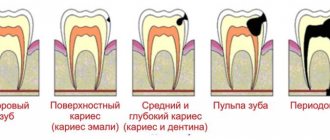
Unlike infectious, arsenic periodontitis is not diagnosed so often. The disease appears due to inflammation of periodontal tissue due to chemical irritation or an allergic reaction. Various medications and filling materials can act as irritants. The cause of this phenomenon may be poor-quality treatment of a damaged tooth. Let us consider in more detail the conditions of occurrence, symptoms and methods of getting rid of this pathology.
The meaning is in the name
As the name implies, arsenic or arsenous periodontitis occurs under the influence of a “killing” arsenic-based paste. It enters the periodontal tissue during tooth treatment through the root canals and the apical foramen located at the end of the tooth root.
Arsenic based paste
Dental treatment is associated not only with the use of arsenic medicine. Other medications or potent substances can also damage periodontal tissues:
- formalin;
- antiformin;
- sodium hypochlorite;
- enzymes;
- silver nitrate;
- antiseptics;
- antibiotics;
- phenol;
- phosphoric acid;
- piocid;
- paraformaldehyde.
Based on this, it is more correct to call the pathology drug-induced periodontitis.
Iatrogenic intervention
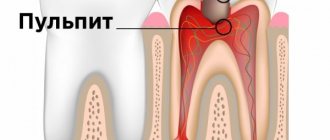
The occurrence of a drug type is influenced by an iatrogenic factor - dentist errors. The doctor may have violated the rules of dental treatment technique when treating cement caries or pulpitis.
For example, the pulp and remnants of the “killing” paste were not completely removed. Prepared (drilled) carious areas without air-water cooling. I washed out the root canals or treated dental cavity with an incorrectly dosed medication.
Drilling a tooth without air-water cooling
How to prevent the occurrence of arsenic inflammation?
The dentist must follow the necessary rules when treating pulpitis. To avoid causing toxic periodontitis, the dose of arsenic should not be exceeded in order to speed up the treatment process. During the treatment process, arsenic is applied only to the exposed pulp horn. Moreover, it should be no larger than the smallest spherical bur head.
In addition, the dentist must explain to the patient the seriousness and danger of the consequences if he misses a visit. It is necessary to tell how important it is to remove arsenic in treatment, what serious health consequences it can cause. If for some reason the patient cannot visit the doctor in the near future, the dentist must explain in detail and show how to independently remove the temporary arsenic dressing.
This toxic and carcinogenic reagent should be applied in close contact with the exposed tissue of the internal tooth structures for a maximum period of 2 days.
Neglect and allergies
Sometimes drug-induced periodontitis occurs due to neglect of the dentist’s recommendations when getting rid of pulpitis.
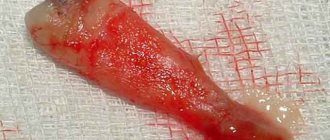
Treatment of pulpitis can take place over several visits. On the first visit, an arsenic paste is applied to “kill” the pulp. Under its influence, the toothache disappears, and the patient decides to reschedule the appointment. Due to overexposure of the medicine, the pulp tissues begin to disintegrate and penetrate into the periodontium along with the paste, causing its inflammation.
Periodontitis that occurs as a result of an allergy to filling material or medicinal drugs is also classified as medicinal. In some cases, an allergic reaction of periodontal tissue is a side effect of an overdose of antibiotics or general poisoning of the body with a genetically foreign substance (antigen).
Cause of the disease
To help the patient, it is necessary to find out what was the root cause of the disease. It could be:
- too much arsenous acid introduced into the pulp;
- the presence of the drug in the dental canal for more than 2 days;
- poor-quality cleaning of the dental canal by the doctor from arsenic and destroyed pulp;
- Another reason may be the patient’s allergic reaction to drugs containing arsenic trioxide, which has strong carcinogenic properties.
