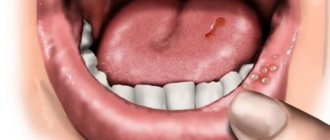
Oral cavity pathologies require careful examination and timely treatment. The most common gum disease in children is stomatitis, but its manifestations can also be detected in adulthood. The disease cannot go away on its own. It requires drug therapy. Stomatitis is dangerous; due to constant pain, patients completely refuse to eat, which leads to a deterioration in their general condition. At the first symptoms, you should immediately visit the dentist and undergo an examination. Early detection of pathology will prevent the development of complications.
General clinical picture
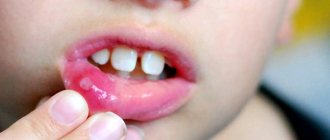
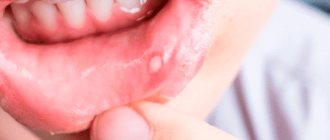
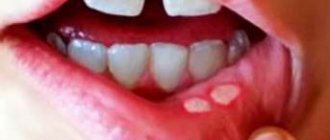
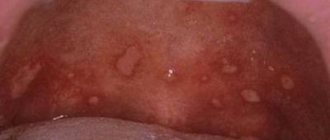
Gum stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of small wounds or ulcers. They can be single or formed in several places. The lesion causes specific symptoms that cause severe discomfort. They differ depending on the stage and form of the pathological process. The patient also experiences general disorders in the form of a reaction to pathogenic flora. Find out why teeth decay and what you need to do to protect them here.
Often, with viral or bacterial stomatitis, body temperature may increase.
Signs of stomatitis:
- the appearance of wounds, blisters and ulcers on the gums;
- pain when brushing teeth and eating;
- enlarged lymph nodes (more often in children).
Characteristic reasons
The main causes of gum inflammation include several factors. Most often, they cause the disease, but in rare cases, stomatitis can be caused by some unusual circumstances.
The most common cause of gingivitis is mechanical damage to the gums: microcracks, cuts, burns, injections, and so on. As a result, pathogenic microflora penetrates into the resulting gap in the epithelium.
Often, gingivitis in adults is provoked by the patient himself, regularly weakening his body with poor nutrition and bad habits. Smoking is especially dangerous in this case, since cigarette smoke greatly dries out the mucous membranes of the mouth and can cause minor burns on the lips and gums.
The infection is caused by:
- careless adherence to the rules of brushing teeth;
- entry of pathogenic microflora into the mouth from dirty hands and unwashed food;
- allergic reactions to components of toothpaste, rinses, medications and other synthetic substances;
- diseases in the digestive tract and general intoxication of the body;
- diseases of the teeth and oral cavity;
- HIV infection and blood diseases;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs.
In general, the likelihood of developing the disease greatly depends on the general tone of the patient’s immunity. The normal state of the body's defense system neutralizes the threat even in the presence of a number of the listed risk factors.
Stages of disease development
Stomatitis is not a harmless disease. As the infection progresses, the focus of infection expands, which can lead to complications. In total, there are 3 stages of disease development:
- light. There are no visible changes. During this period, the pathogen penetrates the gum mucosa and becomes active. A mild degree is characterized by tissue redness and slight swelling. Due to irritation, the gums become dry and shiny. At this stage, it is quite difficult to determine stomatitis without a specialist. Many patients attribute these symptoms to other factors;
- average. In the absence of measures, after just two days the pathogens continue their vital activity, and the symptoms expand. A white coating forms on the gum in a limited area. With some types of stomatitis, it can spread from the gums to the tongue and cheeks. During this period, the patient needs to find out the cause of the pathology and urgently begin treatment in order to prevent the last stage;
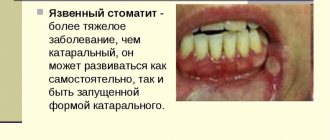
- heavy. In place of the white coating, wounds and ulcers clearly appear. The gums become very inflamed, any mechanical movement can lead to pain. The bubbles fill with liquid and then burst. Gradually, the wound surface becomes covered with a crust or continues to ooze.
