6400
Salivary stone disease or sialolithiasis is the formation of mineral neoplasms in the structures of the glands.
Their occurrence often causes severe pain, and over time can lead to complete blockage of the ducts and inflammation of the submandibular glands.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, specialists often resort to conservative treatment, but at an advanced stage it is impossible to do without surgical intervention.
Causes
The occurrence and growth of stones in the salivary glands is most often a consequence of a disturbance in the body's calcium metabolism, accompanied by a lack of retinol.
This situation often occurs in people suffering from the following diseases:
- diabetes;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- excess vitamin D in the body;
- pathology of the functioning of the endocrine system – hyperparathyroidism.
In addition, experts note that there are some prerequisites for the accumulation of mineral or organic formations in the glands.
The main ones are considered to be:
- mechanical damage to the ducts due to incorrectly selected dentures or sharp edges of teeth and crowns;
- the occurrence of crystallization or stagnation of saliva secretion due to a slowdown in its separation;
- the presence of inflammation in the oral cavity , which causes compression of the salivary ducts and accumulation of pathogenic microflora;
- the development of an inflammatory process as a result of the penetration of foreign particles into the ducts , around which bacteria accumulate and multiply.
Various age groups of the population are susceptible to salivary stone disease, however, the disease is most often diagnosed in men and women aged 25-45 years who abused smoking or took certain groups of medications.
Characteristics and symptoms
The process of blocking the ducts with mineral formations, which can be from one to a whole group, is also called sialolithiasis of the submandibular salivary gland. This disease occurs in no more than 1% of the population in middle age.
Stones can form in glands such as:
- submandibular;
- parotid;
- sublingual;
- small;
- Wharton duct;
- Stensen's channel.
A stone in the salivary duct can occur in almost everyone, but the difference is that small particles are washed out independently by saliva in the absence of disorders and pathologies. Problems begin if salivation is weakened or stones are large and in the plural.
They can be completely different in shape. As a rule, the salivary stone, which forms closer to the gland itself, has a more rounded shape, as well as a distorted surface. Stones that appear directly in the duct are more elongated and pointed in appearance.
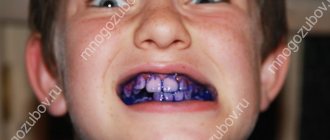
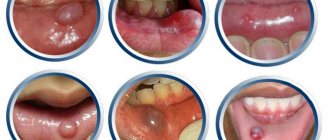
Stone in the salivary gland: photo of the extracted formation
A stone in the duct of the salivary gland is characterized by a yellowish-grayish tint and a layered structure. One stone has a base in the center, the so-called core, around which the remaining parts - salts - are layered. If you look closely, you can find small channels through which saliva follows.
The size and weight of stones may vary depending on the nature of their occurrence and the severity of the disease. Thus, they can reach several centimeters and weigh up to several tens of grams, but their weight and size are not interrelated.
At the very beginning of the onset of sialolithiasis, no symptoms may be observed.
In addition, at this stage, stones can independently leave the body along with saliva.
The presence of a foreign body in the ducts and glands can be detected randomly during examination of another disease.
However, for those who have any pathologies, there may be a delay in the secretion of salivary fluid, which is why the stones cannot be removed, but only become more clogged. The same applies to large stones, which, among other things, were formed in the submandibular duct.
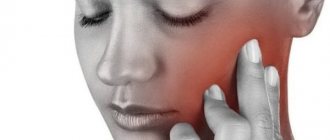
As the disease progresses, pain begins to be felt when eating, as well as some discomfort, similar to “bloating” of the gland.
This phenomenon is called salivary colic and can last from several minutes to several hours. Once it has stopped, it may be triggered again by the next meal.
It can be quite difficult to detect the disease at this stage. In addition, pain may not bother you for years, but the ducts may not have been fully cleaned. As a rule, the nuance can be determined only through a detailed examination and identification of a slightly enlarged gland.
As the disease “ripens” and the stone grows, pain may occur when swallowing and also radiate to the ear. In addition, low-grade body temperature, general malaise and fatigue, headache, and heaviness may be observed. If the ducts are severely blocked, cellulitis or abscesses may form.
