The temporal mandibular joint (TMJ) is a paired formation located behind the earlobe. It connects the temporal bone of the skull to the lower jaw and allows it to move in three directions. Any abnormalities in its functioning or neighboring structures cause pain, discomfort and impaired articulation.
The jaw joint is of a combined type: movements on the left and right sides are carried out synchronously. It consists of:
Malfunction in the temporomandibular joint or temporomandibular joint dysfunction is a set of symptoms that can occur in very different ways, combining one or more of the following. Painful manifestations. - joint manifestations: joint sounds, painful restriction or no opening of the mouth, discomfort in chewing and eating, joint instability sensation, blocking the mouth closed or otherwise blocking the open mouth. - other manifestations such as tinnitus or neck noise.
The various mechanisms that cause temporomandibular joint malfunction are complex, but various risk factors are known and are often confused, leading to malfunction. They are often associated with the stress of daily life and deviations from dental articulation. 5 - hyperlaxity is due to the presence of ligaments, too loose, too stretched. This is typical for young women.
Joints move in three planes:
- frontal - up and down;
- sagittal - forward and backward;
- vertical - in the lateral direction.
Blood is supplied by the branches of the external carotid artery, and its outflow is provided by the venous network of the jaw. Lymph drains to the cervical lymph nodes. Because of this, their increase is one of the symptoms of TMJ inflammation.
This leads to the fact that maximum mouth opening is too important. This contributes to clogging of the open mouth. 6 - Rheumatic disease can occur in the jaw joint. The jaw joint is a joint located in front of the ear that connects the top of the jaw to the skull.
This articulation has the peculiarity of representing the meniscus. When someone opens their mouth, the condyle rotates and moves forward. The meniscus follows the movement, moving forward. What are the different stages of the disease? The first stage of the disease corresponds to the pure muscular stages. Abnormalities in muscle function responsible for pain are caused by muscular compensations for positional disorders of the mandible. These positional abnormalities in the mandible are associated with articular joint problems and parafunctions.
Important!
The innervation of the TMJ is provided by the ternary nerve. Therefore, the reason why the jaw hurts may be hidden in pathologies of other parts of the face.
Provoking reasons
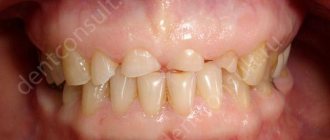
An incorrect bite provokes a loud crunching sound in the temporomandibular joint.
- injuries of varying severity;
- congenital TMJ anomalies;
- malocclusion;
- low-quality or poorly selected dentures for teeth;
- complete or partial absence of teeth;
- genetic factor;
- hormonal imbalance;
- arthrosis of different localization;
- a poorly placed filling, as a result of which the symmetry in the functioning of the joints is disrupted;
- unconscious grinding of teeth at night, which wears away tooth enamel.
Surgical methods of treating the disease
Surgery is considered only if the patient has tried all kinds of medical procedures. Surgical methods are necessary for severe pain and limited functions of the temporomandibular joint. Treatment for TMJ arthritis involves several different procedures:
- discectomy;
- recontouring;
- arthroscopy.
Sometimes total endoprosthesis replacement is required. The procedure requires a hospital stay of several days, and recovery time after surgery is four to six weeks. The cost of operations depends on various factors, such as the general condition of the patient, age, and course of the disease. Medical intervention methods may include the installation of orthodontic braces and implants. Dental adjustments help make your jaw easier to move.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
The whole essence of the pathological process comes down to the natural processes of malnutrition of the joint, which leads to its regular traumatization, reduces the ability to regenerate and resist damage. Along with the articular cartilage, the ligamentous apparatus along with the muscles are also affected.
There are quite a lot of trigger factors for the development of this complex joint disease. They include long-acting predisposing factors in which regenerative processes and normal tissue nutrition decrease over time, triggering a chain of irreversible reactions that cause arthrosis of the jaw with its characteristic symptoms, which requires immediate treatment.
