October 24, 2017
Periodontitis and periodontal disease are diseases of the periodontium - the complex of tissues around the tooth and the ligaments that hold it in the alveolus or socket. Despite the fact that these problems are fundamentally different both in clinical manifestations and in terms of treatment, many patients often confuse them. Moreover, often even doctors pass off one disease as another.
It is noteworthy that periodontitis occurs in 95% of the adult population, and periodontal disease occurs in only 2%. The first occurs most often due to dishonest or insufficient oral hygiene, but the second is usually associated with general diseases of the body.
UltraSmile.ru offers to understand what “periodontitis” and “periodontal disease” are, and what is the difference between the two diseases.
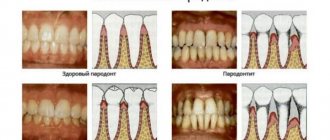
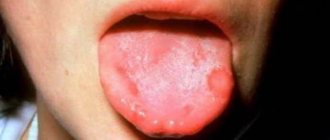
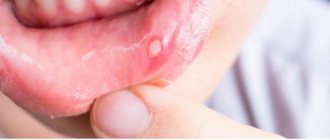
Periodontal disease (photo on the left) and periodontitis (photo on the right)
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the periodontium1, simply an inflammation of the gums, as well as the ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket. Periodontal disease is a systemic periodontal disease, that is, it occurs without inflammatory processes and is characterized by progressive gum atrophy. But in order to see the full picture of the differences, let's look at the comparison table.
| Periodontitis | Periodontal disease | |
| Gum condition | The gums become inflamed, become scarlet, bleed, swell and noticeably increase in size. | There are no inflammatory processes - the gums become white-pink and shrink in volume |
| Presence of bleeding gums | At first it occurs due to mechanical impact (food, brush), over time it becomes permanent | Absent |
| Swelling of the gums | Present | Absent |
| Presence of gum pockets | Present. Their depth varies up to 3.5 mm in the initial stage and up to 5-6 mm in severe form | None |
| Tooth mobility | Appears as the disease progresses, occurs due to inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus | Missing for a long time, but if the disease is not treated, the tooth can still be lost |
| Exposing teeth | Only in severe forms, when voluminous periodontal pockets are formed | Present – due to the reduction in gum volume, the necks and roots of the teeth are exposed, the teeth visually lengthen |
| Bad breath | Present, caused by the process of decay of food debris in the gum pockets | Absent |
| Main causes of the disease | Neglect of good oral hygiene, advanced gingivitis | Age-related changes, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus |
| Main consequences of the disease | Rapid loosening of the tooth, its loss, bone tissue atrophy and difficulties during implantation. The disease cannot be cured completely; it often recurs if it has reached a chronic generalized stage, when all teeth on one or both jaws are affected | Violation of the aesthetics of a smile, since the teeth are exposed and gaps between them are visible in the gum area. Teeth can also be lost, but the process of gum atrophy is slower than with periodontitis. In addition, teeth quickly decay, since the exposed parts have thin enamel that is not able to protect them from external influences |
| Features of treatment | Removal of dental plaque, anti-inflammatory therapy, cleansing and removal of gum pockets, treatment with ultrasound and Vector, Varius devices, platelet injections, splinting of teeth using thread or clasp dentures (in the absence of some elements of the dentition) | Physiotherapy to restore nutrition to the gums, treatment of the underlying disease that caused periodontal disease, surgery to correct the position of the gums |
Among other things, in both cases it is important for the patient to prepare for long-term treatment, which may not be limited to one month. You will also have to maintain strict control on your part, taking an active part in getting rid of the problem: strengthen oral hygiene, follow all doctor’s recommendations, purchase floss, rinses and irrigator, take medications, make applications from gels and medications.
Features of periodontitis treatment
Treatment of periodontitis directly depends on the degree of tissue inflammation - the more advanced the disease, the more complications, the more difficult and lengthy the treatment. Doctors strongly recommend starting the fight against periodontitis in the early stages, when the damage is localized and affects only a few teeth. Then the problem can actually be eliminated without further consequences.
Important! No matter how bitter the truth is, it is almost impossible to get rid of diseases in the chronic stage, this applies to both periodontitis and periodontal disease, forever; you can only temporarily bring the patient’s condition into remission. In most cases, loose teeth will have to be removed and ways to restore them will have to be found. Today it is not difficult to do this - it is possible to acquire a new smile in 3 days, even in conditions of acute bone atrophy, with the help of progressive implantation methods that allow you to restore teeth for a long time (one might even say lifelong) in just a couple of days.
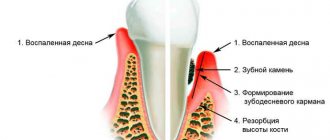
Treatment consists of mandatory cleaning of teeth in periodontal pockets - bacteria and plaque accumulate in them, which provoke tissue inflammation. For these purposes, ultrasound and hand instruments are used; gum curettage can also be performed - this is a surgical operation in which the gum is cut, peeled off from the surface of the tooth, and all foci of inflammation are cleaned out from under it. Next, the mucosal flap is returned to its place, and the gum is sutured. This procedure is necessary in case of large periodontal pockets formation, if they cannot be cleaned in any other way.
Cleaning periodontal pockets
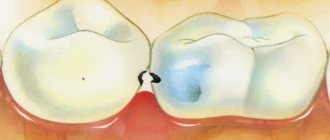
With an integrated approach, splinting of mobile teeth can also be carried out - a thin fiberglass splint is placed on them, as well as healthy neighboring ones on the inside. It unites teeth into groups and allows you to fix loose ones in a motionless state. At the same time, anti-inflammatory therapy, rinsing and physiotherapy are prescribed. If several teeth are missing in the oral cavity, clasp removable dentures can serve as a splint - their design contains a metal base and hooks, so the denture is quite solid and reliably keeps the teeth from loosening. And at the same time it allows you to close the “holes” in the row.