Doctors identify the following causes of drug-induced periodontitis:
- Exceeding the period of presence of arsenic-based devitalizing paste in the tooth cavity. Some patients neglect the doctor’s recommendation to come for a follow-up appointment on time. This medicine kills the nerve within 2 days and the pain in the tooth disappears, so the person believes that his problem has been solved, and the visit to the dentist can be rescheduled. Untimely removal of the decaying nerve causes the development of an infection, during which arsenic enters the periodontium.
- Medical error, consisting in an overestimated dosage of a drug that kills a nerve. The doctor installs a filling, and arsenic, when the devitalizing paste leaves the top of the root canal, begins to irritate the periodontium, causing its inflammation.
- The cause of infection of the tooth cavity can also be insufficient cleaning of the root canals at a repeat appointment. Residues of arsenic and disintegrated pulp remain under the filling.
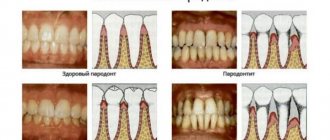
Gradually, the toxic substance will begin to destroy the periodontium, located between the tooth root and the alveolus. This leads to impaired blood circulation in the gums, resorption of bone tissue and loosening of teeth.
Serious consequences
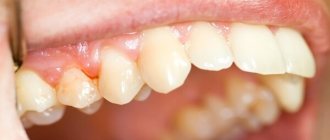
All medical causes lead to burns and death of periodontal tissue. The disease develops rapidly, regardless of the depth and extent of the lesion. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a dentist at the first pain and suspicious symptoms.
Lack of treatment leads to the peeling of dead connective tissue and dental lining. The tooth begins to become loose and then falls out. Periodontitis tends to infect adjacent tissues. The consequences of inaction may include inflammation of the gums, mucous membranes of the mouth or nose, purulent-necrotic destruction of bone tissue, and death of a molar that has not yet erupted.
Consequences of an advanced disease
Diagnosis of arsenic poisoning
The method of measuring the concentration of arsenic in the body, the time of sampling and the interpretation of the results depend on the nature of the poisoning (acute, subacute, chronic, long-term consequences) and the clinical picture.
Test results may be influenced by factors such as the accumulation of organic arsenic compounds (eg, dimethylarsenite and arsenobetaine) in chronic renal failure or their intake from food. In urgent cases, before starting treatment with complexing agents, determine the concentration of arsenic in a single portion of urine. A high concentration with a typical history and clinical picture confirms the diagnosis, but a low concentration does not yet exclude poisoning.
If the urinary arsenic concentration is only slightly elevated, the history and clinical presentation should be taken into account, as it is known that eating seafood can transiently increase the urinary arsenic concentration to 1700 µg/L. If seafood could be the source of the poison, they find out which compound is contained in the urine.
Some laboratory values are important in the diagnosis of both chronic and subacute poisoning, in the latter case they may change several days or weeks after acute arsenic poisoning. These include a clinical blood test, liver enzyme activity, kidney function indicators, general urinalysis, and arsenic concentration in daily urine.
Possible normocytic, normochromic or megaloblastic anemia, leukocytosis followed by leukopenia (the number of neutrophils decreases to a greater extent than the number of lymphocytes), relative eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, a rapid drop in hemoglobin levels (a sign of hemolysis or gastrointestinal bleeding), basophilic granularity of erythrocytes.
Serum creatinine and bilirubin concentrations and aminotransferase activity may increase, and haptoglobin concentrations may decrease. Proteinuria, hematuria and pyuria are possible. Once exposure to arsenic is discontinued, urinary excretion gradually decreases over time, but small amounts of arsenic may be excreted even several months later.
X-rays of the abdomen taken shortly after ingestion of the poison may reveal radiopaque material in the gastrointestinal tract. The sensitivity and specificity of this method are unknown, so a negative result does not rule out poisoning. The ECG shows flattening of the T wave, ventricular extrasystole, unstable monomorphic ventricular tachycardia and torsade de pointes. To diagnose axonopathy, including asymptomatic ones, the speed of excitation propagation along the nerves is examined.
