Causes
There are many reasons for the appearance of tumors on the lips, including:
- mechanical injuries (bruises, cuts, from contact with prostheses, implants);
- genetic predisposition;
- infection with viruses and fungi;
- smoking, alcoholism, unhealthy lifestyle;
- dental diseases (cheilitis, stomatitis);
- chemical or thermal effects;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- allergic reaction to foods, medications, household chemicals, cosmetics;
- failure to comply with oral hygiene rules;
- HIV – infection;
- malocclusion;
- changes in hormone levels in the body.
To correctly determine the nature of the disease in the form of a tubercle on the lip, you should first consult a dentist.
Symptoms
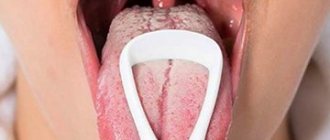
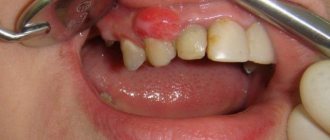
A dense lump forms on the inner or outer part of the lip, maybe with pus, watery, keratinized, bleeding. Some types form in the form of a scar, on which a growth then appears.
Basically, bumps on the lips are painless at the initial stage, causing only discomfort when eating or talking, and also disrupt the aesthetics of the face. With a hemangioma, a lump develops from a small spot. When examined and palpated, it will be hard. When pressing, exudate may be released and pain may occur.
Variety of symptoms on the inside of the lip
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient needs to visit a dentist, who will examine the oral cavity, palpate the lump and collect an anamnesis (medical history).
After establishing a preliminary diagnosis of the problem, the dentist directs the patient to do:
- Ultrasound to determine the size and structure of the tumor;
- puncture to determine what liquid is inside;
- probing and sialography, computed tomography, which will reveal the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant), the presence of stones, the condition of the ducts of the salivary glands;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine for the presence of viruses and bacteria.
It is important not to ignore the appearance of growths on the lips, and at the first appearance of them, even if the problem seems minor, contact a dentist who will help diagnose and eliminate the bump.
Diagnostics does not always use all methods; they differ for different diseases:
- Ultrasound, sialography, puncture, probing are done for retention cysts, mucoceles;
- Ultrasound and puncture for fibroma, nevus, hemangioma, lip cancer;
- for herpes and furunculosis, an initial examination and palpation by a dentist is sufficient;
- with advanced furunculosis, puncture of the contents from the lump is added.
Based on the obtained tests, the doctor draws up a drug treatment plan or prepares the patient for surgery.
Blood ball in the mouth: what is it and what to do with it
The oral mucosa is an important component of the human body, which consists of different tissues that perform protective, absorption and excretory functions. It is involved in thermoregulation and is responsible for the perception of the taste of food. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the oral mucosa and, if there are changes in the integrity of the epithelium, consult a doctor.
Characteristics of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
The mucous membrane protects the entire body from the negative influence of the environment, from harmful microorganisms, various types of pollution, and also has a fairly high level of regeneration. If blood blisters regularly appear on the oral mucosa, then you should take this signal seriously and take action.
A bloody ball in the mouth is a hematoma (bruise), which is characterized by the accumulation of blood in a certain place in the oral cavity. The appearance of bloody blisters is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs as a result of trauma to the capillaries and thin vessels of the mucous membrane.
A blister on the mucous membrane may contain clear serous fluid without the presence of blood. This means that the vessels were not damaged and the resulting wound is superficial. Such blisters on the mucous membrane heal much faster. The presence of blood in the bladder indicates a deep injury and a longer period of healing and blood resorption.
The main causes of a blood blister
The general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa usually indicates the level of health of the body. Often, by examining the appearance of the oral mucosa and blisters, the doctor makes a final diagnosis.
After all, the symptoms of most infectious, bacterial, chronic, and acute processes that occur in the body are associated with changes in the integrity and color of the oral mucosa.
Therefore, it is important to understand the main reasons that cause blood blisters to appear in the mouth.
Multiple blood blisters on the oral mucosa occur with stomatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
The cause of the sudden appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth is damage to the mucous membrane.
There are the following types of injuries to the oral cavity:
- mechanical injury.