Photo: splinting teeth
Patients should remember that it is impossible to cure periodontitis - you can only delay the process of tooth extraction and temporarily relieve tissue inflammation. If your teeth are very loose, the best option would be to remove them and replace them with implants - this will achieve a more lasting treatment result.
Splinting teeth for periodontitis
Periodontitis and its course
Gum periodontitis is a set of inflammatory processes that occur in periodontal structures and are characterized by the destruction of the alveolar jaw process, caused by the activity of certain microorganisms or bacteria. Symptoms of periodontitis:
- bleeding of gum tissue when biting food or while brushing teeth, unpleasant pain or itching;
- gum hyperemia, swelling, the appearance of plaque;
- increased viscosity of saliva;
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- hypersensitivity of teeth as a result of exposure of nerves;
- pathological loosening of teeth, their possible displacement or loss.
Features of periodontal disease treatment
But the treatment of periodontal disease is fundamentally different from the treatment of periodontitis. This is due to the absence of gum pockets, tissue inflammation and tooth mobility. With periodontal disease, the gums, on the contrary, are reduced in volume due to metabolic disorders, so all efforts should be aimed at improving the nutrition of the mucous membranes.
For this purpose, a whole range of measures is used aimed at stabilizing the physiological parameters of not only the periodontium, but also the entire organism as a whole. Massages and physiotherapy are performed to stimulate local blood circulation, the patient is prescribed vitamin complexes (including in the form of injections into the gums). It is also recommended to periodically apply protective compounds to exposed areas of the teeth, which will strengthen the enamel and reduce susceptibility to bacteria.
Massage gums using an irrigator
The editors of the portal strongly recommend that you sound the alarm already when you encounter a symptom of bleeding gums. Otherwise, get ready for a long treatment, or better yet, opt for implantation, because in most cases with periodontal disease, this is the only option that will help you return to a healthy and happy life.
Prevention of dental diseases
Visit your doctor regularly to prevent gum disease.
Prevention measures for all oral diseases are almost the same. To avoid serious problems with teeth or gums, you need to follow the recommendations:
- Regularly visiting the dentist , 2 times a year, will be enough to identify the development of any diseases and be able to prevent them in time.
- Practice good oral hygiene every day. Ideally, they look like this: you should brush your teeth in the morning and evening, and after each meal you should rinse your mouth to get rid of food residues. You can also use medicated dental floss once a day to remove any stuck bits between your teeth. It is not recommended to use it more often, as this can lead to an increase in interdental spaces or injury to the gums.
- The diet should be healthy , containing fruits and vegetables. Also, in order to keep your teeth strong, you need to periodically chew on hard foods, such as carrots or apples.
- You should always monitor your health and strengthen your immune system. To do this, you just need to get rid of bad habits, do exercises every day or start playing some kind of sport, eat healthy food, and also create a daily routine in which rest alternates with work and healthy sleep is a must.
Bad habits have a very negative impact on oral health. Smoking makes teeth yellow, smoke constantly affects the gums, and bad breath increases. The same goes for alcoholic drinks.
Periodontal diseases. What gum diseases are there?
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
gum disease
1 Beloklitskaya G.F. Clinical forms of generalized periodontitis and their significance for its differentiated therapy.
Consulting specialist
Geraskina Inna Igorevna
Doctor rating: 9 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist, orthodontist Experience: 10 years
What is periodontal disease: symptoms, causes
Periodontal disease is rare, occurring in 5-10% of all gum diseases. This is the stage of development of the disease when negative changes that have occurred in the tissues affect not just the condition of the periodontium (the tissue around the tooth), but also the general condition of the body. The risk of periodontitis is high in those who suffer from diabetes, atherosclerosis, and various types of hormonal disorders.
Periodontal disease is damage to the gums around the tooth, which can be either mechanical (due to scratches, impacts) or internal (due to a malfunction in the body, the gums do not receive the necessary nourishment). Periodontal disease can be diagnosed by X-ray examination, because the problem manifests itself in the tooth processes, which atrophy.
Due to atrophy of the alveolar processes, the bone marrow space and tissue mass in the interdental septa decrease, signs of osteoporosis appear, and the bone pattern also changes, it becomes finely meshed and sclerotized.
In the first stages, periodontal disease develops unnoticed by a person, but when the disease has already progressed, it does not go unnoticed. You should pay attention to the following symptoms :
- gums do not bleed: no signs of inflammation appear,
- The periodontium loses its color. Healthy gums are deep pink in color, and it changes closer to red,
- the height of the gums decreases and the root neck opens,
- the enamel may “wear off”, a “wedge-shaped effect” may appear or enamel erosion may develop,
- Periodontal disease is often accompanied by heart disease, endocrine problems and metabolic problems.
Periodontal disease often develops asymptomatically.
Diagnosis of periodontal disease and periodontitis
The diagnosis is made according to the following scheme:
- Collection of medical history. The doctor finds out the patient’s complaints and the duration of the disease.
- Examination of the oral cavity. During a visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity, the specialist pays attention to the condition of the gums, teeth, location and configuration of the dentition. When examining periodontal patients, the dentist additionally determines the size of the periodontal pocket and the degree of looseness of the teeth.
- X-ray examination of bone tissue. A pantomogram of the upper and lower jaw allows us to establish the final diagnosis and stage of the disease.
Causes of periodontitis and periodontal disease: what are the differences?
Periodontitis differs from periodontal disease in terms of its triggering factors. In the latter case, the mechanism of occurrence of the disease has not yet been established with complete accuracy, but there are a number of pathologies against which the risk of its occurrence is higher:
- atherosclerosis;
- hypovitaminosis;
- diabetes;
- problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- cardiovascular dysfunction;
- heredity.