The main reasons for the development of arthrosis of the TMJ:
- Injuries;
- Congenital disorders of maxillofacial proportions;
- Long-term or frequent arthritis (direct inflammation of the temporomandibular joint);
- Bite disorders;
- Low quality dentures;
- Complete or partial absence of teeth;
- Maxillofacial surgical interventions;
- Changes in hormonal levels during menopause;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Other arthrosis;
- Long-term open mouth (frequent visits to the dentist, prosthetics);
- Poor quality dental fillings, leading to asymmetry in the functioning of the joint;
- Bruxism is the unconscious grinding of teeth at night, leading to the gradual wearing away of tooth enamel.
In most cases, the cause of inflammation is an infection that has entered the human body. Treatment must be correct and timely. The doctor’s task is to correctly determine what triggered the development of the disease. The choice of treatment method for inflammation of the mandibular joint depends on this.
Modern medicine distinguishes between infectious and traumatic types of infection. The main infectious factors that can provoke the disease:
- overwork;
- hypothermia of the oral cavity;
- mastoiditis;
- osteomyelitis of the lower jaw bone;
- otitis;
What does the lower jaw joint consist of?
- inflammatory process of the salivary gland;
- tonsillitis;
- flu;
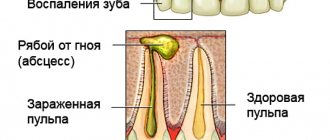
- any dental disease (for example, caries);
- any form of tuberculosis;
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- fungus actinomycetes.
The temporomandibular joint is usually damaged as a result of trauma to the lower part of the face. This could be the result of a blow, dislocation, fracture or crack. There are two forms of this disease: chronic and acute. The first manifests itself mainly as a result of infection or another disease.
Inflammation of the temporomandibular joint is a complex disease that requires scrupulous treatment. Therapy includes taking the necessary medications and a number of procedures. Treatment methods can be completely different. One of the new but popular ways to combat the disease is laser therapy. With its help, you can effectively cure inflammation of the mandibular joint.
Today there are many drugs that will help in the fight against the disease, but one cannot be absolutely sure that they will not give any side effects. For inflammation of the maxillofacial joint, laser treatment will not create such problems. Such therapy will even help cope with the negative effects of traditional medications.
Laser for physiotherapy procedures
The patient may be offered to undergo laser therapy if the inflammation affects:
- main joint in the jaw;
- temporomandibular joint;
- mandibular joint.
For any inflammatory processes, laser therapy is used to relieve tension, swelling and pain. It is necessary to treat diseased joints in several stages. The initial task is to get rid of pain. Then - overcome the root cause of inflammation. And in the end, such treatment allows you to completely get rid of the disease.
The last step is usually the most difficult. It is enough to simply eliminate the symptoms of the disease and overcome the infection that provokes them. But in order to achieve a complete recovery, a long course of rehabilitation using anti-inflammatory and painkillers is necessary.
As soon as the patient’s pain disappears, he is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment methods vary depending on the underlying cause of the inflammation. The patient may be prescribed intra-articular injections, non-steroidal drugs, antibacterial or antirheumatic drugs.
Only a doctor can choose the right therapeutic agents, so you should not self-medicate. The specialist prescribes medications taking into account the severity of the disease and its causative agent. Recipes from traditional medicine can be used, but it is advisable to first consult with your doctor.
Pain in the jaw joint is a common reason patients seek help. It is caused by a number of reasons for changes in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). In general, there is no single classification that is used by all doctors.
In our country, the classification presented by Sysolyatin and Ilyin is widely used. They divide all TMJ diseases into 2 groups: articular, that is, the joint’s own damage, and non-articular, which affects the muscular system.
Signs of inflammation of the temporomandibular joint are very often disguised as other pathologies. This leads to the patient seeking medical help late.
Inflammation of the temporomandibular joint can be acute or chronic. The main symptoms of acute inflammation:
- Sharp dagger-like pain, which tends to intensify with movements (turning the head, talking, eating, etc.). The patient is unable to open his mouth wide, since all sensations increase significantly. When the trigeminal nerve is involved in the pathological process, pain radiates to other parts of the head that it innervates.
