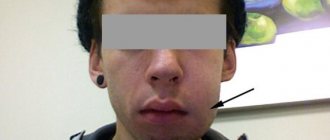
Drainage in dentistry is the drainage of excess fluids from a wound or socket of an extracted tooth.
Gum drainage is a fairly common practice in dentistry. A special device is fixed in the soft tissue incision and ensures the outflow of pus to avoid its accumulation in the wound. Many people don’t even know what drainage looks like, let alone why it is needed and what it is used for. Therefore, later in this article we will discuss in detail this method of preventing purulent-inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, analyze the indications and contraindications for its use, and also consider step by step the process of attaching the drainage structure.
Flux and great swelling. What to do after a gum incision?
My son has a lot of swelling and, of course, gumboil. Yesterday we went to the doctor, they opened his gum. We started taking the antibiotic doxycycline and rinsed with chlorhexidine, as the doctor who made the incision said.
But I want to ask you: the swelling is very large, almost up to the eye, what to do in this case? And how will the swelling go away? At least tell me approximately. And what else can you do?
The doctor made a relieving incision to relieve the exacerbation. Subsequently, the cause of the swelling must be determined and treated. The swelling should go away within 3-4 days. See your doctor again for an examination.
Contact phone number
Comments and reviews 32
My daughter (6 years old) had swollen gums, so we went to the dentist. The doctor removed the filling and the pus drained out. She prescribed rinsing the tooth cavity and Sulfadimethoxin tablets. We do everything and drink, but the tooth hurts and the gums are still swollen. On what day should the swelling on the gums subside, or should I go to the doctor again? Answer
An examination and a targeted x-ray are required. It is possible that the tooth cannot be treated and will need to be removed or the treatment plan adjusted. Everything is individual. Swelling of the gums may subside for 2 days or more. It is better to consult in person with a pediatric dentist. Answer
General dentist
The tooth is broken, only slightly sticking out, the cheek is swollen, i.e. gumboil has appeared. I assume that they will cut the gum. Tell me, how painful is it to cut the gum? I know that with gumboil, painkilling injections do not help much. And what actions will follow next? I'm very afraid. Answer
We advise you to read: Facial swelling after dexamethasone injections
At the moment, a large number of painkillers have appeared; it is not at all necessary that there will be severe pain. In any case, the longer you delay a visit to a specialist, the more difficult and painful the manipulations will be. It will be necessary to remove the causative tooth, open the purulent-necrotic process, create drainage for the outflow of contents, and a course of antibiotic therapy and other medications will be prescribed. Answer
General dentist
Help me decide if I should panic. The tooth was destroyed, it was rooted, it began to bother me, and the gums underneath it were swollen. I came to the hospital, the roots were removed, an incision was made, and a drain was installed. After a couple of hours, my cheek became swollen, and after two days the swelling subsided. Nothing hurts. But the gums were densely swollen and remained, even more than before removal, the drainage has not yet been removed. Is this the norm or not? Answer
Some swelling after removal is normal for some time; it is important to follow the recommendations of your doctor and arrive on time for your appointments. Maintain oral hygiene, rinse your mouth with an antiseptic (miramestin, chlorhixedine) after eating, unless there are contraindications to these drugs. Answer
General dentist
Hello, I went to a specialist with flux and acute pain, as a result of which two teeth were removed and the gums were opened, drainage was not installed (5 days ago). I feel a dull pain, the gums are swollen, there is a white coating in the sockets, is this normal? Answer
It is worth contacting a specialist again for an examination. The described picture is characteristic of a relapse (i.e., resumption of the inflammatory process). The presence of plaque on the tongue, swelling and pain indicates the presence of a purulent-inflammatory process. Answer
General dentist
Good afternoon Yesterday I was diagnosed with a flux, but no drainage was installed. The cheek tumor appeared in the morning and is accompanied by a dull pain and a temperature of 37.3. I went to the doctor, he looked at it and answered that this is how it should be. Is it so? How long? Why didn't they install drainage? Answer
Without a clinical examination it is impossible to make a clear judgment. Drainage may not be installed if the created outflow is sufficient. Typically, a low-grade fever may persist for several days, but swelling should decrease. Answer
Yesterday I was diagnosed with a flux, but no drainage was installed. The next morning, my cheek became swollen, accompanied by pain and a temperature of 37.3. Today I went to the doctor again. The doctor replied that it should be so. I take antibiotics. Why didn't the doctor install drainage, how long will the swelling and pain last? Answer
Drainage is installed according to indications, based on the initial clinical picture. Pain and swelling after opening the flux can last up to 7 days. You should follow all recommendations of your dentist. To relieve swelling, you can use antihistamines. Answer
General dentist
Today they cut my gums because I had gumboil. The tooth was not removed, after 1 hour a large amount of clot began to collect under my lip. I would say a very large number. Should it be like this? Answer
It is impossible to judge without a clinical examination. If drainage conditions are created, the exudate leaves the periapical tissue. Answer
General dentist
At the first consultation, the dentist prescribed Cifran 500, took it for 2 days, and the swelling did not go away. I had to open the gum. Another doctor prescribed Amoxicillin and took it for 2 days. What is better to drink now after opening the gumboil? Answer
It is impossible to change antibiotics from one to another without drinking the full course of treatment. Consult in person with a dental surgeon; opening the flux is not enough; it is necessary to eliminate the problem and cure the causative tooth. An antibiotic can be prescribed only after studying the history of life and disease. Answer
General dentist
Today I had surgery on my upper wisdom tooth. They removed the tooth, made an incision, and installed a drainage rubber. An hour after visiting the surgeon, a tumor appeared in the temple area. Within an hour I slept heavily and was barely visible. How does this relate to flux? The tumor did not reach the temple. Answer
Yes, this may be associated with an inflammatory process in the periapical tissues. If there is drainage, the exudate will exit through it. Answer
General dentist
I am treating a difficult tooth. After the gum incision, rinsing was prescribed. I rinsed my mouth with Chlorhexidine immediately after brushing my teeth. The tongue is numb and tingling. The night passed, but so did the feeling. Will this pass? Answer
Yes, the discomfort should go away within two days. Answer
Why is drainage installed in the gums and what is it even?
