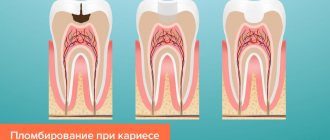
Today in dental clinics, each patient can choose any material for himself. There are many types of dental cement, which differ in aesthetics, strength and durability. Installing a crown will help preserve and restore the attractiveness of a diseased tooth. Any dentist knows that prosthetics will be successful only if high-quality dental cement is used for reliable fixation.
Properties
High-quality dental cement must have certain properties. The first is to be biocompatible. Only in this case will it be tightly attached to the real tooth. As a result, the likelihood that the filling will fall out and intermediate caries will develop will be minimized.
The material must have an optimal hardening time. There should be enough time for the doctor to slowly place a high-quality filling. It is also necessary to take into account that it will be difficult for the patient to sit for a long time with his mouth open while waiting for the material to harden.
The dental cementitious composition should:
- be hypoallergenic;
- have a uniform structure. In this case, the mixture will be able to adhere tightly to the remaining part of the tooth. As a result, there will be no empty cavity left where bacteria that cause caries can multiply;
- be extremely durable. A strong mixture is able to withstand heavy loads when chewing and grinding solid food.
The material, in its structure and color, should be as close as possible to the enamel given by nature, and also not be susceptible to staining. Over time, the filling should not lose its original color, despite exposure to different dyes.
General characteristics and functions of dental cement
Dental cement is calcified dental tissue, similar to bone, but, unlike it, devoid of blood vessels and not subject to constant restructuring. Cement covers the roots and neck of the tooth. According to most researchers, in 60-70% it partially penetrates the enamel (the so-called coronal cement), in 10% it does not reach it (Fig. Na-c).
According to information obtained in recent years, direct contact of enamel with cement is much more common than previously thought, and the area observed in 10% of teeth at the light optical level as a gap between cement and enamel is in fact covered with a very thin layer of cement.
The thickness of the cement layer is minimal in the area of the tooth neck (20-50 µm) and maximum at the root apex (100-1500 µm or more, thicker in molars).
Due to the continuous rhythmic deposition of cement on the surface of the tooth root throughout life, the thickness of its layer triples from 20 to 60-70 years. The strength of completely calcified cement is slightly lower than that of the underlying dentin. It is the least mineralized of the hard dental tissues, but still contains more inorganic substances (about 60%, mainly hydroxyapatite) than bone tissue (about 50%).
Functions of dental cement:
1) is part of the supporting apparatus of the tooth, providing attachment to the fibers of the periodontal ligament;
2) protects root dentin from damaging influences;
3) performs reparative functions during the formation of so-called resorption lacunae and during tooth root fracture;
4) deposited in the area of the edges of the newly formed fibers of the regenerating periodontal ligament after its damage, helps restore its attachment to the tooth root;
5) deposited in the area of the root apex, it ensures the preservation of the total length of the tooth, compensating for the abrasion of the enamel as a result of its wear (passive eruption).
Structure of dental cement
Cementum consists of cells (not present everywhere) and calcified intercellular substance (matrix), including collagen fibers and ground substance. Its nutrition is carried out diffusely from the periodontal ligament. Cementum is divided into acellular (primary) and cellular (secondary).
Acellular (primary) cement is formed first during development and covers the surface of the tooth roots in the form of a layer of insignificant (30-230 µm) thickness - minimal in the area of the cemento-enamel boundary and maximum at the apex of the tooth. It is the only layer of cement covering the neck of the tooth, and in some teeth (for example, the lower front incisors) it almost completely covers the root. Acellular cementum does not contain cells and consists of calcified intercellular substance, including densely located collagen fibers and ground substance. On its surface there is a layer of non-calcified organic material - precement (cementoid) - 0.25-5.0 microns thick, which contains collagen fibrils. It reveals striations directed perpendicular to the root surface (formed by periodontal ligament fibers interwoven into the cement), as well as layering parallel to the surface of the tooth root (due to the periodicity of deposition of the cement itself). The growth lines in acellular cement are located close to each other, and its border with dentin is not clearly defined.
