Acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis is an infectious acute disease that affects areas of the palatine tonsils. According to the pathomorphological classification, this disease can occur in several forms: follicular, catarrhal, necrotic and lacunar form. The last three types of disease differ from the first by the presence of purulent discharge on the tonsils, due to this, they are popularly united under the common name - purulent tonsillitis. The disease not only causes severe pain, but can cause serious complications. What to do and how to treat purulent sore throat at home?
Cause of purulent sore throat
The cause of this disease is an infection of bacterial origin . The pathogen passes into the tonsils from foci of chronic damage in the body or from the outside. The majority of cases of acute tonsillitis are caused by a bacterium called group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, and only 25% of the disease is caused by streptococci and their combination with staphylococci.
The main risk factors for acute tonsillitis are:
- reduced immunity;
- local (near the throat) or general hypothermia of the body;
- bad habits (especially smoking);
- excessive air dryness, gas pollution and dustiness;
- sudden changes in temperature.
Tips for preventing purulent tonsillitis
To prevent the development of purulent inflammation of the tonsils, it is necessary to follow a number of measures aimed at increasing the overall resistance of the body. For this it is recommended:
- monitor the condition of the teeth, sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- avoid hypothermia, do not drink cold drinks;
- Avoid contact with ARVI patients.
Important! Compliance with preventive measures is especially important during pregnancy. At this time, a woman’s body experiences significant stress, so the risk of developing infectious diseases is greatest.
Epidemiology
Purulent tonsillitis is one of the most common diseases of the upper respiratory canals. This disease most often affects children over 7 years of age, as well as adults of working age. The disease is characterized by a pronounced seasonality - the peak of the disease occurs in spring and autumn.
The source of infection is an asymptomatic carrier of streptococcus, as well as a person with tonsillitis. The main method of transmission of the disease is airborne, however, the role of both nutritional (that is, with food) and contact-household (using household items) mechanisms cannot be ruled out. This is a highly contagious infection, the greatest susceptibility to this disease is observed in children and adults with lesions in the oral cavity of chronic infection.
Causes
Purulent tonsillitis is a fairly contagious disease. Represents a danger in the first days of development. Transmitted by airborne droplets.
The culprits of the disease are bacterial and viral infections that penetrate the oral cavity. The tonsils perform a protective function and prevent pathogenic microbes from penetrating deep into the body, which is why they are the first to suffer with a sore throat.
In addition to infection entering the oropharynx, there are factors that contribute to their proliferation on the mucous membranes and the development of the disease.
Factors for the development of tonsillitis:
- Weakening the body's immune defenses
- Poor oral hygiene
- Lack of timely treatment of oropharyngeal diseases
- Hypothermia of the body
- Respiratory tract pathologies
- Diseases that cause difficulty breathing through the nose
- Close contact with a person carrying the disease
- Pathology of tonsils
Alone or in combination, all these factors can cause increased cell division of pathogenic bacteria and the development of purulent sore throat.
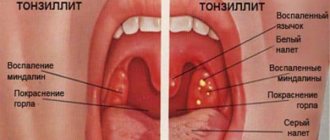
Symptoms of the disease
This disease, as a rule, begins acutely and passes very hard. The incubation time (from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease) is several days. In the foreground are the general symptoms of intoxication of the body :
- lethargy;
- severe weakness;
- increase in temperature to febrile value (39-40 degrees);
- loss of appetite;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- increased sweating.
Against the background of intoxication symptoms, a person develops a sore throat, mild at first, but over time they become stronger, reaching their peak on the 4-5th day of the illness. At this stage, the pain becomes more pronounced, bothering the patient constantly, interfering with nasal rest and making the swallowing process impossible - the person cannot eat food.
Inflammation of the regional lymph nodes is often observed - they are painful when touched, hurt when swallowing, and increase in size.
Treatment
By medication
For the treatment of purulent sore throat, the following medications must be used:
- Antibiotics. In most cases, doctors prescribe protected semisynthetic aminopenicillins and cephalosporins. This includes antibiotics such as amoxiclav, cefuroxime, and so on. If you are allergic to penicillins, macrolides, such as azithromycin, are recommended.
- Local preparations. These drugs are intended for gargling. They are usually available in the form of solutions, sprays (Lugol, Ingalipt) or lozenges (Trachisan, Gorlospas). They contain antiseptics.
- Anti-inflammatory, antihistamine drugs. Their action is aimed at relieving swelling and sore throat. These are drugs such as, for example, paracetamol, Erius.
