Flux is an infectious bone lesion localized under the gum. It occurs as a result of caries or another disease, becoming a factor in the unfavorable condition of the oral cavity. The pathology develops rapidly, spreading to the bone within a day after its appearance. Whether a tooth can be removed with gumboil depends on several factors. But first you need to visit a doctor and find out the cause of the problem; no folk remedies or simple painkillers will slow down the development of gumboil.
If you try to get rid of the symptoms of flux at home for a long time, inflammation and a purulent process will begin. The infection will penetrate the blood and lead to the development of dangerous complications. This can only be prevented by visiting a dentist.
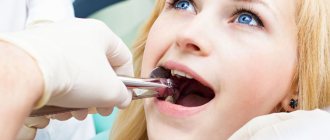
Should I remove the tooth?
It is not always recommended to remove a tooth damaged by flux - only in extreme cases, if treatment of inflammation has not yielded results or there is no access to the source of infection. In some cases, tooth extraction due to gumboil is necessary.
The disease often recurs, literally 2-4 weeks after the elimination of the first inflammation. A recurring infection can spread throughout the body and have an even more dangerous effect.
Types of flux and symptoms
A person experiencing severe toothache, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and swelling at the site of inflammation with redness of the mucous membranes, is a patient with symptoms of periostitis (we recommend reading: what to do if the temperature rises with a toothache?). At the initial stage of development of the disease, he may experience only unpleasant toothaches with redness of the mucous membranes at the site of inflammation.
READ ALSO: how is toothache treated during breastfeeding? If you do not see a doctor for a long time, then the pain will intensify, chills, weakness will appear, and your general condition will worsen. The inflammatory process can provoke swelling, which, increasing in size, can affect the lips, wings of the nose, lower eyelid, etc.
Flux has two types of disease: acute and chronic:
- With acute flux, the patient experiences severe pain in the area of inflammation, and a high body temperature is noted. The person is in a depressed state, he is tormented not only by dental pain, but also by headaches, which can radiate to the neck, shoulder, etc. The disease, which occurs in an acute form, is accompanied by swelling of the cheek at the site of inflammation.
- In the chronic course of the disease, a person experiences less pronounced pain, the body temperature remains elevated (37.8 - 38.5 degrees), which indicates an inflammatory process occurring in the body. The swelling becomes large and can affect the area at the temple or go lower, involving the neck. The patient often experiences pain while speaking or swallowing.
READ ALSO: how to quickly remove toothache at home without pills?
Symptoms of pathology
The symptoms of flux, which sometimes needs to be removed, are similar to the general signs of dental problems: inflamed lymph nodes, general weakness and fever, acute toothache, swelling, a feeling that the gums are bursting.
Even if the sensations are mild, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will accurately diagnose and tell you whether the tooth needs to be removed or not.
Important! If the pain is localized in the area of the upper canine, this is the most dangerous type of gumboil.
In this area, accumulation of pus occurs in the periosteum - symptoms develop faster, swelling is more pronounced. When entering the phlegmon stage, pus can spread into the circulatory system. Blood poisoning can lead to brain damage.
What is flux and what is its danger?
Flux, called periostitis in dentistry, is a serious inflammation that affects the periosteum of the upper or lower jaw. It manifests itself in the form of a purulent abscess on the gum, which takes on the appearance of a swelling near the tooth. Main causes:
- caries, chronic periodontitis, alveolitis, periodontitis;
- inflammatory processes between the tooth and gum tissue;
- mechanical damage that occurs during tooth extraction or after jaw injury;
- untimely replacement of a temporary filling with a permanent one;
- bacterial environment;
- diseases associated with the spread of infection - sore throat, otitis media;
- hypothermia of the body, physical and mental overload.
Read also: After removing a baby tooth, how much should you not eat?
Timely contact with a specialist will help avoid many complications. These include:
- Symptoms of the disease are a feeling of swelling in the gums, pain begins to radiate to the ear or temple, and a putrid odor is felt when breathing. The lymph nodes become inflamed, the temperature rises, the cheek swells, and health worsens.
