What is special about wisdom teeth?
The maximum set of molars for an adult is 32. In this case, it is considered normal to have 28 teeth, since four teeth are the so-called eighth molars or wisdom teeth. For some, they do not erupt at all, for others, when “eights” appear, complications and pathologies arise, but in other cases, wisdom teeth occupy the correct position in the dentition and do not bother their owner. “Eights” usually appear between the ages of 17 and 27, that is, during the period when a person has already formed an attitude towards hygiene and his own dental health. Why is it important? Due to the remote position of wisdom teeth, it is quite difficult to carry out high-quality cleaning, so only very good hygiene can reduce the risk of dental damage. In reality, it is the third molars that are in the top in terms of the number of cases of caries and its common complication - pulpitis.
Prevention of pulpitis and caries
There is nothing new in the prevention of caries and pulpitis:
- careful oral hygiene;
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- timely treatment of dental diseases;
- regular preventive visits to the dentist;
- timely professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar.
Only a qualified specialist can adequately assess the situation and make the right decision about wisdom teeth treatment. In some cases, it is more appropriate to remove a tooth rather than treat it, but of course this depends on the specific case. In order not to provoke various complications, it is necessary to contact your dentist in a timely manner.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: symptoms and treatment
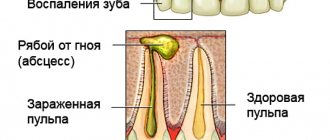
Pulpitis affects the connective tissue of the tooth - the pulp. It has a crown and a root part: depending on the shape and degree of the disease, one or both parts may be affected. The symptoms of wisdom tooth pulpitis are exactly the same as in the case of other teeth.
- Painful sensations.
In acute pulpitis, the pain is acute and paroxysmal, and can be felt in the temples, ears and other parts of the jaw. The pain intensifies at night and when exposed to irritants (temperature, chemical or mechanical). With chronic pulpitis, the pain is dull and less pronounced, which makes it difficult to diagnose the disease, given the location of the wisdom tooth;
- Bleeding.
It appears only in chronic hypertrophic pulpitis, when granulation tissue grows;
- Change in tooth color.
Observed in the case of tissue necrosis with gangrenous pulpitis.
When a wisdom tooth hurts, pulpitis is just one of the options that could be the cause. To diagnose pulpitis, a visual examination, x-ray or EDI (electrodynamic diagnostics) is required. Of course, such procedures are carried out only by professionals, so if you suspect pulpitis, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor. Most patients who face a similar problem have two questions: is wisdom tooth pulpitis treated and is it worth treating wisdom tooth pulpitis. The answer to the first question is yes, but to answer the second, you need to consider each clinical case separately.
Pulpitis and caries
The pulp is a bundle of nerves and vessels located inside the tooth. People simply call it a nerve. Pulpitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the pulp. This disease is quite common, and among all the most common problems with which people go to the dentist, pulpitis makes up about 20%. ,
The pulp is the last barrier between pathological bacteria and periodontal tissue, therefore, after the dental nerve dies, pathogenic microorganisms without obstacles penetrate both the mucous and bone tissues of the tooth, causing various complications.
Regardless of the reasons that caused the disease, the development of pulpitis occurs in three stages:
- alteration – a primary change occurs in the dental nerve;
- exudation - blood flow is disrupted;
- proliferation - reproduction of cellular elements.
Moreover, exudation is more pronounced in the crown part of the tooth, and proliferation is more pronounced in the root part.
As for caries, it is the leader of dental diseases; it occurs in people of all age groups. This disease begins with a tiny spot and can lead to the loss of an entire tooth.
Structure of teeth
At its core, caries is the destruction of hard dental tissue, which occurs with the participation of microorganisms and the presence of food debris in the oral cavity. The disease develops in 4 stages:
- stain stage (white or dark) – the enamel surface remains shiny and smooth, no signs of destruction or enamel defects are observed;
- superficial form – destruction of the surface layer is observed, while the dentin remains intact;
- medium form - the upper layers of dentin are involved in the pathological process;
- deep caries - complete destruction of dentin, including deep layers.
Pulpitis of the wisdom tooth: treat or remove?