The causes of periodontitis are known. More precisely, there is only one - this is an infection. Even plaque can become a “trigger mechanism” if the crowns and oral cavity are not regularly cleaned of it, thereby allowing bacteria to spread among dead cells and food debris.
Provoking factors are also:
- bad habits;
- chronic diseases;
- poor hygiene;
- weak immune system;
- poor nutrition;
- abnormal bite.
Sometimes the pathology develops after suffering from gingivitis.
Therapy methods
Treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease must be comprehensive.
This therapy has the following goals:
- elimination of the main risk factor that provokes the development of inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the bone tissue of the jaw;
- symptomatic elimination of the inflammatory process;
- the maximum possible restoration of chewing and aesthetic function.
Treatment of periodontal diseases is carried out using the following methods:
Local therapy
At the local level, therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating damaging factors (pathological microflora, dental plaque, sharp edges of fillings, low-quality orthopedic and orthodontic structures).
Therapy is carried out in the following order:
- professional oral hygiene, during which the dentist uses an ultrasonic scaler to remove hard and soft plaque;
- sanitation of the oral cavity and replacement of restorations with sharp edges of fillings;
- complete and high-quality prosthetics of dental defects;
- orthodontic treatment of abnormally located teeth;
Drug therapy for sore gums
In patients with periodontitis, gingivitis can occur in the form of catarrhal, ulcerative or hypertrophic inflammation. Depending on the type of gingivitis, doctors apply the appropriate treatment regimen.
Conservative treatment of periodontal pockets
In therapeutic dentistry, pathological pockets are treated with the following medications:
- antiseptic - furatsilin or potassium permanganate;
- antibacterial drugs - nitrofurans, broad-spectrum antibiotics and sulfonamides;
- local painkillers - microcide with novocaine, anesthesin with glycerne and mefinamine sodium salt;
- anti-inflammatory medications – non-steroidal and steroidal pharmacological drugs;
- proteolytic enzymes – chymotrypsin, trypsin and ribonuclease;
- enzymatic inhibitors - trasylol and contrical.
- Stimulators of regeneration of soft tissues of the oral cavity - galascorbine, metacil and vitamins A, B, C and E;
- Activators of gum epithelization - vitamin A solution and aniline dyes.
It should be noted that antibiotics for periodontitis and periodontal disease can be used in the form of local powders, and in the form of tablets and injections for internal use.
Surgical methods for treating periodontal pockets
Radical intervention for generalized periodontal lesions is carried out in the following forms:
- curettage is a surgical method of cleaning the periodontal gap by scraping the inner surface of the periodontal pocket;
- gingivotomy – linear dissection of periodontal pockets to expose the source of suppuration or perform open curettage;
- gingivectomy – complete excision of a pathological pocket together with its contents, which is performed when the depth of such a formation is over 4 mm;
- flap operations - the formation and suturing of a muco-bone flap, which allows eliminating a deep periodontal pocket and preventing further gum resorption.
The cost of surgical treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease will be the highest, but doctors observe the highest effectiveness of such therapy.
Orthopedic techniques
Dental prosthetics for periodontal diseases is aimed at eliminating traumatic occlusion, splinting teeth and replacing dental defects.
Only complete oral prosthetics for periodontal disease and periodontitis contribute to the restoration of chewing function and speedy rehabilitation of the patient.
Physical methods of influence
The main methods of physical procedures in periodontics include:
General treatment
General therapy is carried out by taking antibacterial, immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory drugs. Periodontal patients also need diet correction, vitamin intake, and medication to normalize metabolic processes.
Source: Denta.help
Propaganda and advertising of a healthy lifestyle are gradually doing their job, and today everyone knows how important strong teeth, healthy gums and a clean surface of the oral mucosa are for a modern person. Moreover, there are more and more opportunities for quality oral care every day.
Proper oral hygiene, regular visits to the dentist, timely diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane are a necessary part of every person’s daily care for their health.
Hundreds of different types of bacteria “live” in the oral cavity, most of which are opportunistic. The more we eat sweets, the more plaque will form on our teeth and tongue due to the accumulation of bacteria. The coarser and harder the food, the healthier it is, since, firstly, it does not create a favorable breeding ground for bacteria in the mouth, and secondly, it mechanically cleanses the teeth and is a constant strengthening “gymnastics” for the gums.
Daily brushing of teeth with a brush and toothpaste is a mandatory procedure . It must be done twice a day - in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed. If you are concerned about gum problems, then the number of teeth brushings is increased to 3–5 times a day, after each meal.
Complete oral care takes no more time than applying makeup - 10, maximum 15 minutes a day. And the benefits of time invested in your health and quality of life cannot be overestimated!
But what to do if, despite proper oral care, your gums become inflamed and bleed? They feel sore and burning, and discomfort appears when eating hot, cold and solid foods. In such situations, when signs of inflammation are obvious, it is necessary to consult a dentist. Inflammatory oral diseases (IODs) not only create physical and psychological discomfort; if not treated appropriately and promptly, they can have serious consequences and lead to tooth loss in adulthood.
Despite the successes of modern dentistry, the prevention and treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa still pose significant difficulties today.
Different diseases of the oral mucosa may have similar clinical manifestations, which makes it difficult to diagnose them and choose an effective treatment method. Lesions of the mucous membrane can be independent diseases that develop as a result of injuries or the activity of microorganisms, or they can be one of the symptoms of general somatic diseases (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, blood, metabolic disorders, etc.). The most common inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity include stomatitis, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
Currently, a promising link in the complex treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa and periodontal disease is the use of combined herbal preparations with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Human acquaintance with the medicinal properties of plants dates back to ancient times. In modern medicine, medicinal plants not only have not lost their position, but today they are increasingly preferred in the prevention and treatment of various diseases. Medicinal plants have little toxicity and can be used for a long time without side effects.