- The transition of the disease to a chronic form - the disease will last for 6-8 months with periodic exacerbations.
- Risk of developing into phlegmon or osteomyelitis. The inability for pus to escape will lead to its penetration into the soft tissues and then into the blood. There is a risk of infection and spread of infection through the bloodstream to other organs, in particular to the brain.
Other complications of flux
If a tooth is not removed in time due to flux, phlegmon develops. But there are other serious diseases associated not only with purulent inflammation:
- osteomyelitis – inflammation of bone tissue;
- inflammation of the cranial sinuses - infection affects the brain;
- abscess - purulent cavities that appear in the area of damage to the tooth.
If the pus comes out of the lesion before going to the dentist, the patient will feel temporary relief. However, without removal, flux can become chronic.
Causes of flux
Flux occurs when harmful microorganisms penetrate into the periodontal tissues. Inflammation develops suddenly and is a consequence of untimely consultation with a doctor for pulpitis or caries. Such neglect of the health of the oral cavity will certainly lead to the development of gumboil. This disease can also be caused by mechanical damage to the gums or bones. If oral hygiene is not maintained, harmful microbes penetrate the tissues adjacent to the teeth and lead to their inflammation.
Another reason that can lead to the appearance of microbes and, ultimately, to gumboil is difficulties with teething. Suppuration and a serious complication may appear under the mucous membrane if the accumulated pus is not removed in time. Damage to the tooth canals can provoke periostitis.
Indications for tooth extraction
The doctor decides whether it is worth removing a tooth due to gumboil. In some cases, this is the only way to completely eliminate the disease. At home, it is prohibited to use traditional medicine methods to combat the disease, since such therapy is ineffective.
During the diagnosis, the doctor must identify several conditions that allow the tooth to be removed: infection of the surrounding tissues, severe damage to the tooth, closed infection - inside the cavity of the tooth or root, it is impossible to cure the root canal, anti-inflammatory medications do not work.
If at least one indication is detected, the doctor begins the operation.
Causes of Undesirable Conditions
In some cases, long-term tolerance of the unpleasant symptom of pain in the area of chewing elements causes further growth of the infection, either due to caries or poor condition of the root. As a result, swelling of the cheek appears, with fever. This is most often the result of a poor tooth condition that needs to be treated or removed. If the cause of inflammation is the pulp, then the nerve is urgently removed, and when the root and crown are destroyed, the tooth is removed with flux.
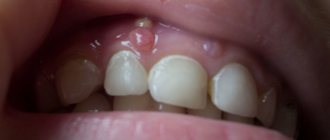
An unpleasant manifestation of swelling of the cheek due to an internal inflammatory process in the oral cavity (with gumboil)
Many people patiently wait for such an unpleasant increase in the volume of soft tissues to pass, and do not know whether it is possible to pull out a tooth due to gumboil. Patients are afraid of such situations and do not seek help. Someone does not know what to do in this condition and they are tormented by the question: if there is gumboil, is it necessary to remove the tooth in this situation.
- gum disease;
- poor quality dental treatment;
- trauma, tooth fracture.
A complication in the form of flux can be provoked by caries in a living tooth, after removal of a decayed tooth, and in a pulpless tooth, after endodontic treatment. In the latter case, the cause is poor quality treatment: a poorly sealed canal or a crack at the root becomes a “home” for pathogenic microorganisms.
A “dead” tooth does not clearly respond to various irritants such as hot/sweet, but simply hurts - an abscess begins to form in the unfilled cavity and with its accumulation the pressure inside the gum increases. If the patient is lucky, the pus breaks out through the fistulous tract and flows into the mouth. But, if there is no way to get out, it accumulates under the periosteum of the upper or lower jaw - periostitis develops.