The cause may be various objects, solid food, biting the cheek; - chemical injury.
It occurs due to the consumption of spicy, salty foods, and exposure to chemicals on the mucous membrane. This irritates the delicate oral mucosa and causes injury; - thermal injuries.
Their appearance is provoked by too cold or hot food or drinks.
The mechanism of formation of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
Bloody blisters in the mouth in most cases are not life-threatening. They are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. When microtrauma occurs, harmful microorganisms attack the damaged area.
After this, a number of responses are activated in the human body:
- The immune system is activated. Monocytes and leukocytes, as well as macrophages, instantly arrive at the damaged area, attacking the harmful pathogen and quickly destroying it.
- Immune cells die. This is a signal for other cells and substances are released in the affected area that are mediators of inflammation of the mucous membrane - serotonin, histamine and bradykinin.
- These substances cause a strong spasm of the circulatory system and the outflow of blood is hampered. After the spasm is relieved, all accumulated blood immediately flows to the site of inflammation. It moves at high speed and under pressure. A detachment of the mucous membrane occurs in the mouth, and a bloody blister appears.
Treatment of bloody blisters in the mouth
A blood blister in the mouth is only part of the body’s defense reaction and goes away on its own within a week.
If this does not happen, then you should consult a doctor to rule out serious diseases of the body and neoplasms.
He will be able to make an accurate diagnosis after a thorough examination, studying the data of clinical tests and histology. After this, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment.
The process of treating a blood bladder in the oral cavity is closely related to the cause of its appearance and therefore treatment depends on several important factors:
- volume of surface damage;
- degree of filling with serous fluid;
- the nature of the contents of the blood bladder;
- location.
The volume and nature of the damaged surface is important when prescribing treatment for a bloody blister in the oral cavity. After all, the larger the volume of the blood bladder, the worse it heals and resolves.
Treatment of a large bladder with blood can develop from conservative treatment into surgical intervention. Small blood blisters resolve quickly and do not require special treatment.
A blood blister on the oral mucosa must be carefully examined to exclude hemangioma and vascular tumor. A doctor can do this when examining the oral cavity. Hemangioma is sometimes left without much treatment if it does not grow. If it grows rapidly, it should be removed surgically.
Many bloody blisters in the mouth can be associated with syphilis, sometimes pemphigus.
Small red blisters on, under, or on the side of the tongue may indicate the presence of glossitis, an inflammation of the surface of the tongue caused by harmful microorganisms.
Treatment will consist of treating and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions and eliminating the disease, which was the main cause of the appearance of blood blisters.
It is not necessary to treat a bloody blister in the mouth if it is isolated and does not bother the person. If it interferes, the doctor performs a puncture after a thorough examination and diagnosis.
To strengthen the walls of blood vessels and the immune system, vitamins E, A, C, K, B vitamins, and multivitamin complexes are prescribed.
The appearance of bloody blisters in the mouth indicates an oral injury or is a symptom of a disease in the body. Only a doctor can establish the true cause of this formation and prescribe effective treatment. If you seek qualified help in time, this disease will not cause discomfort and will not lead to serious consequences.
Source: https://www.LiderStom.ru/articles/zdorove-zubov-i-desen/krovyanoy-sharik-vo-rtu-chto-eto-i-chto-s-nim-delat/
What diseases are hidden under this symptom?
