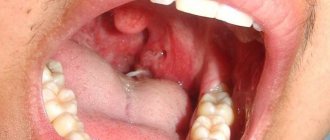
Why is a hematoma in the mouth dangerous and how to treat it? Sore throat after choking
A hematoma is a hemorrhage in the submucosal layer, so it will look like a bloody bubble, a burgundy or bright red ball. The blood inside it may be liquid or clotted. Hematomas that appear in the submucosal layer of the oral cavity are called superficial submucosal.
In addition, the hematoma cavity may be filled with colorless serum fluid secreted by the serous membranes. Such a neoplasm forms without damage to blood vessels, as evidenced by the absence of blood in the hematoma cavity. The healing period of the hematoma in this case will be shorter.
A hematoma in the mouth, due to the sensitivity of the soft tissues, can cause significant discomfort. But as a rule, the pain goes away 1-3 days after the bloody blister appears.
Hematomas can be localized on the palate, tongue, cheeks and gums.
Why do hematomas form?
The formation of a blood bladder is preceded by injury to the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity: a blow, bruise, pinching or squeezing of tissue. Mechanical injury is possible when accidentally biting the mucous membrane; for this reason, a hematoma most often forms on the inside of the cheek.
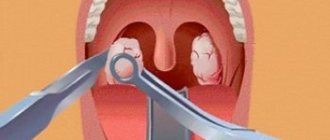
In addition, the formation of a blood bubble is possible during dental treatment if the dentist handles instruments carelessly, for example, during a tooth extraction operation, forceps can come off the crown and injure the mucous membrane. In a child, a hematoma on the gum, cheek or tongue may occur as a result of an accidental fall.
Blows to the face and bruises received in accidents, falls from a height, or in a fight can also cause a tumor in the mouth.
Do you know how much dentists earn? We recommend reading our article.
We advise you to find out why jaw dislocation occurs and how to set it.
A blood bubble formed on the mucous membrane is a protective reaction of the body. The mechanism of hematoma formation is as follows:
- when tissue is injured, the immune system is activated;
- monocytes, leukocytes and macrophages are “pulled” into the damaged area, whose task is to destroy the enemy agent;
- the death of immune cells provokes the release of inflammatory mediators - seratonin, histamine and bradykinin;
- they cause vasospasm, disrupting the outflow of blood at the site of injury;
- as soon as the spasm passes, the accumulated blood flows into the damaged area;
- detachment of mucosal tissue occurs, the formed bubble fills with blood.
Note: in people with impaired vascular permeability, problems with blood clotting and fragile blood vessels, the likelihood of hematoma formation increases.
Severity of pathology
The intensity of pain depends on the severity of the pathology.
There are 3 degrees of severity of the condition:
- mild degree: in this case, a blood bubble forms within the first 24 hours after injury, while the victim feels moderate pain;
- moderate degree: a blood bubble forms several hours after the injury, the injury site swells, and severe pain appears;
- severe: a bubble forms within 2 hours after tissue damage, the victim feels severe pain, and a possible rise in body temperature.
Why are hematomas dangerous?
Small hematomas resulting from minor injuries usually do not pose a serious danger. They go away on their own, however, complete healing of the tissues will take a lot of time - about 2 weeks.
Note: During the healing process, the color of the blood bladder changes from purplish-red to blue-yellow. This occurs due to the breakdown of hemoglobin.
Pain associated with the presence of a tumor in the mouth, as a rule, goes away within 2-3 days from the moment of injury.
However, if a hematoma in the mouth (on the palate, cheek, gum, tongue) does not disappear within the specified period of time, you should definitely see a doctor.
Important: numerous blood blisters in the oral cavity may indicate the development of dangerous diseases such as syphilis and pemphigus.
It is also worth knowing that a hematoma can become infected and fester when a person’s immunity is reduced, which develops when the body is exhausted, a long-term illness, or the presence of diseases of the immune system. In addition, a natural decrease in immunity occurs in older people, pregnant women, and young children.
Therefore, if the pain does not go away within 3 days after the formation of the bubble, and even more so, if the discomfort intensifies, other unpleasant symptoms appear, such as swelling, temperature, bad breath, do not delay a visit to the doctor. If a hematoma appears on the gum, you need to contact a dentist.
The treatment of hematomas in the mouth is carried out by a dentist-therapist.