- Infusion-detoxification therapy. It is prescribed for intoxication of the body or when complications occur. For this purpose, glucocorticoids and infusion-detoxification therapy are used.
- Prevention with bicillin-5. It is needed to block the exacerbation process. Therapy continues for six months.
Purulent tonsillitis requires immediate treatment. Under no circumstances should you prescribe medications on your own. This can provoke the development of complications or the transition of purulent sore throat to a chronic form.
If a person suffers from purulent sore throat more than seven times a year, it is recommended to remove sore throats.
Folk remedies
It is recommended to use folk remedies for the treatment of sore throat in combination with medications prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies are used to treat the mucous membranes of the throat and oral cavity, strengthen the immune system, and relieve inflammation.
- Aloe compresses. The fleshy part of the plant is cut off and applied to the cheek. It's better to do this at night. The procedure should be carried out until the disease is completely defeated.
- Tincture of Cahors, aloe and honey. Three hundred and fifty grams of aloe leaves are crushed and mixed with six hundred grams of honey. The resulting mixture is poured with Cahors and infused for five days in a cool and dark place. To treat purulent sore throat, take one tablespoon of tincture three times a day before meals (an hour).
- Propolis tincture. Thirty grams of propolis are frozen and then crushed. Mix propolis with one hundred grams of alcohol and infuse the resulting mixture for two weeks. Treat the throat with this tincture using a cotton swab. A burning sensation may be felt.
- Beetroot infusion. The beets are grated on a fine grater and poured with boiling water in a one to one ratio. Leave for two hours and then gargle.
- Rubbing with iodine. I put a few drops of iodine on a cotton pad and wipe the throat with it. One such procedure is enough.
- Salt rinse. Dissolve one teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. Gargle several times a day after meals.
- Rinse with tea. Brew a glass of strong black tea, add one teaspoon of soda and salt to it.
- Inhalations with potato peelings, sage and thyme. Peels from ten potatoes are mixed with a teaspoon of thyme and the same amount of sage. Keep the mixture in a water bath for two minutes and add a couple of drops of fir oil. Inhalation lasts five to ten minutes.
- Onion juice. One teaspoon of onion juice is taken before meals three times a day. You can eat onions raw.
- A decoction of milk and garlic. Boil a glass of milk and add three cloves of garlic. Infuse the decoction for thirty minutes. Drink the decoction in small sips twice a day.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of purulent tonsillitis is based on examination of the oropharynx - pharyngoscopy, medical history (acute course of the disease) and human complaints (characteristic clinical picture). During pharyngoscopy, the doctor will determine what form of acute tonsillitis the patient has:
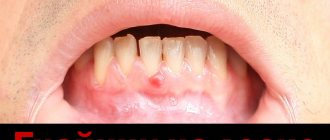
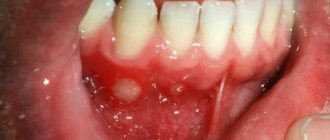
- necrotic - the tonsils are sharply swollen and hyperemic, covered with gray or dark green plaques, during the removal of which a deep bleeding defect remains; the infection can also extend beyond the tonsils, moving to the uvula and the back wall of the larynx;
- lacunar - the lacunae are enlarged, the tonsils are swollen, brightly hyperemic, they contain purulent contents that form small films or foci on the surface, protruding beyond the lacunae, these films are removed without a trace and are easily removed with a spatula;
- follicular - the tonsils are sharply swollen, hyperemic, enlarged, yellow-white formations 3-4 mm in size can be observed on their surface - suppurating follicles.
A general blood test may show an increase in the number of leukocytes - leukocytosis, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in ESR, in some cases up to 45-55 mm/h.
You need to know that infection of the tonsils is not always primary - in some cases it appears against the background of such serious infectious diseases as infectious mononucleosis and diphtheria. In doubtful situations, a sick person may be prescribed specific blood tests to identify the pathogen or a bacteriological examination of plaque, which is taken from the surface of the tonsils. To prevent the spread of infection, the patient may be hospitalized in an infectious diseases hospital.
Traditional medicine
As an auxiliary to the main drug therapy, with the permission of the doctor, traditional medicine can be used. They cannot replace medications prescribed by the doctor, and especially antibiotics, as this will worsen the condition.
Rinsing is a good help to alleviate the patient's condition. For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal herbs such as chamomile, St. John's wort, eucalyptus, and oak bark are used. These plants have anti-inflammatory effects.
In addition to decoctions, a soda-salt solution is used for rinsing. To prepare the product, add a teaspoon of soda and salt and a few drops of iodine to a glass of boiled, cooled water. Treat the throat 3-4 times a day. Salt removes swelling, soda relieves irritation, iodine disinfects.