In most cases, a wisdom tooth with pulpitis is removed. The main indications for removing a diseased “eight” are developmental pathologies, as well as being outside the bite (in this case, the tooth has no function). We are talking, first of all, about retention and dystopia. An impacted wisdom tooth is completely or partially hidden in the jaw, and a dystopic wisdom tooth has an incorrect position relative to the rest of the dentition. These pathologies in themselves are a good reason for removing the “eight”, however, if pulpitis occurs due to the impossibility of full treatment, such teeth are definitely removed.
Treatment and preventive measures
A wisdom tooth is an ambiguous vestige. On the one hand, its presence is not necessary, but on the other hand, it can be useful for prosthetics.
Is it worth removing or treating the affected eight?
In the case when eruption occurs without any complications, and access for examination and dental procedures is maintained, then it can easily be treated effectively and filled.
Such conditions should not be ignored and rush to pull out a tooth, as it can become a good basis for bridge prosthetics. Removing the figure eight is strongly recommended only in particularly advanced cases, as well as in the absence of access, which happens most often.
Photo: wisdom tooth removal
Speaking about the prevention of development, only specialists can provide tangible help and support in this case. Consulting a doctor during the eruption of wisdom teeth can protect not only from pulpitis, but also from inflammatory processes in the periodontium.
Treatment of wisdom tooth pulpitis
Treatment of wisdom tooth pulpitis is carried out in the same way as on other teeth. In 90% of cases, the doctor performs complete removal of the pulp: only in the initial stages of chronic fibrous pulpitis is it possible to save part of the pulp. However, even if the wisdom tooth is positioned correctly and has completely erupted, very often the doctor suggests extraction rather than treatment. This is due to some features of wisdom teeth that reduce the likelihood of a successful treatment outcome.
- Location of position. Wisdom teeth are difficult to reach, and treatment of pulpitis requires almost pinpoint precision.
- Wisdom teeth have curved roots, which sometimes makes the depulpation procedure extremely difficult.
Despite the difficulty of treatment, sometimes preserving wisdom teeth is advisable. First of all, this applies to situations where, of all the molars, only “eights” remain (in the future, a prosthesis can be attached to them), as well as in the initial stages of the disease, when the chances of a successful and predictable result are higher.
How to treat pulpitis
There are three options for treating the disease:
- The first option: the doctor completely preserves the nerve.
- The second option: the doctor partially removes the nerve.
- Third option: the pulp is completely removed from the root canals.
Patients often come to the doctor with already complicated forms of pulpitis. Therefore, the first treatment option is used very rarely. If the doctor decides to preserve the nerve, he will resort to treating the tooth with drugs containing calcium.
The second treatment option is used only in the case of a complex canal structure or if there are foreign bodies in it.
The effectiveness of treatment is achieved only with medicinal treatment of the canals and filling with hardening pastes. Pulpitis can be cured in 1-4 visits to the dentist. They will definitely put arsenic in the canal, treat it with an antiseptic, and only then install a filling.
After proper treatment of pulpitis, unpleasant pain should not occur. However, it is possible to experience discomfort after the filling procedure for 5-7 days. The pain will increase when chewing solid food.
Should I save my wisdom tooth if it decays?
There is an opinion that treating wisdom teeth is a useless exercise. Despite the efforts expended, the tooth soon collapses, and the fillings do not last long. In fact, this is not entirely true. Any dentist will tell you that removing the figure eight is an extreme measure that is not always worth taking. It was not in vain that nature gave us these pairs of teeth; sometimes they are needed for prosthetics or maintaining chewing function.
You can save a wisdom tooth destroyed by caries if the following conditions exist:
In what cases is it better to remove the third molar?
Wisdom teeth are reluctant to be treated even with moderate or deep caries. And pulpitis is considered a serious reason for extraction. The indication becomes clear when:
- the third molar has grown incompletely or incorrectly - to the side, to the side or outside the dentition;
- the wisdom tooth puts pressure on neighboring crowns, leading to their destruction or displacement;
- there is recurrent pericoronitis - a disease in which inflammation of the gingival hood occurs;
- There is not enough space on the jaw arch to accommodate all the units.
Also, pulpitis and figure eight caries are not treated if the crown is severely damaged. There is no point in strengthening it with pins or fixed prostheses - the structure will not last long, and the patient will overpay for useless treatment.
