The state of oral health seriously affects the entire body: diseased teeth or gums can disrupt the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, and provoke the development of respiratory infections and diabetes. Often, incipient problems are signaled by changes in the gum tissue - inflammation, swelling, and bleeding are experienced by up to 80% of people throughout their lives, regardless of age.
Beautiful gums
Means for treatment and prevention
To get rid of infection, antiseptics are traditionally used - disinfectants that prevent the growth of microorganisms. When choosing such a drug, you need to focus on the effectiveness and ease of use. An antiseptic must have a pleasant taste and smell, be comfortable to use, and maintain the whiteness of fillings and tooth enamel.
It is optimal if it is a remedy with a complex effect that will reduce inflammation, at the same time fight infection, reduce pain and restore freshness to breath.
How to choose a product
All requirements for antiseptic products for the oral cavity are met by the “Parodontocide” series of products. It is based on a unique combined composition consisting of natural plant components:
- sage oil - has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
- clove oil - destroys pathogenic bacteria.
- peppermint oil - helps cope with pain and refreshes the oral cavity.
- oregano – has an antibacterial effect.
- thymol - helps get rid of pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
- eugenol – destroys pathogenic bacteria.
- phenyl salicylate - has an antiseptic effect.
- allantoin - quickly heals damage to the mucosa.
The combined combination of organic components has a soothing, anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antibacterial effect in the oral cavity, and also normalizes its microflora and eliminates unpleasant odor.
It is known that antiseptics containing triclosan, chlorhexidine or metronidazole can disrupt the balance of the oral microflora, and products with chlorhexidine can stain the tongue, teeth and dental fillings\).
The unique composition of the “Parodontocide” series of products allows you to avoid the troubles typical of using antiseptic drugs. An additional advantage of the series is the variety of release forms - rinse solution, mouth spray, rinse, gum gel and even toothpaste. The “Parodontocide” assortment includes all the necessary products for complete oral hygiene.
Diagnostic tests
Schiller-Pisarev test
This test is based on determining the level of glycogen in the gum. Its amount increases significantly during inflammation, while healthy gums do not contain glycogen. Lubricating the inflamed gums with Schiller-Pisarev solution gives a color change reaction from light brown to brown. This research method is used to make diagnoses of both periodontitis and gingivitis.
Assessment of oral hygiene level
A solution (2 g of potassium iodide, 1 g of crystalline iodine, 40 ml of distilled water) is applied to the outer surface of the six lower front teeth.
The assessment is carried out using a five-point system and each tooth is assessed separately:
- 5 points – complete staining of the entire tooth surface;
- 4 points – staining of ¾ of the tooth surface;
- 3 points – staining of half the tooth surface;
- 2 points - staining of a quarter of the tooth surface;
- 1 point - absence of any staining of the tooth surface.
Then the scores of all examined teeth are summed up and divided by their number (usually the test is carried out on six teeth). This is how the hygiene index is obtained.
As a result, the quality of hygiene is assessed:
- 1.1-1.5 points – good hygiene index;
- 1.6—2.0—satisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.1—2.5—unsatisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.6—3.4—poor hygiene index;
- 3.5-5.0 - very poor hygiene index.
Vacuum test according to Kulazhenko
Using a Kulazhenko vacuum apparatus, it is possible to determine the time of hematoma formation when a vacuum is applied to the gum area. Typically, the test is carried out in the incisor area by placing a tube of the device on the gum. The formation of a hematoma in 60 seconds indicates the normal condition of the gums, while the appearance of a hematoma in 29-30 seconds signals an inflammatory process.
Oxygen tension in gum tissue
The sensor of the device is applied to the gum, and the device records the level of tissue hypoxia. Reduced oxygen tension indicates a prolonged inflammatory process.
How to use: prevention
The “Parodontocide” series of products can be used in combination or by choosing individual products for yourself. All products in the series combine perfectly with each other, complement and enhance each other’s effects.
Fig. 1 Series of “Parodontocide” products for the treatment and prevention of oral diseases.
After hygienic brushing of your teeth, you can rinse your mouth with a solution or rinse called Parodontocide. And at work or on the road, it is recommended to use a spray - you can use it after every meal. This prevents gum inflammation and helps fight bad breath. If damage occurs to the mucous membrane, then Parodontocide gel comes to the rescue, which can be applied to the damaged area 2-3 times a day.
Tips for gum health
Good oral hygiene is the easiest way to keep your gums healthy.
The following tips can help a person maintain good oral hygiene:
- brush your teeth for at least 120 seconds twice a day or more often
- floss every day
- rinse your mouth with a product containing fluoride once or twice a day.
- after eating sugary foods or drinks, rinse or brush
- Replace toothbrushes or toothbrushes every few months or when they look worn.
- exercise at least 30 minutes a day.
- visit the dentist regularly
- avoid smoking or using tobacco products
It is also important to eat a healthy, balanced diet. This should include plenty of whole fruits, vegetables and grains. Your diet should include good sources of iron such as lentils, peas, beans and dry meats.
How to use: treatment
For diseases of the oral cavity, hygiene measures can be supplemented with the use of “Parodontocide” gel and more intense rinsing.
For chafing from braces or dentures, it is enough to apply a little Parodontocid gel to the damaged areas. It promotes mucosal restoration and prevents the development of inflammation.