The duration of stomatitis from penetration of the pathogen depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the level of immunity and treatment. On average, the change of stages is observed from 2 to 14 days. Sometimes the pathology occurs again.
Forms
The course of stomatitis varies depending on the factor that provoked its occurrence.
Viral
Viral or herpetic stomatitis is the most common among all types of this pathology. Bubbles filled with clear liquid form on the gums. When palpated, they can easily break through, becoming affected by a secondary infection.
Sometimes the virus manifests itself in minor symptoms.
Gradually, the contents of the pustules become cloudy and come out. Erosion is visible at the site of the formations. The incubation period for herpetic stomatitis can be as little as 3 days. During this period, the patient is infectious to others. Learn about angular stomatitis and its treatment in this material.
Bacterial
Superficial infection. Intoxication occurs in the body. Appetite is impaired, body temperature can reach 37.5 degrees. Discomfort manifests itself when food gets on the gums or when brushing teeth. Salivation becomes profuse. When examining the oral cavity, white plaque is found on the gums in different places, bleeding, the mucous membrane of the inner part of the gut looks inflamed.
Deep or ulcerative necrotic infection. The patient experiences a serious deterioration in his condition with headache and sleep disturbances. Temperatures increase to 38-39 degrees. Appetite disappears completely, body weakness and mood changes are noted. The pain persists constantly, intensifying with mechanical stress. An unpleasant odor emanates from the gums.
When examining the oral cavity, traces of bleeding on the gums and an abundance of ulcers are visible. Initially they are small in size, but within a few days they change color and increase in size. Wounds appear with tissue breakdown.
Fungal
Infection of the oral cavity with candidiasis is the most dangerous type of stomatitis. If left untreated, pathogens can penetrate inside, affecting organs. The affected gum becomes dry and acquires a bright red tint. A distinct white coating gradually forms, its structure reminiscent of cottage cheese.
At the beginning of the pathology, the film is well separated from the soft tissue. Gradually it thickens, merges with the mucous membrane, and if damaged, leaves a bleeding ulcer. The patient has difficulty eating and may lose weight.
Allergic
Stomatitis of this nature occurs due to contact of the mucous membrane with an allergen. A complex of symptoms appears, which quickly goes away after eliminating the stimulus. Allergic gum disease often occurs when taking medications or due to autoimmune disorders associated with the production of histamine. Read about the treatment of ulcerative stomatitis in the mouth here.
Allergic stomatitis cannot be neglected. In an advanced stage, it can lead to the formation of bleeding ulcers.
Already in the initial stage, the patient feels dryness, irritation and itching in the oral cavity. Taste sensitivity may be impaired, and eating is accompanied by pain.
Diagnostics
In its initial development, stomatitis is difficult to determine. Self-examination of the oral cavity does not produce results; only redness is visually determined. But already a few days after the formation of the ulcer, stomatitis can be assumed. To clarify the diagnosis, it is better to consult a specialist. The sooner the cause of the pathology is determined, the sooner the patient will undergo treatment and return to his usual lifestyle.
In the middle stage, the dentist immediately identifies stomatitis. Next, laboratory tests are carried out. The pathogen is identified using polymerase chain reaction. To date, this analysis is the most informative. It allows you to rule out other possible gum problems.
Better to play it safe
While stomatitis in any part of the gums progresses, its causative agent spreads throughout the body through the circulatory system and saliva. First, this leads to intoxication, characterized by high temperatures, fever, headaches, joint and muscle pain, nausea, and then vomiting.
When the pathogen takes over the entire body, sepsis will develop. To prevent these complications from ending in death, the patient is admitted to the hospital under the supervision of doctors.
In order to avoid complications at all, you need to see a doctor at the beginning of the development of stomatitis. Its diagnosis and treatment in adults can be carried out by a dentist or therapist. Children will receive help from a pediatric dentist and pediatrician.
If necessary, the doctor can write out a referral to an immunologist, orthopedist, periodontist, cardiologist or other specialists. Regardless of the direction, it is recommended to visit an allergist who can help prevent allergies when using medications for stomatitis. After a complete examination, the doctor will draw up a treatment plan based on the collected data, the age and well-being of the patient.