Clinical picture
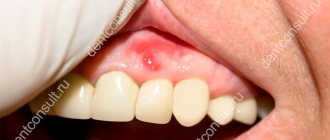
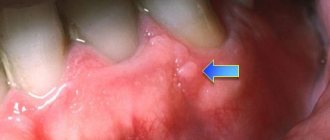
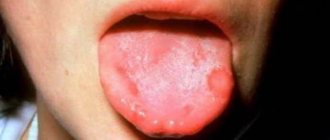
The medicinal type of the disease is accompanied by aching or throbbing pain in the area of the treated and filled tooth. The pain is aggravated by pressure on the tooth when biting and chewing food. In some cases, the pain may spread to adjacent teeth or to different parts of the head.
Due to the feeling of fullness, the tooth seems to “grow” and move out of the general row. Redness and swelling of the gums, swelling of the area of the cheek near the suspicious tooth, and its loosening are possible. Dying periodontal tissue can cause putrid breath.
Historical information.
Arsenic belongs to the five “alchemical” elements discovered in the Middle Ages (surprisingly, four of them - As, Sb, Bi and P - are in the same group of the periodic table - the fifth). At the same time, arsenic compounds have been known since ancient times; they were used to produce paints and medicines. Particularly interesting is the use of arsenic in metallurgy.
Several thousand years ago, the Stone Age gave way to the Bronze Age. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Historians believe that the first bronze was cast in the Tigris-Euphrates valley, somewhere between the 30th and 25th centuries. BC. In some regions, bronze with especially valuable properties was smelted - it was better cast and easier to forge.
As modern scientists have found, it was a copper alloy containing from 1 to 7% arsenic and no more than 3% tin. Probably, at first, during its smelting, the rich copper ore malachite was confused with the weathering products of some also green sulfide copper-arsenic minerals.
Having appreciated the remarkable properties of the alloy, the ancient craftsmen then specifically looked for arsenic minerals. For the search, we used the property of such minerals to give off a specific garlic odor when heated. However, over time, the smelting of arsenic bronze ceased. Most likely this happened due to frequent poisoning during the firing of arsenic-containing minerals.
Of course, arsenic was known in the distant past only in the form of its minerals. Thus, in Ancient China, the solid mineral realgar (sulfide with the composition As4S4, realgar in Arabic means “mine dust”) was used for stone carving, but when heated or exposed to light, it “deteriorated” as it turned into As2S3. In the 4th century. BC.
Aristotle described this mineral under the name "sandarac". In the 1st century AD The Roman writer and scientist Pliny the Elder, and the Roman physician and botanist Dioscorides described the mineral orpiment (arsenic sulfide As2S3). Translated from Latin, the name of the mineral means “golden paint”: it was used as a yellow dye. In the 11th century alchemists distinguished three “varieties” of arsenic: the so-called white arsenic (As2O3 oxide), yellow arsenic (As2S3 sulfide) and red arsenic (As4S4 sulfide).
White arsenic was obtained by sublimation of arsenic impurities during the roasting of copper ores containing this element. Condensing from the gas phase, arsenic oxide settled in the form of a white coating. White arsenic has been used since ancient times to kill pests, as well as...
In the 13th century Albert von Bolstedt (Albert the Great) obtained a metal-like substance by heating yellow arsenic with soap; This may have been the first example of arsenic in the form of a simple substance obtained artificially. But this substance violated the mystical “connection” of the seven known metals with the seven planets; This is probably why alchemists considered arsenic a “bastard metal.”
Arsenic was clearly identified as an individual substance in the mid-17th century, when the German pharmacist Johann Schroeder obtained it in a relatively pure form by reducing the oxide with charcoal. Later, the French chemist and physician Nicolas Lemery obtained arsenic by heating a mixture of its oxide with soap and potash. In the 18th century arsenic was already well known as an unusual "semi-metal".
Tooth preparation
Treatment of the disease begins with preparing the tooth. To do this, the tooth cavity is first opened, removing the filling. Access to the pulp chamber is drilled and the pulp is removed. The root canals of the tooth are cleaned and their length is measured. Expand and align dental canals. Treated dental viscera are disinfected with antiseptic agents.
To relieve inflammation and pain, small sterile cotton wool or gauze swabs are inserted into the prepared root canals. They are pre-impregnated in special solutions that play the role of an “antidote” or antidote for arsenic poisoning. For example, in five percent unithiol (sodium dithiolpropanesulfonate) or one percent iodinol.