The first device designed to drain purulent masses from a wound was invented by the French surgeon Chassagnac. To do this, he proposed using simple glass or rubber tubes, through which excess fluid was removed from the patient’s tissues and cavities. For this purpose, the structure was installed for several days1. By now, a lot has changed: the tubes have become very thin and elastic. However, the main purpose of the design remains the same and includes the following functions:
- drainage does not allow the wound to heal prematurely,
- ensures removal of blood, pus, ichor from the wound,
- used to inject medication directly into infected tissue.
Drainage is quite often used in dentistry.
Obviously, many people are concerned about the question of how long drainage should be worn and how many days it is usually installed for. As a rule, the device is removed after the swelling subsides, which is the main sign of complete cleansing. For tissue healing, various drugs are prescribed, mainly for external use.
“I had a situation where the doctor installed a drainage after removing a tooth and opening the gumboil. This tiny piece of rubber fell out for me literally on the second day. To be honest, I didn’t even notice at first, I only saw it in the evening. But the swelling subsided, and after 3 days I felt much better. I just rinsed my mouth every two hours.”
Liliya R., Novorossiysk, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
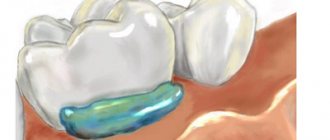
This is what drainage structures look like.
Currently, drainage structures are made of rubber and latex - they are absolutely moisture resistant, so they hold securely in the cut and do not allow it to close prematurely. In this case, part of the tube remains outside and ensures the outflow of pus without much discomfort for the patient.
We cut the flux and inserted drainage - My Dentist
Purulent inflammation of the gums - gumboil, fortunately, is not as common a disease as, for example, caries. It can develop due to tissue infection after tooth extraction or as a result of advanced pulpitis.
In the soft tissues next to the affected unit, swelling occurs, a purulent focus forms, and an incision in the gum and installation of a drainage system is required to remove the pus.
What is it, does it interfere with the healing of the incision and is it possible to rinse your mouth when a drainage is installed in the mouth?
Why install drainage?
In dentistry, drainage is used in the following cases:
- for tissue healing after removal of a problematic tooth;
- with alveolitis;
- after opening the flux;
- when an abscess or cyst forms;
- for administering medications directly into the wound.
READ ALSO: how to remove a tumor caused by flux?
The patient should not worry if his gums were cut and a drainage system was installed. Drainage is used to remove purulent exudate and ichor. If drainage is not installed, the opened source of infection will heal quite quickly after cleansing, but if the inflammatory process is not stopped, the formation of purulent masses will begin again. In this case, a new operation will inevitably be required.
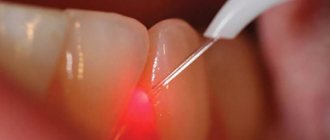
How is the drainage tube installed and what does it look like?
The drainage in the gum (look at the photo) looks like a small tube. Today, experts prefer drainage made of latex or rubber. Both materials are waterproof, due to which the device is retained in the infected tissue for a long time, is well tolerated by the patient and does not allow the wound to heal.
Before installing a drainage system, the dentist must first determine the location of the lesion and send the patient for an x-ray. During the examination, the depth and size of the abscess will be determined.
The doctor's next steps depend on the results of the x-ray. If the image confirms the destruction of the tooth root, the dentist must remove it, and then install a drainage tube into the open hole without an additional incision in the gum (see also: how to remove a tooth if its root remains in the gum?). In all other cases, the drainage procedure includes the following steps:
INTERESTING: what does a hole usually look like after tooth extraction?
- administering local anesthesia;
- direct dissection of the gum tissue with a scalpel and its treatment with an antiseptic;
- fixation of the drainage system.
In case of flux, the doctor will make a releasing incision, that is, opening the abscess, after which he will install a system for the outflow of pus.
The drainage tube can be felt with your finger or tongue, but it should not rub the inside of your cheek. An indicator of normality is the release of pus, ichor or clear fluid in the first days. If installed correctly, the patient should feel relief within the first 24 hours after the procedure.
How long does drainage last?
Usually the drainage remains in the gum for 2–4 days. At this time, the patient takes antibiotics and antiseptics.
If the patient’s cheek is swollen and the swelling does not disappear even after 3-4 days after drainage, a consultation with a dentist is necessary (we recommend reading: what to do if the cheek is swollen after a tooth extraction procedure?).
After examining the patient, he will either remove the tube and clean the wound again, or leave the drain for a few more days. Therefore, the question of when to remove the drain is very individual.
What if the tube falls out?
If the drain falls out, the patient should immediately consult a dentist. Returning the drainage system to the gum on its own can lead to wound infection and serious complications.
The doctor will examine the oral cavity and assess the situation. The absence of swelling after the drainage system falls out indicates the end of the process of outflow of pus - in this case, its re-installation is not required. If the swelling does not subside, the dentist will install the system into the gum again. Reasons that can cause a drainage tube to fall out include:
- improper brushing technique;
- excessive number or intensity of rinses;
- errors in the process of fixing the tube.