- A retention cyst is a benign ball-shaped tumor that is formed as a result of blockage of the salivary glands. Causes painful sensations. Such a cyst grows quite quickly up to 2 cm and should be operated on, since this tumor tends to become malignant over time;
- Mucous cyst (Mucocele) - most often formed after biting the lip on the inside, it becomes a characteristic blue color, as if caused by an injury, and does not cause serious pain. At the base of the cone is salivary fluid, its size can be up to 1 cm;
- Lip cancer most often begins on the upper layer of the lip - the red border, and as it grows it goes deeper into the lip mucosa. There are several forms;
- Papilloma is a benign tumor that does not cause pain; it requires removal; in advanced cases, it causes pain and develops into a malignant one. Looks like a white growth;
- Hyperkeratosis (Dyskeratosis) is old, undead cells that form a thick keratinized layer that gradually thickens and takes on the shape of a lump;
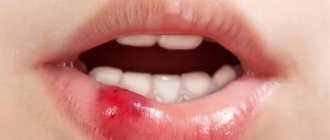
- Herpes manifests itself in the form of small watery blisters, causing mild pain and a desire to scratch. It can form both on the inside and outside of the lip;
- Fibroma - occurs on the mucous membrane, a benign tumor. It comes in soft and hard forms, in the form of a red bump or keratinized area. It does not cause any symptoms or pain; it can be smooth or lumpy. It grows slowly and can be detected by examining the oral cavity or by palpation;
- Hemangioma is a benign tumor consisting mainly of blood vessels. Most often it is flat, but in some cases it is in the form of a ball, with a blue, red or purple tint. Swells and in some cases, with deep penetration, causes pain;
- Furunculosis is inflammatory in nature and affects the sebaceous glands in the form of a round abscess. Can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus. Occurs below or above the lip. Furunculosis should be treated promptly or serious complications will subsequently arise;
- Fungal infections of the lip mucosa appear less frequently than in the oral cavity. In some cases, small balls form on the mucous membrane. There is pain, dryness, burning, itching - caused by Candida fungi;
- Nevus (birthmark, mole) is a compaction in the form of a dark pigmented spot, sometimes swollen. It can grow, quickly capturing tissues around the lips up to 10 cm. It has different forms and the nature of its occurrence. In some cases, removal is required, but some people live their whole lives with a nevus, without additional problems, putting up with the aesthetic defect;
- Allergic reaction to medications, food or after dental procedures. It goes away quickly as soon as the source of the allergy is eliminated. Causes itching, redness, reaches 1 cm;
- Keraoacanthoma is a benign formation that can develop into cancer if left untreated. A formation with a depression filled with horny mass, which is removed to reach the base. Does not cause pain. In case of deformation, it is important to quickly decide to visit a surgeon;
- Reaction to mechanical damage , for example, after piercing or other traumatic punctures. It appears in the form of a ball, sometimes with a “grain” inside, and can cause burning, itching, and bleeding if disturbed. Such bumps go away quickly when using absorbable ointments.
Symptoms of seals on the lip
A lump on the lip inside the photo of which is shown below causes discomfort in its owner and interferes with talking and eating. In diameter it sometimes reaches two centimeters or more. The formation is solid to the touch, and with mechanical damage, pressure, in particular chewing food, a whitish-yellow liquid or reddish discharge may flow out of it if the vessels inside are damaged.
It is not recommended to engage in self-treatment, squeezing, or picking or smearing swellings and bumps on the lip.
A lump inside the lip may not only have a cystic nature of the tumor. When you press it during the test, it goes deeper inside and returns to its place, which is also the behavior of formations associated with the glandular epithelium. Such tumors are formed as a result of increased activity of the endocrine system in infancy or adolescence.
When the cyst empties, refilling occurs in the capsule, which serves as a shell. It has mobility, elasticity, and is little surrounded by soft tissue. Pain occurs in case of inflammation. The cyst often has one chamber, but sometimes there are many. Diagnosis is carried out using canal probing to determine the width of the duct and identify salivary stones.
A lump on the lip is not only an aesthetic problem. The resulting growths cause discomfort, difficulty speaking, and eating. They can also signal the manifestation of a disease.
If a lump appears on the lip, there are two possible approaches: the first - the person does not think that the growth needs to be treated and puts off seeing a doctor, the second - begins to study it, turn out the lip, bite - and damages the cyst.
To clarify the nature of the origin of the neoplasm, you need to consult a doctor. A local therapist, dermatologist, or dentist can provide advice. Only a doctor will be able to collect an anamnesis, explain why a lump appeared on the lip and cure it. The specialist examines the likelihood of a viral origin of the formation. About 90% of the population is infected with the herpes virus, which is integrated into the genetic apparatus of the cell and manifests itself in relapses.
Viruses
A rash of grouped small painful blisters is accompanied by itching, burning, and fever. The localization site first swells and the bump that appears on the lip looks inflamed. Afterwards, small blisters appear filled with transparent contents. After a few days they burst.