It is worth understanding that treatment of pulpitis of the third molar will cost more than other teeth. Thus, the price for treatment of ordinary units in Moscow clinics starts from 5,000 rubles. And for the restoration of the extreme crown you will have to pay from 7,000 rubles.
The doctor must warn about all possible risks of treating pulpitis in the wisdom tooth. But the final decision remains with the patient. To be on the safe side, you can consult several dentists. If they all insist on being removed, the G8 will have to get rid of.
Pulpitis is different
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
At the site of inflammation, pulpitis is:
Methods of treating various pathological conditions of eights. Cases when wisdom teeth are filled
The treatment of wisdom teeth does not differ in therapeutic measures from the treatment of other molar units. The main difficulties arise only when accessing them.
Inflammation of the figure eight and gums around
Inflammation of the gums around the tooth is accompanied by severe pain and the primary task of a specialist is to provide symptomatic treatment. Systematic inflammation of soft tissues is provoked by pathological processes in hard tissues. Tooth extraction helps solve the problem and sanitize the oral cavity.
Sometimes removing figure eights is cheaper than therapeutic treatment.
If gum inflammation is caused by the formation of subgingival stone or the presence of caries, then the inflammation is stopped by eliminating irritating factors:
- Carious cavities are cleaned of pathogenic microorganisms and filled with filling material.
- The specialist performs professional cleaning of the teeth from hard deposits with ultrasound.
- Measures to sanitize wisdom teeth are possible only if they are correctly positioned relative to the dentition. If the molar is positioned incorrectly, removal is indicated. Together with the third molar, its antagonist (paired tooth) is also removed.
The inflamed gum heals in the usual way after removal.
Swelling of the hood
The hood is the part of the gum that grows over the molar and forms a cavity. Food debris and bacteria get into the space between the gum and tooth. Due to the position of the gums in the form of a hood, access to the tooth is limited, removing food debris from it is problematic, this leads to the development of pericoronitis.
Pericoronitis causes swelling of the hood and gums, often the inflammatory process spreads to the cheeks. Under the hood, caries develops on the tooth.
In this case, an integrated approach to eliminating the pathology is needed. Standard therapeutic measures are used to treat caries. To treat pericoronitis, the method of excision of the gingival hood is used. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, is inexpensive and has no complications.
If the tooth under the hood is severely damaged, then it will have to be removed to eliminate the symptoms of pericoronitis.
Pulpitis
The development of caries provokes the penetration of infections into deep dentin through the carious cavity. The pulp becomes inflamed and reacts with acute pain, the disease is called pulpitis.
The inflamed pulp reacts sharply to external irritants - the patient experiences pain when temperature changes in the oral cavity and from organic acids entering the oral cavity. The patient's body reacts by increasing body temperature.
If the tooth has erupted correctly, then treatment follows the standard treatment regimen for pulpitis. Next, a filling is installed and the inflammation goes away.
But if the tooth is positioned incorrectly, then filling and treatment is a waste of time and money. The best solution would be to remove it.
Caries and its treatment
The formation of carious cavities on the surface of wisdom teeth is the most common clinical case with molars in therapeutic dentistry.
Caries often forms on third molars due to their inaccessibility to cleaning. At home, the lack of professional oral hygiene provokes the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms and the appearance of carious cavities.
When caries appears, the question arises: are wisdom teeth filled? The answer is contradictory. Filling and treatment of figure eights is indicated if they are successfully located relative to the dentition. But if they have a defective location, the doctor removes the tooth.
zubnoimir.ru
Pulpitis: what is it?
There are two types - acute and chronic pulpitis.
Acute and its symptoms
The infection enters the internal tissues through a thin wall that is destroyed by caries.
- very severe pain , which intensifies at night;
- sensitivity to thermal effects (cold), which does not stop after the stimulus is removed;
- Possible painful sensations on the face due to damage to the trigeminal nerve.
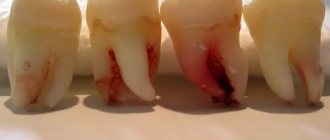
Photo 1. Gray-black softened dentin, indicating acute inflammation and the need for urgent treatment.