- Symptoms of inflammation of the jaw joint include swelling of the tissue in the joint area. The skin over it becomes red as a result of the release of a large number of inflammatory mediators, which indicates the progression of the disease.
- Local increase in temperature over the joint. It is caused by the expansion of blood vessels, as a result of which blood actively flows into the pathological focus.
- Feeling of fullness. It develops as a result of tissue swelling and the occurrence of intra-articular effusion.
- Hearing impairment. It appears as a complication of pathology when the inflammatory process spreads to the external auditory canal. If the disease is infectious, bacteria can penetrate into the middle and inner ear, which can lead to the development of serious complications.
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile. Occurs most often with purulent lesions of the jaw joint. In addition to fever, patients complain of chills, muscle pain, intense weakness, and severe fatigue.
Chronic TMJ is characterized by less severe clinical manifestations. All the signs are present, as in the acute course of the disease:
- The pain becomes aching or pulling, and mainly appears when the affected joint is loaded.
- As a result of edema, stiffness of movements develops, the person cannot chew or speak fully, and involuntarily tries to spare the sore spot.
- There is morning stiffness that goes away during the day.
- The joint space narrows, resulting in a crunching sound accompanied by pain with any movement.
- Occasionally, general signs of inflammation are present - slight low-grade fever for a long time, weakness and severe fatigue.
Symptoms and types of arthritis of the maxillofacial joint and its treatment
When palpating the joints, the pain increases significantly, general intoxication of the body occurs and increases. Arthrosis of the maxillofacial joint, in contrast.
This is a high-precision research method that combines x-rays and computer technology. Acute phase proteins are special substances that are released into the bloodstream during any inflammatory processes in the body, and the increase in their concentration is directly proportional to the activity of the inflammatory process.
The energy emitted by this field is absorbed by cells in the affected area, which leads to tissue warming, improved blood and lymph circulation, and normalization of nervous and endocrine processes.
Complex treatment of jaw arthrosis includes therapeutic methods (medicines, physiotherapy), diet, lifestyle correction (including getting rid of bad habits), and, if necessary, the use of orthopedic or surgical treatment.
Physiotherapeutic treatment may include ultrasound, laser, microwave therapy, magnetic therapy, and electrophoresis procedures.
Degrees of inflammation of the jaw joint
| Stage | Peculiarities |
| I | Increased mobility of the ligamentous apparatus |
| Slight narrowing of the joint space | |
| II | Severe pain in the jaw joint |
| Impaired motor activity | |
| III | Cartilage tissue is completely destroyed |
| Mobility is severely limited | |
| Bone distance increases | |
| IV | The articular surfaces fuse together, as a result of which ankylosis is diagnosed |
Disease prevention
Inflammation of the jaw joint is often a secondary ailment that occurs against the background of caries, otitis media, influenza and a number of other diseases. Consulting an appropriate doctor is the first step to preventing arthritis. This also applies to inflammation of the joint due to injury.
Don't forget about vitamins, which also play a role in disease prevention. They contribute to the proper development of cartilage tissue, the main component of the joint.
source
Treatment of arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint
- Primary - in which dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint occurs for no reason, treatment is described below, most often it is one of many arthrosis throughout the body;
- Secondary – arthrosis of the jaw joint, the symptoms of which develop naturally, according to the reasons described above.
Stages of the disease:
- Stage I – debut changes, characterized by excessive mobility of the ligaments with uneven narrowing of the joint space;
- Stage II – severe pain in the jaw joint, with signs of decreased motor functions;
- Stage III – complete destruction of cartilage tissue, severe limitation of mobility, increase in bone distances;
- Stage IV – formation of fibrous fusion (ankylosis) of the articular surfaces.
Arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint at the onset of the disease may have a sluggish development. Initial manifestations occur with excessive loads on the area of the upper and lower jaws. The disease begins gradually, often the patient has previously been bothered by inflammatory diseases or causeless pain in the jaw joint.
Often the patient consults a doctor at the stage when the jaw joint hurts very badly and then urgent treatment is necessary. Treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint and all its symptoms should be comprehensive and multifaceted to ensure a speedy recovery and improve the patient’s quality of life. Particular attention should be paid to reducing the load on the joint, normalizing diet, sleep and wakefulness, eliminating stress and nervous strain.
