Symptoms at the initial stage
At the initial stage, the child may be concerned about the following factors indicating the presence of the disease:
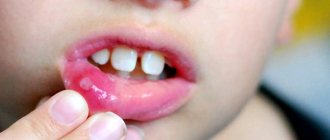
- the mucous membrane in the child’s mouth (both outside and inside) is red;
- When eating, painful sensations often occur, which are explained by the presence of small ulcers in the mouth;
- bad breath;
- If you give a child a piece of apple, he most likely will not be able to eat it;
- the child develops weakness, fatigue, tearfulness and irritability;
- body temperature rises.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the ulcers, which may look like small blisters, may merge with each other. Then the child experiences increased pain in the oral cavity and swelling. It becomes more difficult for the patient to eat normally.
Herpes form
This type of stomatitis can occur among both children and adults. Anyone will get herpes at some point, but the body reacts to this virus in its own way. If the protective functions are weakened, herpetic stomatitis may appear. It manifests itself and is treated in almost the same way in children and adults:
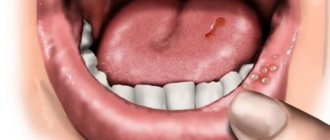
- Small ulcers form in the mouth, causing pain and discomfort.
- The baby is capricious, cries a lot, often puts his fingers in his mouth, and does not want to eat or drink.
- The acute form of stomatitis is similar in symptoms to ARVI: the temperature rises, lethargy, nausea, headaches, chills, and the lymph nodes become inflamed.
What can speed up recovery
The most important factor in getting rid of a disease is eliminating the cause of its occurrence. This applies to any form of the disease.
The following factors and actions can also speed up recovery:
- a good level of immunity, which can be increased by taking the vitamins necessary for the body;
- for any form of stomatitis - rinsing with a water-soda solution is recommended to be done at least every 2 hours, you can also use other solutions, for example, furacilin (1 tablet per glass of warm water), this will prevent the further development of stomatitis;
- it is necessary to pay attention to the child’s nutrition; you should not give him solid food, since the mucous membrane may be damaged;
- if the baby has an elevated body temperature, it is necessary to give him antipyretic drugs;
- food should not be hot; the optimal temperature is as close as possible to body temperature.
A sick child can infect others. In this regard, it is necessary to provide him with proper care, and it is better to periodically carry out hygiene procedures for healthy family members.
Causes
One of the fundamental reasons for the development of stomatitis in children is a low level of immunity, since it is not yet able to adequately repel multiple pathogenic attacks. The mucous membrane is very sensitive to any, even minor damage. This often happens in babies in the first year of life, when they, actively exploring the world around them, pull various objects into their mouths. At the same time, the child’s saliva is not yet able to fully protect the oral cavity from pathogenic microflora. All this leads to the occurrence of disease.
It should be noted that improper behavior of parents or close relatives can also lead to stomatitis in a child. In the case of the herpetic form of the disease, this occurs very often when parents prone to the disease continue to kiss their child during an exacerbation period, without observing the rules of personal hygiene and, thereby exposing the child to unintentional infection.
Pregnant women with untreated infections also expose their babies to the risk of infection, including stomatitis.
We suggest you read: Stomatitis in a child does not go away - ProfiMed
Other reasons that provoke the occurrence of stomatitis are:
- prematurity of the fetus during pregnancy;
- lack of oral hygiene or violation of its rules;
- dental diseases (caries, tartar formation);
- use of braces;
- high susceptibility to colds (flu, ARVI);
- frequent treatment with antibiotics, hormonal agents;
- vitamin deficiency.
Patient age
According to medical statistics, adult patients suffer from dental lesions on average several days longer than children. This is due to the characteristics of the immune system (in children, although it is not as stable, it is more flexible). The acute phase of stomatitis in a child aged 2 to 12 years lasts from 3 to 12 days. After this, spontaneous improvement occurs.
In an adult patient, the disease lasts almost one and a half times longer. The recovery period ranges from 4 to 18 days, sometimes the illness lasts longer. At the same time, the child experiences pathological symptoms (pain, fever, etc.) to a lesser extent. This trend in the course of the disease does not apply to infants. They suffer from stomatitis for 7-21 days.
At the end of the acute phase, aphthae and ulcerative-catarrhal lesions may continue to hurt. However, the condition goes into remission.
Where does it come from?
In the structure of pediatric pathology, viral stomatitis in children occupies one of the first places, surpassing even scarlet fever, but slightly inferior to chickenpox. It should be understood that viral herpetic stomatitis is a manifestation of a primary herpetic infection acquired from adults.