Features of the flow:
- At first, the inflammation is focal in nature and localized in the mucous membrane. Short-term pain appears more often in the evening .
- If left untreated, after a few days the inflammation progresses to a purulent stage . Acute pain can last for several hours and intensifies with mechanical stress. There is a deep carious lesion and accumulations of purulent exudate.
- In the absence of adequate treatment, acute pulpitis becomes chronic .
Chronic
- prolonged pain syndrome even in the absence of an irritant;
- red and inflamed molar tissue;
- Possible destruction of enamel and bleeding.
Photo 2. A chronic form of the disease, which is characterized by long-term pain that occurs for no reason.
Features of the flow:
- Fibrous stage (aching pain when changing temperature, feeling of heaviness, unpleasant odor).
- Hypertrophic pulpitis (feeling of fullness in the figure eight, bleeding, swollen inflamed pulp).
- Purulent process (the presence of pus in the pulp chamber, the pain is constant and spreads throughout the oral cavity).
Toothache: pulpitis or periodontitis?
Doctors, however, treat teeth differently - as a delicate instrument that reacts to everything that malfunctions in the body or has an external influence on it: the environment, poor diet, drinking alcohol, and even more so, biting threads or opening beer bottles... They We often have to complain that the majority of patients are irresponsible people and go to the doctor when the pain is so severe that they can no longer eat, drink, or sleep. Or they endure the pain, swallowing pills and bringing the tooth to such a state that it is impossible to save it. The most common explanation for this behavior is fear. Despite the fact that Soviet anesthesia-free dentistry is long gone, there are still many people who are still afraid of the dental chair or drilling machine. Although the latter now work almost silently, and many patients in modern comfortable dental chairs even manage to take a nap during treatment.
To permanently cure your fear of modern dentistry, try to imagine that you were born in a time when the creation of the dental chair was still several centuries away.
Lunar therapy
Ancient doctors recommended exotic recipes to treat toothache. For example, Pliny advised spitting in a toad’s mouth on a full moon night and saying “Take away my pain!” An alternative method is to place bird droppings mixed with oil in the ear on the side of the affected tooth. And to prevent teeth from decaying (to prevent caries), he recommended biting off the head of a mouse once a month. Other aesculapians advised more harmless methods, for example, sitting with your mouth open at night, turning towards the Moon. Later, in the Middle Ages, dentistry consisted of instilling various tinctures into the ears, poultices, inhalations, and even taking laxatives.
Our great-grandfathers believed that the tooth deteriorates from what is in it, so caries was called caries. They tried to expel the worm with a hot iron, molten wax, even acid... But the main method of treating a diseased tooth until the 20th century was extraction. Blacksmiths, barbers, and bathhouse attendants “torn” teeth. Peter I was known as a master at removing teeth from his subjects; historians claim that he always had pelican forceps with him for this task.
200 years ago
Only at the beginning of the 19th century did special burs for drilling teeth appear, which had to be rotated manually, and at the end of this century a foot-driven burr was invented. Almost simultaneously with it, a dental chair was created. In a word, it was the 19th century that became a period of breakthrough in dentistry: most of the devices, instruments and treatment methods invented during that period are still used today, naturally, in an improved form. Well, the sensations of patients of past centuries, when Novocaine had not yet been invented, can be easily compared with those that we experienced during the treatment of pulpitis in the Soviet way - without anesthesia.
But this was already a great blessing, because before the invention of the X-ray machine, treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis teeth was practically useless; most often they had to be removed. Namely, with pulpitis and periodontitis - serious complications of caries - we experience the most severe pain.
Hello, pulpitis!
Pain is the body’s natural reaction to some kind of problem, signaling that it needs help. At first it is quite tolerable - the tooth begins to react to sweets (jam, sweets), then to hot and cold. For now it's just caries. But if you do not consult a doctor at this moment, the process of tooth damage will worsen and a moment will come when the pain appears for no reason, intensifying at night.
And, as they say: “Hello, pulpitis!” At this stage of caries complications, it is already difficult to figure out which tooth is affected, because the entire jaw, temple, and sometimes the ear also hurts and throbs.
Painkillers relieve the condition for a short time, but that’s all.