Routes of infection: airborne, birth, sexual, contact. The extremely resilient virus is transmitted by talking, sneezing, or shaking hands. It is able to be encapsulated on personal household items (towel, handkerchief, toothbrush) and move to the next recipient.
In addition to common symptoms, atypical ones are possible. Clinical manifestations: precursors in the form of burning, tingling, itching. A lump may appear on the inside of the lip. Classic signs (bubbles) may not come out. In cases of HSV diagnosis, even vague classical symptoms, without blisters, are treated with the usual protocol.
A lump on the inside of the lip does not necessarily indicate herpes. The main function of the epithelium and mucosa is protection. Damage to this system opens the door for pathogenic microorganisms to enter. Chronic phenomena of this nature can develop into systemic diseases or, in especially severe cases, become malignant. Trauma and microtrauma of soft tissues provoke a lump that appears on the lip.
The outer, outer surface is covered with several layers of keratinized epithelial tissue, inside of which there are sweat, sebaceous glands with ducts and hair follicles. In the intermediate part, the transition of squamous epithelium to the mucous membrane occurs. The ducts of the mixed labial glands (sometimes called minor salivary glands) are located on the mucosa.
What can cause injury:
- hit;
- inflammation;
- habit of biting lips with teeth;
- smoking (chronic burn);
- wearing braces;
- dentures;
- piercing
The cyst manifests itself as a scar on which a dense, solid, hard ball develops. There is no sensation of pain, only discomfort when talking and eating. Over time, the ball becomes damaged and develops into inflammation, abscesses, and purulent lesions. If the neoplasm is in the nature of tumors, the following manifestations are observed:
- papillomas;
- lichens with erosions;
- cheiloses.
When a white lump appears on the lower or upper lip, a hemangioma is diagnosed. It appears in the first days of birth in the form of a spot, which will begin to increase over time. In the older generation, age-related hemangiomas occur, but the symptoms do not differ. The diameter of the cone is from 2 cm, its color is red, white, milky.
For the initial diagnosis of a lump on the lip, the doctor collects an anamnesis.
During diagnosis, the doctor must collect an anamnesis. This action will help you find out why the problem may be occurring. The doctor also examines the appearance of the formation, location (on the upper or lower lip). After filling out the relevant information, the patient is sent for blood and urine tests and instrumental examination. Instrumental diagnostics determines the benignity of the tumor, its internal structure, and the depth of the inflammation.
The results of tests, oral responses from the patient and examinations serve as the basis for the doctor to establish the correct diagnosis. It is not recommended to independently diagnose your disease, much less treat it. The following instrumental research methods are used:
- probing of gland ducts;
- ultrasound examinations;
- sialography;
- X-ray (done in rare cases).
To clarify the nature of the origin of the neoplasm, you need to consult a doctor. A local therapist, dermatologist, or dentist can provide advice. Only a doctor will be able to collect an anamnesis, explain why a lump appeared on the lip and cure it. The specialist examines the likelihood of a viral origin of the formation. About 90% of the population is infected with the herpes virus, which is integrated into the genetic apparatus of the cell and manifests itself in relapses.
Viruses
Many viral diseases are found in the oral cavity, caused by herpes simplex viruses, Coxsackie viruses, enteroviruses, vesicular stomatitis virus, herpes zoster, etc. Herpes infection is of particular importance. There are common names: fever, cold.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with a swollen lump on the lip, what is it
Routes of infection: airborne, birth, sexual, contact. The extremely resilient virus is transmitted by talking, sneezing, or shaking hands. It is able to be encapsulated on personal household items (towel, handkerchief, toothbrush) and move to the next recipient.
In addition to observation, modern medicine offers two ways to treat a lump inside the lip: conservative and radical.
Conservative traditional therapy includes:
- Immunotherapy. Prescription of immunomodulators and immunoregulators.
- Antiviral therapy. Suppression of virus replication and inhibition of the stages of virus-cell interaction.
- Physiotherapy. UV treatment, oxygen therapy, dosed hypothermia.