To maintain the drainage tube throughout the required period, the patient must adhere to certain rules. These include:
- intake of liquid and pureed food;
- drinking clean water;
- rest on the cheek opposite the affected area;
- exclusion of solid foods and sweets from the diet.
When will the incision heal?
Patients who are preparing to install a drainage system are always interested in how long it takes for the gums to heal after dissection (see also: how long does it normally take for gums to heal after tooth extraction and how long does it hurt?). On average, 1–2 months after the gum incision, it tightens. Complete tissue restoration can take up to six months. The incision healing process includes several stages:
- formation of a blood clot after surgery;
- maturation of new granulation tissue within 3–4 hours;
- epithelization over 7–10 days;
- wound regeneration 14–21 days after dissection;
- formation and compaction of young bone tissue over 2–4 months;
- fusion of tissue with the jawbone after 5–7 months.
After surgery, dentists give recommendations, adherence to which will promote tissue healing as quickly as possible. The most effective rules include:
- Postoperative diet. Many doctors focus on how long after tooth extraction and dissection of the gum tissue you can eat (we recommend reading: how many hours after tooth extraction can you eat?). Dentists allow you to eat food no earlier than 3-4 hours later. Doctors also talk about the benefits of dietary nutrition during this period.
- Postoperative regimen. Dentists strongly recommend that the patient avoid physical activity, going to the sauna and the gym after the incision has been made. It is also necessary to stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
READ ALSO: How many hours after tooth extraction can you drink alcohol?
Contraindications and complications of the procedure
Dentists exclude the procedure only in the most extreme cases. Contraindications include:
- disorders of the lymphatic system and blood clotting;
- predisposition to an allergic reaction to anesthetics.
Failure to comply with medical recommendations, the presence of infection or reduced immunity leads to complications. If a patient has a swollen cheek, pain, fever, or bleeding after his gum has been cut and a drainage system has been installed, he should immediately contact his dentist.
INTERESTING: what to do if your gums are swollen, but it doesn’t hurt?
When an immediate visit to the doctor is not possible, the patient can use antiseptics that will help temporarily relieve pain and relieve swelling.
You can rinse your mouth more often with a warm aqueous solution of soda, salt and iodine, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Chlorophyllipt, or lubricate the affected area with anti-inflammatory gels, for example Solcoseryl (we recommend reading: how to rinse the mouth after a tooth has been removed?).
It must be remembered that rinsing in the presence of a drainage system in the mouth should not be too intense.
Source:
After the gum incision, the swelling does not subside
Drainage is installed in the gums during purulent-infectious processes. It is indicated for periostitis (flux), cysts, granulomas, phlegmon, alveolitis, after tooth extraction complicated by inflammation, when it is necessary to inject medications directly into the periodontium.
The drainage is a thin hollow tube made of latex, silicone or rubber. It promotes the outflow of pus, ichor and blood. This dental instrument prevents premature healing of wound edges and the spread of pus.
After installation, care must be taken not to complicate healing. Dentists give patients the following 10 tips.
Rest after surgery
The first few hours after drainage installation are the most critical. During the procedure, the dental surgeon needs to administer anesthesia, cut the gum, pump out the pus, and perform an antiseptic treatment of the cavity. The patient is weakened by the infectious process and the operation itself. Therefore, upon returning home, it is recommended:
- sleep for a couple of hours;
- take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs after the anesthesia wears off - Nimesil, Nise, Nurofen, Ketanol;
- do not drink or eat for several hours.
Do not apply warm compresses
Heat increases inflammation and accelerates the spread of pus. Therefore, it is impossible to warm the affected area in any way. This applies to wet and dry hot compresses, tying the cheek with a scarf, and even drinking hot drinks.
But cold, on the contrary, relieves swelling. Such compresses are especially effective on the first day after surgery. A handkerchief soaked in water or ice wrapped in cloth is applied to the cheek for 10–15 minutes every 1–2 hours. However, you should not apply cold directly to the wound: this leads to vasospasm and infection.
Sleep on the opposite side
To prevent the drainage from moving and the cheek to become swollen, it is recommended to rest on the other side. It is best to sleep on your back or half-sitting. This way, blood will not flow to the wound and swelling will not appear.
Advice! If the patient turns around in his sleep, you can build a barricade of pillows.
To refuse from bad habits
The speed of regeneration is highly dependent on alcohol consumption and smoking. Alcohol and hot smoke slow down healing significantly. Therefore, cigarettes and alcoholic drinks are excluded for a while.
In addition, during treatment the patient takes medications that are incompatible with alcohol. And nicotine and tar are deposited on the enamel and provoke the development of tartar.
The most difficult thing for patients is to quit smoking. If it is difficult to quit a bad habit, it is recommended to eliminate cigarettes at least for the first day or, in extreme cases, for several hours after surgery. Anti-nicotine medications can help.
Stick to a diet
The diet while wearing drainage is special. Food should be:
- mushy or liquid consistency;
- room temperature;
- do not irritate the mucous membrane.
Possible gum damage also depends on how you eat. It is better to chew in small portions on the opposite side.
Additional Information! You can eat anything that does not injure the wound. Avoid hard, salty, smoked, spicy, sticky foods - they slow down healing and become clogged into the cavity.
Take prescribed medications
Postoperative treatment of purulent gum diseases is supplemented with drug therapy. Usually prescribed:
- antibiotics to relieve infection – most often “Lincomycin”, or analogue drugs “Tsifran”, “Amoxiclav”;
- anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain, heat, swelling - “Nimesil”, “Nurofen”, “Nise”, “Ibuprofen”;
- wound healing ointments to speed up healing - “Levomekol”, “Levomethyl”, “Metrogil Denta”.