Stomatitis and gingivitis require mandatory daily treatment of the oral cavity 2-3 times a day with an antiseptic solution - using a spray or rinse solution.
Well, in case of severe problems, an enhanced combination is used: in addition to daily brushing of teeth with a special treatment and prophylactic paste, Parodontotsid, daily treatment of the oral cavity with other means of this line is added: antiseptic gel 2-3 times a day + irrigation of the mucous membrane 2-3 times a day.
Fig.2 Products of the “Parodontocide” series for complex therapy of oral diseases
The “Parodontocide” series will help restore the healthy condition of the gums and oral cavity. A unique combined composition, based on natural ingredients, has a complex effect necessary for the prevention and treatment of oral diseases. Protect yourself from gum problems!
* E.V. Zoryan, etc. Experience in the clinical use of antiseptic drugs for periodontal diseases // Medical business - 2007 - No. 4.
The problem of gum disease can affect anyone, regardless of age. The onset of the disease may seem minor and harmless - slight redness of the gums or bleeding when brushing your teeth. Diseases of the oral mucosa in children and adults are a rather serious problem, and it is not always possible to get rid of it in one visit to the dentist.
Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor promptly when the first symptoms occur and begin treatment. Taking care of your gums is no less important than taking care of your teeth. Maintaining healthy gums is necessary not only for the oral cavity, but also for the entire body as a whole. A description of the names, symptoms and treatment can be found in this article.
Treatment options
The choice of treatment method directly depends on the factors that provoked the development of the inflammatory process. If this is due to the formation of tartar, then first you need to get rid of them. Only after this the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy to the patient. As noted earlier, a dental filling, when installed by the doctor, can also lead to redness of the gums. In this case, the product must be reinstalled.
Professional teeth cleaning is carried out in cases where insufficient oral hygiene has become the main cause of the disease. Then the patient is prescribed special medications, the regular use of which will return the gums to their previous condition. To relieve inflammation in dentistry, various methods can be used, including the use of pharmaceutical drugs and folk remedies. Let's consider each of the methods separately.
Pharmacy products
To relieve or alleviate symptoms, modern medicine offers many medications, the most effective of which include:
- Holisal;
- Polyminerol;
- Maraslavin;
- Periodonticide.
All these drugs are available in different forms, but most often dentists recommend using a cream or gel to relieve the inflammatory process. This will relieve not only inflammation, but also bleeding gums, and also protect the body from infection.
In pharmacies you can find other drugs that can relieve redness in the gums. These are Dental, Asepta, Parodium and others. But even if you purchased one of these products, no one canceled your visit to the doctor.
How to reduce inflammation
Oral hygiene is perhaps the main factor influencing the occurrence of many pathologies, including inflammation. If a person takes proper care of his oral cavity, this will protect him from such troubles. But if the inflammatory process in the gums does begin, you need to know how quickly you can reduce it. Below are step-by-step instructions that will help relieve inflammation at home.
Step 1. Dental plaque often leads to an inflammatory process, so to remove it, regularly brush your teeth at least 2 times a day. In this case, the duration of the procedure should be 2-3 minutes. This will also prevent relapses. Change your toothbrush every 3 months. The same applies to paste, which needs to be changed periodically.
Step 2: Don't ignore flossing. This is a great way to clean the interdental spaces from accumulated food debris and plaque. But you need to resort to threading no more than once a day. All movements must be careful so as not to damage the gums. Otherwise, along with redness, bleeding gums may also occur.
Step 3: Rinse your mouth regularly with saline solution. It's no secret that salt has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, so regular rinsing of the mouth will reduce redness of the gums. Simply mix a glass of warm water with 1 tsp. salt. Just don’t swallow the solution.
Step 4. Apply compresses to your teeth. This will relieve inflammation. Wet a small piece of cloth with warm water and apply it to the sore spot to relieve pain. You can also apply a cold compress. To do this, place a few ice cubes in a clean cloth and press gently to the desired location.
Step 5. If you happen to encounter redness of the gums, then it is advisable to give up bad habits during the treatment period. The fact is that tobacco and alcohol negatively affect the condition of the gums and also weaken the human immune system.
Step 7. Gum massage will help relieve inflammation. Massage your gums with gentle finger movements, spending 1 minute for each session.
Step 8. Use clove oil to relieve inflammation. To do this, you need to moisten a swab with oil and apply it to your gums. Due to its beneficial properties, the oil relieves redness and eliminates pain. After application, rinse your mouth with warm water.
ethnoscience
In folk medicine, there are many different recipes to relieve redness and pain in the gums, but the cause of this disease cannot be eliminated. One of the most effective methods is rinsing, which allows you to eliminate unpleasant symptoms before visiting the dentist. Let's look at the most common recipes.