- Drug therapy. Irrigation, creams, ointments, vitamins.
- Antibiotics. A sensitivity test is required.
- Traditional medicine. Medicinal plants (Kalanchoe, aloe, chamomile, etc.) in the form of decoctions, solutions, lotions.
- Vaccination. Lesions of a viral nature are easier to prevent with vaccine therapy.
Cystectomy of a retention cyst is performed by a dentist using a surgical scalpel, laser, ultrasound or radiofrequency devices.
Cases in which treatment of a lump on the lip from the outside involves surgery:
- Cyst recurrence. The cyst must be removed completely (the shell along with the contents). Otherwise she might jump up again.
- Very active tumor growth. Untimely treatment aggravates the pathological process and the tumor tends to spread to neighboring tissues.
- Induration of the cyst. Stagnation creates favorable conditions for the degeneration of a cyst into scar tissue (fibroadenoma).
A lump on the lip can appear both on the inside and on the outside. In some cases, the lump resolves on its own, while in others treatment is required. To choose the right therapy, it is important to know the nature of the tumor.
The cause of a lump on the inside of the lip may be the following pathologies:
- . This is a new formation:
- looks like a bulging ball;
- is a cavity in the thickness of the lip tissue filled with exudate;
- appears in connection with .
A retention cyst is painless. Sometimes it occurs not only on the lips, but also on the mucous membrane of the tongue, sublingual area and the inner surface of the cheeks.
- - benign tumor. This lump could be:
- soft or hard;
- smooth or with tubercles:
- in the form of a red swelling or area of keratinized epithelium. The tumor grows slowly and does not cause pain symptoms.
Treatment methods
Diseases with different etiologies require a wide range of treatment methods:
- Laser therapy is a modern, fast treatment and recovery. It is performed under local anesthesia for up to 1 hour. This treatment is safer with fewer side effects.
- Cryotherapy is used in cases where other methods are powerless. The cone is frozen with liquid nitrogen and removed.
- Corticosteroid injections help relieve symptoms of inflamed mucous membranes.
- Homeopathy can cure cysts, papilloma and hemangioma with drugs such as Arnica, Psorinum.
- Drug treatment consists of taking antibiotics of the penicillin group (Tetracycline), anti-inflammatory (Diclofenac), painkillers, immunostimulating agents (Echinacea, Eleutherococcus), and includes rinsing the mouth with antiseptic agents.
- Surgical operations are most often prescribed for malignant neoplasms and to remove cysts. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
- Hirudotherapy – leeches are used to dissolve benign lumps.
- Traditional methods: decoctions, lotions, infusions. They are used as a concomitant treatment with the main treatment.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine has in its arsenal a huge number of recipes for infusions, lotions and rinses. To get rid of a bump on the lip, you can use the following remedies.
Mouth rinse solutions:
- from sea salt: dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm water 37°C. sea salt;
- a solution of baking soda is made by analogy with sea water;
- iodine and soda. Soda and iodine are dissolved in warm water. To do this, take a glass, add a teaspoon of soda and 3-5 drops of iodine;
- solution from furatsilin tablets: grind the tablet to a powder, pour into a glass and fill with water 37-38°C;
- saline solution of regular or iodized salt: 1 tsp. Pour iodized salt into a glass of warm water. This solution can be supplemented with soda or a few drops of iodine;
- solution with linden honey (you can also use another type of honey): dissolve a dessert spoon of honey in a glass of warm water. For greater effect, you can add soda or herbal decoction;
- Herbal decoctions for rinsing or making lotions are brewed according to the same recipe: pour 1.5 tsp into a glass of water at 37-38°C. medicinal plant or mixture thereof. Sage, chamomile, calendula, fireweed, oak bark, yarrow, coltsfoot, St. John's wort, linden are suitable.
Lotions are made using a cotton swab, onto which a few drops of freshly squeezed juice of beneficial plants (you can use garlic sprout) or oil are dripped and applied to the bump for 10-15 minutes. For lotions the following will be effective:
- aloe leaves that are at least 3 years old;
- Kalanchoe leaves (it is better to take not from a flowering one);
- Crassula leaves (another name is money tree);
- garlic.