Chemical composition
Stone formation begins around the core, which may be an accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms or have a non-microbial structure.
It is often based on epithelial cells and foreign particles - toothbrush villi, small non-decomposing particles of food products.
The process often occurs against the background of changes in the qualitative composition of saliva, a decrease in the rate of its separation, changes in the amount of mineral salts and acidity.
Stones that form in the tissues or ducts of the salivary glands are composed of organic and mineral components . The elements of organic structure include mucoproteins and amino acids.
The stones contain about 15-25% of these substances. The remaining 75-85% are minerals such as sodium, potassium, calcium, iron, and phosphates.
Reasons for performing sequestrectomy for osteomyelitis and preliminary diagnostic measures.
This material contains detailed information about osteosynthesis of the lower jaw.
Here https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/operatsii/udalenie-kapyushona-mudrosti.html we’ll talk about the price of wisdom tooth hood removal.
Effective techniques for removing stones from the salivary gland
943
Salivary stone disease is an accumulation in the ducts or in the parenchyma of secreting glands, a salivolith component that has a solid structure.
Excessive formation of this substance negatively affects salivary production and leads to blockage of the ducts.
At a certain stage of progression, the disease is associated with pain of varying severity.
Causes
A number of factors that have both local and general significance can cause the formation of stony deposits in the salivary glands.
Experts consider an imbalance of calcium metabolic processes against the background of a lack of vitamins of group A in the human body as a common factor, and it is also the predominant one in morbidity statistics.
The risk category includes patients diagnosed with:
- pathologies of the urolithiasis system;
- gout in the chronic stage of its course;
- excess vitamin D;
- diabetes at any stage of its progression;
- nicotine addiction.
Local factors include:
- narrowing of the duct walls;
- pronounced defects in the structural structure and violation of the integrity of the glandular membranes;
- failure of the secretory function of the ducts;
- sialedenitis.
Chemical composition
The initial stage of the disease, when the stone is just beginning to form, is localized in the encircling zone of the nucleus, which has both microbial and non-microbial origin.
In the first option, the core consists of a conglomerate of pathogenic organisms. In the second, its chemical composition consists of dead epithelial cells and foreign substances that have penetrated into the ducts.
These are decay products of food fragments - fish bones, small pieces of the hard part of fruit, berry seeds.
The stone includes particles:
- organics - it accounts for up to 30% of the total volume of formations. This is the epithelial layer, mucin, amino acid compounds;
- minerals – they contain at least 70%. This includes sodium, potassium, phosphate elements, chloride and magnesium components, iron and calcium carbonate.
In its composition, salivary deposits are close to the stone that forms on the surface of tooth enamel.
Symptoms
External manifestations of a developing disease are often long-lasting and secretive. They are diagnosed, as a rule, by chance - during an x-ray examination based on the presence of other ailments.
It is especially difficult to detect the presence of salivary stones localized in the parenchyma of the gland.
The main symptoms of the pathology are:
- feeling of fullness in the mouth;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor , which cannot be called pungent, but at the same time it is difficult to stop;
- severe swelling of the secretion-producing glands;
- acute pain attack - reminiscent of colic. The reason for this phenomenon is salivary retention against the background of a sharp increase in the size of the ducts;
- pain when swallowing , radiating to the temple - appears at a stage when the disease is too advanced and there is no treatment;
- fever, weakness, headache are signs that also indicate rapid progression of the pathology;
- an abscess and the appearance of phlegmon are symptoms signaling serious complications that have begun in the body.
Diagnostics
It is possible to diagnose the disease using the following methods, which require complex use:
- visual examination - allows you to determine whether the glands are enlarged in size, how dense their consistency is than normal, and also to understand whether palpation causes pain to the patient;
- probing the ducts - this way you can identify the stone. During the procedure, unpleasant-smelling purulent masses begin to be released from the area where the anomaly is located;
- fluoroscopy - confirms the presence of solid deposits and indicates their location. For a more accurate result, it is possible to use a contrast agent;
- Ultrasound of the glands - at the time it is performed on the monitor, the doctor can see in detail the location, size, shape of the formation;
- sialometry - is done to determine the degree of functionality of the ducts and the ability of the glands to produce saliva;
- a study for biochemical pH analysis - gives the most detailed picture of the chemical content of the secreted secretion.