The high prevalence (about 70%) in children between one and three years of age is associated with the lack of antibodies that were previously obtained from the mother interplacentally. But by this age, children still lack developed systems of specific immunity and the main role of nonspecific defense.
- Also, a significant role is played by the morphological features of the oral mucosa in children of this age: thin epithelium, loose membranes, high permeability of barriers - all this contributes to such a high incidence in children.
- Viral stomatitis in children is very contagious: the source can be sick children with acute viral stomatitis, adult carriers, as well as adults with relapses of herpes labialis.
- The pathogen is transmitted very easily: not only through contact and household contact, but also through airborne droplets, as well as through vertical transmission:
- through kisses;
- through things of common everyday life;
- toys;
- cough;
- during pregnancy.
It recurs during a chronic process against the background of decreased immunity, which occurs due to a number of reasons - vitamin deficiencies, hypothermia and overheating, prolonged exposure to the sun, emotional experiences, long-term use of antibacterial drugs, etc. The most common incidence is observed during the off-season.
As mentioned above, children usually get sick in the age range from one to three years. Bubbles, ulcerations, hyperemia, and a large amount of saliva are found on the oral mucosa.
Diet
First of all, drink plenty of fluids at a comfortable temperature. In case of acute inflammation of the oral mucosa, thermal and mechanical sparing is indicated. The child can be given exclusively thermally processed vegetables, slimy porridges, meat with fibers that are easy to chew (stewed pollock fillet, for example), pureed soups, compotes.
You can make a stew from soft meat, zucchini, potatoes, carrots in a thick sauce. During the acute period, pureed dishes are useful. Preferably less sugar. As for infants, they should be supplemented with clean water more often. After milk and complementary foods, they are also given one sip of clean water.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Medicine for stomatitis for children under one year of age and older: ointments, gels, sprays, solutions and tablets
In addition, if viral stomatitis recurs again and again, it is necessary to pay attention to the child’s diet: in addition to taking courses of general strengthening complexes (vitamin and mineral preparations), they switch to a diet rich in protein foods and omega-3, 6 and 9-unsaturated fatty acids.
To do this, you need to include in your child’s diet:
- fatty red fish or fish oil capsules;
- season salads and cereals with a small amount of olive, linseed, and sea buckthorn oil;
- spinach
- avocado;
- nuts and seeds;
- seaweed;
- chia seeds.
The proportion of omega-6 should not exceed the proportion of omega-3.
Of course, there must be moderation in everything, and we should not forget that the ratio of proteins and fats in the daily norm for a child is 1 to 1.1. The daily requirement for omega-unsaturated fatty acids is small, but it is significant not only for children who often suffer from viral stomatitis, but also for healthy children.
Just a spoonful of flaxseed oil in porridge or a small piece of fatty sea fish per day is enough, no more.
How quickly does chronic stomatitis return?
Inflammation of the oral mucosa with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Depending on the form, the chronic course is accompanied by either diffuse or limited redness of the mucous membrane, the formation of vesicles and ulcers.
It is rare, about 5% of cases are chronic.
Any type of stomatitis can become chronic if treatment was not timely, incorrect or not completed, which is the most common reason.
Depending on the frequency of exacerbations, there are 3 types:
- mild degree – once every few years;
- average – 1 – 3 times a year;
- severe - 4 times a year, and sometimes every month.
Symptoms of appearance are similar to aphthous stomatitis.
Treatment of chronic stomatitis can take several months.
Complications
Severe consequences of the disease are not common, since the symptoms, especially in the acute form, are quite severe and require mandatory consultation with a doctor and timely treatment. However, the acute clinical picture can turn into a chronic form with improper therapy or its absence. This, unfortunately, happens if treatment of stomatitis is carried out by an unqualified specialist. A dentist can give an exact answer to the question of how to treat the disease as soon as the cause of the disease is established.
Against the background of stomatitis, the risk of developing colds, such as acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, etc., increases. In addition, an infection parasitizing in the oral cavity can migrate further along the larynx, causing inflammatory processes (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.).
Fungal stomatitis can cause genital candidiasis, visceral candidiasis, and candidosepsis.
Since the disease is localized mainly on the oral mucosa, the accompanying symptoms can lead to serious dental pathologies, for example, gingivitis, periodontitis, tooth loss, and loose tooth enamel.
How to speed up recovery time?