Oils:
- tea tree;
- sea buckthorn;
- castor;
- coconut;
- Aloe Vera.
Rub vitamin A or E into the bump and around it or as a lotion.
Infusions are made on an alcohol and non-alcohol basis:
- an infusion of propolis is sold in a pharmacy or you can make it yourself: propolis the size of a tennis ball, pour 0.5 liters of vodka and leave in a dark, cool place for 7 days;
- It is also made from ficus leaves on an alcohol basis (medicinal alcohol, vodka): fill a 0.5 liter jar one third with chopped ficus leaves and fill with alcohol. Send to a cool, dark place for 3 days;
- An infusion from horseradish root is made according to the same principle as the previous one.
Before using any traditional medicine, you must consult with your doctor so as not to aggravate the situation and not lead to serious complications of the disease that has arisen.
How to solve a problem
Taking into account the reason why the tumor appeared, as well as its type, doctors prescribe conservative treatment or radical removal. This problem should not be ignored, as this is fraught with the proliferation of atypical cells and the development of a malignant process. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and determine treatment methods.
Drug therapy
If a ball of bacterial or viral origin appears on the skin, you can get rid of it with the help of drug therapy. A comprehensive treatment regimen involves the use of the following categories of drugs:
- Antibacterial agents with a wide spectrum of effects. These are tetracyclines and penicillins.
- Immunomodulators of synthetic or plant origin - cycloferon, echinacea extract, proteflazid.
- Painkillers in the category non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - ibuprofen, nimide.
- Means for accelerating the recovery of damaged tissues - solcoseryl.
- Use of antiviral drugs.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment. UV therapy, oxygen therapy.
What medications to use if a lump comes out should be decided only by the doctor. It is also recommended to use antiseptic solutions for rinsing, irrigation or oral baths (oracept, hepilor). Dental gels are used - Camident, Metrogyl, with the help of which, some time after the start of treatment, itching and painful sensations are relieved. This treatment is also advisable after injury to the lip or oral mucosa.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine should be used only after prior consultation with a doctor. And only as an auxiliary means, and not the main one. If epithelial lesions form, treatment can be carried out using the following folk remedies:
- propolis tincture;
- tincture of calendula;
- For rinsing, decoctions based on medicinal plants are used - chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, nettle, oak bark. With their help, an antiseptic and astringent effect is achieved;
- Kalanchoe juice, aloe juice;
- chlorhexidine or miramistin have antiseptic properties.
It is best to select a treatment method together with a doctor. The effectiveness of folk remedies directly depends on the degree of the disease, the depth of the cyst, and the duration of its development.
Surgery
When surgical treatment is required:
- retention cyst. The specialist must completely remove the growth shell along with the liquid that is inside. Otherwise, there is a high risk of relapse of the disease;
- excessively active growth and proliferation of neoplasms. If therapy is not carried out on time, this is fraught with aggravation of the pathological process and an increase in the size of the formation;
- too dense formation. In the presence of stagnation, positive factors are created so that the cyst grows into scar structures.
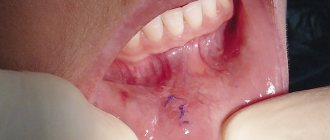
Surgical intervention is performed if a hard ball on the outer or inner side of the lip does not pass on its own. Radical removal is carried out using local anesthesia. After surgery to remove the white formation, the patient receives stitches. After surgical treatment, swelling of the lip may persist for several days. To reduce bleeding, after surgical manipulations the lip is intensively clamped. Removal of the lump is done very carefully. It is very important not to disturb its lining, because if the fluid leaks out, the contours of the cyst will be lost and it will be difficult to remove it completely. If some part of the formation remains, there is a danger of relapse.