Treatment
If the stone is almost on the surface, in close proximity to the mouth, the doctor can remove it with dental tweezers or squeeze it out mechanically.
In more complex clinical situations, the following treatment methods are carried out.
Surgical intervention
Depending on the size of the formation, its location and structural composition, various methods can be used to quickly solve the problem:
- Interventional sialendoscopy is the most innovative technique, widely practiced in domestic clinics. Makes it possible to remove deposits using an endoscope, while preventing the formation of scars on the walls of the ducts;
- extracorporeal lithotripsy is a more gentle procedure. It consists of crushing the stone into small fragments using directed beam flows. As an alternative, chemical dissolution with a composition based on 3% citric acid;
- dissection of the excretory duct - performed against the background of processes complicating the disease, for example, an abscess. The focal area is opened, purulent formations are removed, after which the edges of the wound are pushed apart, ensuring the passage of the stone;
- extirpation of the salivary gland - indicated for the development of relapses in the form of multiple stony formations or the development of irreversible processes that disrupt the salivary organics and the structure of the gland.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment involves taking antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Discomfort and pain are relieved by a course of targeted painkillers.
In addition
, you should rinse your mouth with antiseptics several times a day. This will minimize the risk of developing purulent accumulations.
As a comprehensive effect on pathology, the following procedures are recommended to the patient:
- massage;
- electrophoresis sessions;
- hirudotherapy;
- ozone baths;
- physiotherapy.
ethnoscience
The principle of treatment with folk remedies is to normalize metabolic processes that provoke the development of the disease.
The following tools are suitable for this purpose:
- viburnum - the berries are thoroughly ground with honey in a 1:1 ratio, poured with boiling water. Leave for 1-1.5 hours. Drink as tea at the rate of 150 g at a time. Course – until the result improves;
- nut - unlike traditional recipes, in this case it is not the kernels that are used, but the leaf of the plant. For 0.5 liters of boiling water, take 2 heaped tablespoons of finely chopped leaves. The mixture is boiled for five minutes, then left for half an hour. Then filter and take 100 g 4 times a day.
Relapse and exacerbation
The main reasons that can provoke a relapse of the disease are exacerbations of chronic diseases that develop into an active form.
Against their background, there is a general decrease in immunity, metabolic processes occurring in the body are disrupted, and its resistance to secondary infections drops sharply.
If the disease cannot be cured completely and it transforms into a latent, chronic condition, there is a high risk of its periodic exacerbation due to the reasons mentioned above.
You can eliminate processes by taking the following measures:
- dry heat;
- warm camphor compresses;
- sessions of iodide electrophoresis;
- taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- carrying out conical probe bougienage.
Forecast
The surgical solution to the problem gives a fairly optimistic prognosis for recurrence of the disease.
However, during the operation, the natural microflora of the oral cavity is disrupted, the teeth become more sensitive to external negative influences and are quickly destroyed, which, in turn, affects the patient’s quality of life.
Therefore, doctors try to resort to this method of treatment only when more gentle methods do not give positive dynamics. In more than 85% of clinical cases, surgery can be avoided.
Symptoms
The initial stage is asymptomatic, so the development of the disease can only be detected through instrumental examination - taking an x-ray.
The appearance of signs of pathology development is often observed when the stone reaches a large size and blocks the lumen of the excretory canal.
The patient experiences the following symptoms of sialolithiasis:
- increased dryness in the mouth due to the production of insufficient saliva;
- replacement of saliva with mucous contents with a purulent admixture;
- swelling of the facial and cervical area due to fluid accumulation;
- pain when opening the mouth , chewing food and swallowing, which can radiate to the ear;
- feeling of fullness in the problem area , swelling in the lower jaw and neck;
- redness of the skin of the face and neck in the area of stone formation.