This indicates that the carious process has penetrated deeply and reached the pulp (dental nerve). If the patient had turned to the doctor at the stage when the tooth was only reacting to external stimuli, everything would have been done by removing the tooth tissue affected by caries and installing a filling made of light-curing material. In the case of pulpitis, serious painstaking treatment is required.
The doctor resorts to endodontic treatment (endo - inside, dont - tooth). If he sees that the root canals can be treated and filled right away, he will certainly do it. But in a situation where the canals are curved, narrowed, or inflammation has spread to the tissues surrounding the tooth, the treatment can be divided into two or even more stages. That is, if in a problem-free situation the patient is given anesthesia, the carious cavity is prepared, the inflamed pulp is removed, the canals are treated, and then the tooth is immediately filled, then in a complex situation, the carious cavity is first treated and medicine is added (safe arsenic substitutes) to relieve acute pain and inflammation.
At the next appointment, the same procedures are carried out as in a normal situation. At the same time, modern endodontics is necessarily carried out under double control - x-rays and an apex locator - a device that allows you to control the passage of the tooth canal. Once the canals are sealed, a permanent filling is installed. On the one hand, the tooth is as good as new: it doesn’t hurt and looks decent, on the other hand, it has become “dead.” This means that it can serve you for the rest of your life, or under unfavorable circumstances it can become even more ill than with pulpitis (and they also say that a bomb does not fall into the same funnel twice!).
And the "dead" hurt
Periodontitis is inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. It often develops if a person has experienced pulpal pain with the help of analgesics, they have subsided, but he has not consulted a doctor. Over time, the nerve is destroyed and the tissue that holds the tooth in the jaw is affected. Another, most common cause of periodontitis is poorly treated canals after nerve removal. In addition, it can develop due to injury - a blow or an incorrectly installed filling pressing on the tooth.
The intensity of pain in this disease may well compete with pulpal pain. At the same time, sometimes there is no strength even to close your mouth - when the lower and upper jaws close, it seems that the diseased tooth has grown and any touch to it responds with a new outbreak of pain. This happens because purulent exudate accumulates at the root apex in the form of a cyst or granuloma.
Whether conservative treatment makes sense is determined based on the radiograph. With its help, the doctor determines whether the root canal has been filled, what size the “cyst” reaches, and how damaged the tooth is.
If it turns out that the treatment is advisable, the doctor reports that it consists of several stages and can last for 2 - 3 months, so you should be patient and strengthen your immune system, since the dentist only helps the body eliminate inflammation, mainly with the pathological process The body copes on its own.
During the treatment, the doctor removes the infected tissue that has filled the root canal and thoroughly cleans it using modern, durable, flexible and very thin instruments. If the canal was sealed a long time ago using old technology, it is difficult to unseal it, reach the source of inflammation and eliminate it using conventional instruments. In such situations, a special apparatus is used to carry out the depophoresis procedure. This is one of the methods of physiotherapy; it consists in the fact that, with the help of a small current, ions of the medicinal substance permeate the entire root tissue and affect the granuloma.
The cleaned canal is temporarily filled with medication for one or several weeks until the pain subsides. At the next visit, the canal is processed again and filled very tightly.
Teeth freed from periodontitis can be used for prosthetics. But this issue is resolved in each specific case individually.
Unfortunately, such a tooth cannot always be cured using conservative methods; you have to resort to the help of a surgeon - either to perform a resection of the root apex, along with which the cyst is removed, or to remove the entire tooth.
If it doesn't hurt, then it's not scary
A modern dentist, before taking the drill, will definitely numb the inflamed area - he himself is interested in ensuring that the patient feels comfortable during treatment and does not interfere with his work. Especially when it comes to root canal treatment and then tooth restoration - work that, without exaggeration, can be called jewelry.
The patients of neither Hippocrates, nor Paracelsus, nor the European and Russian dentists of the beginning of the last century could dream of getting rid of suffering so efficiently and completely painlessly, and at the same time preserving a bad tooth. So we are incredibly lucky that we live in times of rapid development of dentistry, which can, if not do everything, then do a lot. And to get rid of the fear of treating pulpitis and periodontitis, remember our great-grandfathers and sympathize with them.
© Dr. Peter