In addition to traditional removal of the growth, there is also laser treatment. This method is effective, safe, and does not leave scars. Can be performed using local anesthesia. The recovery period lasts up to six months, depending on the extent of the lesion. In most cases, removal occurs without consequences or complications. A month later, the wound heals. It is better if a small cyst is removed to prevent the development of all sorts of consequences.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of a bump on the lip, it is important to follow several rules:
- Strengthen the immune system (drink vitamins and minerals, harden yourself);
- Get rid of bad habits such as smoking, alcohol;
- Do not drink or eat very hot or cold foods;
- Avoid mechanical damage, injuries, bruises, lip bites;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Eat vegetables, berries, fruits fresh and in season;
- Do not chew seeds and nuts with your teeth;
- Avoid spicy foods and hot spices;
- Adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, use individual means for cleaning teeth;
- Visit the dentist regularly (2 times a year);
- Select high-quality dentures, implants, crowns, braces.
Preventive measures will help avoid the occurrence of many diseases.
For any incomprehensible manifestations in the form of lumps or balls on the lip, you should immediately contact your dentist. The doctor will conduct a study, diagnose and cure the disease. You should not waste time and put off visiting a medical facility until later, so as not to suffer from complications that may arise.
Reasons for the appearance of a ball on the lip
In some cases, the cyst may be congenital in origin, which is most often observed when a cyst is found in the mouth of a child. In this case, the formation is formed inside an additional rudimentary duct, which is formed during embryonic development.
Externally, a cyst in the oral cavity is a mobile, round-shaped formation protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane. The cyst does not cause pain. A large cyst located under the tongue can interfere with talking or eating. A cyst in the mouth on the roof of the mouth that has reached a large size can also cause discomfort during conversation.
If left untreated, the cyst can cause the development of an infectious process in the oral cavity and cause serious complications (abscess, phlegmon).
Treatment of cysts in the mouth is carried out by specialists in maxillofacial surgery (otolaryngologist or dental surgeon) and involves only surgical removal.
At the end of November 2014, I felt a small lump under my tongue and during the first week of December the lump began to grow, it became bigger and bigger. The dentist examined me and decided to pierce my lump. After the lump was cut, liquid (thickened saliva) came out.
I went to the pharmacy and bought a syringe and at home in front of the mirror I pierced the lump with a syringe needle. A salivary gland cyst is a tumor-like formation of the maxillofacial area in the form of a cavity filled with liquid contents. Salivary gland cysts are relatively uncommon. The only way to get rid of a sublingual cyst is through surgery, namely by removing it.
- So, the day came when I had to come to the hospital for surgery. I was in the hospital for 6 days, rinsed the former cyst 5 times a day with a solution of furatsilin, and I was also given intramuscular injections (antibiotic Cefson) 2 times a day. Well, something like this, I’ll end the article here, I’m waiting for your comments.
- It’s a shame that you suffered so much from the lump under your tongue. It doesn’t hurt to give the injection at all))) If you have a sublingual cyst, then there is no way to do without surgery! Yesterday I discovered a small lump under my tongue that burst when I spoke. In addition, it can easily be confused with other diseases that cause growth in the oral cavity.
- It has been suggested that such blisters under the tongue are formed due to injuries in the oral cavity. However, a cyst is formed not due to the fact that saliva accumulates and lingers in this area, but due to the fact that transudate is released more strongly.
This is due to the fact that the capillary epithelium and gland epithelium are transformed. The sublingual cyst has many similar manifestations to ranula. It must be distinguished from cyst-like extensions of the epithelium.
This tumor increases significantly after eating. A real cyst cannot change in size so dramatically. In this case, the patient does not feel pain, only some discomfort due to the fact that a foreign body is felt under the tongue.
Gradually, the cyst expands and moves into the tongue area, under the tongue and into the jaw. In most cases, such a growth is located closer to the middle of the area under the tongue. In some cases, the cyst can empty itself, so it disappears, but only for a while.
Drug treatment, various procedures and recipes from traditional medicine will not help to completely get rid of this growth.
Removal of the cyst must be carried out in a dental or otolaryngology department, depending on its location. The cyst must be removed through the mouth. In this case, the patient is administered a local anesthetic drug.
As a rule, it is not possible to completely remove a cyst, especially if it reaches a large size.
So, on the Internet, I still found several articles that said that the lump under the tongue is a sublingual cyst and that it can be treated through surgery.