Additional Information! Medications make recovery easier after drainage is installed. If you do not accept them, the process will be delayed. There is also a high chance of relapse of the disease.
Do antiseptic rinses
An important stage in the treatment of purulent periodontal pathologies is rinsing with antiseptic solutions. Apply:
- chlorhexidine;
- furatsilin;
- "Miramistin";
- "Stomatophyte";
- "Chlorophyllipt";
- solution of soda and salt;
- herbal infusions - chamomile, calendula, sage, oak bark.
The solution should be slightly warm. It is better to make oral baths than to rinse - under the pressure of the liquid you can wash the drainage. Procedures are carried out 3 to 5 times a day.
Maintain good oral hygiene
Brushing your teeth after any type of surgery is scary. Therefore, patients completely refuse hygiene or do not clean the operated area.
However, this situation is dangerous. Food debris and plaque accumulate in the oral cavity, are processed by bacteria and microbes, releasing toxins, and provoke inflammation.
It is necessary to maintain the highest quality oral hygiene. First, clean the interdental spaces with floss, then the crowns with a brush and paste, and complete the procedure by rinsing with an antiseptic.
Note! The teeth near the drainage are brushed very carefully so as not to displace the tube or injure the gums. You can use a soft bristle brush in this area.
Avoid physical activity
The patient is prohibited from doing anything that provokes bleeding:
- engage in any sport;
- lift weights;
- do difficult homework;
- to take a bath;
- go to the sauna and solarium;
- travel for a long time in vehicles or fly on airplanes.
Read also: Doxycycline for flux
Important! If you do not follow these recommendations, the wound will bleed, heal for a long time, and pus may spread into nearby tissues.
Avoid gum damage
If you handle cutlery, hygiene products carelessly, or get bumped or dropped, the drainage will not be level, will move, or will fall out prematurely. This is extremely undesirable, since the outflow of pus stops, and the edges of the wound begin to shrink.
Source: https://stomatolog161.ru/protezirovanie/razrezali-flyus-i-vstavili-drenazh.html
In what cases is drainage installation indicated?
So, first, let’s look at the situations in which a patient can have a drainage structure installed:
- flux - the appearance of a lump on the gum against the background of swelling of the soft tissues and cheeks, which is a direct consequence of the development of the pathological process - periostitis,
- the presence of an extensive wound after a complex tooth extraction - to speed up healing,
- alveolitis - inflammation of the tooth socket after its extraction,
- the need for systematic administration of the drug into infected tissues,
- the presence of pathogenic formations at the tooth root - the formation of a cyst or abscess.
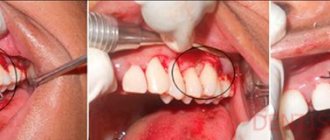
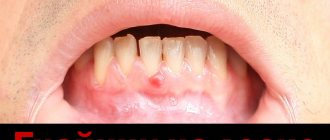
The photo shows flux on the gum.
Drainage is a reliable and proven way to remove pus and foreign fluids from wounds, tumors and inflamed areas of tissue. There is no need to be afraid of the procedure, since the installation is performed under local anesthesia.
Pain after removing drainage from the gums. Purpose of drainage in the gums
In dental practice, drainage in the gum is used to drain purulent fluid, as well as blood and serous discharge from areas of inflammation. The device looks like a synthetic tube made of materials resistant to high humidity.
The main indication for installing a drainage system on the gum is the presence of flux resulting from periostitis. This disease, characterized by an inflammatory process in the periosteum of the tooth, leads to redness and swelling of the tissue. If treatment is not timely, pus accumulates at the site of inflammation, it becomes noticeable and quite painful.
The patient often experiences an increase in body temperature and a sharp increase in pain when pressing on the tooth. Flux treatment is carried out using complex actions:
- taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate the infection;
- local application of gels and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions to relieve swelling;
- use of anesthetics to relieve pain.
The main indication for installing a drainage system on the gum is the presence of flux.
If the doctor diagnoses the rapid development of inflammation, the flux is opened to drain the pus. The operation site is treated with antiseptics, and then drainage is installed on it. Such actions lead to an improvement in the patient’s condition in the first hours after the procedure.
Features of installing drainage on the gum
Gum drainage is installed directly into the inflamed tissue through a surgical incision. It is not removed until the outflow of pus has completely stopped, which indicates the cessation of the development of inflammation.
Important! Installation of a drainage system after surgery is mandatory. Otherwise, the wound will quickly be overgrown with new tissue, and re-inflammation will develop in its place.
If the drainage tube falls out before treatment is completed, the patient will need to see a doctor to have it re-inserted. Failure to comply with this rule is fraught with the development of an abscess complication, which can be eliminated in more serious ways.
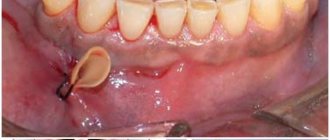
This is what the drainage tube looks like.
With adequate treatment of the flux, swelling and tenderness of the tissues disappear after a few days. After removing the drainage, the surgical site must be treated with antiseptics in the form of rinses and ointments until the swelling is completely eliminated.
Other indications for drainage installation
In addition to removing fluid during treatment of periostitis, drainage can be used for the same purpose after tooth extraction. For some time after this procedure, there is a high risk of developing inflammation, accompanied by the discharge of pus. Installing a drainage tube helps prevent infection of soft tissues and speed up their recovery.
The diversion system is also used to transport necessary medicinal substances to the site of inflammation. This method greatly simplifies the treatment of soft tissues in inaccessible places.