Let's look at how to treat stomatitis that affects the mucous membrane of the gums.
We suggest you read What to do if your lips dry out
Treatment
Measures aimed at eliminating stomatitis are carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Only if all recommendations are followed and the oral cavity is treated in a timely manner, the disease can be overcome within 7-15 days.
Medication
Anesthesia. It is used to relieve oral discomfort and symptoms, but does not act as a treatment. Anesthetics and painkillers in the form of ointments protect exposed affected gum tissue, reducing the risk of damage. This link will tell you how to relieve toothache during pregnancy.
List:
- Lidocaine (Trimecaine, Benzocaine);
- Kamistad;
- Holisal;
- Anestezin.
Antiseptics. They are used to cleanse the oral cavity of a large number of microbes, preventing their deep impact on the soft tissue. Disinfection occurs immediately after using the drugs, but be careful when using brilliant green as an antiseptic. The most popular are:
- Horhexidine;
- Furacilin;
- Metrogil Denta;
- Hydrogen peroxide;
- Betadine;
- Yodovidone
- Chlorophyllipt.
Antibiotics. Required for the treatment of microbial stomatitis. After applying the drug to the gums, the pathogen is inhibited. Antimicrobial agents can also be used systemically. The course lasts from 7 days.
Pills:
- Agumentin;
- Amoxicillin
- Lincomycin;
- Clarithromycin.
Ointments:
- Levomycetin;
- Gentamicin;
- Erythromycin.
Healing drugs. Helps smooth out symptoms during the formation of ulcers and rapid regeneration of gum tissue. After regular treatment, the risk of formation and tearing of crusts is reduced:
- Panthenol;
- Vinylin;
- Balm lifesaver;
- Solcoseryl.
Immunostimulants. Necessary for strengthening general and local immunity. Promote the development of a normal reaction of the body in response to pathogenic microflora.
Kinds:
- Immunal;
- Immunoflazid;
- Laferon;
- Socloseryl;
- Proteflazid.
How to treat stomatitis in children's mouths at home
Damage to the oral cavity in childhood is typical not only due to decreased immunity. At this time, the permeability of blood vessels in the blood supply system is high. This facilitates the penetration and spread of infection throughout the body. In adults, saliva contains enzymes that have partially antiseptic properties. Children have few such substances, so they remain at risk.
Following the dentist’s recommendations will quickly help you cure stomatitis at home:
- Increase fluid intake. For infants, plain water or breast milk is suitable. Older children are given juices and fruit drinks.
- Avoid spicy foods. Do not add even a small amount of black pepper, vinegar or other irritating foods to food. Herbs and spices will develop additional irritation and pain reaction. In addition, they reduce the regeneration process of affected areas.
- Consumption of gentle food. All products should be well chopped, not hot and not very cold.
- Support cutlery frequency. It is necessary to pay attention to the treatment of bottles and nipples for infants. After each feeding, they should be thoroughly washed and treated with a weak antiseptic solution.
Ointments and gels
To select a drug for the treatment of stomatitis in children, it is first necessary to determine what type of inflammation is present in the child. The effect should be not only local, but also on the entire body as a whole, so the treatment effect will be much higher. The following ointments and gels for stomatitis are prescribed for treatment:
- Nystatin. Used for fungal stomatitis. The polyene antibiotic is integrated into the structure of the fungus and destroys it. Only the affected areas should be smeared. A 5% product is suitable for application. Treatment is carried out twice a day, until the pathological process stops from 3 to 7 days.
- Methyluracil. Well tolerated by children of any age. Provides regeneration of soft tissue lesions. With stomatitis, it easily copes with the pain reaction and the inflammatory process. Suitable for ulcerative and bacterial lesions of the mucous membrane. Methyluracil can be prescribed in combination with other drugs.
- Holisal. This is a dental gel that has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Within 2–3 minutes the therapeutic effect is noticeable. Can be used on babies up to one year old. For treatment, a 0.5 cm long strip of the product is sufficient, which is actively rubbed into the affected areas.