Causes of laryngeal injuries
In general, the larynx is one of the most protected organs in the human body, so the likelihood of accidental injury is minimized. It is fenced from mechanical influences from all sides:
- from above - the lower jaw;
- from below - the handle of the sternum;
- in front - the thyroid gland;
- behind - the bodies of the cervical vertebrae;
- on the sides - by the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
With light impact, due to its anatomical mobility, it is able to absorb pressure and shift. Therefore, injuries of various types, causing serious damage to the health and life of the victim, are usually received in extreme situations.
Among the random factors leading to laryngeal injury are:
- foreign body entering the larynx;
- unintentional ingestion of alkali or acid;
- hitting the steering wheel with the neck area during an accident.
External laryngeal injuries most often occur due to:
- direct blows to the neck area (fist, foot, heavy object);
- impacts on a protruding surface (car steering wheel, railing);
- injuries of various types;
- hanging.
Internal injuries of the larynx can be caused by:
- ingress of a foreign body with sharp edges;
- inaccurate intubation, bronchoscopy or artificial ventilation;
- removal of a foreign body (not only from the larynx, but also from the pharynx);
- surgical manipulations on nearby organs (for example, bougienage of the esophagus);
- inhalation of hot steam;
- inhalation of caustic substances;
- ingestion of chemicals.
Now let's look at the causes of certain types of laryngeal injuries.
A concussion can occur as a result of any violent impact on the larynx; a concussion occurs with a small push or blow to the neck area that does not cause damage to the skin.
Dislocation of the larynx occurs when there is strong compression (with a rope or hands). A similar action performed with great force leads to a fracture of the larynx.
Etiology of injuries to the larynx and trachea
Injury to the larynx and trachea can occur with general neck trauma. The causes of closed laryngotracheal injuries are a blow with a fist or an object, a car injury, attempts at suffocation, a blunt blow to the chest. Penetrating wounds are usually knife or gunshot wounds.
Isolated injuries to the larynx and trachea occur with internal trauma. Internal trauma to the larynx and trachea is often iatrogenic in nature (intubation, prolonged artificial ventilation).
Injury to the larynx and trachea is possible during any manipulation of the larynx, including during endoscopic examinations and surgical interventions. Another cause of internal injury to the larynx and trachea is the entry of a foreign body (fish bone, parts of dentures, pieces of meat, etc.).
Internal trauma to the larynx and trachea also includes burn injuries (thermal, chemical).
Lump in throat feeling of nausea
[Show] In some situations, a person develops symptoms such as a lump in the throat Parents 0
Mucus in the throat cannot be swallowed
[Show] What to do if the mucus in your throat does not clear up? Accumulated mucus in the throat Parents 0
What will CT scans of the neck show for a cartilage fracture?
- Fracture line (usually on the anterior surface)
- Hematoma of the periglottic tissue (fresh hemorrhage is hyperintense) can cause displacement of the trachea
- Sometimes there is extravasation of contrast material due to ongoing bleeding.
- With soft tissue emphysema, subcutaneous air accumulation is usually observed.
Possible displacement of the arytenoid cartilage: Non-physiological position or rotation of the arytenoid cartilage
- Edema of the aryepiglottic fold
- Fixation of the ligaments when pronouncing the letter “i” or performing the Valsalva maneuver.
In what cases is an MRI of the neck necessary for a fracture of the thyroid cartilage?
- Fracture line
- Depending on the time elapsed since hematoma formation, it may be hyper-, iso-, or hypointense to muscle tissue on T1- and T2-weighted images
- There is no signal enhancement after gadolinium administration.
External laryngeal injuries
Injuries to the larynx most often occur in the following cases:
- blows to the area where the organ is located (with a hand, foot, sports equipment);
- knife wounds;
- injuries from shell fragments and gunshot wounds;
- hitting the front of the neck against any objects (a stretched wire, the corner of a table, the steering wheel of a car, motorcycle or bicycle);
- suicide attempts (hanging).
Mechanical injuries may cause contusions, bruises, soft tissue ruptures, dislocations and fractures of the laryngeal cartilage, or various combined injuries.
In this case, bruises usually cause the development of shock in the victim, and damage that violates the integrity and structure of the larynx leads to bleeding and the inability to perform its functions in full.
In the near future, after exposure to a traumatic agent, laryngeal edema develops, which contributes to respiratory disorders.