To reduce the treatment period for stomatitis to a few days, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and, in addition to following the doctor’s prescriptions, maintain hygiene in the home, care for the child’s mouth and teeth, change the toothbrush in case of infection and disinfect the teether. Each type of stomatitis is treated differently:
- herpes requires the prescription of antiviral drugs based on acyclovir;
- angular stomatitis is treated by taking vitamins and iron-containing medications;
- candidiasis requires antifungal therapy;
- for allergic stomatitis, antihistamines can be taken.
The room in which the child spends the most time must be thoroughly cleaned and ventilated every 2 hours. The room should not be dusty or too hot; it is better to remove animals for a while. Family members and guests coming from outside must wash their hands before interacting with the child.
Causes of stomatitis
Long-term, recurrent stomatitis in a child is associated with a disruption of the immune system, the presence of a chronic infectious or hormonal disease.
The maintenance of foci of stomatitis is facilitated by traumatic factors: a diseased or improperly grown tooth, a disorder of the nervous system, insensitivity to burns. This determines how long stomatitis lasts in children.
In infants under one year of age, recurrent stomatitis of a fungal or viral nature is caused by maternal illness (thrush or herpes).
We invite you to read Is it painful to treat caries: patient reviews
READ ALSO: How to treat stomatitis in a 3-year-old child at home?
In children with chronic respiratory diseases caused by bacteria of the genus Streptococcus, stomatitis recurs over time simultaneously with an exacerbation of the underlying disease.
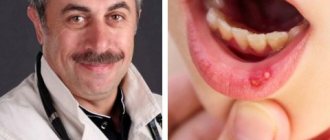
Herpetic stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is common not only in children, but also in adults. Sooner or later, everyone goes through a herpes infection; another question is how the body itself will react to this virus. If the immune system is weakened, herpetic stomatitis may develop. In children, the symptoms and treatment of this disease are almost the same as in adults:
- A distinctive feature is small ulcers in the mouth, which cause pain and discomfort.
- the child becomes capricious, cries a lot, puts his hands in his mouth and refuses to eat and drink;
- If stomatitis in young children becomes acute, it manifests itself with all the signs of an acute respiratory viral infection: high fever, lethargy, swollen lymph nodes, nausea, headaches and even chills.
In case of acute illness, the child must be admitted to a hospital. It is difficult to say how long stomatitis lasts in children in severe cases, but it is important to be constantly under the supervision of doctors. If the form is not very severe, then it can be treated at home, but with tireless observation and control of the process. Treat the oral cavity with decoctions of chamomile or sage, which have an anti-inflammatory effect. In order to reduce pain, children over 4 years old are prescribed antiseptics. And to heal wounds, you can apply sea buckthorn oil or rosehip oil with a cotton swab.
Types of stomatitis in children
Medicine knows several types of stomatitis in children:
- Candidal stomatitis (thrush) occurs in infants of the first year of life. A white coating appears in the mouth, which is not washed off with water and cannot be removed with a cotton swab. A baby can become infected during childbirth from its mother. Fungal infections are activated due to low immunity, prematurity or insufficient amount of saliva and its weak antibacterial properties. Sometimes thrush appears after taking antibiotics.
- Children aged one year and older sometimes suffer from herpetic stomatitis. Herpes causes painful mouth sores that make it difficult for your child to eat. He is capricious, refuses food, and develops a fever. The risk of infection increases from May to October, a period when children play a lot in the sandbox.
- During teething, children often experience traumatic stomatitis, caused by the child biting their cheeks or lips. In addition, the baby can be injured by the sharp edges of the toy or cutlery not intended for children. An infection gets into the wound and infection occurs. The child has a headache, a fever, and is feeling unwell.
- Allergic stomatitis is uncommon and is typical for those who suffer from an increased tendency to allergies. If ulcers appear in the child’s mouth, it is necessary to exclude contact with the allergen. It is permissible to use antihistamines approved for patients of this age.
- Bacterial stomatitis is typical for children over 2 years of age and occurs due to infection with a sore throat or insufficient oral hygiene. It manifests itself as deep purulent ulcers and is quite painful, accompanied by high fever, general malaise and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and under the chin.
- Angular stomatitis can be identified by the appearance of cracks in the corners of the lips, the so-called “jam”. They appear when there is a lack of B vitamins and iron in the body. Infection gets into the cracks and inflammation develops. To combat the disease, it is necessary to take vitamins and microelements; to reduce pain, local use of anti-infective ointments is indicated.
READ ALSO: what to do if your child often has a headache?
How to distinguish herpetic and aphthous stomatitis
- Herpetic stomatitis is characterized by the formation of a large number of blisters in the oral cavity, which after some time turn into ulcers. In aphthous disease, the ulcers are single in nature and are quite large in size - up to a centimeter in diameter.