Basic pharmaceutical drugs used for arthrosis of the maxillofacial joint can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Main groups of drugs used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Such as ibuprofen, etoricoxib, ketorol, diclofenac and others. Please draw the attention of your doctor to possible diseases of your gastrointestinal tract when prescribing this group of medications. If necessary, drugs that reduce acidity are taken, for example: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole;
- Vitamin therapy: complexes of vitamins C (ascorbic acid) and D (cholecalciferol), as well as calcium preparations, for example: Calcium-D3-Nycomed Forte, Calcemin and others are more often used;
- Medicines that protect and renew cartilage tissue, such as: chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid;
- Hormonal correction is possible in women after menopause under the mandatory supervision of an endocrinologist and gynecologist;
- For severe and prolonged pain in the jaw joint, intra-articular injections of long-acting hormonal drugs, for example Diprospan, can be used. This type of treatment is advisable no more than once every 4-6 months.
- Electrophoresis with potassium iodide and novocaine;
- Massage;
- Therapeutic exercise, special gymnastic exercises, for example, according to Rubinov;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- Laser therapy;
- Galvanic currents;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Paraffin therapy;
- Microwave therapy;
- Infrared irradiation;
- Ozocerite therapy.
With the capabilities of orthodontists, it is possible to restore a normal bite, install braces, prosthetics, and grind teeth if the chewing surfaces do not conform. Thus, removing the causes of arthrosis.
In advanced stages, destruction of articular surfaces, surgical interventions are recommended, such as:
- Removal of an intraarticular disc;
- Transplantation of the articular head of the lower jaw;
- Removal of the head of the mandibular bone;
- Joint replacement.
All food should be mechanically processed (mashed, grated) and chewed using minimal movements in the temporomandibular joint.
Excluded from the diet: smoked foods, strong tea, alcohol, spicy snacks, chocolate, meat, chewing gum and everything that involves a long chewing process.
Recommended: dairy products, eggs, fruits, vegetables, cereals, soups.
Garlic-cranberry mixture: 500 grams of wild cranberries are mixed in a blender with 200 grams. peeled heads of garlic, then add 1 kg. honey The mixture is consumed one teaspoon before each meal.
In oriental medicine, bee venom was often used in the treatment of arthrosis.
The temporomandibular joint is a three-way movable connection between the temporal bone and the lower jaw. It contains a cartilage disc and is surrounded by a capsule that produces a special joint fluid.
Thanks to it, the joint moves smoothly, providing the function of chewing and articulation. Among the possible pathologies of this formation, arthritis and arthrosis are the most common. The first is inflammation of the joint structures and nearby tissues, and arthrosis is its degenerative changes.
Arthrosis develops as the last stage of changes in the TMJ. As a result of constant microtrauma, the balance between the pressure on the joint and its physiological endurance is disrupted. There are two types of osteoarthritis: sclerotic and deforming. The first develops in older people. Deforming arthrosis is characterized by various bone growths on the surface of the cartilage, detected only by x-ray methods.
Patients complain of limited movements on the affected side, movements lose smoothness and become step-like. The pain spreads to the ear and eye, headaches and hearing loss occur. The diagnosis is made on the basis of an x-ray or linear tomography. Treatment of osteoarthritis is very difficult. For degenerative changes in the joint, chondroprotectors and drugs that improve local blood circulation are prescribed. In case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, severe pain and limitation of movement in the joint, surgical treatment is recommended.
Treatment
Treatment for TMJ dysfunction depends on the type of pathology and the cause of its occurrence. There are several methods of therapy:
There are two possibilities: 1 - either the dislocation spontaneously decreases. This is then a subluxation, which often manifests itself as a feeling of joint instability. This is facilitated by joint hyperlaxity. 2 - or the dislocation remains. That's when it's real dislocation, requiring a reduction in urgency. It is very different from a meniscus dislocation or meniscus slip.
What is temporomandibular osteoarthritis?
