear:
- palpation of this area becomes sharply painful;
- education “presses the neck”;
- hyperemia is observed;
- the configuration of the temporomandibular joint is disrupted.
Pathology
Patol, processes in P. zh. similar to those with damage to other salivary glands. On patol, the condition of the gland is indicated by an increase in sublingual folds, painful in acute inflammation, painless in chronic inflammation, dense consistency in tumors and soft consistency in pancreatic cysts.
Damage
P.J. are relatively rare. In case of a gunshot wound, they are usually combined with damage to the bones of the facial skull. In addition, there are cases of damage to the pancreas. disc during the preparation of lower jaw teeth for crowns, during surgery for acute inflammatory processes in the sublingual region, when removing salivary stone (see Sialolithiasis) from the middle or posterior sections of the submandibular duct. Damage to the gland can be diagnosed by examining the wound, in which the glandular tissue can be clearly visible. Patients are bothered by pain when talking or eating. As a result of scarring of the wound, the outflow of secretions from the ducts of the pancreas. may be disrupted, which leads to the appearance of a ranula - a retention cyst (see Cyst).
Diseases
P.J. include reactive-dystrophic processes, acute and chronic inflammation, cysts, tumors (see Salivary glands).
Reactive-dystrophic diseases are usually not an isolated lesion of the pancreas: they develop with systemic damage to the salivary and lacrimal glands - Mikulicz's disease (see Mikulicz syndrome), all excretory glands - Sjögren's syndrome (see Sjögren's syndrome), as well as other autoimmune and endocrine diseases (see Salivary glands). P.J. At the same time, it increases in size, becomes denser, and subsequently a decrease in its function is observed.
Rice. 2. Sublingual area with acute inflammation of the sublingual salivary glands: sublingual folds of uneven thickness (indicated by arrows), the mucous membrane of the sublingual area is swollen. Rice. 3. Sublingual area with chronic inflammation of the sublingual salivary glands: 1 - tongue, 2 - frenulum of the tongue, 3 - thickened, raised sublingual folds, 4 - tuberous surface of the right sublingual gland.
Inflammation of the pancreas. can be acute or chronic. The cause of acute infection can be mumps viruses with an atypical course (see Epidemic mumps), influenza (see), etc. The disease begins acutely and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. The gland is enlarged in size, sharply compacted on palpation, and painful. The sublingual folds are thickened, the oral mucosa is swollen (Fig. 2). These phenomena persist for 4-5 days, then the infiltrate slowly resolves and the condition returns to normal. On the 2-3rd day of the disease, an abscess may develop. Treatment is conservative, in case of an abscess - surgical. Chron, inflammation of the pancreas. is observed relatively rarely, is usually bilateral and is combined with damage to the parotid or submandibular salivary glands (see Parotid gland, Submandibular gland). Clinically manifested by swelling of the pancreas. If left untreated, the gland slowly enlarges, thickens, and becomes lumpy (Fig. 3). Pain appears only when the process worsens. Treatment includes general measures aimed at increasing the body's resistance; novocaine blockade is applied locally. In addition, treatment of concomitant diseases is necessary.
The most common patol, process in P. g. is a retention cyst, which occurs when the outflow of secretions from the pancreas is disrupted. The shell of the cyst consists of connective tissue rich in blood vessels, the bundles penetrate into the connective tissue layers of the lobules of the pancreas. In the peripheral parts of the cyst shell there are elongated cells such as fibroblasts; very rarely one or two rows of cubic or multirow cylindrical epithelium cells are found on the inner surface of the cyst shell. The first wedge, a symptom of a cyst, is the appearance of swelling in the sublingual area (painless, soft or elastic consistency), the edges, slowly increasing, can spread to the submandibular area. When the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth in the sublingual region becomes thinner, spontaneous opening of the cyst and its emptying may occur. In this case, it decreases in size or is not detected at all, but after a certain time (weeks, months) it reappears and increases. Treatment of the cyst is surgical: a cystotomy is performed (opening the cyst and emptying) or the cyst is removed along with the pancreas.
Sublingual salivary gland cyst
Formed under the base of the tongue, it has a spherical or oval shape and an unusual bluish-gray tint.
As the cyst increases in size, it provokes displacement of the frenulum of the tongue and interferes with normal speech and eating. After its spontaneous emptying, relief occurs for a while, which is then replaced by discomfort as the cyst fills with secretion.
Minor salivary gland cysts
When cysts of the minor salivary glands form, patients complain of small transparent blisters, usually localized on the lower lip.
The formations are so small in size that they can go unnoticed for a long time. However, as they grow, the bubble begins to interfere, pushing against the front incisors, and eventually bursting. Once its contents are emptied, the process starts again.
Diagnostic methods and specific signs
Despite a number of specific signs that are obvious after collecting anamnesis and visual examination, doctors still send patients for additional diagnostic methods to clarify the diagnosis and exclude diseases with similar signs.
The main diagnostic methods are:
- detection of cysts on ultrasound;
- radiography of the gland and its ducts;
- puncture of the gland with a description of the cytological picture of the contents.
In some cases, it is advisable to use CT or MRI.
Diagnostics
At the initial examination, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis based on the identified symptoms. The pathology of the salivary glands has its own characteristic signs, some of which are difficult to confuse with something else. However, to clarify the diagnosis, in any case, additional tests and laboratory examinations are prescribed.