Cellular (secondary) cement covers the apical third of the root and the bifurcation area of the roots of multi-rooted teeth. It is located on top of acellular cement, but sometimes (in the absence of the latter) it is directly adjacent to dentin. The boundary between them (unlike that with acellular cement) is clearly expressed. The thickness of the layer of cellular cement varies widely (100-1500 microns) and is most significant in molars.
Cellular (secondary) cement consists of cells (cementocytes and cementoblasts) and calcified intercellular substance.
Cementocytes lie in special cavities inside the cement - lacunae - and are similar in structure to osteocytes. Between their plasmalemma and the calcified wall of the lacuna there is a pericementocytic space filled with organic material. Cementocytes are flattened cells with moderately developed organelles and a relatively large nucleus.
Their numerous (up to 30) branching processes with a diameter of about 1 µm reach a length of 12-15 µm and connect neighboring cells due to the presence of numerous gap junctions (nexuses) and tight junctions. The processes are oriented predominantly towards the periodontal ligament (source of nutrition). The tubules connecting the lacunae and containing the processes of cementocytes form a continuous system that extends from the inner to the outer surfaces of the cementum layer.
Cementoblasts are cells involved in the formation of cement and located on its surface - in the peripheral areas of the periodontal ligament around the tooth root. The description of these cells is given above.
When acellular cement is formed, cementoblasts move outward from the intercellular substance they produce, and when cellular cement is formed, they become immured in it. In the latter case, plunging into cement, these cells gradually turn into cementocytes, decreasing in volume and losing a significant part of the organelles.
The intercellular substance of cellular cement includes fibers and ground substance. Cement fibers are formed by type I collagen and are divided into “intrinsic” or “internal”, i.e. formed by cement cells and running predominantly parallel to the surface of the tooth root, and “external”, which includes fibers of the periodontal ligament - Sharpey’s fibers (oriented perpendicularly root surface).
The ratio between the two types of fibers varies widely in different areas of the cement. In the cement of humans and animals, like bone tissue, a number of non-collagenous proteins (sialoprotein and osteopontin), proteoglycans (versican, decorin, biglycan and lumican), glycosaminoglycans (absent in acellular cement) are found.
The intercellular substance of human tooth cement contains a special CAP protein, which determines the adhesion of periodontal fibroblasts, cementum-derived growth factor (CGF), which has pronounced mitogenic activity. In addition, cement, like bone tissue, contains high concentrations of growth factors - such as IGF-1, IGF-P, TGF-31 and TRGF, which are released in significant quantities, especially after damage, and promote the regeneration of this tissue .
Varieties
Various types of adhesives are used in dentistry, for example, there are those that are used for removable dental bridges. This cement is effective for approximately 24 hours. During this time, the composition does not harden and remains elastic. Buy this dental cement at the pharmacy. Often compounds are used to fasten a broken bridge.
The advantage of this type of adhesive masses is that they freshen breath and also have antibacterial properties. Only a dentist should prescribe the product necessary to install and secure dentures.
The bite and duration of attachment depend on the composition and type of cement. Thus, the cement composition, which is intended for fixing inserted dentures, lasts only for a day, and for crowns - for several weeks.
You can buy material of various consistencies:
- liquid;
- semi-liquid;
- thick.
More thick and viscous cement is always taken than semi-liquid or liquid.
Period of wearing a temporary crown
From the very name “temporary” it becomes clear that you only need to wear such a crown for a limited time. Often, it is worn for 2-5 days, maximum period is 7 days. It should be worn until the laboratory can make a “permanent” crown. If during the period of wearing the temporary crown falls out for some reason (this happens extremely rarely), you should consult a doctor to have it reattached.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Removable dentures: types, pros and cons, which are better for prosthetics of the upper and lower jaw?