Table. Recipes for folk remedies for gum inflammation.
| Product name | Application |
| Lemon juice | Lemon is often used in folk medicine to treat oral pathologies. To relieve inflammation, treat the affected areas of the gums with a special solution made from lemon juice and warm water. To apply the solution, use cotton wool or a soft brush. Avoid getting the product on tooth enamel. |
| Lemon oil | Grind several lemon peels using a blender or on a fine grater, then mix the resulting pulp with vegetable oil. Leave the resulting product in a dark room for 2 days, then apply to the inflamed area of the gums several times a day. |
| Melissa infusion | Melissa helps relieve inflammation. To prepare the infusion, pour 500 ml of boiling water into 1 tbsp. l. herbs and leave for 3 hours. The cooled infusion should be strained through cheesecloth, then rinse your mouth with it 2-3 times a day. |
| Aloe | This medicinal plant has an anti-inflammatory effect on the body, so aloe is often used in alternative medicine for redness of the gums. Cut an aloe leaf in half and rub the inside of it on the sore gums. Repeat this procedure 2 times a day. |
| Fir oil | Soak a cotton swab or bandage with fir oil and treat the inflamed gum surface. After 10-15 minutes, rinse your mouth with warm water. The procedure is recommended to be carried out daily before bedtime. |
| Calendula | Prepare a solution of 1 part water and 10 parts alcohol tincture. Rinse your mouth twice a day. The result can be seen almost immediately. |
If traditional medicine still does not help relieve inflammation and pain, then it is still not recommended to take painkillers before visiting a doctor. First of all, this is due to the fact that such drugs can provoke the body to develop immunity to various dental procedures, for example, to “freezing”. Therefore, when visiting a doctor, the patient may experience discomfort.
If you can’t see a dentist right away, then as an exception you can take a pain reliever called Ibuprofen. This will relieve pain until you visit a doctor.
Signs of healthy gums and common causes of disease
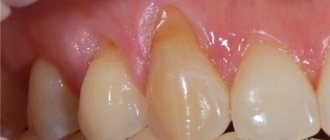
What are they like - healthy and well-groomed gums? Gums in a healthy state are not blue or red, but have an even pale pink color. The periodontal tissues appear without signs of swelling and redness. There is no pain, bleeding or discomfort when brushing your teeth. The absence of a bad odor and a constant bad taste in the mouth can also indicate healthy gums.
Currently, the factors that cause diseases of teeth and gums are known (see also:). There are two main criteria for gum problems. These include:
- Common reasons. This group includes diseases of the circulatory system, hormonal disorders, hypovitaminosis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Local reasons. These include pathologies of the tongue frenulum, malocclusion, tartar and hard plaque on the surface of the teeth.
Very often, inflammatory processes occur as a result of improper care of teeth and gums. Due to irregular, insufficiently thorough brushing of teeth or the wrong choice of oral care products, active proliferation of microorganisms occurs. Thanks to their vital activity, soft plaque over time can turn into hard interdental deposits that injure the mucous membrane. The infection, getting to the injured areas, provokes the appearance of the disease.
The causes of inflammation can be the consequences of damage from incorrectly installed fillings or dentures that are not selected according to size. Quite often, the pathological process can develop as a result of thermal or chemical burns of the oral mucosa. As a result of injury, it sometimes happens that the frenulum is torn or damage to the mucous membrane occurs. An open wound can become a source of infection if antibacterial treatment is not timely.
Characteristic symptoms
The onset of the inflammatory process in the gums will be indicated by symptoms that appear gradually. But after some time they will increase intensively.
The clinical picture of gum inflammation looks something like this:
- bad breath;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- painful sensations.
Redness of the gums, which immediately catches the eye, occurs already at an early stage of the development of the disease, as a result of which the gums turn bright red. If you notice that your gums are starting to turn red, but there are no other symptoms yet, you should still visit your dentist's office.
Bleeding occurs at the second stage of development of the inflammatory process. As a rule, blood appears only when brushing teeth or mechanical impact. This is a rather serious phenomenon, the presence of which indicates a long course of the disease. In this regard, you need to start treatment immediately. Even slight touches to reddened gums can cause discomfort or pain. This also applies to food intake, because when chewing, the gums are subjected to severe stress.
The next stage of development is accompanied by swelling of the gums, and pus begins to collect in the gum pocket, which causes the patient to have bad breath. In rare cases, bad breath may be the only symptom of the inflammatory process.
Improper treatment can cause the patient's gums to atrophy. As a result, the patient may lose one or more teeth. To prevent this, it is extremely important to treat the pathology immediately after the first symptoms appear, that is, at an early stage of its development.
Classification of gum diseases, their symptoms and principles of treatment
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to find out from me how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
Gum diseases are divided into several groups, depending on the location of inflammation and the stage of the disease. Gingivitis and periodontitis are inflammatory infectious diseases, most often they develop in pregnant women, children and adolescents (we recommend reading:). When gingivitis develops, the dental tissues are not affected, only the mucous membrane around a particular tooth becomes inflamed.
With periodontitis, the ligament between the bone and the tooth is destroyed, and the supporting apparatus loses its functions. As a result, a kind of pocket appears in which food particles accumulate. Bleeding, swelling of the mucous membrane, and increased sensitivity of the gums appear (we recommend reading:). Periodontitis can cause tooth loss that becomes dislodged and loose.
Periodontitis occurs due to inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and is a complication of periodontitis. Periodontal disease is a problem mainly for older people who have reduced vascular conductivity and impaired blood supply to tissues.
Gingivitis: inflammation of the gum lining
Gingivitis occurs due to the accumulation of plaque and food debris in hard-to-clean areas and interdental spaces. Most often, inflammation occurs due to insufficient oral care. Gingivitis affects dentin tissue, periodontium and gingival papillae. Signs of the disease: red or blue gums, swelling, pain when brushing your teeth. Your gums may bleed and you may experience bad breath. Types of gingivitis are divided into:
- catarrh;
- gum hyperplasia;
- ulcerative-necrotic stage.