Plant extracts Stomatofit® and Stomatofit® A demonstrate new possibilities and benefits of herbal medicine. The preparations were developed specifically for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity: stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc. The variety of therapeutic properties of the extracts is due to the combined effect of the plant components included in their composition. The combined composition of the drugs ensures their complex action, which significantly increases the effectiveness of treatment regardless of the etiological factor of the disease.
Stomatofit® is used as a rinse 3-4 times a day, the course of treatment is 10-15 days. The drug helps to effectively relieve the symptoms of inflammation, reduce bleeding gums and unpleasant odor.
Stomatofit® A has a pronounced analgesic effect. The thick consistency of the drug helps to retain it on the affected area, which provides a longer therapeutic effect. They need to lubricate the affected areas at least 3 times a day.
The healing properties of medicinal plants and the achievements of modern pharmacology have made it possible to create drugs that are at the same time natural, safe, effective and very easy to use.
Clinical studies of the drugs Stomatofit® and Stomatofit® A, conducted at Moscow State Medical University in 2002 and 2009, proved their high efficiency and safety.
As an advertisement
Source: www.medkrug.ru
What is the difference between periodontal disease and periodontitis?
Correct treatment begins with a correct diagnosis, so consult a doctor at the first appearance of symptoms. It is impossible to cope with advanced cases of pathologies at home. These two problems can be easily confused because the symptoms are similar. Professionals distinguish several differences between periodontal disease and periodontitis:
- Periodontitis is a disease that manifests itself already in the first stages and is accompanied by acute and unpleasant pain in the gums and teeth, while periodontal disease cannot be diagnosed by external signs. Its presence or absence can be determined by the results of medical studies;
- The difference between these two diseases lies in the causes of their occurrence. Periodontal disease is caused by internal changes in the body - heredity, chronic diseases (diabetes, ulcers, diseases of the cardiovascular system), complications after injuries to the gums and teeth;
- Manifestation of diseases: periodontitis “makes itself felt” already from the first stages of the disease: the gums bleed and swell, swelling of the cheeks is observed, and pain in the throat may appear. With periodontal disease, it is almost impossible to notice the signs in the first stages, only with the help of special equipment;
- Area of damage: periodontitis does not appear on all teeth, but on one or a group and does not spread to the remaining teeth if treatment is started, while periodontal disease gradually affects all teeth.
Important! It is impossible to treat periodontitis and periodontal disease at home. In the later stages of the disease, surgical intervention is possible, but all manipulations must be performed by a specialist.
What can happen if periodontitis is not treated?
The acute form of periodontitis, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to the appearance of flux, and then a purulent abscess on the patient’s face. Also, from the acute form, periodontitis can develop into sinusitis and osteomyelitis.
The chronic form is dangerous because cysts can form against its background, which fester, grow into the maxillary sinuses, and cover the gums of other healthy teeth.
Photo: osteomyelitis, as a result of advanced periodontitis
Read what are the consequences of periodontitis here. Also, periodontitis is dangerous for the entire human body since it is a source of infection, which can cause complications in the heart. Periodontitis is also very dangerous during pregnancy.
Watch the video “Dental periodontitis and its treatment”
Important! Very often, periodontitis can result from periodontitis. This mechanism works like this: the infection from the gums affected by periodontitis, without resistance, begins to move further into the depths of the tooth. Through microcracks or perforations of the tooth root, or in chronic pulpitis, pathogenic microflora enters the periodontium, affecting it. So timely treatment of periodontitis is extremely important, as it will protect your teeth from further more serious problems.
Development of periodontitis
Periodontitis is based on an inflammatory process that occurs as a reaction to damage of any type (mechanical, chemical, infectious, thermal). Prolonged inflammation deteriorates the characteristics of the soft tissue of the gums.
Long-term exposure to these factors leads to changes in the cellular structure of the gums. At the same time, local metabolism and blood supply to tissues are disrupted, and vascular permeability increases. Pathological processes begin in the gum tissue. Over time, the destruction of the structure becomes so strong that its properties do not allow the teeth to be held normally.
At approximately this stage, due to tissue destruction, a periodontal pocket appears: the connection between the tooth and the gum is lost. The neck of the teeth is exposed and they become noticeably mobile. If the disease progresses further, the next stage will be the separation of the front teeth in a fan-shaped manner.
Etiology and therapy of periodontitis
Periodontitis clearly manifests itself in the first weeks and is acute: the gums bleed, hurt, and swell, so the disease is easy to recognize immediately. However, if immediate attention is not paid to treatment, the inflammation penetrates deeper, affecting the periodontal ligament - the tissue that connects the teeth. The destruction of the ligaments leads to the formation of a periodontal pocket - the detachment of the gum from the tooth, creating an environment for the formation of tartar, the accumulation of plaque on the teeth and gums, and the proliferation of bacteria.
During this period of the disease, pus is often released from the gums, there is bad breath, and tooth sensitivity increases. The result of periodontitis is rotting of the gums, adjacent tissues, and exposure of the roots. The teeth become loose, the chewing function of the dentition is impaired, and a feeling of gaps appears between the teeth. The disease leads to the decomposition of the jaw bone tissue and the loss of one or more teeth.
The main difference between periodontal disease and periodontitis is that bacterial damage (periodontitis) more often affects teeth one at a time or affects several adjacent units. The disease spreads to neighboring teeth if it is not stopped in time. Periodontal disease spreads and progresses evenly throughout the entire jaw and dentition.
Bone decomposition during periodontal disease does not immediately manifest itself as clear symptoms, and this is the danger of such gum disease. For a long time, tissue destruction occurs without obvious symptoms and often without pain. Visual signs of periodontal disease are tooth mobility, receding gums, exposed roots, thinning of the dentition and cracks in the enamel.
The resulting space - pockets - is attractive for the growth of bacteria, and often periodontal disease becomes the cause of rapidly progressing periodontitis in several areas or in the entire oral cavity at once.