It should be noted that if you do not have the opportunity to replace “temporary” with “permanent”, then it is worth knowing that within 20 days the crown is completely worn out, which entails a displacement of the nearby teeth towards the crown, and this already entails a change in the bite. A temporary restoration is not designed to perform all the functions of a healthy tooth.
Pros and cons of the polymer type
The positive qualities of polymer compositions include:
- excellent strength;
- presence of a homogeneous structure;
- maximum viscosity.
Thanks to the last two properties, no gaps form between the enamel, cement and soft tissues of the tooth.
The disadvantages of polymers are frequent allergies and a clearly visible difference between natural enamel and filling material.
Attachment to implants
Such prosthetics do not require treatment of adjacent teeth. The structure itself can be installed in two ways:
- Screw fixation, when the crown is connected to the abutment adapter outside the oral cavity. After which the entire structure is screwed to the implant using a screw that passes through the hole in the prosthesis. After which the canal is closed with a special filling material. This method is more suitable for single crowns. Cement fixation, when the abutment is first fixed to the implanted root, after which the crown is fixed to it using cement. This method is preferable when prosthetics are performed on several teeth at the same time.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the LARYNX and THROAT - structure, dangerous and typical diseases
Pros and cons of the phosphate type
Phosphate permanent dental cement has a number of undeniable advantages. It contains zinc powder and phosphoric acid. Due to its strength, it is excellent for filling teeth that experience a lot of stress when chewing. The composition is easy to mix and hardens quickly.
There are also disadvantages, and they are as follows:
- Increased acidity. If the composition gets on the pulp, the nerve endings may become inflamed.
- Lack of antibacterial effect.
- In the future, there is a possibility of clouding of the material, which will lead to a change in the color of the filling.
Pros and cons of the polycarboxylate type
The main component is specially processed zinc oxide, without residual products, which reacts quickly with polyacrylic acid. The positive properties of polycarboxylate compounds are the rare occurrence of allergies and good adhesion to enamel and dentin. The hardening time is 7-8 minutes, which is optimal.
The downside is that it is not strong enough, because it is temporary dental cement. It is used only for non-permanent fillings and fixation of prostheses. To dilute these compositions, distilled water is required.
Pros and cons of silicate phosphate type
These cements contain aluminosilicate glass in powder, which is diluted with phosphoric acid. Silicate phosphate mixtures have their advantages. One of them is versatility. They can be used for all sorts of purposes. This material has increased strength. Just like natural enamel, silicate phosphate mixtures are partially transparent.
The disadvantage is that it hardens very quickly. Within 5 minutes, the doctor must place a filling, which often affects its quality. The material is available only in powder-liquid form.
Pros and cons of glass ionomer type
The liquid part of the material is represented by polyacrylic acid. Glass ionomer dental cement has antibacterial properties. It minimizes the risk of caries development. Benefits include:
- the best combination of strength and elasticity;
- presence of excellent aesthetic qualities;
- no allergic reaction;
- high biocompatibility;
- resistance to dyes.
However, the material takes a very long time to harden. Although the main hardening takes 6 minutes, it reacts to irritants within 24 hours. In addition, glass ionomers are difficult to polish.
Release form
Dental cement contains powder and liquid, which when mixed form a paste-like mass. As it hardens, it begins to harden and becomes like stone. The components enter into a chemical reaction, resulting in hardening.
Dental cement is available in the form of:
- Separate liquid and powder. This form is used most often. The filling material is prepared manually by the doctor right before use. In this case, you can adjust the density of the composition, but if the dentist does not have the proper experience, the mixture may turn out to be very thick or thin.
- Powder. Distilled water is used here.
- Ready-made mixtures in vacuum syringes. They are prepared in a standard way, with the liquid and dry parts optimally selected.
- Individual dosed capsules with liquid and powder.