Catarrhal inflammation occurs due to poor hygiene, but pain makes it impossible to carry out. The doctor performs professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. It is recommended to rinse the mouth with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial solutions for several days. As an addition, electrophoresis and hydromassage are used, which show good results in the treatment of gingivitis.
Hypertrophic gingivitis is a chronic continuation of the acute form. Factors in the development of hyperplasia can be: traumatic bite, reaction to taking certain medications, hormonal imbalance, dysfunction of the endocrine system.
Ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane can be a stage of gingivitis, or arise as an independent pathology. The infection occurs against the background of active proliferation of microorganisms in the interdental spaces due to poor oral hygiene.
Treatment of gingivitis occurs in several stages. First, the specialist eliminates dead periodontal tissue using anesthesia. Then the mucous membrane is treated with antimicrobial agents. A comprehensive treatment is prescribed, which includes treatment with antiseptic and antimicrobial drugs.
Periodontitis: inflammation of the gums
Periodontitis is a chronic disease that affects not only the gums, but also all periodontal tissues. The destruction of the periodontal tissue fibers that hold the bone tissue and tooth together occurs. Mobility of teeth appears and increases, and their loss is possible. Symptoms of periodontitis depend on the severity of the disease:
- the mild form is characterized by the formation of a bone pocket about 3.5 mm deep;
- with an average degree, periodontal pockets reach 5 mm;
- severe form - the depth of the bone pocket is more than 5 mm.
In mild forms, bleeding occurs when brushing teeth and discomfort while chewing. Then gum bleeding may begin spontaneously, patients try to avoid talking and even skip meals. With the development of severe periodontitis, a putrid odor may appear, tooth mobility becomes more pronounced, and tooth loss may occur. See the photo for more details.
Curing periodontitis is not easy, but it is quite possible. The course of treatment includes the prescription of medications, surgical procedures and orthopedics. The specialist removes hard dental deposits and pathologically altered tissues, after which he granulates the bone pockets. Drug treatment of gum disease includes taking antibiotics, immunomodulators and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
Periodontitis: consequences of the spread of the inflammatory process
What is periodontitis? This is the development of a pathological process in the area of the ligamentous tissue of the tooth, as a result of which suppuration forms inside. In cases where the disease becomes chronic, there may be no obvious symptoms. This can be misleading; the absence of pain may be regarded by the patient as the cessation of the disease. If the inflammatory process is started, the spread of infection continues. Treatment of periodontitis comes down to eliminating the inflammatory process of the tooth root.
Periodontal disease: age-related changes in the gums
Gum disease in old age causes a lot of inconvenience for patients. Over time, the function of the blood supply to the oral mucosa is very often disrupted. As a result, symptoms such as damage to tooth enamel and bone tissue, receding soft gum tissue, and pallor of the mucous membrane appear (we recommend reading:). In severe forms of periodontal disease, teeth may become loose and fall out.
Treatment of periodontal disease is aimed at stopping the pathological process and stabilizing the general condition of the patient. After a comprehensive examination, dental plaque is cleaned. After which the doctor prescribes a vitamin-mineral complex and the use of medicated toothpastes.
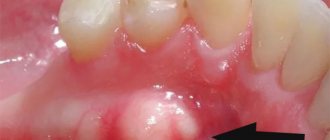
Cysts and microtraumas
The causes of cysts are: advanced caries or pulpitis, poorly healed root canal, periodontitis. The presence of microtraumas, hypothermia and insufficient hygiene aggravate the development of pathology. The growth of a cyst on the gum can provoke the formation of a fistula - an opening through which purulent contents are released. Treatment in this case can be surgical or therapeutic. Drug treatment is carried out if the disease is at an early stage. Antimicrobial, decongestant and wound-healing drugs are prescribed. To eliminate pain, drugs from the analgesic group are used.
Causes
The appearance of a blue tint on the gums can be caused by various reasons. This is mainly teething, prosthetics, diseases of periodontal tissue and the oral mucosa, or as a local symptom of the pathology of another body system. Depending on the cause, manifestations can be temporary or permanent.
Causes of blue gums in a child
The period of teething, which occurs in children in 2 stages (temporary and mixed dentition), occurs individually in each case. When the formed rudiment leaves the jaw bone, the mucous membrane, which contains a large number of vessels, is injured. As a result of ruptures, blood enters the soft tissues. Thus, a hematoma is formed.
A large number of microhematomas contributes to the formation of an externally visible blue spot. Also, the process of teeth appearance is combined with the dilation of microvasculature vessels. Against the background of such changes in the lumen of the vessel, an increase in blood volume occurs. This also causes the gums to turn blue.
In children, gums can also change color for other local reasons:
- Periodontal tissue diseases: gingivitis. With gingivitis, inflammation covers the gums without disturbing the periodontal attachment. The gums may be blue, in combination with a red tint, only in limited areas of the mucous membrane and more often in the area of the neck of the tooth. The child may be capricious and refuse to eat.