For purulent tonsillitis, thermal procedures such as steam inhalations and compresses should not be used. Under the influence of heat, bacterial microorganisms increase their growth and reproduction. The process will move into a more complex form.
Traditional medicine.
Purulent sore throat: how to treat purulent sore throat in adults?
Treating purulent tonsillitis should only be done under the supervision of a doctor. Delayed or incorrect treatment can lead to serious complications, which in some cases can even lead to death.
It is unacceptable to treat this disease exclusively with traditional medicine!
Since purulent tonsillitis, as a rule, resolves with pronounced symptoms of intoxication of the body, in the acute course of the disease the patient is advised to rest in bed, maintaining vocal rest and limiting contact with other people.
In order to prevent trauma to the inflamed mucous membrane, the food that the patient eats during the illness must be warm and soft, and to enhance the human body’s immune system, it must be fortified. For a faster release of toxins, the patient is advised to drink plenty of fluids, naturally, warmly: green tea with lemon, vegetable and fruit drinks, still mineral alkaline water, milk with honey - these drinks should be almost the basis of the daily menu of a patient with a sore throat.
Drug therapy includes such treatment procedures as inhalation of drugs, irrigation and rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic solutions, use of drugs parenterally (using infusions and injections) or orally (that is, by mouth - tablets).
The main component of the treatment of acute purulent tonsillitis is and is always antibiotic therapy . This point should never be neglected, since a bacterial infection from the tonsils can spread to vital organs - the kidneys and heart. The most commonly used are macrolides (Erythromycin, Azithromycin), 2-3 generation cephalosporins (Zinnat, Cefuroxime, Cefix, Ceftriaxone), phenoxymethylpenicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin, Amoxiclav). The antibiotic must be taken for another three days after the body temperature has returned, and only after this period can the drug be discontinued.
The use of the local antibiotic Bioparox during acute tonsillitis is also very important, as is systemic antibiotic therapy. This remedy acts on the source of inflammation itself, killing bacteria immediately at the site.
In addition to Bioparox, the disease can be treated with lozenges and topical sprays that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties: Trachisan, Decatylene, Ingalipt, Neo-angin, Septolete, Faringosept, Kameton, Tantum Verde - there are a very large number of these drugs, and every doctor has a lot of these drugs for the treatment of sore throat I have a few particularly favorite remedies in mind.
Also, during a purulent sore throat, it makes sense to gargle . For this purpose, solutions of various antiseptics (alcohol chlorophyllipt, Stomatidin, furatsillin), herbal decoctions (chamomile, chamomile) are used. The more often you gargle with this disease, the greater the effect will be noticeable. If you treat this disease, then 4-5 gargles a day will be pointless; you need to gargle at least once an hour, and even better, every half hour. The solutions used can be used one at a time.
Also, for purulent sore throat, Lugol's solution or, as people say, Lugol's is often used. It is not used as a rinse solution, but is applied with a cotton swab to the tonsil area itself, while simultaneously removing purulent films from them. In addition to Lugol, an oil solution of Chlorophyllipt can be used for this.
For purulent sore throat, treating this disease with inhalations is not relevant, but performing this procedure using a simple saline solution, solutions of antiseptic herbs or alkaline mineral waters will improve the discharge of sputum and soften the inflamed mucous membrane.
To reduce swelling of the tonsils, the patient may be prescribed antihistamines (Zodak, Erius, Aleron).
For regional lymphadenitis, compresses with medications (may include antiallergic drugs, antibiotics, Dimexide, antiseptic solutions, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs) and warming compresses (for example, semi-alcohol).
At the recovery stage, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures - electrophoresis and UHF on the tonsil area .
Purulent sore throat: treatment at home
In treatment, rinsing with various infusions of plants and herbs gives positive results. An infusion of eucalyptus, chamomile, sage, celandine, and calendula can help a sore throat. A decoction can be made from one herb or from several at the same time. If you want to make a decoction from one medicinal plant, then you need to take it in the ratio of one glass to one cup of boiling water. You need to give the mixture time to brew. As a rule, one hour is enough for this. Afterwards, express the infusion and gargle once every 2-3 hours.
When you want to gargle and treat with several herbs at the same time, you need to purchase 2-3 types of medicinal plants and mix them in equal quantities. Then take one tablespoon of the mixture and add a glass of boiling water to it, let it brew, express and gargle the sore throat.