Periodontal disease itself slowly progresses and leads to the loss of the entire dentition after 10-15 years. This disease is much less common; people suffering from immunodeficiency are at risk.
We suggest you read: What is better: braces or plates
Note! Periodontitis is often called periodontal disease, without suspecting that completely different diseases are hidden behind similar names. Doctors strongly do not recommend treating periodontal disease and periodontitis at home, because only an experienced dentist can distinguish gum disease, and the methods of treating periodontal disease and periodontitis are different.
Medical treatment of gums is a long and complex process. Folk remedies for the fight against periodontal disease are ineffective, and you cannot resort to strong pharmaceutical remedies without the advice of a dentist - self-medication can aggravate the situation, ruin teeth and damage other organs.
It is rarely possible to cure periodontal disease completely: the cause of the disease lies in the weakened state of the body and the improper functioning of organs. This is why older patients most often suffer from gum disease.
However, proper treatment stops the development of the disease, prevents it from progressing, and damaged teeth and tissues can be restored.
The first stage of periodontal disease treatment is examination.
Without high-quality diagnostics and analysis of gums and teeth, it is impossible to cure periodontitis. To establish the causes of the disease, it may be necessary to examine not only the mouth, but the entire body.
At the LeaderStom clinic, examinations are carried out using modern equipment, which accurately determines the cause and extent of the lesion:
- An orthopantogram and an x-ray of the oral cavity will show how deeply the disease has penetrated and what tissues it has affected;
- Analysis of periodontal tissue (gum tissue) will reveal the presence of pathogenic bacteria and the concentration of microorganisms in the mouth.
The result of an in-depth examination of the oral cavity is a comprehensive gum treatment plan.
When periodontal disease has not yet destroyed bone tissue, it is easier to cure teeth and gums. To begin with, ultrasonic cleaning of the oral cavity is carried out, which removes plaque, tartar and deposits.
Afterwards, drug treatment of periodontal disease is prescribed:
- General therapy includes taking hormonal and immunomodulating drugs and antibiotics. The exact selection of medications for periodontal disease is made by a dentist; the treatment method depends on the cause of the disease. This is why doctors do not recommend self-medicating without consultation and resorting to traditional medicine - these ineffective remedies create the illusion of treating teeth and gums while the disease progresses.
- Strengthening the immune system. Drugs that boost immunity actually help the body cope with the destruction of gums, tooth roots and bone tissue faster, but only a doctor can prescribe them, and only after conducting a series of tests that will show what substances the body lacks. Contrary to popular belief, special diets do not help get rid of periodontal disease, but dentists recommend excluding spicy, fatty and fried foods - such foods irritate damaged gum tissue and negatively affect the microflora of the oral cavity. It is recommended to eat more fruits and vegetables, because they strengthen the immune system.
- Local therapy. Injections into the gums for periodontitis, gels, painkillers and disinfectants. The main goal of such treatment is to prevent the return of plaque or inflammation.
If gum disease was not noticed immediately and has already manifested itself through external destruction - receding gum tissue, wedge-shaped changes or tooth mobility, treatment of periodontal disease will be much more difficult:
- After the examination, the dentist will indicate which teeth cannot be restored and must be removed, and will also clean the oral cavity from plaque, tartar and microbes.
- The next step in the treatment of periodontitis is splinting. The purpose of the procedure is to bind the remaining teeth and prevent further loosening and loss. A horizontal groove 1-1.5 mm deep is drilled into each tooth, into which a fiberglass construction tape is poured. A light composite is applied on top, which returns the teeth to their natural aesthetics.
- If periodontal disease has been advanced, teeth can only be restored with the help of prosthetics - making a bridge. The prosthesis not only creates an aesthetic effect, restoring the beauty of the smile, but also replaces the chewing function of lost teeth, and also strengthens and does not allow the remaining teeth to decay.
Treatment of periodontal disease is accompanied by strengthening the immune system and drug therapy. Dentists at the LeaderStom clinic will definitely tell you about caring for your teeth during and after periodontal disease treatment.
Seeing blood on your toothbrush and in the sink while brushing your teeth every day is not pleasant. You can solve the problem of bleeding gums in just one visit with the help of deep mouth cleaning using the Vector device.
This procedure does not provide visible aesthetic results: the teeth do not become noticeably whiter or straighter, so patients tend to classify it as a minor procedure. This is a fatal mistake, because it is with tartar, bleeding and periodontitis that serious problems with teeth begin: loosening, exposure of roots and loss of dentition units.
The Vector device fights gum problems, strengthens tissue, cleans out inflamed pockets, destroys germs, saving gums from infection. The complex effect of Vector restores the adherence of the gums to the teeth, closing periodontal pockets that are attractive to infections.
The revolutionary principle of longitudinal movement of the Vector Paro Pro!
- Non-traumatic
- Antibacterial
- Strengthening method
It is the tartar deposited in the pockets that is the main cause of bleeding gums, since when you press on this place with a toothbrush or while eating, the gums are injured, wounds appear, into which pathogenic bacteria enter - the cause of inflammation of the oral cavity.
VECTOR is the only way to perform deep teeth cleaning efficiently and painlessly. Contact LeaderStom for cleaning to treat bleeding gums and prevent the development of periodontitis. The clinic regularly holds promotions and discounts for comprehensive treatment of gums and teeth.
LeaderStom is the ideal price-quality ratio for dental services: treatment of diseases of the teeth and gums is performed by highly qualified periodontists. Dentistry is developing every day, which is why our doctors undergo advanced training courses, get acquainted with new methods and devices that restore health to teeth and gums.
The doctor begins therapy only after a complete examination of the oral cavity, since some gum diseases can be the cause of other serious disorders in the body: hypovitaminosis, malfunction of organs or infectious diseases. If there are no other diseases, the periodontist performs probing (penetrating examination of the gums and teeth), based on the data of which the treatment tactics are determined.