Just like the hip or knee, it reflects the wear and tear of all joint structures. This is manifested by joint pain, aggravated by chewing, squealing noises, which are associated with the friction of two worn surfaces of the joint against each other. When this is important, it causes a painful restriction in mouth opening.
- Immobilization.
It is used for traumatic lesions after appropriate measures: reduction of dislocation, comparison of bone fragments. Immobilization of the jaw is also necessary if there is a possibility that the jaw joint may become dislodged or if a fracture is suspected. - Drug therapy.
Aimed at eliminating pain and suppressing the growth of pathogenic microorganisms. Appointed:
- analgesics: paracetamol, Nurofen;
- non-steroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Diclofenac, Nimesil, Affida Fort, Prednisolone;
- antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Tetracycline;
- antifungal agents: Nystatin, Fluconazole;
- cytostatics: Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine.
3. Physiotherapy.
Used after acute symptoms are relieved. Most often prescribed:
Temporomandibular osteoarthritis sometimes occurs spontaneously, sometimes it may be an evolutionary result of old temporomandibular dysfunction or a true rheumatic disease. Conventional occlusion device treatment is much less effective than the general case. Surgery is often necessary, but prosthetic rehabilitation of posterior asthenia, often associated with temporomandibular osteoarthritis, remains essential.
What are occlusal devices?
Occlusal dipo-positives can be presented in different ways. There are two types of occlusion devices most widely used. Occlusal groove. This is a kind of "tooth guard" which is wedged into one of the two dental arches by one of these faces and whose other face is smooth. - retro cutting bite plan. This is a device that wedges into the palate and prevents the teeth from snagging because it has extra thickness behind the incisors. These occlusal devices interfere with the dental joint. When anomalies of the articulated teeth occur at the onset of symptoms, these occlusal devices allow their temporary elimination and therefore the disappearance or improvement of pain.
4. Surgical intervention.
Used when other treatment methods do not give a positive result or for extensive injuries (displaced fractures and multiple fragments). Infectious processes, for example, purulent arthritis, are also indications for surgery. The technique consists of opening the cavity, cleansing it of pus and areas of necrosis.
They also have a muscle relaxing effect. In fact, it becomes impossible to clench the teeth, this prevents the jaw muscles from pushing out and gives way, over time, to vicious circles that maintain muscle spasm. The disappearance of muscle spasms causes the disappearance of pain.
Moreover, by inhibiting dental articulation, they do not allow the parafunds to express themselves. With the help of these devices, the temporomandibular joint and the lower jaw are rebuilt into an ideal position, without being limited by the traumatic position associated with dental malocclusions.
Important!
As an additional therapy, therapeutic exercises are prescribed to increase jaw mobility.
How to recognize?
Inflammatory processes are accompanied by pain and swelling.
Pronounced symptoms are characteristic of an acute inflammatory process near the temporomandibular joint. With this disorder, the patient has severe jaw pain, the pain can vary in severity. Pain during the acute stage intensifies when talking, eating and other movements. If the joint is inflamed, it is impossible to open the mouth more than 1-2 cm.
- swelling and redness of soft tissues in the area of the movable joint;
- local temperature increase up to 38 degrees;
- impaired hearing function;
- feverish condition;
- feeling of fullness in the area of the jaw joint.
What is arthritis of the maxillofacial joint, symptoms and treatment.
Any arthritis is characterized by an inflammatory process. The reasons that can trigger the development of the disease are:
- Infection - the catalyst is past illnesses. Gonorrhea, flu, acute respiratory viral infections and even colds can lead to inflammation.
- Injuries - fractures, bruises, and even sudden opening of the mouth can cause inflammation over time.
- Rheumatic processes. Changes and disturbances in metabolism can cause mandibular or maxillary arthritis to develop. The most common diseases are gout, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Treatment drugs are aimed at combating the cause of inflammation. Therefore, before prescribing a course of therapy, the doctor must conduct a general examination of the body in order to identify the etiology of the disease.
Effective conservative treatment of temporomandibular joint arthritis is aimed at combating the symptoms and cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
This pathology is initially encountered by sports medicine doctors, dentists, maxillofacial surgeons, traumatologists and rheumatologists.
