From this article you will learn:
- what methods of treating pulpitis allow you to keep the tooth alive,
- what is the vital amputation method,
- stages of biological treatment of pulpitis.
The biological method of treating pulpitis is a conservative method that is aimed at completely preserving the pulp as viable. The use of this method is possible only if the following 2 conditions are met. Firstly, the patient should seek help from a dentist at the earliest stage of the development of pulpitis, i.e. at the very beginning of the development of pulp inflammation. Secondly, the age of the patient to whom the doctor can offer this method is very important, because Treatment without nerve removal is carried out only in children, adolescents and people no older than 25-27 years.
The latter is associated with the ability of the dental pulp to heal itself, which also depends on the age of the patient. In addition to the biological method, there is also a method of vital amputation, in which the pulp remains partially viable. This method involves removing the pulp only from the coronal part of the tooth, preserving it in the root canals. But the indications for such therapy are limited - it can only be carried out in multi-rooted teeth (they have a clearly defined transition between the coronal and root pulp).
Important: in dentistry, unfortunately, doctors very rarely offer conservative methods for treating pulpitis, even if the patient is suitable for their use. This is due to the flow of patients and the desire to use the usual familiar methods. It is best to ask your doctor whether such treatment methods are indicated for you, and if he answers “no,” then you must clarify: “why this method is not indicated specifically for you.”
What it is
Purulent pulpitis or pulpal abscess is a lesion of the dental pulp in which pus appears in the area of the pulp chamber. Typically, pus forms during improper or unqualified dental treatment by a doctor. When the level of serous matter in the pulp increases, oxygen deficiency occurs. All this leads to metabolic disorders and disturbances in the acid-base balance, which results in an increase in lactic acid levels and a decrease in the protective properties of cell activity.
This picture shows healthy and infected teeth. Visually presented is purulent pulpitis and the resulting pulp abscess.
The tissue breaks down and signs of an abscess appear. And when the doctor opens the pulp chamber, all the accumulated pus begins to come out, while the pressure in the chamber decreases and the pulp fully restores all its regenerative functions. If the opening of the purulent cavity occurs spontaneously, then the pus can penetrate into the carious cavity, and pulpitis becomes chronic. In addition, purulent pulpitis can be provoked by various irritating factors of the pulp - strong antibiotic drugs, medicinal pastes, filling materials.
Differential diagnosis
With characteristic symptoms, diagnosing pulpitis usually does not cause difficulties. It makes sense to count on the reversibility of pulpitis only in cases of traumatic etiology (including iatrogenic nature) and the duration of complaints is no more than 7 days. With a deep carious cavity, it can be difficult to visually determine whether it is still caries or already pulpitis. X-rays do not always help clarify the situation. The use of electroodontodiagnostics (EDD) to differentiate caries and pulpitis is not informative. The best (and often the only) way to distinguish caries from pulpitis in this case is a visual examination after removal of carious tissue. If, after preparing necrotic dentin, the pulp is not exposed, it means it was just caries. If a minimal opening occurs, you can hope for the reversibility of pulpitis and do not rush into pulp removal. If there is extensive communication between the carious cavity and the tooth cavity, it is necessary to remove the “nerve”.
Pulpitis can be differentiated from periodontitis by the absence of pain when biting and the absence of foci of bone tissue destruction at the apexes of the roots on an x-ray. In multi-channel teeth, pulpoperiodontitis occurs (living pulp in one of the roots and necrotic pulp in the other). Treatment for pulpitis and periodontitis is almost the same, only the latter usually requires one more visit.
It is possible to differentiate pulpitis and trigeminal neuralgia by the presence of the causative tooth. It should be noted that some patients, having difficulties in diagnosing pulpitis, almost happily pick up the idea of neuralgia, as soon as it is mentioned in passing (and some count on it even before any mention). The thought of “the nobility of my illness” warms the soul of some, but the vast majority of them, fortunately, do not know and will never know what real neuralgia is. The probabilities of pulpitis and neuralgia differ by several orders of magnitude.