- Diseases of the mucous membrane: stomatitis. Stomatitis in children is characterized by rapid and massive development of inflammation of the mucous membrane. The bluish area most often corresponds to the corolla, located along the diameter of the rash. Rashes on the mucous membrane can be of different types (spots, blisters, erosions and ulcers). During the erosive-ulcerative stage, a child may experience fibrinous plaque on the element. Characterized by severe pain in the mouth. In severe cases of the disease, the temperature may rise up to 40. Both gingivitis and stomatitis occur more often in weakened children with reduced immunity.
Causes of blue gums in adults
If the gums turn blue in adults, then the cause should be sought in the dental intervention performed, the presence of periodontal diseases (gingivitis) or systemic pathology. The occurrence of such blue discoloration is quite low. More often, a stain occurs as a result of dental intervention.
Basically, a dentist can provoke the development of pathology by irrationally performed prosthetics. When the crown moves deeply into the subgingival area or other points of trauma are created, gum trophism is disrupted. Against the background of such changes in the microvasculature, blood stagnation occurs, swelling and hypoxia of mucosal tissue occurs. Less often, this is possible when performing restoration, when the filling material was applied to the gum.
Solving problems in the dentist's office
An experienced specialist will help you get rid of problems with your gums and teeth. First of all, a diagnosis is carried out, as well as the necessary examination. If necessary, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests, and based on their results, a treatment plan is determined. To remove hard plaque, ultrasonic cleaning or the Air Flow method is used.
Air Flow Treatment
You can get rid of plaque with professional cleaning at your dentist's office. Under high pressure, an air-water jet is directed to the required area. Gentle and thorough cleaning occurs thanks to the abrasive filler in the mixture. The advantage of this method is the destruction of solid deposits in hard-to-reach places.
Ultrasonic cleaning
Ultrasound cleaning remains one of the most effective, safe and painless methods for removing plaque and formations on teeth. A special feature of the method is the use of high-frequency sound, which has a destructive effect on hard formations on the teeth. The procedure is prescribed as an addition to massage and rinsing for gum inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory treatment
To prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, laboratory tests are necessary. A smear is taken from the mucous membrane to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. The duration of the course of antibiotic therapy is from 7 to 10 days. Depending on the patient’s condition, the timing can be adjusted by the attending physician. The use of anti-inflammatory ointments and gels gives good results.
Surgical intervention
Surgical procedures are performed in case of formation of a fistula or cyst. The bone fragment is removed, the wound is washed, and temporary drainage is installed. For periodontitis, root canal treatment is performed. If a root filling was previously installed, surgical intervention may be necessary. The dental cavity is opened and dead areas of the pulp are removed. Then the root canals are cleaned, washed and dried. After eliminating the inflammation, the canals are filled. To monitor a possible exacerbation, it is recommended to conduct an X-ray examination every three months.
Oral diseases can also be treated with folk remedies. Essential oils that have antibacterial, soothing and anesthetic properties are very popular. Rinsing your mouth with a decoction of oak bark has a healing effect. Scurvy can be cured with a decoction of lingonberries and calamus root. It is necessary to rinse your mouth with warm broth after each meal. The use of any traditional medicine must be agreed with the attending physician.
The main reasons for the appearance
| Reason name | Symptoms |
| Neoplasms | If white spots appear on the gums of adults near a tooth, it is quite possible that these are wen, which are also considered benign. They do not pose a danger to humans, but if they are not treated, the wen may begin to increase in size, and then the person will need the services of oncologists. |
| Lack of vitamins (calcium) and minerals in the body | Whitening of the gums can also occur due to hypovitaminosis. If you start to carefully monitor your diet and additionally saturate your body with foods with high levels of calcium, then the problem will go away on its own. But even in this case, you need to go to the dentist. |
| Violation of hygiene rules | If you do not keep your mouth clean for several days or brush your teeth poorly, then whitened gums are the result of poor hygiene. White plaque near the tooth and on the gums must be cleaned with a toothbrush, but the entire procedure must be done very carefully so as not to damage the tissue. After this, you need to thoroughly rinse your mouth with special rinses that “fix” the result. |
| Thermal effects | The gums become covered with white spots if you drink something too hot (tea, coffee) or eat too hot food. |
| Whitening | The whole process significantly affects the general condition of the oral cavity, so it is quite possible that after whitening some areas of the gums may turn white. If during this the gums do not bleed or swell, then you need to wait a little and the problem will disappear, that is, the gums will acquire a normal color. But as soon as you observe this phenomenon, immediately inform your dentist who performed the procedure. |
| Stomatitis | This is not a very dangerous, but discomforting disease that develops less often in adults than in children. As soon as you see whitened gums or a pale grayish-white coating on your child, then it is quite possible that this is stomatitis. Caused by poor oral hygiene. As soon as this is discovered, you immediately need to begin complex treatment consisting of a specialized diet (at this time you should not eat spicy, overly salty or sour foods), plus the affected areas are treated with ointments (the doctor or pharmacist at the pharmacy will tell you which ones). It is also recommended to additionally rinse the oral cavity with solutions (can be herbal), then the whitened part of the tissue will begin to return to its usual color, and the purulent plaque will simply be removed. |
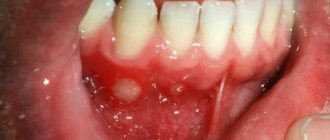
| Cyst | If a small white lump appears in the area of the tooth, then it could be a cyst, because one of its symptoms is an abscess. To treat this disease, X-ray diagnostics is necessary. For some reason, people do not pay special attention to such seemingly insignificant symptoms, although in the end they bring many negative consequences. Alternatively, this could be tooth extraction. |
| Candidiasis or thrush | This disease is characterized by pale gums, which become so due to the fact that the body does not have enough vitamins, so the immune system weakens. Thrush can affect both adults (usually women) and their children. They can occur after taking antibiotics, which have a strong effect on the microflora of the body. The gums around the tooth also turn white due to the fact that harmful microorganisms of fungal cultures actively multiply in the oral cavity. |
| Periodontitis | The white dot in this case will be a fistula, with the help of which pus comes out of the gums. |
| Diabetes or HIV | If the reason that your gums have become paler or completely white is that your body suffers from these diseases, then you need to seek help not only from a dentist; in such situations, it would not be superfluous to have an additional consultation with a doctor - an immunologist and an endocrinologist. They will give clear instructions on what type of treatment is suitable for a patient with special requirements. |
Disease prevention measures
Regular visits to the dentist and careful oral care will help prevent dental and gum diseases. It is necessary to follow simple rules to avoid gum problems:
- eat foods rich in proteins and vitamins;
- use high-quality brushes for dental care;
- Massage your gums daily with a brush to improve blood circulation.