One of the routine and most accessible research methods is radiography of the affected joint (if necessary with intra-articular contrast enhancement), thanks to which it is possible to determine not only the presence of the disease, but also its stage.
There are also highly specialized examination methods:
- CT scan;
- Use of specialized braces;
- Electromyography.
To exclude jaw fractures in arthritis of traumatic origin, the patient undergoes a radiograph of the TMJ. It is not possible to detect inflammation itself on an x-ray. There may be only a slight widening of the joint space in the image due to edema. With the development of a complication such as ankylosis, the joint space, on the contrary, narrows or becomes completely invisible in the image. Basically, diagnosis consists of assessing clinical symptoms and taking a medical history.
Physiotherapy to alleviate the patient's condition
It is possible to detect synovitis and other inflammation of the joint in the jaw area only with the help of instrumental and laboratory methods. If there is a deviation, contact a rheumatologist, traumatologist, dentist, or maxillofacial surgeon. The doctor examines the damaged jaw area and collects information about the course of the disease. It is possible to confirm the diagnosis using the following examinations:
- X-ray of the damaged jaw joint;
- CT and MRI;
- electromyography;
- laboratory testing for protein content;
- general analysis of urine and blood.
Physiotherapy will help you fight the disease, remember this and don’t miss sessions.
Physiotherapy is designed to develop and restore the motor functions of the temporomandibular joints. During the treatment period, you should eat soft foods such as yogurt, mashed potatoes, cottage cheese, boiled fish, baked fruits and vegetables. Avoid hard and crunchy foods; if they get into a sore spot, they cause severe pain.
When the basic procedures listed above fail, the dentist recommends one of the following procedures:
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation relieves pain by relaxing the jaw and facial muscles.
- Ultrasound treatment improves mobility and reduces pain.
- Radio wave therapy increases blood flow to the joint, causing pain to go away faster.
- Acupuncture.
Physical therapy is also used after surgery to speed up healing. It is carried out together with the use of medications. Any therapy that involves moving the jaw can aggravate joint problems. Physiotherapeutic procedures should be carried out in the presence of an experienced physician.
Complications of arthritis of the jaw joint
Inflammation of the jaw joint often develops due to infection entering it. But sometimes it is aseptic, i.e. is formed without the participation of microorganisms. Such aseptic inflammation can result from an acute closed injury or chronic overload of the joint. The latter develops as a result of the removal of a large number of teeth on one side of the jaw or improper prosthetics of missing teeth.
Inflammation of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is characterized by the appearance of throbbing pain, which sharply intensifies when opening the mouth and any movements of the jaw. The intensity of the pain increases when pressing on the joint anterior to the ear, as well as when pressing on the chin. The joint area may swell. If nearby soft tissues are involved in the process, hyperemia (redness) of the skin in the ear area and its adhesion are sometimes observed. At the site of inflammation, the skin cannot be folded.
A pronounced limitation in mouth opening develops, when the patient cannot open it wider than a few millimeters. The course of acute inflammation is accompanied by fever, chills, dizziness and other manifestations of general intoxication. Due to increasing swelling, the external auditory canal narrows, causing a feeling of ear fullness.
Such signs can be observed on one side, for example, with arthritis due to osteomyelitis of the lower jaw. Bilateral arthritis is characteristic of hematogenous infections (influenza), autoimmune diseases and sepsis.
Among the purulent complications of inflammation of the jaw joint are phlegmon of the temporal region, the development of meningitis or sepsis. In these cases, pus from the joint cavity spreads beyond its boundaries by breaking through the joint capsule. First, it can accumulate in soft tissues, and then spread through the vessels to other areas, incl. dura mater. The development of complications is accompanied by low immunity. Most often they develop in patients with immunodeficiency (HIV infection, etc.)
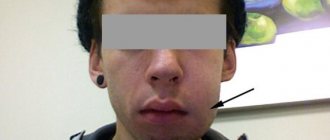
If acute arthritis is not treated in time, it can become chronic with the development of adhesions inside the joint cavity. In this case, fibrous ankylosis develops first. And then, as calcium salts are deposited, bone ankylosis forms with the development of complete immobility of the joint. This condition is accompanied by the inability to open the mouth with bilateral lesions or significant asymmetry of the face with unilateral lesions.