And one more important point. Two pulpitis in different teeth at the same time is extremely rare (about the same as two meteorites falling into one crater). Even if both teeth at first glance are equally badly damaged. Therefore, it is not reasonable for either the patient or the dentist to sign a verdict on both diseased teeth - most likely, only one of them deserves depulpation. And in the second tooth the pain only radiates - when the culprit is cured, it will go away.
Causes
There may be several reasons for the appearance of acute purulent pulpitis, but all of them cause the appearance of an inflammatory process in the area of the innervated fibrous trunk. The main causes of acute pulpitis:
- The occurrence of caries. This lesion is a common factor in the development of pulp disease. Cariogenic microflora, through microscopic tubules that are located in the dentin area, can enter the structure of the internal cavity of the tooth and cause inflammatory processes there;
- Presence of mechanical traumatic damage. When you receive blows to the jaw, falls, or other injuries, the integrity of the crown may be compromised, which ultimately causes a breakdown of the dentin protection and part of it becomes exposed. In these cases, even a slight touch to the exposed area of the nerve plexuses can cause increased pain;
- Iatrogenic injuries.
Attention! Pulpitis can appear as a result of poor-quality medical intervention. An inflammatory process in the pulp can appear as a result of poorly performed caries treatment procedures - caries preparation without the use of water-air cooling, etching with a special composition without following the technique, deep and extensive tissue removal without taking into account the anatomical structure of the pulp - Location near the source of infection. The appearance of acute pulpitis can result from the close proximity of the problematic tooth to the area with infection - sinusitis, periodontitis, affected wisdom tooth. Pathogenic microorganisms can spread through the blood or lymphatic vessels and lead to pathological changes in the area of the pulp chamber;
- Penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through the periodontal pocket. In these cases, in the presence of diseases of the marginal gum, microbes penetrate into the damaged periodontal junction and enter the apical foramen. As a result, this can cause the appearance of periodontitis or retrograde pulpitis.
Purulent pulpitis is a disease of the dental pulp, which is characterized by the presence of pus in the pulp chamber. One of the main causes is the penetration of microorganisms from the carious cavity into the pulp chamber, which causes the development of the inflammatory process.
Etiology
There are only two causes of pulpitis: bacterial and traumatic. In first place in terms of frequency is caries. The pulp resists the effects of bacterial toxins from the carious cavity that penetrate into it through the dentinal tubules. But when the destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth (not stopped in time) reaches the pulp itself, the flow of pathogens becomes so great that it triggers an acute inflammatory process. When a tooth is broken and the pulp is exposed, the microflora of the oral cavity also begins to affect it. Plus, bleeding and hematomas in the pulp enhance the damaging effect. A similar picture occurs in severe forms of pathological abrasion and wedge-shaped defect. An alternative option for the development of pulpitis is bacterial invasion from the root apex. In this case, the tooth may be completely intact, and the microbes have reached the pulp through a deep periodontal pocket. The version of the possible introduction of bacteria into the pulp through the bloodstream (anachoresis) currently has no evidence.
Symptoms
It is simply impossible to diagnose yourself. This can only be done by an experienced doctor using special equipment. But it is still important to know the basic signs that will help you understand that there is a pathological process in the tooth. In addition, these signs will be the main signal that you need to go to the doctor for examination and further treatment. Usually, with acute purulent pulpitis, the patient experiences a feeling of general weakness, and also deteriorates in health. In addition, there are a number of symptoms that you should pay close attention to:
- The appearance of strong pulsating pain that is long-lasting. However, it cannot be reduced with the help of various analgesic drugs;
- Pain can occur without an irritant, and it increases at night;
- Any touching of the teeth can cause a feeling of discomfort, and this often results in a repeated attack;
- The pain is intensified by hot temperatures, but may subside by cold;
- Painful sensations can pass along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. When the upper units of the dentition are affected, pain can radiate to the temporal part, cheekbones, and lower jaw area. If there is pulpitis in the area of one of the lower teeth, then the pain will move to the back of the head and the submandibular part. If the lesion is on the anterior units of the dentition, then the pain may radiate to opposite sides;
The development of pulpitis can affect the trigeminal nerve. It is a node from which three “branches” are formed that extend from the brain stem to the person’s face, supplying it with nerves and connecting it with the central nervous system. - When examining the affected tooth, you can find a deep carious area, at the bottom of which there is pigmented, softened dentin. When softened dentin is removed, the pulp chamber opens. In this case, the formation of a purulent compartment is observed, which, when released, causes a decrease in pain;
- There is a whitish coating on the surface of the mucous membrane and tooth;
- Swelling of the gums and tooth mobility are observed.