When a mineral formation reaches a large size, a person can determine its location during an external examination or palpate it.
At an advanced stage of development of the disease, a person experiences general signs of intoxication of the body - a slight increase in temperature, lethargy .
A severe form of the disease can lead to the formation of a through hole in the wall of the salivary gland, through which the stone exits into the soft tissue.
Symptoms of salivary gland stones
A stone in the salivary gland is a pathology that occurs for a long time without visible symptoms. Often, stones are discovered in a patient by accident during a routine examination in the dental office or simply by touching with your own tongue. A stone in the salivary gland is revealed by its compaction; it causes a delay in the secretion of saliva during meals. The swelling in the area of the gland is painful, the unpleasant sensation goes away after saliva enters the oral cavity. Quite often, the formed stone causes an inflammatory process of the salivary gland, which has characteristic symptoms:
- feeling of dryness in the mouth;
- the presence of a specific taste in the mouth;
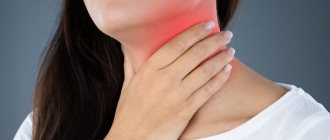
- pain in the neck and mouth;
- change in the position of the earlobe and the formation of swelling in its area;
- increase in body temperature.
If a stone in the salivary gland provokes an inflammatory process, then the patient begins to feel fatigue and general fatigue, along with this, the body temperature rises. Dry mouth causes problems with eating and even facial expressions. If you ignore a visit to the doctor for a long time, an abscess may form, characterized by a large accumulation of pus in the area of the salivary gland, which can lead to its breakthrough into the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
To diagnose salivary stone disease, specialists use a combination of various examination methods:
- with the help of external examination and palpation, an increase in the size of the gland is detected compared to the norm, an increase in the density of its consistency is detected, and pain when pressed is determined;
- instrumental diagnostic methods, in particular radiography, contrast study of saliva, ultrasound, make it possible to confirm the presence of a mineral formation and determine its size and position in the parenchyma of the gland;
- Sialometry is the optimal way to determine the secretory function of the salivary glands .
In addition to the above studies, saliva is often taken from the patient to determine its acidity and qualitative composition.
In combination with other examination methods, this makes it possible to differentiate sialolithiasis from phlegmon, abscess, and neoplasms of the oral cavity.
Main methods of treatment
The goal of treatment when diagnosing stones in the salivary gland is to remove the formation from the duct to completely release it. The content of the course of therapy depends on the characteristics of the formations. For small stones, stimulation is carried out with salivary drugs in order to try to remove them naturally.
For simple pathologies, a dentist can perform the removal and does not require complex surgical instruments. In some situations, massage may help the stone pass.
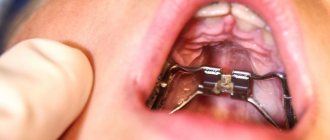
Surgical intervention is prescribed for relapses and in cases of irreversible changes. The most commonly used method for surgical removal of formations is sialoscopy. The removal process is as follows:
- local anesthesia is administered;
- Using special surgical instruments, the doctor fixes the stone in the duct;
- The cork is grabbed with forceps and pulled out.
See also
Causes, symptoms and treatment of laryngeal perichondritis
Read
The removal operation does not take much time and after removing the stones, the patient can immediately go home. Surgical intervention is not classified as complex, but requires special attention from a doctor. After the procedure, painkillers and antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent the development of complications.
In addition to sialoscopy, the following methods are used:
- expansion of the duct by inserting a probe;
- ultrasonic stone crushing;
- dissolving the formation by introducing a 3% solution based on citric acid.
After the operation, the patient can return to normal life. Modern advances in medicine today provide an almost 100% guarantee of a favorable outcome and recovery.
Treatment
There are various methods for treating salivary stone disease, depending on the degree of its development.
At the initial stages of pathology, specialists often give preference to minimally invasive techniques that facilitate spontaneous stone passage.
At an advanced stage of the pathology, surgery may be required.