You can also make this solution to gargle and treat your throat. Take one teaspoon of salt and soda and stir in a glass of water. Three drops of iodine are dripped into it. The composition is thoroughly mixed. You need to gargle with this solution every 2 hours. This remedy perfectly relieves swelling and pain of the mucous membrane.
To cure purulent sore throat at home, you can use onion juice. It is taken orally, 1 tsp. 5-6 times daily.
To treat this disease you can use propolis. You need to chew a piece of propolis for 30 minutes. You can chew it every two hours.
Drug therapy
When the first symptoms indicating tonsillitis appear, you must contact a medical facility for differential diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. In the early stages, diseases of different etiology are similar in their symptoms.
First of all, the doctor conducts an examination, determines the degree of damage, collects an anamnesis of the patient’s life and complaints. To make an accurate diagnosis, you will need to undergo a series of studies, including pharyngoscopy, a clinical blood test, a swab from the throat and nose to identify the pathogen, and an antibiogram. Only based on the test results, drug therapy is prescribed.
Mild forms of purulent tonsillitis are treated at home. In advanced cases, the patient is hospitalized in an inpatient department to monitor the temperature and general dynamics.
Antibiotics are the mainstay in the treatment of purulent lesions; without these drugs it is impossible to completely overcome the infection. Drugs are prescribed based on the results of the antibiogram. Amoxicillin drugs (Augmentin, Ospamox, Amoxiclav), cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone, Cefuroxime), macrolides (Ampicillin, Azithromycin) are used. If after three days of treatment there is no positive dynamics, the antibiotic group is changed. To prevent dysbiosis, medications containing lacto and bifidobacteria (Lactiale, Yogurt, Bio-Gaya) are prescribed.
In addition to etiotropic therapy, drugs are prescribed to reduce symptomatic manifestations:
- Antipyretic. Purulent tonsillitis rarely occurs without fever. To alleviate the patient's condition, antipyretics are prescribed. In addition to the main effect, they reduce the severity of pain (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol).
- Anti-inflammatory. They reduce the activity of the inflammatory process and enhance the regeneration of damaged tissues (Erespal, Inspiron).
- Antihistamines. Reduce swelling of inflamed tissues, thereby facilitating the process of swallowing and breathing (Eden, Cetrin, Zodak).
In complex therapy of purulent tonsillitis, local drugs are also used. Antiseptics are prescribed for rinsing; they destroy pathogenic microorganisms on the surface of the tonsils and prevent the spread of the inflammatory process. In addition, the tonsils are mechanically cleaned and the mucous membrane is moisturized. For these purposes, Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine are used.
Also for local treatment, solutions are used to treat the tonsils (Lugol), sprays (Hexasprey, Forteza), lozenges and lozenges (Doctor Mom, Strepsils, Septifril). These drugs have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, and mild analgesic effects.
To alleviate the patient's condition, procedures for removing purulent plugs are prescribed. This can only be done by a doctor; performing the manipulation yourself can cause harm to the body.
Medications for the treatment of purulent tonsillitis are prescribed only by a doctor. Improper management of the pathology leads to serious, life-threatening complications for the patient.
Drug therapy.
Complications of purulent sore throat
If untimely or improper treatment is used, acute tonsillitis can cause some complications, which are conventionally divided into late and early:
- Early ones are caused by the spread of infection to the tissues and organs adjacent to the tonsils. These are otitis, peritonsillar abscess, purulent lymphadenitis of regional lymph nodes, sinusitis. These conditions usually go away without leaving a trace, however, they require urgent treatment.
- Late complications, as a rule, appear one month after treatment of purulent tonsillitis. These include arthritis, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, rheumatic heart disease (formation of defects). These diseases require long-term, in some cases lifelong, treatment and can lead to disability for the patient.
Complications
Purulent tonsillitis is dangerous because the inflammatory process can spread to other ENT organs. In addition, this disease can also provoke more severe pathology. Therefore, according to the severity and extent of the lesion, local and systemic complications are distinguished. The first group includes otitis media, laryngitis, pharyngitis, phlegmon and throat abscesses.
Treatment of the above inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs is usually not difficult. Systemic complications of angina are much more dangerous:
- joint damage - arthritis, arthrosis;
- heart defects;
- meningitis, sepsis.
Even after successful treatment of sore throat and complete elimination of the symptoms of the disease, one should remember about the possible development of rheumatic heart disease. This complication is autoimmune in nature. The causative agents of sore throat carry on their surface proteins similar to those that make up the tissues of the heart. Therefore, the body begins to perceive them as strangers and tries to destroy them.