Dislocations and fractures of the cartilaginous rings of the larynx in their pure form are rare. Persons over 40 years of age are more susceptible to such damage, since at this age the larynx becomes less elastic and mobile. Displaced fractures can injure the mucous membrane, thereby causing internal bleeding and the development of emphysema of surrounding tissues, which poses a threat of asphyxia.
With penetrating wounds, the laryngeal cavity may be open and communicate with the esophageal cavity or the cellular spaces of the neck.
The most severe of all external injuries to the larynx are shrapnel and gunshot wounds. In most cases, they are incompatible with life, as they affect nearby vital structures (large vessels and nerves, as well as the spinal cord).
Forecast
- With timely treatment, the prognosis is usually favorable
The prognosis for laryngeal injuries is completely different, as it depends on the degree of damage, aggravating circumstances and the development of complications. In general, with prompt first aid, stopping bleeding and re-opening the airway, the prognosis is favorable.
You should beware of combined injuries, in which damage to structures adjacent to the larynx is even more dangerous than damage to the larynx itself.
Source: https://probol.info/travmy-sustavov/chem-opasna-gematoma-vo-rtu-i-kak-ee-lechit-bol-v-gorle-posle-udusheniya.html
The sky is bleeding, what should I do? Causes of palate pain in the mouth and treatment for it
The palate of a person is located in the oral cavity. This is a horizontal partition that separates the cavity of the upper respiratory tract - the nose - from the oral cavity. It is involved in the process of sound reproduction - it is part of the articulatory apparatus.
The palate consists of a soft and hard part. The hard part is the anterior section, which is covered with mucous membrane. The soft palate hangs over the base of the tongue and is located along the posterior bony wall of the convex arch, which divides the nasopharynx into 2 parts.
Painful sensations often occur in the soft part, and the palate can hurt both when swallowing and at rest.
What to do if you bruise your teeth and gums - symptoms and treatment of injury
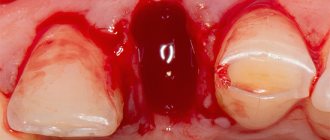
A tooth bruise is a closed injury caused by a blow. In this case, the integrity of the bone structures remains normal. The anatomical position of the tooth also does not change. Only periodontal tissues are damaged. It is possible that they rupture, which leads to the onset of bleeding.
With strong impacts, nerve and vascular structures are damaged, which leads to tooth staining in a dark or unnatural color. This occurs due to hemorrhage into the dentinal tubules and pulp tissue. If you consult a dentist promptly, such damage can be cured.
Hemangioma
Blood vessels can form tumor-like lesions, especially in the cheeks, tongue and lips. These benign lesions often appear as blue, ovoid, soft nodules (Figure 11).
Rice. 11. Hemangioma.
These shrinking nodules may turn pale during palpation due to temporary disruption of blood flow to the affected area. Hemangiomas can be surgically removed and submitted for histological examination, especially if they are large or their location causes functional problems (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12. Hemangioma.
Recurrence of hemangioma is possible and depends on the configuration of the lesion and the completeness of removal.
Causes of bruises
Jaw bruises occur mainly in young children and professional athletes. These categories of patients most often present complaints to the dentist. The bruise develops against the background of mechanical impact - a strong blow. The possibility of a domestic injury cannot be ruled out when a person damages a tooth due to his own carelessness or clumsiness.
You can get damaged in a fight or car accident. Cases of bruises due to falls, for example in winter on ice, are becoming more and more common.
Symptoms
Among the main signs of a bruise, one should highlight gradually increasing pain. Discomfort intensifies when pressure is applied to the damaged tooth, which is clearly manifested while chewing food.
Typically, the following symptoms are present:
- Tooth loosening
- Swelling and redness of the gums
- Darkening of tooth enamel
In case of severe injuries, the victim cannot open his mouth. In some cases, speech impairment occurs. This is due to severe damage, which is accompanied by rupture of ligaments, injury to the alveolar process and articular structure.
The nature of the clinical picture depends on the area of localization of damage:
- Tooth bruise – there is relatively little mobility and discoloration.
- Bruised gums - bleeding occurs, swelling and hematoma may form.