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the TMJ. They have various causes of development: traumatic, infectious and, in severe cases, systemic. According to the course, they are divided into acute and chronic, according to pathogens into specific and nonspecific.
Patients complain of local pain in the joint, near the ear, and there are signs of limited movement. Pain is also noted with palpation and pressure on the joint. If the origin is rheumatic, patients often experience limited mouth opening in the morning, which goes away during the day. If this symptom is detected, you should not delay contacting a rheumatologist.
Treatment of inflammatory changes comes down to taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapeutic procedures. In terms of physiotherapy, UHF therapy and phonophoresis with hydrocortisone are preferable. In case of acute purulent inflammation, surgical treatment is performed. All patients are prescribed a gentle mechanical diet and limited mouth opening.
Dangerous complications of TMJ inflammation include abscess, cellulitis, meningitis and blood poisoning. First, necrotic masses accumulate in soft tissues, and then spread throughout the body through the bloodstream. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the membranes of the brain and infect them. Complications especially often develop against the background of reduced immunity.
A terrible consequence of acute arthritis of the jaw is the transition of the disease to a chronic form with the formation of adhesions inside the joint cavity. As calcium salts are deposited, another problem develops - ankylosis, in which a person completely loses jaw mobility. Ankylosis leads not only to functional, but also aesthetic problems - facial deformation, jaw asymmetry.
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to promptly treat ENT infections and dental problems, since TMJ arthritis often develops against their background. You should not forget about regularly taking vitamin complexes. Microelements contribute to the normal development of joint cartilage tissue.
Arthritis of the maxillofacial joint is a rare disease, so its diagnosis is significantly complicated.
Having received an injury or experiencing pain in the mandibular region for no reason, a person does not associate this feeling with damage to the joints, so he puts off a visit to a specialist as long as he can.
As a result, arthritis of the temporomandibular joint becomes chronic, difficult to treat. To avoid missing warning signs of arthritis, it is important to know what to look for if your mouth hurts when you move.
The peculiarity of arthritis of the jaw is that it can develop gradually, accompanied by increasing pain symptoms, or it can begin suddenly with sharp pain - this mainly depends on the individual characteristics of the human body.
At the initial stage of the disease, the patient may feel a slight pain near the ears while moving the lower jaw - when chewing or yawning.
There is a feeling of stiffness in the lower jaw after sleep or a long period of rest; it may seem that it is not listening.
Without treatment, health quickly deteriorates; pain may occur with the slightest movement of the mouth, at which time the maxillary joints may click.
In the infectious form, severe pain when moving the mouth radiates to the back of the head, shoots into the temple, or spreads over the entire head. Sometimes the sensations are not associated with the fact that inflammation of the jaw joint has begun, and it is believed that this is a banal headache.
The most severe form is purulent inflammation of the jaw, when pus accumulates inside the joint. It is important to pay attention to the following symptoms of maxillofacial arthritis:
- redness of the skin in the temporomandibular region;
- congestion and noise in the ears;
- a feeling of partial deafness due to a decrease in the size of the ear canal in the maxillofacial area;
- increase in ESR in blood test;
- symptoms of TMJ arthritis are similar to the presence of an inflammatory process - headache, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness.
It is important to recognize inflammation of the jaw joint at an early stage and begin timely treatment, otherwise the disease will develop into a chronic form, which requires long-term therapy, and no one has the right to guarantee a positive outcome.
This course of the disease is accompanied by pronounced painful sensations when moving the mouth; clicking and crunching constantly occurs in the damaged joint.
Externally, the maxillary sections may look healthy, but upon palpation a painful feeling appears.
TMJ arthritis is a disease of old people, but this does not mean that young people are immune from it.
Older people are more likely to develop joint inflammation, especially if the disease has occurred in the past.
Arthritis of the temporomandibular joint can be divided into two groups depending on what was the root cause of the disease:
- traumatic;
- infectious.