Tampons in dental canals
The tooth is covered with a temporary filling for 48 hours. If the pain goes away during this time, a final filling of the root and crown of the tooth is performed.
Treatment options
After diagnosis, the dentist carries out a step-by-step treatment process, the purpose of which is to remove the source of inflammation from the tooth cavity, eliminate the symptoms of intoxication and prevent the spread of the pathological process to neighboring tissues.
At the first appointment, treatment of arsenic periodontitis involves the dentist performing the following actions:
- injection of local anesthetic into the gum area of the affected element;
- removal of temporary or permanent filling;
- opening the tooth cavity using a fissure bur;
- cleaning the root canals from the remains of the devitalizing paste and disintegrated pulp, followed by rinsing with an antiseptic solution (Chlorhexidine), which will prevent the further spread of pathogenic microorganisms;
- determining the length of the canals and expanding their walls with special files;
- secondary treatment with an antiseptic;
- Turundum impregnated with an arsenic antidote (solution of 5% Unithiol or 1% Iodinol), an antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drug is injected into the cleaned canals for 2 days;
- The tooth cavity is closed with a temporary filling.
In this case, the tooth is not covered and the patient must follow the following rules:
- rinse your mouth with a soda-salt solution with the addition of iodine (for 200 ml of warm boiled water you need 1 teaspoon of salt, 0.5 teaspoon of soda and 3 drops of iodine) in the morning and evening, as well as after each meal;
- cover the tooth cavity with a piece of sterile bandage or cotton wool at the time of the meal - this will prevent food debris from entering the tooth and clogging the canals, which will aggravate the course of the pathological process;
- after eating, it is tedious to remove cotton wool from the oral cavity, since food debris accumulates on it, which, when rotting, will become an ideal environment for bacteria;
- Do not apply heat to the area of the affected element.
We suggest you read: Reviews of Metrogyl Denta gel - instructions for use, price
During the second visit, the doctor performs the following therapeutic procedures:
- removes temporary fillings and medicated turundas;
- the patient is given an x-ray to check for signs of inflammation;
- carries out antiseptic treatment and filling of root canals;
- restores the damaged part of the crown with permanent filling material, the color of which is pre-selected to match the shade of healthy teeth.
Medicines do not always eliminate the inflammatory process in 2 days. In such cases, a pad soaked in medicated paste is re-placed in the root canals, and the patient is given a date for the third appointment.
Severe cases of arsenic periodontitis require extraction of the affected element and bone area, followed by transplantation of the affected tissue:
- poor patency of the root canals, which does not allow for high-quality cleaning;
- lack of positive dynamics with conservative treatment. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory pastes do not stop inflammation;
- high degree of tooth mobility;
- necrosis of bone tissue.
After this procedure, soft tissue is transplanted from the patient's palate to the damaged area located along the gum line. Bone is also restored by transplanting donor or own bone tissue into the root area of the affected unit. The possibility of developing such serious consequences indicates the need to immediately consult a doctor when the first symptoms of periodontitis appear.
Transchannel electrophoresis
If the pain does not go away, treatment continues. The effect of therapeutic tampons is replaced by physiotherapeutic procedures.
Transcanal electrophoresis helps well - the introduction of potassium iodide into periodontal tissue through the dental canals using a direct electric current. The method allows you to relieve inflammation, sterilize dental canals, and restore tissue. The use of electrophoresis is contraindicated in the case of a severely damaged tooth crown or when the periodontal gap expands from the apex of the tooth root to its crown.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
If there is a strong inflammatory process, dentists prescribe the patient a course of physiotherapy aimed at achieving the following therapeutic effects:
- improvement of blood flow in affected tissues;
- stimulating the restoration of destroyed periodontal cells;
- preventing the growth of granulation tissue;
- relief of the inflammatory process;
- improving the supply of nutrients to tissues, which allows accelerating the process of regeneration of damaged cells, as well as restoring structure and function;
- reduce the negative impact of harmful substances;
- increasing the phagocytic ability of leukocytes, preventing the process of reproduction of infectious agents. This helps increase local immunity.