Features of the examination
In order to find out an accurate diagnosis, you first need to visit a dentist. At your appointment, the doctor will conduct an examination and determine the exact cause of pain and other unpleasant feelings. Typically, during an examination, the doctor performs the following procedures:
- He visually examines the condition of the tooth and carious cavity. He examines the condition of the carious cavity, determines its depth, whether there are affected, infected tissues in it that are painted in a characteristic color;
- Be sure to do probing, which determines the nature of the pain - pain can occur throughout the bottom or at one point;
- Inspects the status of communication with the pulp chamber. The connection with the pulp chamber may either be completely absent or represent a small hole in the gaping horn of the neurovascular fiber;
- Percussion of the vertical plane is performed, which usually does not increase pain.
Probing is the feeling of teeth using a special instrument - a probe. This method allows you to check the visual impression of the damaged integrity of the tooth and determine the degree of damage to hard tissues.
In order to exclude other dental diseases, the doctor must conduct a differential diagnosis. Typically, comparison is made with the following nosological types of pathologies:
- State of nerve hyperemia. In appearance, this pathology resembles a carious lesion. Usually, when exposed to certain irritants, short-term pain occurs;
- Papillitis. This condition is characterized by the appearance of inflammation of the interdental papilla. The interdental papilla is usually very inflamed, red in color, and can sometimes bleed;
- Acute form of apical periodontitis. In this condition, the pain sensations are aching in nature, they intensify during pressure, and sometimes there may be a sensation of a protruding tooth;
- Neuralgia nervus trigeminus. When touching the skin of the face, when talking, when eating food or touching trigger areas, shooting pain appears;
- Sinusitis - this condition is accompanied by nasal congestion and the appearance of pus from the passages, and there is also a deterioration in health, headaches, and hyperthermia;
- Hole pain. This is alveolitis, which manifests itself as a result of infection of the socket of a recently extracted tooth.
Features of therapeutic therapy for purulent pulpitis
The main principle of therapeutic therapy for this form of pulpitis is to cleanse the canals of pus. But before starting treatment therapy, it is worth assessing the general condition of the pulp. Typically, the presence of purulent discharge causes the pulp to quickly lose its functionality and ability to recover further. Therefore, during acute purulent pulpitis, complete or partial removal of the pulp is often performed.
Treatment of purulent pulpitis consists of cleansing the carious cavity, determining the degree of infection of the pulp, partial or complete removal of it, treatment of the tooth, filling and restoration of the aesthetic appearance.
Purulent pulpitis can affect not only the molars, but also the primary dentition. When acute purulent pulpitis appears in baby teeth, treatment therapy is the same as for lesions of the molars. However, when treating primary dental units, the doctor must carefully determine the dosage of medications and methods of pain relief.
Important! Particular attention should be paid to purulent pulpitis in pregnant women. The appearance of this form of the disease is quite dangerous. The doctor must take gentle methods of therapeutic therapy that will reduce pain and other unpleasant feelings.
But it is important to save the tooth and harm the child. After treatment, the doctor must monitor the patient’s condition and if suddenly there is a need to take the necessary emergency measures.
When to treat pulpitis and fight for a tooth
Reversible pulpitis
Reversible pulpitis refers to mild inflammation of the pulp and, if the tooth is treated in time, the soft dental tissue can be preserved and the tooth restored.
The main symptom of reversible pulpitis is a short, sharp pain when eating cold or hot food or drinks. The pain is felt only when food or drinks come into contact with the tooth and stops after a few seconds.
Unfortunately, patients seek help only when they feel such pain, and to avoid such a situation, it is very important to visit the dentist regularly, even if you do not have toothache. The earlier pulpitis is detected, the faster, easier and cheaper its treatment!