Surgical intervention
Today, there are four methods for eliminating stones from the salivary glands:
- Interventional sialendoscopy. The essence of the intervention is that using a thin flexible instrument with a camera at the end - an endoscope.
When introduced into the salivary ducts, the specialist is able to examine them and remove stones. The procedure is minimally invasive and is performed under local anesthesia. - Extracorporeal lithotripsy involves ultrasonic exposure of stones from the outside, as a result of which they are crushed.
This creates the possibility of further endoscopic extraction and washing of the ducts with a special solution, which prevents the development of the inflammatory process. - Dissection of the duct used when the stone reaches a large size and it is impossible to remove it using a minimally invasive method.
In this case, access to the mineral formation can be through the skin or mucous membrane of the oral cavity.Stone removal is performed using a surgical spoon or finger tweezers. Most often, suturing and drainage of the duct wound is not required.
- Extirpation of the salivary gland or the procedure for its removal is the most radical method of treating salivary stone disease.
The operation is used only if it is impossible to eliminate the pathology in another way - with repeated formation of stones or irreversible changes in the parenchyma of the gland. The procedure is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia.
What problems are solved with the help of flap surgery in dentistry, and what are the indications for it?
In this publication we will talk about the effectiveness of plastic surgery of the anastomosis with the maxillary sinus.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/operatsii/udlineniya-i-puti-resheniya.html we will talk about the intricacies of surgical lengthening of the coronal part of the tooth.
Medicines, physiotherapy
A non-invasive technique for eliminating stones from the salivary glands is based on freeing the clogged duct and activating the process of self-removal of the mineral formation.
This treatment option is suitable only when the disease is detected at the initial stage. Conservative treatment of sialolithiasis is based on the following measures:
- Taking medications prescribed by your doctor. Most often, the basis of treatment is anti-inflammatory drugs, medications that enhance saliva secretion, and antibacterial drugs.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, in particular electrophoresis, fluctuarization, UHF, contribute to the expansion of the salivary ducts and the unhindered passage of stones through them.
- A special diet containing acidic foods and drinks activates saliva production, which also helps remove stones through the ducts.
Professional massage performed by a specialist is another way to remove small mineral formations from the salivary glands. However, the decision on the need for it is made only by the attending physician.
ethnoscience
Non-traditional treatment methods can only be used in conjunction with conservative therapy to remove small mineral formations. According to people's reviews, the following folk recipes are most effective:
- Dry sage leaves are poured with boiling water in the proportion of 400 ml of liquid per 2 tablespoons of the plant, and infused for 1.5-2 hours. Rinse the mouth with the strained solution every 2-3 hours.
- Fresh cranberries are ground to a pasty state, then dissolved in a teaspoon before each meal for 10 minutes. The product helps to increase salivation and remove stones.
- Non-canned birch sap is taken daily, one glass. The liquid helps dissolve calcium-based compounds present in mineral formations.
Remember! The use of traditional methods of treatment is permissible only after consultation with a specialist, in parallel with the implementation of his recommendations.
Treatment of salivary gland stones
Treatment for salivary stone disease involves removing the stone. Removing stones from the salivary gland occurs in two ways, depending on their location. When a stone is localized at the mouth of the duct, it is dissected and removed into the oral cavity. The effectiveness of the method is high, but various risks are associated with it:
- impaired taste and tactile sensitivity of the tongue due to nerve damage;
- formation of hematitis and bleeding as a result of damage to large vessels;
- worsening of the disease as a result of displacement of the stone deeper into the duct;
- partial removal of stones.
In some situations, stones are located deep in the ducts or in the thickness of the gland. This position of the stones forces them to be removed along with the gland, which leads to serious consequences. The operation requires hospitalization of the patient and the use of anesthesia. As a result of surgery, there is a risk of the following complications:
- tongue nerve damage;
- vascular trauma leading to life-threatening bleeding;
- injury to the facial nerve, leading to impaired facial expressions;
- scar formation.