Flux on the gum after tooth extraction does not mean that the dental surgeon did not remove the roots well - often periostitis occurs not because of the removal, but in spite of it.
- Severe pain, often throbbing, radiating to the ear, eye, temple, neck.
- The gums become swollen and inflamed; at the advanced stage, the cheek on the side of the diseased tooth swells.
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
- Pain when talking, biting, chewing.
- Periostitis in the molar area often causes numbness in the lip and part of the chin.
- Increased body temperature, general weakness of the body.
Flux in a child
Flux on the gums is more common in adults than in children. Most often, the cause of periostitis in a child is a poorly treated tooth, tooth trauma, or damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity. Flux on the cheek forms on both permanent and baby teeth and is dangerous because in the event of a breakthrough, the infection enters the blood and attacks muscle and bone tissue.
What to do if a child has gumboil on his cheek, and a visit to the doctor is impossible right now? You can rinse your gums with a “sea” solution: dissolve a teaspoon of salt, soda and 3 drops of iodine in a glass of boiled water. But it is impossible to cure periostitis by regularly rinsing the gums - it will not be possible to completely get rid of the infection only with an antiseptic solution.
Do you experience acute, sharp and unbearable pain? Is it impossible to chew while eating? Are your gums swollen and burgundy-red? Is your cheek swollen on the side of the bad tooth? There is only one answer to all these questions - FLUS!
Flux on the gum on both sides
Flux on the gum near the upper incisor
Flux on the gum from the inside
So, what is flux? This is an extreme degree of inflammation of the periosteum and subgingival tissue. It is expressed in the form of a purulent sac or hilar cyst. The reason for the formation of edema of the mucous membrane of the gums and swollen cheeks is the accumulative process of purulent fluid, which asks to come out.
We suggest you read: Flux after tooth extraction, what to do (photos and videos)
On a note. Flux and periostitis are the same disease.
- Caries has completely affected the tooth. Don't ignore the small black dot you find on your tooth. Caries, like a virus, can devour your tooth from the inside, outwardly appearing as a harmless point. The threat of inflammation begins from the moment the caries reaches the pulp (when pressed, a slight, distant pain appears), continuing to affect the nerve pathways in the tooth canal. The nerve is damaged, pathogenic microflora penetrates deep into the tooth at full speed, affecting the subgingival tissue and periosteum.
- Inflammation of the gum pocket. As a result of untreated or neglected treatment of a disease such as periodontal disease, the gum is separated from the tooth, forming a periodontal pocket. Remains of food are pressed into it and any infection enters, forming particles of putrefactive decay.
- Maxillofacial trauma. In the event of a fracture, dislocation or severe bruise, the soft facial tissue is damaged and an inflammatory process forms in the gum, which is also accompanied by gumboil.
Flux pattern on the gum
Diseases such as periodontitis, purulent abscess, hilar cyst, alveolitis, gangrenous pulpitis, gingivitis. All these and many other purulent-inflammatory diseases can lead to the formation of flux if they are not treated in a timely manner.
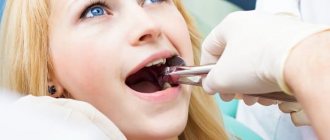
Removal process
The tactics for tooth extraction due to flux are determined during diagnosis. Next, the patient is given painkilling injections in the required quantity. One of the removal methods looks like this:
- An incision is made in the periosteum using a dental instrument or laser.
- The resulting wound is treated with an antiseptic, dried, and the removal of all pus is confirmed.
- They inspect damaged tissues and remove them using surgical instruments.
- Now they begin to remove the tooth - completely, including the nerve and root.
- A drainage is placed in the formed hole and sutures are applied.
- After some time, the patient comes to remove the drainage and remove the sutures; the final examination requires the application of absorbable sutures.
It is very important to comply with sanitary standards to prevent re-infection of tissues or blood.