A healthy oral cavity means a beautiful smile, the absence of an unpleasant and putrid odor, inflammation, pain and bleeding. The basis of healthy teeth is strong gums. It is extremely important to take care of them, follow the rules of care and visit the dental office as needed.
Preventive measures
Following standard procedures will help you prevent plaque from appearing on your gums.
- Careful observance of all hygiene measures: upon arrival from the street, after using the toilet, the first thing to do is wash your hands, especially for children who are not always willing to follow this step. But it is precisely because of this that stomatitis can begin to develop.
- Plus, rinse your mouth with rinses and, if necessary, use dental floss to clean your teeth.
- You cannot start taking antibiotics without a clear prescription from a doctor. After all, failure to follow the instructions correctly affects the immune system, and as a result, a white coating or small ulcers appear in the mouth.
- Pregnant women should treat candidiasis in a timely manner and with approved medications.
- Once a year, a medical examination is mandatory.
- Visit your doctor regularly, even in those moments when nothing bothers you.
White gum over growing wisdom tooth
All these simple precautions will help you avoid additional treatment of your teeth and gums.
Healthy gums should be a relatively uniform shade of pink. They may appear slightly lighter around the teeth and darker on the sides of the mouth. One person's gums may naturally be a little paler or darker than another's.
When a patient notices that the color of their gums is changing, they should talk to their doctor, especially if additional symptoms are cause for concern.
Read on to learn more about the causes of pale gums. We also describe associated symptoms, treatment options, and when to seek medical attention.
Possible gum problems
Among the most common diseases are:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease.
The most harmless of the list is gingivitis. It is characterized by an abundant accumulation of plaque, which over time leads to the formation of stones and the development of pathogenic bacteria. The reason for this is improper or irregular hygiene, poor brushing of teeth, and failure to remove food debris in hard-to-reach places. It is possible to prevent the disease; to do this, you need to use not only a toothbrush, but also dental floss, toothpicks and an irrigator. A device such as an irrigator delivers a stream of water under high pressure, which perfectly removes dirt and helps keep teeth clean even at home.
Redness and inflammation of the gums and adjacent soft tissues indicate the development of periodontitis. Another sure sign of the disease is dental plaque - a stone that can only be removed by professional cleaning at the dentist's office. Long-term and massive deposits of stones lead to the formation of pockets between the gums and teeth, which also contributes to the development of the problem in the future.
It is periodontal disease that wins first place in the ranking of the most common ailments associated with gums. It is quite dangerous for the condition of teeth. Its signs are: inflammation, redness, formation of pus. If you notice that your gums are bleeding, swollen and painful, consult a doctor immediately.
Causes of acrocyanosis
The causes of acrocyanosis are unknown. The underlying skin lesions are most likely a disorder of blood flow regulation in the distal extremities.
It is reliably known that disturbances occur in places where small vessels contract and relax in the distal parts of the extremities, as a result of which blood flow in these vessels slows down. Because of this, the vessels remain filled with venous or deoxygenated blood longer, which leads to bluish skin in the area of vascularization.
Insufficient blood supply to small capillaries
Symptoms worsen when exposed to cold ambient temperatures. They are not accompanied by pain or whitening, and do not lead to skin ulcers or necrosis.
Preventive measures to prevent gum disease
Oral care to maintain healthy gums includes:
- daily brushing of teeth with soft tissue massage with a medium-hard toothbrush;
- consumption of fresh solid vegetables and fruits;
- quitting smoking and eating sweets;
- annual calculus removal and professional teeth cleaning;
- using mouth rinses with oak bark or chamomile.
Even the slightest discomfort in the oral cavity should be a reason to register with the clinic. A self-made diagnosis may turn out to be incorrect, and the lack of necessary treatment will lead to irreversible processes, after which the teeth will need to be restored using prosthetics.
In order for your teeth to remain strong and in place, you need to take care of more than just them.
The health of your teeth also depends on how your gums feel.