We suggest you read: Ketorol or Nurofen, which is better?
Our main principle in treatment is adherence to high quality standards at all stages of treatment: from examination to recommendations for rehabilitation and dental care, the doctor takes care of the patient. We understand that neglect of any stage of treatment leads to relapse of the disease, which means that money for the treatment of teeth and gums was wasted.
The importance of a doctor’s recommendations cannot be underestimated, because the effectiveness of even the most modern treatment of periodontal disease and periodontitis largely depends on proper oral hygiene. Only daily brushing of teeth and caring for gums will help get rid of plaque and avoid the appearance of tartar.
Massaging with the right toothbrush will have a beneficial effect on your gums, and using medicated toothpastes recommended by your doctor will protect against irritation. The periodontist at the LeaderStom clinic will tell you in detail about toothbrushes, how to choose the right toothpaste and what products to use to reliably protect the gum tissue.
What is periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory condition of the gums, accompanied by bleeding and swelling of periodontal tissue. If left untreated, tooth loss may occur. The disease progresses rapidly, affecting the gum mucosa of both the lower and upper jaw. More than 80% of the entire population is susceptible to this pathological process and only a few of them visit the dentist.
Causes
One of the main differences between periodontitis and periodontal disease is the etiology of the disease. Factors that provoke inflammation of the papillary-marginal-alveolar region of the gums with further exposure of the necks of the teeth include:
- active proliferation of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic bacteria (due to poor oral hygiene);
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- decline in the body's protective properties;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- malnutrition;
- pathological bites;
- errors in prosthetics;
- untreated or poorly treated pulpitis;
- thermal, chemical or mechanical damage to the mucosa.
The initial stage of gum inflammation is gingivitis.
Gingivitis and periodontitis have common causes of development, but the main difference between these diseases is the clinical picture. With gingivitis, gum recession is not observed.
Symptoms
Patients with periodontitis complain of:
- itching and pain during mechanical processing of food;
- discomfort during hygiene procedures;
- spontaneous bleeding of the gums;
- halitosis;
- tooth mobility (in moderate and severe stages);
- the presence of stones in the anterior incisors of the lower jaw.
Distinctive features
With periodontitis, the gums around the tooth become inflamed, gradually spreading to healthy tissue. In the absence of proper treatment, the periodontal space is completely destroyed, which will lead to tooth loss. The disease occurs in a more acute form than periodontal disease.
They can be distinguished by the following symptoms:
- When gums are affected by periodontitis, a slow inflammatory process begins.
- With periodontal disease, the gums rapidly deteriorate, leading to tooth loss.
- Periodontitis is an acute disease that lasts from several weeks to a month.
- Periodontal disease takes longer to develop and can last for years. Dental crowns look like wedges. If you are affected by periodontitis, you can lose dentitis in just a few months, and with periodontal disease, teeth will not fall out for about six or more years.
Diseases of the gums and teeth - periodontitis, pulpitis, periodontal disease, caries
The health of teeth, gums and oral cavity depends on a huge number of factors that combine a person’s lifestyle in general and the influence of the environment on his health. To one degree or another, the following elements have a direct impact on dental health:
- Nutrition. Diet, quality and nature of foods consumed affect the condition of teeth. Tooth enamel is sensitive to drinks and food that are too hot or too cold; excessively hard foods can damage the integrity of the tooth.
- Hygiene. If the rules of oral hygiene are not followed, pieces of food that are not removed become the cause of bacterial growth, provoking the process of rotting. Improper brushing of teeth contributes to the accumulation of plaque, the formation of tartar, etc.
- Diseases. Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity or nasopharynx can aggravate existing dental problems or provoke the emergence of new ones. In addition, chronic infection weakens the body's defenses, reducing immunity.
- Environmental factors. The quality of water used for cooking and consumption directly affects the condition of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
In our Dentistry on Shchelkovskaya Diamed, dentists successfully treat diseases of the teeth and gums.
We strongly recommend that if you experience pain, inflammation or other unpleasant sensations, contact the dentist immediately! Do not delay your visit to the doctor, this way you increase the chance of saving your natural tooth and avoiding extraction.
You can make an appointment with a dentist by phone or by filling out an online appointment form. We are within walking distance from Shchelkovskaya m.
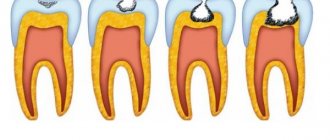
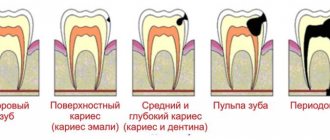
Caries
Perhaps caries can be considered the most common dental disease, occurring in one degree or another in more than 75% of the population.
Only a specialist can unambiguously determine the reasons for the development of caries, since this is associated with many individual characteristics of the patient: lifestyle, age, the presence of concomitant dental diseases and other pathologies, diet, habits, etc.
It was previously thought that tooth decay could be caused by poor oral and dental hygiene; this is still the main cause, but not the only one. Children are often told that eating a lot of sweets can cause tooth decay, but without a number of additional reasons this will not happen.
The most common causes of caries development are:
Insufficient oral hygiene. People who neglect oral hygiene procedures after meals face the problem of caries in 90% of cases.
Insufficient or non-systematic brushing of teeth and failure to use dental floss contribute to the formation of persistent plaque on the surface of the teeth, which subsequently turns into tartar and contributes to the loss of microelements from tooth tissue.
Enamel pathology. Inadequate development of dental tissues can cause insufficient supply of minerals from saliva to the enamel, which interferes with the normal development, formation and functioning of the tooth.