Irreversible pulpitis
This is a severe inflammation of the dental nerve as a result of which the tooth nerve dies. Pulpitis can also be complete, partial, acute, subacute and chronic. And only a dentist will be able to determine an accurate diagnosis and draw a conclusion about what method to treat pulpitis and how many appointments this will require. A tooth with pulpitis can be saved and will last for many years.
Symptoms of irreversible pulpitis:
- Toothache that lasts up to one hour after the source of irritation has disappeared (for example, cold water);
- Spontaneous, spontaneous pain appears without any reason, without an external stimulus;
- The tooth becomes extremely sensitive to cold or hot food or liquid;
- Expansion of painful sensations (pain from the jaw “shoots” into the temple, ear, back of the head)
- Toothache appears in the middle of the night.
In case of irreversible pulpitis, immediate endodontic treatment (cleaning the root canal of inflamed pulp tissue) is necessary in order to save the tooth.
It is important to remember that the stages of pulpitis vary greatly and you cannot decide for sure on your own whether pulpitis can be cured or whether it is time to remove the tooth. If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, contact your doctor immediately. If you delay your visit, you may have to not only fill the tooth, but also undergo complex root canal treatment. You can ask for help by calling 241-10-90.
Treatment methods
During acute purulent pulpitis, therapeutic therapy can be carried out using two methods:
- Vital;
- Devital.
Each treatment method has certain features that are worth considering in more detail.
Vital
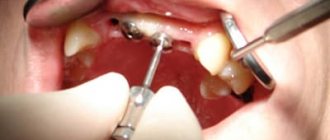
Sometimes a vital method of therapeutic therapy can be used to treat acute purulent pulpitis. During this method of therapeutic therapy, the vital properties of the hilar pulp are preserved, but all areas with necrotic lesions are removed. After this, the tooth and dental canals are filled. The vital method of treatment is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The first step is anesthesia;
- After the injection begins to act, the pulp is opened and areas with necrosis are slowly removed;
- The dental canals are cleaned;
- After cleaning the canals, they are treated with antiseptic drugs;
- Sometimes the doctor puts medicine into the tooth cavity and leaves it for several days. After this, the patient comes to see a doctor for final treatment;
- Next, the tooth canals are cleaned again;
- After cleaning, the canals are sealed;
- The doctor forms the shape of a crown from the filling material;
- At the end, the tooth is restored using a filling or a special crown is installed.
Devital
As a result of treatment with the devital method, the treatment process becomes painless, but the use of special pastes that contain arsenic can change the color of the enamel (the tooth may become pink or orange).
Using the devital method, treatment therapy is carried out in two stages. At the first appointment, the doctor gives an anesthetic, opens the cavity, cleans it and puts a special paste into it. This paste after a certain period leads to complete death of the nerve. To kill the nerve, pastes containing arsenic and other analogues of this remedy are used. At the end of the first appointment, the dentist places a temporary filling. At the second stage, the doctor removes the temporary filling. After this, the doctor cleans the cavity and fills the canals. Finally, a permanent filling is installed.
How is pulpitis treated:
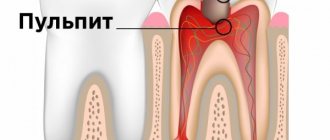
Inflammation of the pulp is called pulpitis.
The pulp is a part of the tooth made up of blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic vessels. It is located inside the tooth under the enamel and dentin and provides the hard tissues of the tooth with nutrients.
Treatment of pulpitis includes removal of damaged tissue and removal of the tooth pulp itself. After the root canal system is cleaned mechanically and chemically, the canals are sealed and sealed.
What causes pulpitis:
- A carious lesion that was ignored by the patient and not treated for a long time, as a result of which it affected the root canals.
- The tooth had been treated previously and the filling had to be replaced several times.
- The tooth was injured when very hard products (crackers, nut shells, etc.) came into contact with the tooth, chronic bruxism (grinding teeth during sleep, constant clenching of the jaws) or due to a jaw injury.
- A dental injury that has disrupted the blood supply to the nerve of the tooth.