Infectious arthritis of the TMJ is in turn divided into specific and nonspecific. These types can have an acute form, or they can develop into a chronic form. The causes of inflammation of the lower jaw include the presence of one of three main diseases in the patient:
- “royal” disease - gout;
- rheumatism of the maxillofacial joints in the past and rheumatism of the joints of the whole body;
- systemic lupus erythematosus.
It is very important to identify the root cause of inflammation of the jaw, because this will determine which specialist should be consulted and what treatment will be prescribed for maxillofacial arthritis.
An incorrect diagnosis will lead to therapy being ineffective, and at this time the disease will progress to an advanced form.
Types of arthritis of the jaw joint are usually divided depending on the cause that led to the onset of the inflammatory process:
- Traumatic arthritis of the TMJ usually affects people at a young age, as it is caused by a blow to the jaw or occurs as a result of wide opening of the mouth. This type is characterized by swelling and severe pain on the injured side.
- Infectious arthritis of the jaw joint is often a consequence of viral diseases: otitis media, influenza. It is dangerous because it can develop into mumps, mastoiditis, etc. The pain radiates to the back of the head or shoots in the temples, sometimes it is so strong that the patient is unable to open his mouth, the damaged area swells. A type of infectious arthritis of the maxillary joint can be specific and nonspecific. Specific jaw arthritis is extremely rarely diagnosed, because it is a complication of not the most common diseases, mainly sexually transmitted diseases - syphilis, gonorrhea.
- The disease TMJ rheumatoid arthritis occurs in those who already have rheumatoid lesions in the joints of the body.
- Purulent TMJ is accompanied by severe headache and other typical symptoms of inflammation.
- Dystrophic arthritis of the TMJ is another rare type of inflammation that occurs due to the fact that a person chews food on only one side, resulting in inflammation of the joint on the opposite side. Only an experienced specialist can make such a diagnosis after a thorough examination.
Symptoms of inflammation
The first symptoms of this condition should not be ignored. A person will lose normal performance when he has pain in the temporomandibular joint. Inflammation, the symptoms of which we will present, is called “arthritis of the temporomandibular joint” in medicine. If inflammation is not treated, it leads to degenerative changes. This condition of the joint will already be called arthrosis. Then you will have to spend more time and money on treatment.
Symptoms differ between acute and chronic arthritis. Symptoms of acute inflammation:
- redness and swelling in the joint area;
- hyperemia of nearby tissues;
- sometimes tinnitus and crunching;
- grinding of the jaw at night;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- sharp pain when moving, radiating to the ears and back of the head;
- dizziness;
- elevated temperature.
With chronic inflammation, the symptoms are different:
- aching pain;
- a feeling of jaw stiffness, especially if the sleeping position is chosen face down;
- the pain intensifies when you press on the jaw;
- Possible hearing loss.
Typically, chronic inflammation is not accompanied by redness of the surrounding tissues or the inability to open the mouth. However, it is still advisable to eat gentle liquid food at this time and treat inflammation. After all, prolonged inflammation without the necessary treatment will lead to facial deformation.
Routes of infection in a joint
Microorganisms can enter the temporomandibular joint in several ways:
- contact: from nearby tissues;
- hematogenous: with blood from distant organs and tissues;
- lymphogenous: with lymph flow;
- from the outside: with open wounds.
Contact arthritis
The contact route of spread occurs most often. In this case, the root cause of inflammation can be:
- otitis (inflammation of the middle ear) and mastoiditis as its complication;
- tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils);
- sialadenitis (inflammation of the salivary glands), often the parotid gland (mumps);
- abscesses and phlegmons of soft tissues of the maxillofacial area;
- boils and carbuncles of the temporal region;
- osteomyelitis of the mandible or temporal bone;
- acute pericoronitis (difficulty in the eruption of wisdom teeth).
Thus, the source of inflammation and the root cause of arthritis can be, for example, a diseased tooth, which, if untreated, develops osteomyelitis of the lower jaw. But arthritis is often caused by diseases of the ENT organs: ear and throat.