Signs of caries are a group of symptoms that can be identified even through self-observation:
- change in tooth enamel - darkening, acquiring a brownish or black tint;
- pain manifested by brushing teeth, using dental floss, chewing food;
- sensitivity of tooth enamel to cold, hot foods and drinks;
- chronic bad breath, regardless of hygiene rules;
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues surrounding the tooth, characterized by the gradual destruction of the connection between bone tissue and the root, increased mobility of the tooth, up to its complete loss.
Periodontitis has an infectious nature of occurrence. The infection penetrates between the tooth and the gum, gradually disrupting the connection between the tooth root and the bone, increasing the mobility of the tooth in place; over time, the connection between the root and the bone weakens, which can threaten tooth loss. Periodontal disease can affect completely healthy teeth that are not affected by other dental problems.
Once an infection is identified, eliminating its causative agents is not particularly difficult, but in this case the consequences of periodontitis are important.
Since after eliminating the infection, soft tissues are restored faster, rather than the ligaments that hold the tooth root in the bone, the resulting pocket is filled with granulation tissue, which contributes to the appearance of pathological mobility and the risk of tooth loss.
Thus, the treatment of periodontitis consists of two main parts: destruction of infection, restoration of bone tissue and ligaments that hold the tooth in the bone.
After a course of treatment for periodontitis, the patient needs to pay special attention to hygiene procedures for a long time, monitor the condition of the teeth and regularly visit the dentist. Often, as a preventative measure, the doctor prescribes special care for teeth and gums using specialized teeth cleaning and oral hygiene products.
Preventive measures are: maintaining hygiene of the oral cavity, teeth, gums; timely visits to the dentist; systematic self-monitoring of dental health.
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is an inflammatory disease of periodontal tissue, characterized by inflammation of the gums, destruction of the connection between the gum and the body of the tooth, leading to loss of teeth from initially healthy teeth due to severe mobility.
Periodontal disease has an infectious nature. The infection penetrates between the tooth and the gum, gradually disrupting the connection between the tooth root and the bone, increasing the mobility of the tooth in place; over time, the connection between the root and the bone is interrupted, the tooth dies and falls out. Periodontal disease can affect completely healthy teeth that are not affected by other dental pathologies.
Once an infection is identified, eliminating its causative agents is not particularly difficult, but in this case the consequences of periodontal disease are important.
Since after the infection is destroyed, the soft tissue of the gums is restored faster, rather than the connection between the tooth root and the bone, the resulting cavity is filled with soft tissues, contributing to excessive mobility of the tooth and, again, its subsequent loss.
Thus, the treatment of periodontal disease consists of two main parts: destruction of infection, restoration of bone tissue and connection of tooth roots with bone tissue.
After a course of treatment for periodontal disease, the patient needs to pay special attention to hygiene procedures for a long time, monitor the condition of the teeth and regularly visit the dentist. Often, as a preventative measure, the doctor prescribes special care for teeth and gums using specialized teeth cleaning and oral hygiene products.
It should be remembered that even completely cured periodontal disease can develop again under unfavorable conditions. Preventive measures are: maintaining hygiene of the oral cavity, teeth, gums; timely visits to the dentist; systematic self-monitoring of dental health.
Pulpitis
Pulpitis is an inflammatory disease of the soft tissues of the tooth, of an infectious nature, which is the most common consequence of untimely or poor-quality treatment of carious lesions, characterized by acute pain and a sharp reaction to temperature stimuli.
Pulpitis is not so much an independent disease as a consequence of improper treatment of dental diseases or lack of treatment as such.
The mechanism of development of the disease is simple: in the presence of carious lesions left unattended, the destruction of hard tooth tissues can reach the root pulp, as a result of which microorganisms and their metabolic products begin to penetrate into the vascular bundle located in the center of the tooth.
Symptoms of pulpitis are varied and depend on the form of the disease. There are acute and chronic forms of the disease. Acute pulpitis is characterized by periodically occurring pain in the tooth, occurring suddenly and disappearing on its own. Most often, pain occurs in the evening and at night.
At the initial stages of the development of the disease, pulpitis may not bother the patient much, but over time, attacks of pain become more frequent and intensified, the pain becomes pulsating in nature and is expressed with greater intensity. Sometimes the pain radiates to the jaw, ear, or nearby areas, which can cause a migraine or headache attack.
Subsequently, the pain becomes unbearable, excruciating and cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Chronic pulpitis manifests itself somewhat differently.
This disease in its chronic form makes itself felt with any thermal changes - painful sensations occur when the temperature changes, for example, when moving from a cold room to a warm one and vice versa, eating very cold or very hot. As the thermal factor is eliminated, the pain gradually subsides. Spontaneously occurring causeless pain is not typical for chronic pulpitis.
Treatment of pulpitis involves removing the pulp and installing a filling on the damaged tooth. If pulpitis is not treated, a number of complications and consequences may develop. The most common include: periodontitis, periostitis; osteomyelitis, etc.
How gum and dental diseases manifest themselves
Regardless of the nature and complexity, dental diseases must be treated. People who visit the dentist at least twice a year protect themselves from the development of dental pathologies and dental diseases with regular visits to the doctor.
Timely consultation with a doctor allows not only to carry out gentle treatment and prevent the development of the disease, but also to completely eliminate the consequences of the disease.
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to the development of complications, the appearance of concomitant diseases, damage to healthy teeth, tooth loss and disruption of chewing functions.
The following symptoms are reasons to consult a doctor:
- change in tooth color;
- The appearance of painful and uncomfortable sensations in the tooth or surrounding tissues;
- Sharp reaction of teeth to cold and hot foods;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth;
- Bad breath;
- Presence of tartar and abundant plaque.
Source: https://smile4you.ru/blog/terapiya/bolezni-desen-i-zubov/
Causes of gum disease
The main cause of periodontitis is traditionally considered to be insufficient oral care. Microorganisms living in the mouth can cause inflammation of the periodontal tissues, so it is important to clean them off along with plaque.