- With stomatitis caused by the herpes virus, the gums are usually affected, causing redness and swelling. This is called gingivitis. With aphthous stomatitis there are no such symptoms.
- Herpetic stomatitis is accompanied by rashes around the lips. Aphthous does not have such symptoms.
How long does stomatitis last in children, how long does it take to treat the disease and how to speed up recovery?
Stomatitis is a generalized name for a group of diseases that have different origins, but similar symptoms: the formation of erosions or ulcers on the inner surface of the oral mucosa, tongue, gums, lips. Often occurs in children aged 0 to 7 years.
It is associated with the active exploration of the world by a small child who does not realize the danger of infection through the mouth and seeks to taste the surrounding objects.
While their symptoms differ, all forms of stomatitis have similar treatment methods, which are determined by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the oral cavity.
The duration of treatment for stomatitis depends on the form of the disease, the individual characteristics of the body and the level of immunity of the child.
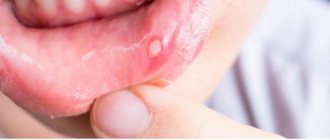
Aphthous stomatitis
The most complex type, since it is very difficult to identify the cause of its occurrence. This can be either an allergic reaction to one of the foods consumed, or disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
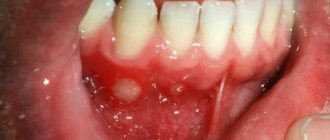
- At the very beginning, the ulcers are similar to lesions of the mucous membrane as with herpetic stomatitis. However, after some period of time they turn into aphthae - white ulcers with regular edges and severe redness of the rim.
- The temperature rises, pain increases when talking and eating, the child sleeps poorly and refuses to eat.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis depends on the causative agent of the disease identified by the doctor. In no case should you self-medicate, as you can let the situation get out of control and introduce an additional infection into the child’s body.
Duration of illness
The duration of the disease may vary depending on several factors: the type of pathology and the speed of treatment, as well as the level of immunity of the body. If it is weakened, then stomatitis will be less responsive to treatment.
How many days does it take to cure stomatitis?
- Thrush appears in a child for various reasons, it can be taking antibiotics, or lack of fluid in the body, and others. In this case, the duration of treatment largely depends on eliminating the cause. If the cause is quickly identified and eliminated, then you can be cured in 4-7 days. With a more complex course of the pathology, it can last up to 2 weeks.
- Herpetic stomatitis has an incubation period of 4 to 8 days. With timely treatment, the symptoms of the disease may disappear within 7 days.
- Aphthous stomatitis has a standard incubation period and lasts a maximum of two weeks.
- Traumatic stomatitis develops without obvious symptoms for about 4 days; with timely treatment, the disease will disappear in up to 5 days.
- The allergic form can be eliminated very quickly if you get rid of the allergen in time and carry out appropriate treatment for the consequences. After diagnosis, you can get rid of stomatitis within 7 days. If there are complications or the immune system is weakened, it is not possible to identify the factor that caused the symptoms, then treatment may be delayed for another 7 days or more.
We suggest you read: Can a general dentist treat children?
If the duration of the disease is more than three weeks, then there is a risk of a chronic form of the pathology. In this case, the disease may appear periodically.
Preventive measures
A child should be taught from an early age to regular oral hygiene, washing his hands, and washing his face. When sick, you should not bathe your child.
Prevention of various types of stomatitis involves basic hygiene rules, such as brushing your teeth at least twice a day. The toothbrush is selected according to age. Wash toys, pacifiers, and feeding utensils periodically in soapy water. It is necessary to keep all items of use with which the child comes into contact clean. During illness, dishes should be immersed in boiling water with baking soda for 2 minutes . When purchasing toys, they are selected without sharp corners and various allergenic paints in order to eliminate the risk of infections. When choosing, you should definitely pay attention to the quality of the product and its composition. It is important to study foods that can cause stomatitis and eliminate them for several weeks during the recovery period. You should periodically take vitamin preparations that strengthen the immune system and prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases.
Stomatitis in a child can last from several days to several weeks.
Stomatitis in a child can last from several days to several weeks, depending on its shape and type. But in any case, self-medication is prohibited. At the first signs, you need to visit a pediatrician, or call him at home, so as not to create complications of the disease.
Stomatitis in young children: danger
It is necessary to treat the disease that has arisen. Regardless of how long stomatitis in children lasts, it can cause unpleasant consequences. Inflammations that appear in the mouth can spread to the lips and facial skin, as well as inside the body. A decrease in immunity as a result of the disease contributes to the addition of a secondary infection.