Modern medicine offers another method of treating salivary stone disease - sialoscopy. With this method, salivary gland stones are detected and removed from the ducts using endoscopes. This treatment takes place with virtually no damage to soft tissues. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia and does not require the patient to be in the hospital. After 30 minutes after the operation, the patient can be discharged from the hospital. During the operation, the doctor inserts small endoscopes into the ducts of the salivary glands, with the help of which the location and number of stones are determined, then they are removed from the ducts using special instruments. Sialoscopy has a number of advantages over other methods for a number of reasons, namely:
- low level of injuries;
- removing stones from different locations;
- use of local anesthesia;
- no risks associated with nerve injuries;
- complete preservation of the salivary gland.
Relapse and exacerbation
Re-formation of stones in the salivary glands after their removal occurs in 8-10% of cases. As a rule, the situation indicates the persistence of problems with the functioning of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders in the body.
The patient may need to consult with specialized specialists who can identify the existing disease leading to the growth of stones.
Often, a relapse of sialolithiasis entails irreversible changes in the structure of the glands, which sooner or later requires their removal.
Diagnosis of salivary gland stones
Suspected salivary gland stones are characterized by certain symptoms, but various tests are used to assess the shape and number of stones, as well as their location. The density of the mineralized stone is quite high, so it is quite clearly visible on x-rays. In some situations, an x-ray is not an effective diagnostic method due to the fact that a shadow may fall on the stone or the stone is not sufficiently mineralized. For clearer X-ray results, before starting the procedure, a special substance is injected into the duct, which makes it possible to view the structure and shape of the ducts; the places of ruptures are stones in the salivary gland.
In modern medicine, a diagnostic method in the form of computed tomography is used. With such an examination, stones of the salivary glands are determined, the size of which is less than one millimeter; it is also obvious how many stones are and where they are located. The disadvantage of the method is the inability to determine the condition of the soft tissues.
A clearer diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is used to determine the condition of soft tissues, but it is not able to show the number and location of stones.
Ultrasound examination is also used as diagnostics, but this method requires a highly qualified doctor.
The most accurate and clear method that gives a complete picture of the disease is sialoscopy. It involves inserting microscopic endoscopes into the salivary ducts, allowing doctors to see a real picture of the processes occurring inside the body.
Forecast
The experience of specialists shows that in 90% of cases of timely seeking professional help, the prognosis in the treatment of salivary stone disease is favorable, regardless of the chosen treatment method.
However, an important factor in a successful outcome and the absence of re-formation of stones is identifying the cause of the pathology and its elimination.
A visit to a specialist at an advanced stage of sialolithiasis most often ends with an operation to remove the salivary gland. In the future, this can lead to disruption of the oral microflora and problems with teeth and gums.
Treatment of the disease
Getting rid of salivary stone disease should be aimed at removing the stone and freeing the ducts. If the detected stone is small in size, it is necessary to begin stimulating it with salivary agents in order to provoke an attempt to remove it naturally. It is possible that a dentist can remove the stone and clean the gland without the use of additional instruments.
Rinse and principles of salivary diet
To try to remove the stone without surgery, you can suck on a slice of lemon. For the period of treatment, the patient is prescribed a special food filled with products that increase salivation: this is a diet using pickles, sauerkraut, fruit drinks made from sour berries - lingonberries, cranberries, viburnum. Due to the large amount of saliva, a small formation can be washed out of the gland on its own.
READ ALSO: causes and methods of treating increased salivation
As a treatment with folk remedies, rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, sage, eucalyptus - can be prescribed. The procedure should be carried out several times a day, as it is harmless, has a disinfecting effect and prevents the development of the disease and the formation of abscesses.
Small salivary gland stones can come out on their own, without additional intervention; they can be helped with special medications aimed at stimulating saliva production. The doctor can push the tumor toward the exit of the duct using massage. You can’t let the disease progress or let it take its course; even a harmless disease can over time give complications that affect the entire face.
If relapses occur during the treatment of salivary stone disease due to a person’s individual tendency to form stones, surgical removal and clearing of the ducts is prescribed. The operation is also indicated if, as a result of the unfavorable development of the disease, irreversible changes have occurred inside the glands. If the disease is accompanied by infection, additional antibiotics are prescribed, and in case of severe pain, painkillers are prescribed.