This will allow us to identify the type of tumor, and will also be needed to determine the size of the benign tumor and to prescribe subsequent treatment. To make a final diagnosis, the attending physician sends the patient for the following studies:
An ultrasound will help determine the size of the lump and its exact location.
- An x-ray of the salivary gland and its ducts allows you to see whether the secretion is disturbed;
- Ultrasound examination will help clarify the size of the seal and its exact location;
- in some cases, a computed tomography scan (instead of an x-ray) is prescribed;
- MRI;
- blood chemistry;
- a puncture is performed to select material, which is sent for analysis to the laboratory. This will exclude the presence of a malignant tumor.
Treatment
The most effective treatment method to get rid of salivary gland cysts is surgery. The use of medications and physical therapy is advisable only after removal of the tumor. Such complex therapy will reduce the risk of postoperative complications to a minimum and eliminate relapse of the disease.
Surgery
The operation is painless (thanks to modern drugs used for local anesthesia). It is carried out intraorally or extraorally (large glands must be removed through an external incision, small ones - through an internal one). Upon completion of the manipulations, the surgeon brings the edges of the wound together and applies self-absorbing catgut sutures.
Is a relapse possible and what to do to avoid it?
If the operation is performed correctly and the patient complies with all rehabilitation measures, relapse of the disease is unlikely. The recurrence of a cyst is possible only if the formation is incompletely removed or a postoperative wound that is not completely healed is traumatized. The only way to avoid the recurrence of a cyst is a competent approach to choosing a qualified specialist and careful handling of the fresh incision and performing all hygienic procedures.
A salivary gland cyst is not as dangerous as malignant tumors, but in the absence of proper treatment, the tumor begins to grow and increase in size, bringing severe discomfort to the patient and threatening the development of various complications. You should not rely on treatment with folk remedies (lemon, sea buckthorn oil, etc.), for which there are so many recipes on the Internet. This may not only not bring the desired results, but also significantly aggravate the existing situation. Only a doctor can help the patient get rid of this pathology.
Traditional methods of eliminating the disease
If stones were the cause, then before starting treatment, it is worth removing them. Oil and alcohol compresses are good for this.
Celandine
Pour 3 tablespoons of dry celandine herb into a container, pour 300 ml of boiling water and place on low heat. Bring to a boil. Remove from heat and let sit for 3 hours. Moisten a piece of cloth and apply it to the swollen gland for an hour. Do this 3-4 times a day.
Simple ways to treat complex diseases:
Horseradish is the only plant that can draw salt through the pores of the skin. Do it - you won't regret it! Horseradish leaves will help get rid of all the salt that has accumulated in the body and can lead to painful salt deposits...Check... Read more
Never give an antibiotic BEFORE you get a blood test with a leukemia formula. Remember, write to yourself somewhere in a visible place!!! INCREASED leukocytes, ESR, lymphocytes - VIRUS. INCREASED leukocytes, ESR, segmented and rod neutrophils... Read more
What 1 glass of this drink will do to your liver can be called a real miracle! If the liver is overloaded or does not work well, we immediately feel it. Weakness, lack of energy, dizziness, nausea, pain in the right hypochondrium, problems with food... Read more
Dandelion is the elixir of life, and what a medicine!!! The medicinal dandelion is an unpretentious plant, but contains a good half of the chemical elements of the periodic table. Sodium, potassium, manganese, magnesium, and... Read more
Seeds that repair tendons and reduce joint pain. We treat osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis of the knee is a type of degenerative joint disease or arthritis that is localized in the knee and can cause pain and di... Read more
INTERESTING fact: Instructions for treatment with motherwort, beneficial and harmful effects of the decoction on the body
Hemlock with carrots
Combine equal parts grated carrots and hemlock tincture. Apply a bandage and cover the sore area for 2 hours three times a day. It is recommended to supplement the therapy with daily intake of 1-2 cups of carrot juice. You can also make compresses from carrot juice 5 times a day.
Collection of herbs
Pass 300 g of celandine roots, 50 g of yarrow and St. John's wort flowers through a meat grinder. Pour the resulting mixture with 0.7 liters of vodka. Place in a cool, dark place for a week. After the allotted time has expired, use the solution for compresses.
Ointment
You can prepare an ointment based on 1 fresh chicken yolk, a tablespoon of white flour, the same amount of bee honey, ½ teaspoon of vegetable oil. Mix everything well and keep on low heat without letting it boil. The mixture should thicken. Place it on gauze or plantain leaf and apply it to the sore spot.
Hemlock tincture
Treatment of salivary gland cysts without surgery can be carried out using the following method. Use hemlock tincture. Remember that this plant is poisonous and you need to be very careful in dosage so as not to cause harm.
INTERESTING fact: The healing properties of aspen in folk medicine
The reception should be carried out three times a day. The intervals should be the same. This could be 06.00, 15.00, 21.00 3-4 hours after eating. On the first day - drop by drop. Then you need to add one more every day. Bring it to 30 and then work backwards. Dilute from 1 to 13 drops in 100 ml of water, 13-26 in 150 ml, 26-40 in 200 ml, 40-50 in 250 ml.
Health to you!