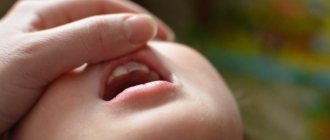
Symptoms of hematomas in the mouth, appearance, photo
The main symptom characteristic of bruises in the mouth is compaction in problem areas and darkening. The surrounding tissues swell, and the pain radiates to the jaw or cheek area. Possible high temperature, purulent inflammation, signs of poisoning. Experts divide the manifestations of this problem into two groups:
- The accumulation of blood in the gum gives it a bluish tint. The tissues increase in volume, the person feels uncomfortable and cannot close his mouth completely. There are problems with chewing and speech. These manifestations are typical for damage to dental pockets.
- If blood pours into the gum pockets, a round swelling is formed that spreads to the cheek from the inside. Such symptoms are often confused with gumboil: patients report severe pain, irritability, and abnormal facial shape. The gums tighten, fever and impairment are possible.
During the course of treatment, the disturbing symptoms are erased, and the cyanosis of the gums gradually disappears. A hematoma on the gum resolves in the same way as on other parts of the body. Usually the defect is corrected within a few weeks.
Source: https://PlastikaPlus.ru/rot/gematoma-vo-rtu.html
Hematoma in the throat on the mucous membrane
Due to various diseases and mechanical damage, manifestations such as bruising in the throat may occur. They usually frighten the patient and often require contacting a doctor.
Causes
A hematoma on the mucous membrane of the throat and palate can be of the very nature. Usually the hemorrhages are small and multiple, this is due to the peculiarities of the blood supply to the mucosa.
The reasons may be:
- Mechanical damage to the palate or pharynx.
- Acute and chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Various infectious diseases accompanied by enanthem.
- Hemangioma is a congenital benign tumor of vascular origin.
- Oncological diseases, often malignant.
From the above we can conclude that there are many reasons for the formation of bruises. It is not always possible to determine the cause on your own, so if new symptoms that are unknown to you appear, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of bruises differs in each specific case and depends on the cause of their occurrence.
Injuries
A single hemorrhage on the mucous membrane of the palate or pharynx is most often a symptom of ordinary mechanical or thermal damage:
Such hematomas do not require special treatment. After an injury, the mucous membrane heals quite quickly, vascular tone returns to normal and hemorrhages disappear.
Pharyngitis
Acute and chronic pharyngitis are very common diseases in any population on our planet. Acute pharyngitis is called a sore throat and can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. The chronic form of the disease develops with insufficient treatment of the acute form or with the peculiarities of local immunity.
Both variants of the disease can be accompanied by bruising in the throat. The mechanism of their formation is as follows:
As a rule, such manifestations disappear along with the underlying disease. Antibacterial and symptomatic agents should be used correctly to treat pharyngitis.
Infectious diseases
Sometimes enanthema, a rash on the mucous membrane of the palate and throat, is mistaken for a bruise. It can occur with a variety of diseases, most often of an infectious nature:
The appearance of enanthema is associated with dilation of the vessels of the mucous membrane (with measles and scarlet fever in children), less often with the direct presence of the pathogen on the palate and pharynx (herpes and syphilis). Less commonly, enanthema can be a manifestation of systemic diseases, for example, lupus erythematosus.
This symptom requires examination by a doctor, since it is impossible to independently determine the cause of the rash. Treatment depends on the causative agent of the disease.
Hemangioma
Hematomas on the mucous membrane of the throat and palate can also be caused by cancer. Among them, hemangioma, a benign vascular tumor, is absolutely harmless.
Hemangioma is most often of congenital origin, does not require treatment and is a proliferation of blood vessels under the mucous membrane.
There are methods for removing such a tumor, but operations are performed solely for cosmetic purposes.
Oncological pathology
Malignant neoplasms can also manifest as hemorrhages in the throat. Pharyngeal cancer is a tumor that is located on the mucous membrane and gradually grows inward.
This pathology can cause dilation and even destruction of blood vessels, which is manifested by hematomas. Other symptoms that should alert a person:
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Pain when swallowing.
- General weakness and malaise.
- Unmotivated weight loss.
- Lack of appetite and aversion to certain foods.
Frequent damage to the mucous membrane and chronic diseases of the pharynx can be factors in the development of the oncological process.
Treatment uses surgical techniques, radiation and chemotherapy. The treatment method is selected individually by the oncologist for each patient.