Against the background of all this, fever, convulsions may develop, damage to the nervous system, etc. may occur. And this may be due to stomatitis in children. Symptoms and treatment should only be determined by a qualified doctor, since the disease can occur individually in each patient.
Do not delay going to the clinic if something worries you about your child’s behavior and health.
Symptoms
If you notice that your child refuses to eat, is capricious a lot, complains of constant pain in the mouth, and upon examination reveals increased body temperature, redness and ulcers on the oral mucosa, you should know that this is stomatitis. It is quite difficult to determine it in infants, since they do not yet know how to speak. While older children can let you know about this disease at the very beginning of its manifestation.
How long stomatitis lasts in children depends on its type and methods of treatment. With properly prescribed therapy, this disease goes away quickly enough and ceases to cause discomfort to your child.
Forms of dental lesions of the oral cavity
In dental practice, there are three main forms of dental lesions:
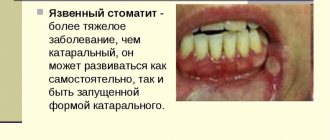
- Aphthous stomatitis. It is an invasion of the oral mucosa, during which on the surface of the epithelial tissues of the cheeks, tongue, etc. aphthae are formed - ulcerative defects ranging in size from 1 to 10 mm or even more. The disease is characterized by the formation of single or multiple lesions of the oral cavity. The duration of the acute phase is about 10 days. Chronic lasts about two weeks in both adults and children.
- Catarrhal form. It is a generalized lesion of the oral cavity involving all mucous membranes. This is one of the most dangerous forms of stomatitis, significantly reducing the patient’s quality of life. The acute phase lasts about 11 days. Chronic recurs constantly. Each relapse lasts about 14-16 days.
- Ulcerative stomatitis. This is the evolution of catarrhal stomatitis. By nature it is a purulent-necrotic process involving all mucous membranes. Lasts on average from 10 to 15 days in the acute phase. Each relapse lasts about 15-16 days.
Only in combination with these factors can one understand the duration of the process, which can range from several days to a month. Only a doctor can predict the type and calculate the duration of treatment after completing all diagnostic measures.
Prevention
- Be sure to wash your hands often and with soap. Explain to your children the importance of personal hygiene. Do not allow them to eat outside, pick up dirty toys, or sit at the table without washing their hands.
- Oral hygiene occupies a special place. Be sure to brush your teeth with a good brush and using the right toothpaste. Teach your child to brush his tongue and rinse his mouth well.
- Be sure to wash all vegetables and fruits brought from the store or market. Most often, it is dirty foods that cause stomatitis in both adults and children.
- If a person with stomatitis appears in the family, be sure to provide him with a personal towel and separate dishes and cutlery, otherwise he risks infecting other family members.
- Take vitamins and immunomodulating drugs. It is good immunity that will prevent the initiation of infection and prevent the virus from entering the body of a small child. For the same purpose, strengthen your children, take them for long walks in the fresh air and generally maintain a favorable atmosphere in the family.
Stomatitis is a fairly common disease in both adults and children. However, if you follow basic hygiene rules, it can be avoided. Be healthy!
Efficacy of therapy
The choice of treatment method can affect how long it takes to treat stomatitis in children. The above duration of any type of disease may increase if the therapy is chosen incorrectly.
Very often, stomatitis goes away slowly due to the independent intervention of parents. It is difficult to establish the type of pathology without professional help. Accordingly, medications have to be selected at random. As a result, you can start the disease and undermine the child’s health.
A pediatric dentist or pediatrician will help prevent serious consequences. The treating doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis using examinations of the child’s oral cavity, a smear from the affected area of the mucous membrane, and blood and saliva tests.
What complications may arise?
An advanced disease can become chronic or cause complications. Through open wounds and ulcers, infection easily enters the body, and re-infection with staphylococci or streptococci is possible. With candidal stomatitis, the infection that enters the bloodstream can spread throughout the body. Many organs will be affected, including the genitals.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Stomatitis in children: Classification, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention.
If children have a stuffy nose with stomatitis, breathing becomes difficult, a runny nose begins, and the disease can spread to the larynx. If the disease is neglected, the child develops laryngitis. During illness, the child’s immunity is lowered, so he can easily become infected with any infections.
Frequent, untreated or chronic stomatitis negatively affects the condition of the gums and teeth. The enamel becomes thinner, creating the prerequisites for the development of caries and periodontitis, which will require serious dental treatment. In general, if stomatitis is not treated, then as a person grows older, his teeth will be weak and susceptible to decay.