Clinical researches
ASEPTA products have clinically proven effectiveness. Repeated clinical studies have proven that the use of ASEPTA adhesive gum balm for a week can reduce gum bleeding by 51% and reduce inflammation by 50%.
As part of the research, it was also proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
How inflammation begins
- how to brush your teeth correctly, - how to choose a toothbrush, - how to choose other teeth-cleaning devices, - how to choose toothpaste, - how to preserve tooth enamel, - how to care for your first teeth, - how to use calcium for dental health, - how sugar and other foods affect dental health, how to use chewing gum correctly, what are the misconceptions about dental health.
Inflammation of the gums, or gingivitis
, provoke bacteria that multiply in dental plaque. They penetrate under the gums and release enzymes and toxins. At the same time, the gums change color. It turns red if the inflammation is acute, or becomes bluish if the process has entered a chronic stage - and swells.
However, the first sign of inflammation that you will notice on your own is bleeding gums.
when brushing your teeth or eating solid foods.
See a doctor immediately
If your gums are bleeding, you need to see a dentist as soon as possible in order to begin treatment while the inflammation in the gums is still reversible.
Without appropriate treatment, inflammation will progress and may progress to the next, more severe stage – periodontitis. This is the destruction of the bone tissue of the tooth socket and the formation of a periodontal pocket - the space between the tooth root and the gum.
In this case, the tooth becomes mobile and, with significant bone destruction, falls out. By the way, it is periodontitis
is one of the most common causes of tooth loss.
How to avoid gum disease
— Visit your dentist
– at least twice a year. A specialist will examine your oral cavity, teach you how to brush your teeth, select the hygiene products you need, and carry out professional removal of dental deposits - plaque and tartar.
- Take regular and thorough oral care
: Brush your teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste, use dental floss and mouthwash as recommended by your dentist.
— For prevention and treatment
In the early stages of gum inflammation, use toothpastes and rinses containing extracts of medicinal plants and essential vegetable oils.
Consult your dentist - he will select the most suitable products for you and tell you how to alternate them so that addiction does not occur.
— Toothpastes and rinses with antiseptics
- chlorhexidine, triclosan, cetylpyridine chloride - as a rule, they are prescribed already in the presence of inflammation. The duration of the course of using these drugs is determined by the dentist.
— Gum massage
helps improve blood circulation. It can be done every time you brush your teeth - at the end of brushing, making light circular movements with the toothbrush with your teeth closed.
— Hydromassage
gums can be repaired using irrigators - special devices that precisely deliver a stream of water or an antiseptic solution under pressure from 0.7 to 4.8 bar.
— Clean between teeth very carefully
so as not to injure the gingival papillae located between the teeth. Chronic trauma from dental floss or toothpicks can cause changes in their contour and the formation of gaps between the teeth.
Diagnostic methods
The main diagnostic procedure for red gums is to study the patient’s medical history and visual examination. The dentist examines the oral cavity, checks the condition of the teeth, and identifies areas of caries formation and tartar deposits.
The main focus during the inspection is:
- degree of inflammation;
- severity of edema;
- hyperemia;
- volume of dental deposits.
On this topic
- Gum inflammation
Find out why inflammation occurred after tooth extraction
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 3, 2020
The doctor may conduct special tests that show the tendency of periodontitis and bleeding. Data for the study are assessed in different occlusion zones on a 4-point scale. Diagnosis is carried out with a periodontal probe.
In cases where the dentist finds it difficult to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, additional coagulation testing is required. The patient is prescribed:
- analysis ;
- counting the value of red blood cells and platelets in the blood;
- coagulogram;
- analysis for the presence of sediment in urine;
- feces for occult blood.
The research results make it possible to more accurately determine the causes of inflammatory processes and bleeding gums.
Eat right
— Eat less foods rich in fast carbohydrates. These include flour products, sweets, and many fast food products. They help increase plaque
and serve as a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria that destroy teeth and gums.
— Include solid foods
- raw vegetables, hard fruits - requiring intensive chewing, which leads to an increase in saliva flow and natural cleansing of the oral cavity. It is advisable to eat hard vegetables and fruits after eating sweet, sticky and soft foods.
— Include enough protein
for normal renewal of the oral mucosa and gums.
— Avoid developing hypovitaminosis. After all, pathological changes in the gums most often develop with vitamin deficiency
A, C and D.
What to remember
The health of your teeth directly depends on the condition of your gums. If the process of inflammation in the gums has gone too far, a person may lose teeth. To prevent gum disease, you need to regularly visit the dentist, clean your mouth properly and avoid sweet and sticky foods, which provoke the growth of bacteria.
The gum is the area of the oral mucosa that covers the lower and upper jaws. The tissues of the teeth are tightly attached to the gums, and healthy gums protect the ligaments of the tooth from exposure to microbes. The percentage of people suffering from gum disease increases with age, and according to doctors, more than 70% of people over 35 years old already have some kind of gum health problem. Gum diseases are unpleasant because they deprive a person of a beautiful smile and good health, and in severe cases they cause tooth loss.
Traditional methods
Non-traditional methods should be used with caution so as not to harm your condition or aggravate the existing problem. But if you choose the right folk remedies, you can significantly speed up recovery.
For gingivitis, recipes based on medicinal plants are effectively used for local treatment of affected gums. For example, sage, oak bark and chamomile, which have anti-inflammatory, hemostatic, and antiseptic effects, are suitable. In addition, you can treat your gums with aloe juice or honey to relieve painful symptoms.