If signs of gumboil or other inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity are detected, a visit to the doctor should not be postponed. Modern methods of dental treatment are characterized by painlessness and speed, while attempts to eliminate the disease with folk remedies will only aggravate the situation.
The appearance of flux in the mouth is a painful and very unpleasant process that causes complications on the mucous membrane. Pus and inflammatory fluid accumulate in the gums, leading to severe swelling and discomfort.
The disease often ends with infection of internal organs and other problems.
To exclude them, the dentist tries to completely remove exudate with bacteria, for which he uses a special drainage on the gum.
In all branches of medicine, a system for the outflow of inflammatory fluid from incisions, called drainage, is widely used. Dentistry has perfectly adapted this find to eliminate the consequences of purulent wounds and fistulas in the oral cavity.
It is no secret that liquid contaminated with microorganisms, along with pus, can enter the lymphatic system and disperse throughout the body. This is fraught with diseases of the heart sac, pericarditis, pneumonia or kidney dysfunction.
The relationship between improper treatment of flux and extensive heart attack has been proven.
The French surgeon Chassignac was the first to invent and apply drainage during abdominal surgery. For a long time he searched for the ideal material that would not get wet from blood and pus and would respond well to treatment with an antiseptic. For many years it was a small tube made of natural rubber or glass; there were attempts to use lightweight plastic.
The work of a dentist is sometimes intricate, so new technologies have greatly improved drainage in the gums. This is not only a narrow tube of different sizes, but also the thinnest strips of latex, rubber, and flexible plastic. Modern developments do not irritate the mucous membrane, do not cause itching and are practically invisible in the wound. This allows the patient to eat and talk normally.
When to place drainage in the gum
Half of all visits to the dentist are for acute conditions: purulent lumps and fistulas on the mucous membrane, painful gumboil or ruptured cyst at the root of the tooth. The person suffers from discomfort and unpleasant sensations, complains of weakness and itching inside the jaw. The abscess often cannot break through the dense periodontal tissue and goes deeper, causing even more pain.
There are several situations when drainage is placed in the gum to remove accumulated exudate:
- periostitis of the jaw;
- severe alveolitis;
- consequences of wisdom tooth removal;
- the presence of a purulent abscess under the molar;
- swelling and voluminous edema of the mucous membrane.
Another reason for installing a strip in a wound is the need for constant delivery of the drug to the very middle of the gums under the periodontal tissue. With its help, the dentist rinses the roots of the teeth when a cyst with dangerous contents ruptures or injects an antibiotic into the fistula tract. This significantly speeds up treatment and reduces the risk of infection of internal organs.
How to install drainage
Usually, before such an operation, the doctor takes several detailed panoramic photographs of the jaw to determine the degree of growth of the abscess and see the fistula tracts inside the bone.
If the cause of the flux lies in the destruction of the tooth root, it will have to be removed. When a cyst with serous contents forms, the dentist drills out the molar and carefully removes the sac through the resulting hole.
Before continuing further therapy, it is necessary to install a diversion system:
- the doctor injects anesthesia, trying to numb the inflamed area as completely as possible;
- using a scalpel, makes a small incision in the mucous membrane;
- serous fluid comes out into the resulting hole, which should be removed using a vacuum without pressure or pressure;
- A miniature latex drainage is inserted into the wound;
- one end should “peek” out and not allow the wound to heal.
A properly installed drainage system should not cause much concern or increase jaw pain. It can be felt with your tongue or finger, but does not rub the inside of your cheek. It is ideal if the wound does not burn after inserting the tube. An important indicator of the quality work of a dentist is an improvement in the patient’s condition during the first 24 hours after the operation.
The doctor decides how long to keep the drainage in the gum based on pictures and visual examination. Usually 3–5 days are enough for complete removal of exudate.
During this period, whitish and yellow pus, ichor, or translucent discharge without inclusions may come out of the wound profusely.
The swelling begins to subside and the patient feels that it becomes easier for him to close his teeth and chew food. Gradually the redness gives way to a normal pink tint.
For the entire time the latex strip is implanted, the patient must follow the dentist’s recommendations: eat only ground liquid food, drink more clean water, do not chew hard foods and sweets.
You will have to sleep and rest lying down on the cheek opposite to the operated area. This will help maintain drainage and will not move it away from the inflamed area. In severe situations with a large amount of pus inside the periodontium, a person will have to visit a doctor every day.
He will clean the wound with an antiseptic and inject a dose of antibiotic into the incision.
Are there any contraindications
As with any dental procedure, the procedure in question also has a number of its limitations. Among the contraindications to fixing the drainage are problems with blood clotting - in such cases, doctors try to avoid dissecting soft tissues altogether. It will also be very difficult to carry out this procedure if the patient suffers from an allergy to anesthetics.
Purulent and bloody discharge must be removed from the wound. Without this simple device it is simply impossible to cure most diseases. One way or another, the procedure must be carried out, since this is a mandatory prevention of the development of sepsis - a general infection of the body.
Indications and contraindications
Why and in what cases is the gum opened to install drainage?
- the appearance of flux, that is, when the patient’s cheek is swollen, which indicates a pathological process called periostitis;
- in order to accelerate tissue healing after severe cases of tooth extraction;
- with alveolitis;
- when it is necessary to periodically inject medications into the wound, which is also done using drainage;
- if pathogenic formations are detected in the root zone of the tooth, for example, cysts or abscesses.
In rare cases, this procedure will not work:
- if the patient has problems with blood clotting, then doctors try to avoid any incisions if possible;
- If you have an allergic reaction to the anesthetics administered, complications may also arise.