Treatment with medications without removal
It is possible to quickly remove a tooth due to gumboil, but this is not always advisable. Dentists, if possible, try not to pull it out, but to treat it. This especially applies to the first stages, when, along with conservative dental therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are prescribed. You should not take them on your own. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause and assess the prospects for such treatment.
Taking antibiotics should be preceded by solving the problem of extracting pus. The doctor cuts the gum and periosteum, cleans the wound and secures a drainage to allow the fluid to drain out. The tablets will eliminate the bacterial component. For these purposes, broad-spectrum agents are used - Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Ampiox or Doxycycline. To eliminate inflammation and swelling, the doctor prescribes:
- Levomekol;
- a mixture of ichthyol ointment and streptocide;
- Metrogyl denta gel.
When fighting swelling, you can also use rinses. They are used before the doctor makes a final decision about whether the tooth needs to be removed or not, that is, in the process of conservative treatment. The following methods are popular:
- Soda solution. You need to dissolve 1 tsp. in 100 ml of water. Rinse up to 6 times a day.
- Miramistin - take 15 ml and rinse the mouth up to 3 times a day.
- A mixture of St. John's wort with sage and oak bark. Take 1 tbsp. l. each herb, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Infuse in a closed thermos for about an hour, and then strain. The procedure is carried out up to 3 times a day.
- Chlorophyllipt - for frequent rinsing, dilute 1 tbsp. l. in a glass of warm water.
Read also: A dystopic tooth is
Therapy after surgery
After tooth extraction surgery, the doctor prescribes additional therapy at home. For this purpose, medications and folk remedies are used. After removal, a person continues to experience discomfort, pain and swelling, which disappear after 3-5 days.
If tooth extraction due to gumboil goes without complications, the doctor prescribes the use of antiseptic rinses and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
It is important to ensure that a blood clot remains in the socket of the extracted tooth after the gumboil . If it falls out, the healing of the wound will be delayed. The patient must comply with the following instructions:
- in the first 2-3 days, eat only soft foods at room temperature;
- no smoking;
- medications for infection and inflammation are taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor;
- teeth are brushed with the softest brush, avoiding the site of the extracted tooth;
- After cleaning, use rinse aids.
In addition to pharmaceutical products to cleanse the mouth, you can use traditional methods.
How long does it usually take for flux to go away after tooth extraction?
Flux treatment is a rather lengthy process. It requires a lot of patience on the part of the patient and his discipline. After surgery, it is common to experience persistent discomfort. The swelling may take up to four days to subside. Self-medication can lead to complications and even death, which is why it is so important to follow your doctor’s instructions.
After tooth extraction, it is necessary to preserve the blood clot in the alveolus of the tooth, this will speed up the wound healing process. For two days after surgery, it is better to abstain from solid foods and avoid temperature changes from hot to cold, and vice versa. It is advisable to refrain from smoking. It is recommended to brush your teeth with a soft-bristled brush to avoid damaging the tissue around the tooth.
After 4-5 days there should be improvement. If this does not happen, the pain remains, the temperature does not subside, the gums bleed, you need to see the surgeon again.
Herbal Recipes
To disinfect the oral cavity, the patient can use tinctures:
- pharmaceutical calendula – 2 tsp. diluted in a glass of warm water;
- lemon balm - a decoction is made from dry herbs according to the instructions, the product restores immunity and accelerates healing;
- sage - an alcohol tincture or herbal decoction is used for rinsing; the product relieves pain and disinfects well.
However, the use of folk remedies should not replace toothpaste or medications prescribed by a doctor.
Rinse
Mouth rinsing is one of the answers to the question of how to remove gumboil at home. For this purpose, various decoctions, tinctures and medicinal solutions are used. Before using any mouthwash, you should consult your doctor.