HELP. Red throat, bruising spots in the mouth and high fever in my daughter
Girls, yesterday the child was 38.5 without any complaints about anything in particular, his throat was slightly red. In the morning there is fever, rash spots on the throat, under the tongue and on the roof of the mouth, near the throat. Rashes like bruises. (if you prick yourself with a needle, such a sign remains small).
The doctor said it was a viral sore throat and prescribed antiviral, antihistamine and streptocide.
But it doesn’t look like a sore throat, we used to have a sore throat, but we didn’t have these abscesses on the tonsils and smudges in the mouth.
Tomorrow we’ll go to another ENT specialist, but I won’t sleep, I’m worried. Who came across it? what could it be?
Fahrengit or, for example, chickenpox occurs in this form
Source: https://adminlen.ru/gematoma-v-gorle-na-slizistoj/
Causes of bruising on the roof of the mouth
Problems with the ENT organs can occur in anyone. It is probably difficult to find someone who has never experienced discomfort in the throat.
Part of the pharynx is even accessible for self-examination, so you can get acquainted with its condition by simply opening your mouth wide. But the picture you see can alarm and make you think.
For example, many people find that red blood vessels appear in the throat. This situation is quite common and requires detailed consideration.
The pharynx is the organ where the upper respiratory and digestive tracts intersect. It connects the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus, respectively. The inside of the pharynx is covered with a mucous membrane lined with ciliated and stratified squamous epithelium. Next comes the connective tissue base, containing lymphoid accumulations (follicles), glands and blood vessels.
Thanks to this structure, the mucous membrane performs important functions, primarily protective. Being the entry gate for various infections, the pharynx must have a developed system to counteract foreign agents.
Its first component is the tonsils, and the second is the mucous membrane. The glandular secretion contains antimicrobial substances (lysozyme, interferon, immunoglobulins). The follicles contain lymphocytes that provide an immune response.
A developed vascular network ensures tissue nutrition and adequate regeneration.
Causes and mechanisms
If you suddenly notice the appearance of red blood vessels in the throat, then you need to understand the reasons for this phenomenon. This effect occurs when they expand. And this is possible in several cases:
- Inflammation (pharyngitis).
- Allergic reaction.
- Vascular tumor (hemangioma).
Changes in the pharyngeal mucosa caused by microbial factors are mediated by exudative-infiltrative or trophic disorders.
In allergic reactions, an increase in vascular permeability comes to the fore, and hemangiomas are associated with an expansion of the arterial wall of a congenital nature. Each situation requires proper consideration and differential diagnosis.
After all, therapeutic measures will largely depend on its results. And you should not assume that you can figure out the causes of redness on your own - only a doctor can do this.
The causes of vascular redness in the throat can be several conditions with different development mechanisms.
Treatment of pharyngitis
The boy at the entrance was sick, but four weeks ago, and at that time we had chickenpox. On the trail. During the day the bruising became smaller, and by Monday it had completely disappeared. They didn't go to the doctor.
So, I don’t know what it was... I found out, I went to an ENT specialist, this is when the blood vessels are weak, for some reason at night, or before going to bed, blood flows down the throat, along the back wall, and in the morning we see a bruise, and this is a stuck clot.
Everyone got sick in two doses. Ilyushon is wearing a T-shirt, or at best a turtleneck... It looks like a bruise. I can't even imagine what it is. Naturally, I'll go to the doctor tomorrow. But I can’t calm down, and I’d like to hear the opinions of different experts.
When I asked if her throat hurt and if she shoved anything into her mouth, my daughter said - no, it doesn’t hurt, she didn’t shove anything... Because... In the morning there is fever, rash spots on the throat, under the tongue and on the roof of the mouth, near the throat.
Rashes like bruises.
4 months ago, in addition to bruises on the throat, one day there was a high fever and red pimples on the palms and soles of the feet; we went to the doctor - Diagnosis: Enterovirus infection.
Translated from Greek, “heme” means “blood.” A hematoma is an accumulation of blood that occurs due to rupture of blood vessels and capillaries due to tissue injury. Hematomas can form in the mouth under the mucous membrane, located in the cheeks, lips, palate, and gums. Why a hematoma in the mouth occurs and how dangerous it is, and how to get rid of an unpleasant tumor, you will learn from our article.
Symptoms
Each disease has characteristic symptoms. The clinical picture consists of complaints and objective signs identified during examination. The latter include precisely those blood vessels that are seen in the throat. But there are many other manifestations that need to be paid attention to. And they often become decisive in making a diagnosis.