But in any case, the procedure for removing purulent or bloody discharge must be carried out, since without this it is almost impossible to cure most diseases. One way or another, the doctor must find a way to do this in order to prevent sepsis.
Description of installation procedure
Everything is clear with the main indications and contraindications for fixing the drainage – it’s time to find out how the structure is installed and how many days it is worn. Below is a step-by-step description of the procedure:
- To begin with, the dentist conducts a visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity, determines the affected area,
- after this, an x-ray may be required so that the doctor can assess a more complete picture, determine the exact location and extent of the spread of suppuration - make the correct diagnosis,
- the doctor injects an anesthetic, after which he makes a small incision on the gum in the area of the affected tissue,
- then he mechanically thoroughly cleans the cavity, injects an antiseptic and antibiotic inside if necessary,
- after this, a latex tube is attached, through which excess liquids will be drained out.
This is what drainage installed in the gum looks like.
This is a generalized diagram of the procedure, which can be changed depending on the treatment performed previously. So, for example, after extracting a wisdom tooth, there is no need to cut the gum tissue - it is enough to fix the drainage in the freed socket. Now about how long to hold and when to remove the device. It is usually fixed for 3-5 days, but the exact timing will depend on the rate of fluid removal. As a rule, the structure is left until the swelling has completely subsided and the infection has been eliminated. If swelling lasts too long, you should definitely see a doctor.
Cheek tumor
Hello. After filling three canals of the 16th tooth. A temporary filling was placed. The tooth ached all day. By evening my cheek was swollen. In the morning, my cheek was swollen even more. I came to the dentist. They cut the gum and installed drainage. They said that the pus did not have time to collect. washed. And they told me to come in a day. The pain doesn't stop. 8 hours have passed since the gum incision. The tumor did not go down. I take ketorol and amoxicillin. Tell me, how long will this last? And is this a normal reaction?
Dentist's answer:
Hello! After the incision, the swelling does not subside immediately, but only within 3-5 days, because the incision, in itself, is an additional injury. It may be that in your situation the incision will not bring a good result. Often, to relieve inflammation, it is necessary to re-treat the canals.
How many days it takes depends on the severity of the tumor and the reason for its appearance. On average, swelling subsides in 2 to 5 days, and full recovery takes from 2 to 4 weeks.
There are two options for the development of flux or, as dentists call it,. In one case, it appears as a complication after removal of destroyed units. In the second, it occurs against the background of inflammatory processes and becomes a reason for extraction. After treatment of both diseases, standard postoperative swelling occurs, which should be distinguished from complications.
Flux, which appeared as an independent disease and led to forced treatment or tooth extraction, develops due to an inflammatory process outside the root apex. As a result, a cavity with purulent exudate appears. Trying to break through, it forms an abscess on the gum. Pathology develops due to:
- advanced caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- poor quality endodontic treatment;
- injuries;
- with inflammation of the gums.
Elimination of periostitis is possible in two ways:
- Without tooth extraction
- using conservative therapy. Repeated endodontic treatment is carried out, ensuring the outflow of pus through the root canals or an incision in the mucosa. If necessary, resection of the root apex is performed - it is cut off if it is impossible to pass through the upper third of the canal.- Through extraction.
Shown when the unit is heavily damaged. It is removed, the wound is cleaned of purulent contents and antiseptic treatment is carried out.
On average, swelling subsides in 2 to 5 days.
Additional Information!
In both options
, after dental treatment, medications are prescribed - anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, antibiotics, wound healing ointments, disinfecting solutions.
The swelling will not go away immediately. In the first day it may even increase - this is considered a normal reaction of the body to intervention. How many days the gumboil will last on the cheek depends on the degree of neglect of the disease. As a rule, the main inflammation goes away within 72 hours. And the wound heals completely within 3 weeks.
If the swelling does not go away within three days, the hyperemia of the mucous membrane increases, and severe pain occurs, you should consult a dentist. Such symptoms indicate the development of complications. They are possible if the patient did not follow the postoperative recommendations, the doctor did not completely clear the hole of pus or left fragments or tooth roots in it.
How to remove drainage yourself and is it possible to do it?
Despite the fact that very small tubes are used today, they are still felt in the mouth and cause some discomfort to the patient. Many people complain of difficulties eating and pronouncing sounds. Therefore, the first thing that worries most patients in such a situation is when the drainage can be removed, how to remove it yourself, and whether it hurts to deliver this tube yourself. Of course, it is better to entrust this to a doctor who knows exactly how to correctly remove the structure from the incision and how to change it, if necessary. However, the patient himself can do this; the doctor warns him about this immediately after the installation is completed and gives recommendations on how to remove the structure if necessary. In addition, the drainage often falls out on its own. Here are some important tips on how to carry out the procedure yourself:
- wash your hands thoroughly and treat them with a disinfectant, you can use special dental gloves,
- rinse your mouth with an antiseptic to disinfect the tissue surrounding the wound,
- stand in front of the mirror and gently grab the outer part of the strip with your fingers, then carefully pull it towards you.
After removal, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic.
Does it hurt to remove drainage from the gums? In fact, this is a simple procedure, which, however, can cause some pain and cause bleeding. Experts advise rinsing your mouth with some antiseptic for some time after removing the drainage. If bleeding does not stop within more than 2 hours after removing the strip, you should urgently go to the doctor.
Drainage in a child’s gums: why is it installed, when and how to remove it?
When treating dental diseases, a wide variety of methods and means are used to help eliminate pathological processes as quickly and effectively as possible.