- Metrogyl denta. It is a special composition based on metronidazole. Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Negatively affects bacteria that cause stomatitis. Thanks to Chlorhexidine included in the composition, Metrogyl Denta has a pronounced antiseptic effect. This ointment for stomatitis in the mouth has a small percentage of active substances, which allows the product to be used for a long time for expectant mothers and children over 6 years of age.
- Kamistad. The active ingredients are chamomile extract and lidocaine hydrochloride. It has a double effect: antimicrobial and analgesic. A serious drawback is that it is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age. There are no restrictions on the course of treatment. The frequency of use is up to 3 times a day.
- Solcoseryl. Its therapeutic effect is similar to the drug Methyluracil. It is used only externally for antiseptic effects and healing of affected soft tissues. The anti-inflammatory analgesic effect is weakly expressed, but taking into account the permissibility of long-term use, Solcoseryl is an indispensable remedy in the treatment of various forms of stomatitis. Before making the application, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic and then thoroughly dried with a cotton-gauze napkin. It is important that there is no bleeding of soft tissues.
Antiseptic rinses
The following products are suitable as rinses for stomatitis for children:
- Miramistin. The product is safe, which allows it to be used even by children under one year old. For infants, oral cavity treatment is carried out using a cotton swab, since they are not yet able to rinse. The drug is also available in the form of an aerosol, which is convenient for applying the drug to the mucous membrane. Miramistin has antiviral, antiseptic and wound-healing effects.
- Iodinol. The antiseptic is produced with a high concentration of the active substance. Therefore, before use it is diluted with water. One tablespoon per glass of liquid is enough. You can rinse your mouth 3-4 times during the day.
- Sodium tetraborate. Suitable for babies. Simply soak the pacifier in the medicine and give it to your child overnight. For older children, the affected areas are soaked with gauze swabs.
- Vinylin. The drug is allowed for use only in children over 14 years of age. Do not allow the product to enter the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, morphological elements in case of stomatitis are processed by application. Treatment is carried out after meals.
Attention! Rinse products, just like other medications, should be prescribed by your dentist. It is important to consider contraindications by age category. This point allows you to eliminate the occurrence of an allergic reaction and overdose of medications.
Antiviral agents
Each type of inflammation of the mucous membrane requires the selection of medications. Therefore, microflora seeding is necessary. It is difficult to treat stomatitis in children's mouths due to the characteristics of the children's age. Antiviral drugs are used from the first day of stomatitis:
- Acyclovir. Antiviral drug. The active substance penetrates the structure of the virus, affecting it from the inside. The ointment is applied as an application using a cotton swab. The product is distributed over the entire affected surface, including healthy areas. The treatment procedure is up to 5 times a day, for 7–10 days.
- Oxolinic ointment. Copes with most types of viruses. Allowed as a prophylactic agent. For stomatitis in children, a concentration of 0.25% is required. Used in the same way as Acyclovir.
- Viru-Merz-serol. Fights the herpes virus, eliminating itching and burning. After application, the pain quickly goes away and the treatment of herpetic stomatitis is shortened. If the effect is positive, use for 5 days, applying to the affected areas of the oral mucosa 3 to 6 times a day. When blisters appear, topical use of the drug becomes ineffective.
- Tebrofen ointment. It is also an antiviral drug with a working concentration of 2%. The course of treatment for an infant is one week, provided that the ointment is applied at least 3 times a day. At an early age, allergic dermatitis rarely appears as a side effect.
Protective film-forming agents
Such drugs have adhesion and remain on the surface of the affected soft tissue for a long time. Depending on the composition, they have analgesic, regenerating, anti-inflammatory or complex effects. These include:
- Stomatophyte. This is a liquid extract that contains plant components. The active ingredients will be sage leaves, chamomile flowers, thyme, mint, arnica herb. Oak bark is presented in the form of an extract. Provides comprehensive treatment to problem areas and covers damaged soft tissues with a film for a long time.
- Hexalize. Prescribed for stomatitis in older children. Dissolve up to 8 tablets per day. The full course of treatment is 10 days. The multicomponent composition provides a comprehensive effect on the sore mouth. For stomatitis in children, it is prescribed as an anti-inflammatory agent.