Recommendations from experts
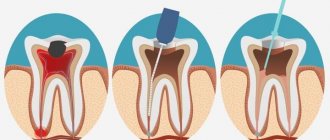
Before installing a crown on a damaged tooth, it is ground down and then dental cement specially designed for this purpose is applied. Thanks to this material, the crown is attached very firmly and does not move when chewing. After hardening, this material becomes very durable. A prosthesis fixed with this mass can last for more than 10 years, while a person does not experience any unpleasant taste or smell emanating from it.
Even if you buy the strongest glue, there is no guarantee that it will be able to withstand heavy loads. It often happens that the crown falls off and you have to go to the dentist. If you cannot visit a doctor, you can try to solve the problem yourself at home.
Temporary fixation technology
At the preparatory stage, the surgical field and orthopedic structures that are to be fixed are dried and isolated from saliva. Degreasing of working surfaces is not required. Temporary cement is mixed taking into account the manufacturer's recommendations. In the future, the fixation technique - using the example of temporary acrylic crowns on eugenol-free cement - looks like this.
- Temporary cement is applied with a spatula to the cervical part of the temporary crown.
- Under bite control in habitual or central occlusion, the orthopedic structure is fixed in the oral cavity.
- After the time specified by the manufacturer, the temporary cement is removed.
- If work is carried out in support of a dental implant, a rubber dam is used to protect the latter.
- The final stage is x-ray control to check the effectiveness of cement removal.
- Fixation is completed by control of occlusal contacts.
- The patient receives recommendations on the rules for caring for the structure (they are practically no different from the case of installing fixed structures on permanent cement, with the exception of replacing dental floss with a dental brush).
Home use
Dental cement used at home can be purchased at a pharmacy. Its composition differs from that used by dentists. However, with its help you can secure the crown for a while before going to the doctor. It must be borne in mind that it is impossible to walk for a long time with a prosthesis secured in this way.
Before gluing the fallen crown, it is cleaned of old cement with a special dissolving liquid and a brush. These drugs are sold in tablet form. A clean denture is washed in water and dried. If the crown is wet, the bond will not be strong.
Then the adhesive is applied to the crown, which is put in place. How to make dental cement at home is indicated in the instructions for the material, which is purchased at the pharmacy. When purchasing any cement, you need to make sure that it is compatible with the crown or denture.
An important point is the accurate and even installation of the crown. Then you need to clench your teeth tightly for a few minutes. During this time, the prosthesis will firmly adhere to the tooth and fall into place. If suddenly excess dental cement comes out when pressed, it needs to be removed. This material is non-toxic. After this, it is forbidden to drink or eat food for at least half an hour.
If you take proper care of your teeth, this type of correction will last from 14 to 21 days. You need to brush your teeth carefully and chew food on the other side, so the crown will not fall off prematurely. It is worth noting that dental cement is not sold in all pharmacies. There are options both cheap and expensive. It is highly recommended to consult a doctor before purchasing one or another type.
How to remove crowns from teeth
Removing dental crowns is not a simple task, especially when it comes to completely preserving the prosthesis for the purpose of later installing it back in its original place.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Pimple on the lip: causes of appearance, how to remove it, prevention.
If it is necessary to remove the crown due to its breakage, when there is no question of repair, then it is sawed with the help of dental instruments and removed in parts from the dental stump.
To preserve the prosthesis when removing the crown from a tooth, there are special tools:
- Crown removers (the most common tool model is the Kopp hook) are flat hooks with an automatic or manual mechanism, which allows, after fixing the crown to the tooth, to apply a certain force and remove the crown. Forceps are tools that allow you to securely fix the crown between the jaws and remove it from the base.
In modern dentistry, crowns are removed using ultrasonic units. When the tip passes around the area where the prosthesis connects with the stump, ultrasound causes crumbling and cracking in the cement, after which it is removed without much difficulty.
Another gentle method for removing crowns is the use of pneumatic tools, under the influence of which the cement is also destroyed and the structure moves away from the support.