Allergy
Sensitization to various allergens that enter the body becomes a key point in the development of immunopathological reactions. And they occur with an increase in capillary permeability and accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space. This becomes the source of the following symptoms:
- Itching and tickling, sore throat.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Dry cough.
On examination, the mucous membrane of the pharynx is pink, edematous, densely dotted with small vessels. If the allergy spreads to the larynx, then patients complain of hoarseness, the cough becomes barking, and breathing may become difficult (false croup). The latter poses a particular danger to children and adults.
What is this symptom?
A blood bubble in the mouth is a bruise, in medical terms, a hematoma. Hematoma is an accumulation of coagulated blood in a limited cavity; it is a hemorrhage resulting from damage to blood vessels or capillaries.
The causes of a blood bladder are damage that differs in the nature of the traumatic factor:
- Mechanical - various objects act as traumatic factors. For example, fish bones when eaten can damage the integrity of the mucosa. Biting while chewing food. Often the seed shell causes damage;
- Chemical - injury to the mucous membrane occurs when eating spicy or salty foods. Heavily salty food irritates the mucous membrane, so it can easily injure it;
- Too cold or hot food and drinks become a thermal factor. For example, we often encounter tongue burns caused by tea.
A blister on the tongue looks like a bubble filled with fluid. Contents may vary in color. The serous fluid in the bladder makes it chalky white, indicating the absence of blood, which means that the wound is superficial - there is no damage to the blood vessels.
Source: https://do-manus.ru/lechim-desny/krovopodteki-na-nebe-u-rebenka.html
Pharyngitis. Causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis and treatment of pathology
Pharyngitis is an inflammation or irritation of the mucous layer of the back wall of the nasal cavity, mouth and larynx, or more simply, the pharynx. As a rule, this pathology accompanies respiratory infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Particularly dangerous is acute pharyngitis, caused by group A streptococcus (hereinafter referred to as GAS). Early diagnosis and correct treatment of this disease can prevent extremely unpleasant consequences - complications on the heart and kidneys.
Did you know?
- Acute pharyngitis is the most common disease of the “winter season” among children from 4 to 7 years old;
- In school-age children, the cause of pharyngitis in 15-30% of cases is GAS infection;
- In adults, 90% of pharyngitis is caused by viruses;
- The sudden onset of the disease with a sore throat is more likely to indicate a GAS infection;
- Pharyngitis, which appears after several days of runny nose and nasal congestion, is most likely viral.
Anatomy of the larynx
- The pharynx is the beginning, but at the same time it is the “crossroads” of two systems – the respiratory and the alimentary. That is, any irritant, be it a virus, bacteria or food allergen, comes into contact with this area.
- Consequently, this is where a whole “army” of protective organs is located - the lymphatic pharyngeal ring.
It consists of three paired and two unpaired formations (tonsils):
- Palatal
- Pipe
- pharyngeal
- lingual
- as well as lymphoid granules and lateral lymphoid ridges on the posterior wall of the pharynx.
- The pharynx is a muscular, hollow organ, and its structure is not particularly remarkable.
It consists of four layers. The first is mucous, then fibrous (dense connective tissue). Next is the muscular and final layer that gives the pharynx mobility - adventitia (loose connective tissue).
With pharyngitis, the inner mucous layer suffers, since it is very rich in capillaries located close to the surface.
- In terms of location, the pharynx can be divided into three parts - the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx. That is why, with pharyngitis, neighboring organs are often “affected” - the nose (rhinopharyngitis), tonsils (pharyngo-amygdalitis or tonsillitis) and the larynx (pharyngo-laryngitis). Also, this explains the abundance of symptoms of pharyngitis. Be patient - we'll talk about this a little further.
- The pharynx is the “entrance” to the pharynx from the oral cavity. Anatomically, it is located between the soft palate, the root of the tongue and the palatine arches. It is the changes in this area that the doctor is interested in when diagnosing pharyngitis: “Show me your throat.”
Causes of pharyngitis
Viruses that most often cause pharyngitis include:
- Adenovirus
- Herpes simplex
- Coxsackie group viruses
- Cytomegalovirus
- Epstein-Barr virus
The most dangerous cause of pharyngitis is group A streptococcus. Most often, this bacterium affects school-age children and, if untreated or improperly treated, leads to very serious complications.