| Sollux | The patient is in a horizontal position. A special lamp is installed on the side of it at a distance of 20-50 cm and, using a reflector, a beam of light is directed to the area of the body being heated. Penetrating deep under the epidermis, infrared rays dilate blood vessels, stimulating blood flow in them. The duration of the procedure is 20-30 minutes. |
| UHF | An active electrode is inserted into the canal, and a passive electrode is placed on the patient’s cheek. The procedure time is 10-15 minutes. |
| Electrophoresis | Electrodes with potassium iodide are inserted into the root canals and the tooth cavity is covered with wax. The end of the active electrode is connected to the minus, and the passive electrode is placed on the patient's forearm. The maximum current is increased to 3 mA. The duration of electrophoresis is 15-20 minutes. no more than 5 procedures are prescribed. |
We suggest you read: Why do you need a temporary crown for an implant, how long to wear it, prices in Moscow
UHF therapy
No less effective is ultra-high frequency (UHF) therapy - heat treatment using ultra-high frequency electromagnetic fields. The method relieves swelling and inflammation, reduces the level of fluid secretion from the inflamed periodontium, stimulates blood circulation in the vessels and metabolism in tissues, and relieves pain.
UHF therapy cannot be used for bleeding disorders, high blood pressure, malignant tumors, blocked veins, problems with the cardiovascular system, or pregnancy.
UHF therapy
If the periodontium has festered
If, due to inflammation, pus begins to ooze from the periodontal tissue, the installation of a permanent filling will have to be postponed. The dentist will open the tooth to drain the purulent fluid and rinse out the resulting cavity.
The patient is sent home, where, for the appointed time, he will rinse his mouth with medications or herbal decoctions. Home therapy methods are described in the article “Methods for treating periodontitis at home.”
In addition to self-treatment, you will have to cover the exposed tooth with a sterile cotton ball before each meal. After eating, the ball should be taken out and the tooth cavity should be carefully cleaned of food debris. In order not to provoke an increase in pus, swelling of the periodontal tissues, gums and face, you should not heat the damaged tooth.
Have you ever encountered this type of periodontitis?
If you found this article useful, please like it and share it with your friends.
How to prevent arsenic poisoning
Any poisoning is better prevented than treated. To avoid exposure to arsenic, you should:
- Always wear protective clothing and a mask when working with this element.
- Do not burn old wood treated with arsenic.
- In regions with high levels of this toxic element in nature, drink bottled water and limit contact with soil.
- Do not use products containing arsenic at home. And if you can’t refuse them, store them in strictly designated places, out of reach of children, in their original packaging.
Compliance with all precautions will help minimize the risk of poisoning. And knowing the symptoms and signs of first aid will help you get out of any dangerous situation with minimal losses.
The 33rd element of the periodic table is familiar to many people. This is arsenic, which occurs in nature in organic and inorganic forms. It is formed as a by-product of human activity in industry. Ancient healers used arsenic as a healing agent and as a poisonous substance.
You can be poisoned by arsenic through negligence or the malicious intent of a stranger. To avoid arsenic poisoning, you need to know the symptoms in humans, and the list of basic materials and products containing this element
You must be able to provide first aid to an injured person. Correct behavior in an emergency helps to quickly relieve the symptoms of poisoning, and even save a person’s life.
Arsenic in its natural state surrounds people on all sides. Dentists use it in dental treatment. Crustacean products, shellfish and sea fish contain arsenic in their body structure. Insect and rodent repellents contain large amounts of arsenic.
The smoke released into the air when burning chemical waste, when burning coal, has a high content of arsenic. The metal is contained in materials such as pesticides and herbicides, non-pharmacologically produced antifungal chemicals, preservatives and dyes in the food industry.
People who work in factories that manufacture various types of glass, electronic devices, and semiconductors can inhale arsenic fumes. In the mountains, in clean and clear rivers, there may be a dangerous concentration of arsenic if the neighboring mountains have arsenic deposits.