If problems arise after incorrect installation of prostheses, agents that accelerate blood circulation are used. For such purposes, you can prepare a decoction of nettle leaves or propolis ointment. It is better not to use products based on pepper or mustard, as they greatly irritate the delicate mucous membrane of the mouth.
If you can’t cope with the problem on your own and there is an urgent question about what to do with blue gums, you should immediately contact a specialist. Timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery.
Gum diseases
The main cause of gum disease is the accumulation of plaque in the mouth. It contains and actively multiplies microorganisms that have an irritating and toxic effect on gum tissue. With weakened immunity, lack of vitamins and some concomitant diseases, the likelihood of developing these diseases increases (for example, diabetes, gastrointestinal diseases, frequent sore throats, tuberculosis). Sometimes gum inflammation appears during pregnancy.
Gingivitis
is an inflammation of the gums in which the pathological process does not affect the bone that supports the teeth. The main cause of gingivitis is the abundance of soft plaque on the teeth. Symptoms of gingivitis are painful and swollen gums, bleeding and sensitivity, bad breath, pain when eating hot food. But sometimes there may be no pain, and the presence of gingivitis is only revealed by the appearance of blood when brushing your teeth.
If you consult a dentist in a timely manner and follow all his instructions, this disease can be treated. But if treatment measures are not taken, then over time gingivitis can develop into a more serious disease - periodontitis.
Periodontitis
is a gum disease that damages not only the gums, but also the bone tissue that supports the teeth. Its cause is the accumulation of soft plaque and further formation of tartar. Tartar can appear not only above the gum, in a visible place, but also under the gum, where it constantly injures the gum tissue. Periodontitis can also develop after a tooth injury or improper installation of a dental crown. Symptoms of periodontitis are redness and swelling of the gums, pain, bleeding even with a slight touch, bad breath, putrid taste in the mouth. Over time, periodontal pockets (narrow cavities between the tooth and gum) form, sometimes with purulent discharge. Tooth mobility begins to appear, tooth roots become exposed. Periodontitis is a dangerous disease of the oral cavity. If measures are not taken to treat it, then after 2-3 years a person may lose teeth involved in the pathological process.
Treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis includes cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar, antiseptic treatment of gums, applications with medications, rinsing with medicinal solutions, physical therapy, and coating with fluoride varnishes. In case of severe inflammatory process with periodontitis, it is sometimes necessary to resort to surgical treatment and further anti-inflammatory therapy. Sometimes splinting of teeth is used (clutching mobile teeth into a block to prevent their further loosening).
Periodontal disease
is a gum disease that is not inflammatory, but dystrophic in nature. It is much less common than gingivitis and periodontitis. Doctors have not identified any obvious reasons for its occurrence. It has been noted that periodontal disease often appears in diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases of internal organs, atherosclerosis, and there is also a hereditary predisposition to this disease. With periodontal disease, there is no inflammation, pain, or bleeding of the gums. Unlike periodontitis, teeth do not become loose. Sometimes the necks of the teeth become exposed and the sensitivity of the teeth increases, itching appears in the gums, and they become paler in color. This begins the process of slow destruction of bone tissue.
Progressing over several years, this disease can also lead to tooth loss. The diagnosis of periodontal disease is made by a doctor mainly from an X-ray of the jaws. Treatment of periodontal disease is selected by the dentist individually. Physiotherapy as well as surgical methods can be used.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms that accompany redness are directly related to the underlying diseases. Discoloration of the gums can be caused by diseases such as gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontitis.
On this topic
- Gum inflammation
All about tooth root inflammation
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 3, 2020
There are a number of symptoms common to all diseases.
- Bleeding. The gums begin to bleed long before more serious symptoms appear. Patients do not attach importance to this phenomenon. Blood formation is the first sign of the inflammatory process.
- Swelling of the gums. The tissue structure becomes more loose, easily injured, and the color changes to dark red.
- Departure from the tooth. Inflamed gums easily detach from the surface of the tooth enamel. Pockets form around the tooth into which food gets trapped. The process of decay and subsequent inflammation develops.
- Unpleasant smell. The smell is persistent and does not go away after hygiene procedures. Its appearance is characteristic of advanced inflammatory processes.
In addition to general symptoms, gum disease is characterized by individual manifestations.
With gingivitis you will notice:
- severe swelling;
- elevated temperature;
- formation of tartar ;
- the appearance of putrid odor from the mouth;
- proliferation of the mucous membrane around the teeth with its subsequent necrosis;
- change in shade ;
- filling the interdental areas with overgrown gums;
- pain during hygiene procedures.
On this topic
- Gum inflammation
How to prevent sore gums
- Olga Alexandrovna Novikova
- September 3, 2020
With periodontitis, some of the symptoms listed above appear. Also added to them are signs characteristic only of periodontal disease:
- loosening of teeth;
- departure of tissue from the neck of the tooth;
- pain when biting food;
- exposure of the neck of the tooth;
If a patient develops periodontitis, then in addition to bleeding and other symptoms characteristic of gum disease, swelling of the face, lips, and cheeks is noted. In advanced situations, a fistula may form, which serves as a release point for the products of soft tissue decay.