Let's look at the most effective types of solutions that can be used to remove flux by rinsing:
A freshly prepared decoction based on oak bark works well as an excellent mouth rinse for flux. To prepare this product, you must purchase at least twenty grams of dry oak bark. You can stock up on it in the summer or purchase it at the pharmacy. Measure out about twenty grams of dry and pre-crushed oak bark and pour half a liter of boiling water. Everything is put on fire and boiled for two minutes, and then put in a secluded place to infuse. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with cooled oak broth at least eight times a day;
Oak bark.- Calamus root. Effective in the fight against gumboil and its manifestations. After grinding twenty grams of dried calamus root, pour half a liter of hot water. Everything is removed for several hours to infuse and cool. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with calamus root after meals throughout the day. On average, the number of rinses should not be less than five times per day. The last time this rinse is recommended is before bedtime;
For flux, you can use a decoction based on rue. You need to stock up on a small amount of this herb and brew it in a glass of boiling water. After steeping for twenty minutes, it is recommended to strain the broth. It is necessary to rinse the inflamed gum with this decoction three times a day;
Rue decoction.- Soda-saline solution . You can get rid of flux using a soda-salt solution. Place a teaspoon of soda and salt into a clean container, and then pour a glass of warm water into it. Mix everything thoroughly until the soda and salt are completely dissolved. The resulting solution must be cooled and only then used as a rinse. It is necessary to rinse the flux every thirty minutes, regardless of food intake. The active components of the soda-saline solution accelerate the maturation of the abscess and help relieve pain;
To prepare this effective remedy for pain caused by flux, brew sixty grams of the following herbs with pre-boiled purified water: periwinkle, angelica, peppermint and birch buds. The resulting solution should be placed in a dark place for several hours to infuse. After three hours, the herbal mixture can be used as an excellent rinse. During the day, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with this herbal mixture at least six times. This remedy is infused not only with water, but also with vodka. It is enough to take it in the amount of eight hundred grams;
Herbal collection.- Chlorophyllipt solution. Using a chlorophyllipt solution, you can not only relieve pain from flux, but also help eliminate it. The antiseptic properties of this substance have been known for decades. To prepare such a solution at home, take a glass of boiled water and dissolve a tablespoon of chlorophyllipt in it. The drug is diluted with thorough mixing, and only then used to rinse the mouth.
Read also: How long to keep cotton wool after tooth extraction
How to remove flux quickly at home? Thanks to medicinal compresses, you can kill numerous pathogenic organisms that have entered the body in a short time. Compresses also help to cope with the pain of flux and relieve the inflammatory process that has begun.
Salt compress
Regular table salt (sodium chloride) is one of the most common substances in the home.
It is used for various purposes, including the treatment of gumboil.
The reason for this is its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
When preparing a salt compress, dilute at least two teaspoons of table salt in a glass of water.
Using a cotton swab soaked in the resulting saline solution, treat the area at the junction of the cheek and gums where the flux has formed. For greater effectiveness, the compress can be applied and left for a while.
Dimexide compress
Dimexide is a unique compound that can easily penetrate to the source of infection. In the case of flux, this is very important.
Within a short time, dimexide can kill pathogens and increase their sensitivity to the action of antibiotics. Thanks to this indirect effect, taking antibiotic drugs for flux will be more effective.
It is very dangerous to use dimexide in concentrated form, as there is a high risk of burning the skin . To avoid this, it is recommended to dilute this substance in water: take one part of dimexide to four parts of liquid.
Using a gauze napkin soaked in a dimoxide solution, make a compress on the sore spot. The duration of the compress should be at least two hours. The frequency of treatment with this method is twice a day.
If the tooth cannot be removed
In some situations, the doctor postpones the removal of a damaged tooth; at this time, it is important to stop inflammation and infection using antimicrobial agents. Soda helps a lot, but you shouldn’t heat the damaged area - this will speed up the process.
It is not recommended to overuse painkillers - this may slow down the diagnosis. You should not take aspirin, which thins the blood, or take antibiotics without a doctor's recommendation.
It is necessary to remove an incisor, canine or molar during flux only according to a doctor’s indications. To avoid this unpleasant operation, you need to contact the clinic after the first unpleasant symptoms appear.