But drainage in a child’s gums, which is installed by a doctor, often worries parents. Will your child be in pain, will he be able to eat with the device in his mouth, how should it be cared for, and how soon can it be removed.
Purpose of drainage
Drainage (diversion system) is an indispensable tool for draining pus and other pathological fluid. Installed in a fistula tract or in a surgical incision, it does not allow pus to accumulate in the tissues or spread to surrounding areas and at the same time provides free access to the pathological focus.
Thus, drainage in the gums of a child allows for regular washing of the cavity of the cyst or abscess with antiseptic and antibacterial solutions. Thanks to this, the effectiveness of treatment is significantly increased, and the drug load on the body is reduced - such washings make it possible in some cases to do without taking medications internally.
Another important property of drainage is that it prevents tissue from overgrowing before the inflammatory or infectious process stops. Otherwise, re-accumulation of pus and corresponding complications almost always begin.
If you are concerned about whether it is painful to remove the drainage from the gums and how unpleasant it is to “wear” it, you should understand that pain and other unpleasant sensations are caused not by the drainage device, but by the disease that made it necessary to install the drainage system. The drainage tube itself is made of silicone or medical rubber, which does not injure the gums or oral mucosa, so there is no need to worry about its possible harm to the health or well-being of the child.
Features of oral care during drainage
The duration of drainage is usually 2-5 days. With qualified and timely treatment, within a day the swelling in the gum and/or cheek area decreases, and the pain becomes less and less pronounced. But some everyday activities may affect the effectiveness of treatment, so you should carefully monitor the following:
- It is advisable to replace brushing your teeth with regular rinsing of the oral cavity. The child should take the antiseptic solution prescribed by the doctor into his mouth and “roll” it with his tongue throughout the mouth. This procedure must be carried out every time after meals and several times outside meals.
- Before eating and rinsing, you should close the outlet of the drainage tube with a turunda made of sterile cotton wool. A tightly rolled “stick” of this material should be inserted at one end into the drainage tube so that the free end can be easily picked up with fingers or tweezers and removed. When removing the turunda, hold the drainage so as not to remove it along with the cotton wool. These actions will protect the cavity into which the drainage system is inserted from the ingress of food debris, soft deposits and bacteria.
- While wearing the diversion system, any rough and dry food should be excluded from the child’s diet. Preferred dishes are pureed porridges, vegetable, fruit, berry, meat purees, broths and other liquid foods. If a drain is installed in the front of the mouth, it is advisable to switch the child completely to liquid food, which he can consume through a straw.
Accidental loss of drainage: what to do?
The drainage system is not secured to the gum by anything - it is held in place by the pressure of soft tissue on its walls. Therefore, it may fall out during a conversation, eating, or simply because inflammation and swelling have begun to go away, and the tube is no longer held tightly in place.
If the drainage has fallen out of your child’s gums, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, who will insert a new drainage system. It is important not to self-medicate and not to try to replace a fallen tube. It must be installed in a sterile environment in a dental or procedure room so that a pre-existing condition is not complicated by a secondary infection.
Remember that washing the fallen drain with antiseptics is not enough before reinstalling it - do not risk the child’s health. And even more so, do not decide instead of a doctor that the diversion system is no longer needed, and further recovery will be completely manageable without it. This can lead to serious consequences, including infection of the entire body through the bloodstream.
Removing the drain
When to remove the drainage from the child’s gums, the attending physician decides during a personal examination. But in some cases, your dentist may set an end date for wearing the diverter system, which you can remove at home.
The “operation” itself does not present any difficulties - the drainage tube is removed in one movement and does not require special skills. But it is important to comply with all requirements for asepsis and antisepsis before, during and after drainage removal:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and treat your fingers (including your nails and under your nails) with chlorhexidine solution. If you plan to use tweezers, the metal tool should be boiled in clean water for 10-15 minutes, and the plastic one should be treated with chlorhexidine (it is best to pour the solution into a small container and leave the tweezers in the solution for 5-7 minutes).
- With your hands treated, make a swab rolled from a sterile gauze pad. To do this, fold the edges of the napkin inward toward the center and fold it twice more. In a correctly rolled tampon, the edges of the gauze from which the threads are separated are completely hidden inside.
- Have your child sit in front of the light source so that you can clearly see the drainage tube. Grab the tip of the tube with your fingers and twist it slightly clockwise or counterclockwise and gently pull it up. The material from which the drainage system is made is bio-inert - it does not “grow” to the tissues, so the drainage is quite easy to remove.
- After you have succeeded in removing the drainage from the child’s gum, immediately apply the prepared sterile swab to the gum and ask the child to clench his jaw tightly.
Removing a drain yourself should only be done as a last resort, or if your doctor has given you permission to do so. In any case, after removing the drainage system, you should visit your dentist, who should confirm that healing and recovery are going according to plan.
Source: https://vzubkah.com/drenazh-v-desne.html
The drainage has fallen out - what to do in such a situation
We figured out how to remove the drain yourself, but what to do if the device fell out on the first day or before the swelling subsided. In this case, you need to rush to a specialist. The problem may be an initially weak fixation of the product in the gum. Remember: when a strip falls out on its own, you absolutely cannot put it back in place on your own - this can lead to relapse and the development of serious complications.
If the swelling has completely subsided and there is no more pus, you don’t have to worry about the drainage tube falling out. At first, it is worth observing the condition of the oral cavity. If the tissue does not begin to swell again, there is nothing to worry about.