Much less often, pharyngitis becomes a companion to allergies, cancer, or reflux of acid from the stomach.
In people with suppressed immunity (diabetes mellitus, chemotherapy, HIV), infection by fungi of the Candida family also occurs.
Why does my throat hurt?
An irritating factor (any of the above) comes into contact with the mucous layer of the pharynx. We mentioned above that it is incredibly rich in capillaries, therefore, viruses or bacteria quickly enter the bloodstream and lead to inflammation and dilation of local blood vessels.
The following table shows the “classic” signs of any inflammation, “translated” into symptoms of pharyngitis.
| Sign of inflammation | Symptoms of pharyngitis |
| "tickle" | |
| "red throat" | |
| sore throat that gets worse when swallowing | |
| Without clinical relationships, in case of pharyngitis |
Some differences are revealed in the picture of pharyngitis, the cause of which is group A streptococcus. This bacterium is also called hemolytic streptococcus. Literally translated from Latin, it means “destroying/dissolving” blood.
Once in the bloodstream, it destroys red cells in the capillaries of the larynx. Clinically, this manifests itself as small bruises on the pharynx, soft palate, and sometimes on the tonsils.
With the Coxsackie and herpes viruses, the connections between the cells of the mucous membrane are destroyed, and they “fusion” occurs. Clinically, it appears as fluid-filled blisters.
Examination by an ENT specialist
- Questioning (history)
- General medical examination - the doctor examines the skin for bruising or jaundice, lymph nodes (which can be enlarged with scarlet fever or mononucleosis), and the borders of the liver (also enlarged with mononucleosis).
- Special ENT examination. The pharynx is examined using a disposable spatula, pressing the root of the tongue down.
Source: https://geraklionmed.ru/gematoma-v-gorle-na-slizistoy/
The child has bruises on the roof of his mouth. Blood vessels are visible in the throat: why
Problems with the ENT organs can occur in anyone. It is probably difficult to find someone who has never experienced discomfort in the throat.
Part of the pharynx is even accessible for self-examination, so you can get acquainted with its condition by simply opening your mouth wide. But the picture you see can alarm and make you think.
For example, many people find that red blood vessels appear in the throat. This situation is quite common and requires detailed consideration.
The pharynx is the organ where the upper respiratory and digestive tracts intersect. It connects the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus, respectively. The inside of the pharynx is covered with a mucous membrane lined with ciliated and stratified squamous epithelium. Next comes the connective tissue base, containing lymphoid accumulations (follicles), glands and blood vessels.
Thanks to this structure, the mucous membrane performs important functions, primarily protective. Being the entry gate for various infections, the pharynx must have a developed system to counteract foreign agents.
Its first component is the tonsils, and the second is the mucous membrane. The glandular secretion contains antimicrobial substances (lysozyme, interferon, immunoglobulins). The follicles contain lymphocytes that provide an immune response.
A developed vascular network ensures tissue nutrition and adequate regeneration.
Additional diagnostics
To understand why blood vessels are visible in the throat, you should consult a doctor. The specialist has the necessary qualifications and experience to conduct a full diagnosis. But a clinical examination may not be enough - then additional studies are prescribed:
- General blood analysis.
- Throat smear (microscopy, culture).
- Allergy tests.
- Pharyngoscopy.
A comprehensive examination will help establish the origin of symptoms and the mechanisms of development of the disease. This is a necessary factor for making a final diagnosis, which, in turn, will be the starting point for treatment measures.
Cosmetical tools
Cosmetic products for removing red spots on the face can also only be used on the recommendation of a doctor. As a rule, they are prescribed after drug treatment already at the stage of final recovery.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Painkillers after a caesarean section for a nursing mother
Removal of redness occurs with the use of tonic, healing, and vasoconstrictors, which include:
- Lotions and decoctions;
- Tonics and ointments;
- Creams and foams for washing.
To combat red spots, products containing aloe, apple, lavender, green tea, almond, and mimosa extracts are ideal. Creams with the listed additives can be purchased either in a store, or you can prepare them yourself using a neutral baby cream.
To quickly get rid of small red dots on the face of a small child, it is advisable to resort to an integrated approach and perform a procedure for cleansing and nourishing the facial skin every day until the redness completely disappears. If your child has red dots on his face within 10-15 days and they do not go away, be sure to consult a doctor.