- Kalgel. Thanks to the adhesion effect, the drug reliably covers the affected areas. Already immediately after application, an analgesic effect is felt. The child can safely eat and drink liquids. It is recommended to use it as a gel at night to relieve pain reactions.
- Lidocaine asept. This remedy for stomatitis is an antiseptic, available in the form of a spray for local application to wounds and ulcers. Transparent yellowish liquid, with the smell of mint, which does not cause unpleasant sensations in children. The drug is prescribed for stomatitis in a child, periodontitis and traumatic injuries to the oral cavity.
Features of the treatment of aphthous stomatitis
For aphthous stomatitis in children, consultation with a gastroenterologist and allergist is necessary. With an unclear etiology, the disease requires an integrated approach to the problem and elimination of all possible root causes. The following approach is used in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children:
- If it is determined that inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs due to an allergic reaction, then contact with the allergen is first excluded. Antihistamines in the form of Citrine or Suprastin will help cure stomatitis. For children, the drugs are suitable in the form of syrup. Used only after 2 years of life.
- Morphological elements require local processing. For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal herbs, a solution of baking soda, boric acid or methylene blue are used. After antiseptic treatment, regenerating agents such as Solcoseryl or Methyluracil ointment should be applied. The affected areas can be treated with an antiseptic with a healing effect. For this treatment, a drug such as Rotokan is suitable.
- Dentists prescribe vitamin therapy as a general treatment. With aphthous stomatitis, children require vitamins B1, B12, B2 and C.
- If the course of stomatitis is chronic, then immunocorrective agents are prescribed. The therapeutic effect of changing the immunological status is provided by Pyrogenal and Dekaris.
If you have aphthous stomatitis, you should never self-medicate at home and rely only on the advice of friends. Also, folk remedies in this case will be ineffective. Medicines for aphthous stomatitis are selected by the doctor after examination.
ethnoscience
Alternative medicine for stomatitis plays a supporting role. Thanks to the action of medicinal herbs, pathology is less complicated. Decoctions can replace antiseptic solutions if they are not at hand.
Rinse:
- decoction of chamomile, calendula and horsetail. Herbs have a powerful disinfecting effect. They can be used several times a day. To do this, the plants are brewed into tea. The mouth is rinsed with warm liquid so as not to injure the erosive gums;
- honey. Has a powerful wound healing effect. Using this product you can significantly reduce the manifestations of stomatitis. For rinsing, take a teaspoon of honey and dissolve it in 100 ml of water. The oral cavity is treated with a warm medicine 4-5 times a day.
Gadgets:
- sea buckthorn oil. Well soothes irritated gums and stimulates the process of cell regeneration. For greater efficiency, lotions are used. To do this, the oil is diluted with boiled water 1:1 and the swab is moistened. Applications are made for 10 minutes, carefully covering the eroded areas;
- carrot juice. It is used to alleviate the inflammatory process in stomatitis with candidiasis. For processing, take freshly squeezed juice and mix it with warm water 1:1. The lotions are applied for about 20 minutes, constantly changing the tampon.
Diet and pain management
The first thing a person with stomatitis needs to do is go on a special diet and change food preparation methods. The list of permitted foods and drinks, the basic rules for serving them on the table are indicated in the article “What can you eat with stomatitis.”
Painkiller "Instillagel"
The pain that appears during the disease will interfere with eating normally. Therefore, 20 minutes before meals, you need to lubricate the damaged areas on the gums with pain-relieving gels: Instillagel or Lidochlor, irrigate with Hexoral or Tantum Verde sprays. You can use Strepsils or Grammidin lozenges. Any medications have contraindications and side effects; consult your doctor before using them.
Nutrition for stomatitis
Any products are crushed as much as possible. It is recommended to consume food in puree form. Spices, excess salt and marinades are excluded. Eating raw vegetables and fruits is unacceptable; acids can irritate tissues. Dishes should not be hot or cold. In case of extensive erosions on the gums, liquid food is taken only from a tube. This article will tell you how to get rid of bad breath during pregnancy.
In case of pathology, it is advisable to follow a diet. This will allow the affected gum to recover faster. Some foods are prohibited as they can cause inflammation.