Recommendations after the procedure
The presence of a drainage system in the gums imposes some restrictions on the usual way of life. As long as the structure lasts, the patient will have to adhere to simple rules:
- Many people are interested in the question of how long after the procedure you can start eating. So, you can eat only after three hours,
- for about 3 days after treatment, you should not open your mouth too wide, eat hard or too hot food,
- you should temporarily avoid physical activity, visiting saunas and relaxing in a hot bath,
- It’s better to try to completely give up alcohol and smoking for at least a week.
You should avoid physical activity.
If your cheek is swollen, the main thing is not to apply hot compresses to it, and do not try to treat the wound with iodine or brilliant green. Heat can cause the active development of pathological processes, due to which the condition will sharply worsen and inflammation will return with renewed vigor.
After the gum incision, the swelling does not subside
If you are planning an implantation or removal of a cyst, be prepared for the fact that the dentist will have to cut into the gum. When an unerupted or incompletely erupted wisdom tooth is removed from the gums, an incision is also inevitable.
After surgery, complications such as swelling, bleeding, and aching pain are possible. The reasons include decreased immunity, infection in the mouth, or improper care during the postoperative period. Therefore, the best thing you can do is to remember and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Tumor (edema)
As a rule, swelling occurs after the removal of a wisdom tooth with an incision in the gum. This is a typical reaction of the body to surgery. However, in some cases, the tumor reaches gigantic proportions, and the cheek or lip swells greatly. This is a clear sign of alveolitis (inflammation of the socket); in this case, it is necessary to urgently visit your doctor!
Heat
An increase in temperature to 37–37.5 degrees is also considered normal. However, if the thermometer shows more than 38 degrees, then most likely an inflammatory process has begun. You need to contact the doctor who performed the operation. You may be prescribed a course of antibiotics.
Pain occurs immediately after the anesthetic wears off (after an hour and a half). Soreness is a reaction to damage to nerve endings with a surgical scalpel. To temporarily alleviate the condition, it is recommended to take a tablet of Ketanov, Pentalgin or Analgin. The pain will gradually subside after 3-4 days.
Bleeding
Excessive bleeding may occur due to damage to the vessel during the injection of the anesthetic, increased capillary fragility, or high blood pressure in the patient.
What stops bleeding? Immediately after the gum incision, the doctor applies a hemostatic sponge and, when the bleeding stops completely, sutures the wound.
But if this doesn't help, call an ambulance.
Flux is an inflammation of the periosteum (dense tissue covering the jaw bone). This complication is a consequence of infection of the gums, after which the infection penetrates deeper and deeper, affecting the periosteum. In the area of inflammation, pus accumulates and a painful lump forms. With flux, a loosening incision is made in the gum (opening the abscess) and drainage is installed to drain the purulent exudate.
How gums heal
After surgery, connections between tissues and cells are disrupted. The healing process is the formation of new physiological and anatomical connections between them.
- Formation of a blood clot - forms within 5-10 minutes after surgery and serves as a protective barrier against infection and harmful microbes.
- Formation of granulation tissue - within 3-4 hours the production of granulation tissue (young connective tissue) begins.
- Epithelization and collagen formation lasts up to 7–10 days and is sometimes accompanied by slight itching.
- Regeneration and maturation - the wound “heals” after 2–3 weeks, but complete healing of the fibers requires several months.
What to do after the procedure
- when you arrive home, you just need to lie down and relax;
- you cannot eat or drink for 3 hours;
- for 3 days after surgery, you should not open your mouth too wide, or eat hard or hot foods;
- limit emotional and physical stress;
- hot baths, visiting the sauna, and exercising in the gym are prohibited;
- It is advisable to completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a week.
Remember: under no circumstances should you apply hot compresses or burn the wound with alcohol, iodine or brilliant green. It will only get worse!
A dental surgeon can prescribe applications of wound healing and antimicrobial ointments (Cholisal, Solcoseryl, Stomatofit, etc.). To strengthen general immunity, you can take immunomodulating agents and multivitamin complexes.
How to rinse your gums after an incision?
Any rinsing should be done strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Usually the doctor recommends rinsing the mouth with a saline solution, a decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage (at room temperature), they have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
Ready-made antiseptic solutions from the pharmacy - Chlorhexidine or Miramistin - are also suitable.
If you feel that gum inflammation has begun after surgery, or notice pus discharge, do not delay your visit to the dentist! In emergency cases, you can contact the doctor on duty at the state clinic; he can even see you at night. You can find the nearest institution on our website.
We also invite you to read the materials about complications after implantation.
Flux and great swelling. What to do after a gum incision?
My son has a lot of swelling and, of course, gumboil. Yesterday we went to the doctor, they opened his gum. We started taking the antibiotic doxycycline and rinsed with chlorhexidine, as the doctor who made the incision said.
But I want to ask you: the swelling is very large, almost up to the eye, what to do in this case? And how will the swelling go away? At least tell me approximately. And what else can you do?
The doctor made a relieving incision to relieve the exacerbation. Subsequently, the cause of the swelling must be determined and treated. The swelling should go away within 3-4 days. See your doctor again for an examination.
Contact phone number
Source: https://askdent.ru/lechenie/desny/posle-razreza-desny-opuhol-ne-spadaet.html
Healing time for soft tissue after an incision
After an incision in the gums, a person may experience unpleasant and painful sensations for quite a long time. Experts in the field of periodontology say that in most cases, complete tissue healing can only be expected after 1.5-2 months. In other situations, for example, when a wisdom tooth is removed, the recovery process can take a longer period.
However, this does not mean that during this entire time the patient will suffer from pain. It’s just that after such soft tissue damage, minor discomfort persists for quite a long time. To guarantee victory over the infection, specialists prescribe a course of antibiotics.
- Wolf G.F., Rateitskhak E.M. Periodontology, 2008.