Acute and chronic purulent tonsillitis are diseases that not only manifest themselves with unpleasant symptoms, but can also lead to the development of severe complications. Therefore, you should not delay visiting a doctor - the sooner proper treatment is started, the lower the risk of an unfavorable outcome.
Prevention of acute tonsillitis
There is no specific prevention of purulent tonsillitis. To prevent illness, you need to pay maximum attention to your health: lead an active lifestyle, get proper rest, and eat right. Timely sanitation and diagnosis of foci of chronic diseases in the body, as well as hardening, are necessary.
To prevent the spread of an infectious disease, it is necessary to isolate the patient as much as possible, use personal hygiene products and individual utensils. In addition, it is necessary to regularly perform wet cleaning and ventilate the room where the patient is located.
Causes of the disease
The formation of pus during tonsillitis is observed in cases where the cause of inflammation is a bacterial infection. This form of tonsillitis is also called lacunar, since the pathological process develops only in the outer layers of tonsil tissue. Pus accumulates in the form of plugs in small depressions - lacunae.
The most common causative agents of acute and chronic tonsillitis are staphylococci and streptococci. However, bacterial inflammation may develop as a complication of a viral infection. Sore throat can also be caused by rarer pathogens:
- protozoa;
- specific microflora in the form of Klebsiella, Haemophilus influenzae, etc.;
- fungi.
These microbes are part of the normal microflora of the human oral cavity. When exposed to unfavorable factors and a decrease in the body's resistance, they begin to actively multiply. After the introduction of pathogens into the mucous membrane of the tonsils, inflammation develops - purulent tonsillitis.
The risk of disease increases when exposed to the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- insufficient personal hygiene;
- the presence of congenital abnormalities of the respiratory system;
- chronic diseases of the tonsils.
Important! In some cases, chronic tonsillitis may develop. This form of infection is bacterial in nature. Its cause is often associated with insufficiently effective treatment of acute inflammation of the tonsils.
conclusions
Inflammation with purulent sore throat most often occurs due to streptococci. The first signs of the disease are sore throat, general weakness, and fever.
Treatment for purulent sore throat should be started as soon as possible. But this must be done under the supervision of a doctor. Folk remedies can only be used in combination with pharmacological drugs. This will speed up the healing process and avoid all sorts of complications.
Miramistin for children: application features and instructions. Vasomotor rhinitis: treatment with folk remedies.
Sore throat in children
First, let's talk about when a child should be hospitalized:
- in the presence of concomitant diseases, including coagulation disorders, diabetes mellitus, renal failure;
- if the disease is complicated by phlegmon of the neck, rheumatic carditis or abscesses;
- severe symptoms of intoxication: confusion, impaired breathing, convulsions, vomiting, high temperature that is not controlled by antipyretics;
- Children of the first year of life should be treated in a hospital.
How to quickly cure a purulent sore throat for a child? Treatment is as follows:
- plenty of drinking regime;
- taking antipyretics and antihistamines;
- antibacterial therapy;
- vitamin therapy;
- gargling.
The use of warming procedures is unacceptable: compresses, hot thermal inhalations, warming ointments or neck creams.
It is unacceptable to constantly use the same medicinal solution for rinsing.
Gargling for children
A child can gargle with ready-made products from the pharmacy. Decoctions of medicinal herbs also have a good disinfecting effect:
- sage;
- chamomile;
- calendula.
Experts say that lubricating the throat with antiseptics can damage the protective layer of the mucous membrane, which will significantly worsen the patient’s condition.
Children over five years old can be given lozenges or lozenges.
Features of treatment for children under 3 years of age
The use of sprays is contraindicated for children under three years of age. By and large, this is not due to the presence of any harmful components, because most often the composition of most solutions is safe for children. When injecting, you should hold your breath, and small children have not yet learned to do this, so using sprays can lead to laryngospasm.
For newborns, you can spray the pacifier itself, and for older children, you can direct the spray towards the cheeks, and not into the throat itself; in any case, the solution with saliva will end up on the tonsil.
You can learn to gargle as early as two years of age. Children under five years of age have difficulty keeping a lozenge in their mouth. This could lead to the child choking on the pill, which could even be fatal.
Antipyretics
Purulent deposits provoke an increase in temperature, so until they are stopped, antipyretic drugs can only bring down the temperature for a short time. However, when using an effective antibacterial agent for several days, the temperature decreases.
Useful tips
When using any drug, be sure to read the instructions. The products should be used only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Some medications and even medicinal herbs can lead to the development of allergic reactions, so you need to monitor your baby’s reaction.