Surgical stone removal
To remove large stones, the doctor may decide to undergo surgery. Nowadays, the most popular method is sialoscopy; it is widely used in European countries and is considered the most effective.
First, the stone is found using very small instruments and visually fixed in the duct. Then the plug is grabbed with microforceps and pulled out, freeing the gland duct. The operation is performed mainly under local anesthesia, takes little time, and after its completion the patient can go home and return to their normal lifestyle.
The operation is not classified as complex, however, it does not exclude the development of consequences that require careful attention from a specialist. These include damage to the facial nerve and the formation of fistulas at the site of removed salivary gland stones.
Prevention
Preventing the development of pathology is much easier than eliminating its consequences, so dentists recommend adhering to the following rules:
- eat fully and balanced;
- drink purified drinking water;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- if there is a high amount of calcium in the body, avoid excessive consumption of foods rich in this element;
- give up bad habits such as drinking alcohol and smoking;
- undergo regular dental examinations.
The video contains additional information on the topic of the article.
Disease prevention
Of course, a radical method of preventing salivary stone disease is to remove its source, namely the salivary glands.
However, this is fraught with much more serious consequences, since it causes a malfunction in the functioning of the entire oral cavity, and also disrupts the usual environment of the necessary microflora.
Therefore, first of all, one should, if possible, exclude factors that contribute to the development of such a disease and monitor the recurrent activity of the disease.
You should prevent disorders in the body that can cause the formation of stones, and also follow the recommendations of your doctor. In addition, you need to monitor the occurrence of symptoms of the disease.
Sialadenitis is inflammation of the submandibular salivary gland. Patients with this diagnosis most often complain of tingling at the site of stone formation and pain while eating.
The formation of a parotid gland cyst is often associated with a violation of the flow or retreat of secretions. Less commonly, the appearance of a cyst is associated with benign or malignant formations.
Gingivitis is the most common disease associated with gum inflammation. This disease is accompanied by bleeding, swelling of the gums and their redness.
Reviews
The formation of stones in the salivary gland is a rather rare disease, but if it is not diagnosed in a timely manner and the initiation of therapeutic procedures, it can lead to serious consequences.
For this reason, dentists strongly recommend not to neglect regular preventive examinations, and not to self-medicate if any painful sensations occur.
If you have had to deal with the need to remove a mineral formation that has formed in the salivary gland, share with your readers the features of the operation and recovery period in the comments section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags salivary gland stone removal surgery
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Traditional methods
In addition to radical medical or surgical methods, treatment with folk remedies is also important for stones in the salivary gland.
It is worth understanding that her methods are applicable only at the initial stage of the disease or in the absence of complications, which can only be dealt with by a more radical method.
The most popular and effective folk recipes for getting rid of stones in the salivary gland are quite simple and do not require much effort.
To eliminate inflammation and pain, you should take 1 tsp. honey, 1 tsp. sunflower or olive oil, chicken protein and a small ampoule of novocaine (0.5%).
The resulting mixture must be used to treat the entire oral cavity, but special emphasis should be placed on the site of inflammation. After a few weeks, you should start using the plant - Siberian istod.
Roots of the Siberian origin
You need to take its roots and grind them, then take a few tablespoons of the resulting mass and pour a glass of room water. Bring the mixture to a boil in a water bath (no more than 40 minutes). After this, you should consume the resulting decoction not 2 tablespoons up to 4 times a day before meals.
When undergoing a course of treatment, both traditional and medicinal, you should refresh yourself with natural juices.
Particular preference should be given to birch. It fights the formation of stones, as well as the occurrence of the inflammatory process.
It is also necessary to alternately drink cabbage and carrot juices, as well as pine infusion. The essence of such drinks is to strengthen the immune system and enhance the body's protective functions. Echinacea tea is also great for this. In addition to drinking it, you should also rinse your mouth with it. It performs an antimicrobial function, which will quickly eliminate the problem.