Pathology can be caused by malocclusion, injuries and poor-quality prosthetics (we recommend reading: is it possible to carry out dental prosthetics for periodontal disease?). Periodontitis is often caused by the removal of sixth teeth, as this disrupts the contact of the jaws. The reason may be wearing braces, the habit of biting nails, chewing on one side of the jaw and exposure to alkalis and acids on the enamel.
Periodontitis can be caused by an incorrectly installed filling. It must fit tightly to the tooth, otherwise microorganisms will penetrate under it, destroying the root. It should not bulge, as this injures the delicate tissues of the oral cavity and prevents the removal of plaque. If the filling is installed incorrectly, inflammation occurs locally.
These factors can cause a generalized pathological process:
- poor nutrition,
- hormonal disbalance,
- immunity disorder
- inflammation of the salivary glands (we recommend reading: symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the salivary glands at home).
Classification of periodontal diseases Periodontium
Periodontium
(Greek about, tooth) - a complex morphofunctional complex of tissues surrounding and holding the tooth in the alveolus.
The periodontium consists of
:
gums, periodontium, cementum and alveolar processes.
Trophic.
Determined by a well-defined branched circulatory and lymphatic network and the content of various types of nerve receptors
Support-holding function
. It is carried out by the complex structure of the ligamentous apparatus of the periodontium, gums and alveolar process, thanks to which the tooth is fixed in the alveolus. Numerous collagen fibers located between the alveolar wall and the root cementum hold the tooth in a suspended state.
Shock absorbing
. Provides uniform distribution of chewing pressure over the dentition and alveolar process of the upper jaw and the alveolar part of the lower jaw. This is facilitated by the presence of a hydraulic cushion of loose connective tissue, a glomerular network of blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as tissue fluid.
Barrier.
It is determined by the morphological integrity of periodontal tissues, the protective properties of the covering epithelium of the gums, its ability to keratinize, the presence of plasma, lymphoid and mast cells that ensure constant phagocytosis, the content of enzymes and their inhibitors, thiocyanates and other biologically active substances. The protective function of the gums is also manifested in the emigration of leukocytes into the oral fluid, which is carried out mainly by the gingival papillae.
Plastic.
Provides high regenerative ability of periodontal tissues due to the content of fibroblasts, mast cells, cemento- and osteoblasts, adventitial cells, a high level of energy processes and intense transcapillary exchange.
Reflex regulation.
It is carried out by an extensive neuro-receptor apparatus of the periodontal and oral mucosa, which regulates the force of chewing pressure depending on the nature of the food, the usefulness of the dentition, periodontal and mucous membrane.
Periodontium
(lat. Periodontium) - a complex of tissues located in the slit-like space between the cementum of the tooth root and the alveolar plate. Its average width is 0.20-0.25 mm. The narrowest section of the periodontium is located in the middle part of the tooth root, and in the apical and marginal sections its width is slightly greater.
The development of periodontal tissue is closely related to embryogenesis and teething. The process begins in parallel with the formation of the tooth root. The growth of periodontal fibers occurs both from the side of the root cement and from the side of the alveolar bone, towards each other. From the very beginning of their development, the fibers have an oblique course and are located at an angle to the tissues of the alveoli and cementum. The final development of the periodontal complex occurs after tooth eruption. At the same time, the periodontal tissues themselves are involved in this process. It should be noted that, despite the mesodermal origin of the constituent components of the periodontium, the ectodermal epithelial root sheath takes part in its normal formation.
The basis of the periodontium is connective tissue. Its main structure is collagen fibers. They form the basis of the periodontal ligament and connect the cement of the tooth with the bone tissue of the alveolus. Despite the lack of elasticity, collagen fibers provide some mobility of the tooth in the socket, mainly due to the slight tortuosity of their course. The sections of fibers that penetrate the cement and bone tissue of the alveoli are called perforating - Sharpey's fibers. The depth of their penetration into the cement is no more than 3-5 μ.t, and into the alveolar bone - up to 20 μ.t. In the periodontal gap, collagen bundles coming from the cement and alveoli form a pronounced intermediate plexus, which ensures the adaptation of the entire tissue complex to changing loads on the tooth. The collagen that is part of the periodontal ligament is typical in its physicobiochemical properties, but its fibrils have a relatively small diameter - no more than 55 μ.t. In addition to the typical collagen fibers in the periodontium, there are immature - elastic - oxytalan fibers. They reach a length of several millimeters and run parallel to the cementum of the tooth root, crossing the collagen bundles at right angles. These fibers are credited with a significant role in the process of regulation and distribution of blood flow during physical stress on the periodontium.
Causes
Periodontal inflammation can be caused by the following reasons:
- medicinal;
- traumatic;
- infectious.
Medication
Inflammation, provoked by the influence of medications and medications, in most cases occurs due to poor-quality medical care in the treatment of caries and pulpitis, especially when the canals are poorly patency. Periodontal inflammation can be caused by long-term exposure to arsenic, although this substance is rarely used in dental procedures today. Periodontitis can also be one of the manifestations of an allergic reaction to drugs.
Traumatic
The causes of traumatic periodontitis are dislocations and fractures of the tooth root as a result of a fall, a blow to the jaw, or damage due to the habit of chewing pencils and other hard objects. Mechanical impact can be systematic when the tooth is under constant load due to the incorrect height of the filling or crown. Due to the inflammatory process, the color of the enamel may change and contrast with the color of the filling material and the installed crown. Due to the dentist's mistakes during filling, the tooth root can be damaged by a pin or instrument fragments that remain in the internal cavity and cause tissue inflammation.
Infectious
Infectious causes of periodontal inflammation are associated with the entry of microbes into this area through the root canal, carious cavities surrounding the gum tissue, or through the circulatory system during inflammatory processes in the body. Often the cause of periodontal infection is pulpitis, chronic caries and advanced periodontitis.