The effectiveness of treating a lump directly depends on how correctly the cause is determined and on the timely diagnosis of any disease. After the diagnosis, the doctor can determine the etiology of the growth, the degree of its development, and the affected area. Only after this the treatment algorithm is determined. The main reasons for the formation of a ball include damage by viral microorganisms and mechanical damage or trauma to the epithelium.
Often people turn to specialists because they have bitten or bit their lip and a ball has formed at the site of injury. This lump is medically described as a mucocele cyst. This dense node on the lip or in the oral cavity can form on the oral mucosa and develops with mucosal contents (salivary fluid).
If the balls in the lips are not treated in a timely manner, this is fraught with the development of an inflammatory process. If white balls appear on the lips under the skin in the form of a retention cyst, this is accompanied by certain symptoms:
- a ball under the lip or outside on the skin, it is dense;
- contains a light yellow liquid inside;
- there is no pain, itching or other signs.
Most often, blisters that appear on the inside or on top of the lip indicate activation of the herpes virus. In this case, many balls may appear. The formation contains liquid, which flows out on its own as the blister matures. Its surface is covered with a crust on top.
If herpes appears, the main reason for its appearance is the activation of the herpes virus or primary infection. The virus can remain dormant for a long time while in the body, and in the presence of favorable conditions (weakened immunity under the influence of various factors) it becomes more active.
Warty seals on the surface of the lip are the main signal of the development of the human papillomavirus. They can occur sporadically. But as the disease worsens, they grow and form on the entire surface of the skin around the mouth. The resulting papilloma must be treated in a timely manner, since some types of virus provoke the proliferation of atypical cells (and this is fraught with malignancy of the formation).
Other reasons
Other reasons for the appearance of nodules on the inside or outside, on the upper or lower lip or in the mouth, include:
- development of fungi on the mucous membrane;
- inflammatory processes of various etiologies;
- thermal burns while eating or drinking;
- wearing uncomfortable dentures;
- development of allergic reactions;
- wearing a piercing.
If a ball appears outside or inside your lip, you should first consult a dentist. After the examination, the specialist will select treatment.
A lump has come out on my lip - what does it mean? The doctor will definitely clarify whether this is a primary lump or a relapse. In addition to collecting anamnesis (according to the patient), an examination is carried out. The seal is examined first from the outside, then the lip is moved back and everted to examine the mucous membrane.
Tumor on the lip
The tumor can emerge in any part of the mouth, but is most often observed as a lump on the inside of the lower lip. A compaction that originates deep remains at the bottom or appears in the upper layers as an asymmetrical thickening, wart, lump, or ulcer. The neoplasm may be filled with a clear white liquid, or have a bluish-bloody tint. Depending on the clinical picture, there are:
- viral rash;
- benign tumors (cyst, papilloma, nevus, connective tissue tumors, vascular);
- cancer.
9 out of 10 patients in megacities (Moscow) complain that a ball has appeared inside the lower lip. The most common benign tumor is a cyst. The main difference between a cyst and a virus is painlessness, lack of burning, and growth. Spontaneous or self-opening of the cyst will lead to re-growth.
The growth of even a benign cyst can trigger the process of malignancy. The transition to lip cancer, from a clinical point of view, goes unnoticed.
We invite you to read Inflammation of the salivary gland: 14 probable causes, 26 symptoms and 18 treatment methods
Injury, crack, or ulcer are no less dangerous: they require observation. The appearance of a white bump on the lip may indicate leukoplakia, a precancerous condition. The disease is a disorder of keratinization. The change happens painlessly, slowly.
Tumor on the lip
- viral rash;
- benign tumors (cyst, papilloma, nevus, connective tissue tumors, vascular);
Often people turn to specialists because they have bitten or bit their lip and a ball has formed at the site of injury. This lump is medically described as a mucocele cyst. This dense node on the lip or in the oral cavity can form on the oral mucosa and develops with mucosal contents (salivary fluid).
Retention cyst
Cysts of small salivary glands are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the surface of the epithelium or after a thermal burn. Also, a blockage of the gland is formed due to the entry of a calculus, which entails the accumulation of salivary fluid and cysts appear from the inside or outside. Most often they form on the surface or inside the lower lip.