In diseases of the oral cavity, not only the gums or mucous membranes are often involved in the inflammatory process. Sometimes spots appear on a child’s tongue that have a pronounced white or red tint and are located in different parts. Parents should consider the causes, photos, study possible diagnoses and treatment methods.
By appearance and outline, one can assume internal pathologies or fungal infections, notice a cold or sore throat. If after rinsing the plaque does not disappear and bare areas remain, you should take your child to the dentist to identify the real cause.
Types of spots on a child's tongue
In a healthy child, the mucous membrane in the mouth has a slight pink tint without rashes or blotches. Increased body temperature or infection causes the color to change to a more intense red or burgundy due to the rush of blood. Therefore, pediatricians always try to examine the mouth of a young patient to identify a possible problem at an early stage.
Experts divide conventionally dark or white spots on a child’s tongue into several groups:
- Unevenly exfoliated epithelium, in which “islands” of food plaque accumulate on the surface.
- Intensive proliferation of mucosal cells in some areas of the tongue, resembling a compaction.
- Spots with clearly defined boundaries, distinguished by color.
In the first and second cases, the appearance of a defect is the result of a mechanical injury. The baby often bites his tongue when excited, pulls objects with sharp or uneven edges into his mouth, and scratches the delicate surface of the organ with internal braces.
Another common way to get a spot or small growth is by eating too hot or sour foods, which damage the microscopic papillae.
A response occurs:
- epithelial cells die from acids and fly off, sticking to each other;
- uncontrolled tissue growth occurs at the burn site.
In case of injury (cut or crack), recovery is quick and does not require special monitoring. Sometimes parents are alarmed by a brown spot on a child’s tongue: this is how a bruise appears after a bite or burn.
After a few days, the ability to sense tastes and temperature returns. To speed things up, you can treat the baby’s entire oral cavity with antiseptics and herbal decoctions allowed in childhood: chamomile, sage, calendula. Sea buckthorn oil has good regenerating properties. They lubricate the affected areas after any meal.
If increased formation of thickenings is observed, it is imperative to find the cause of this failure.
It is often associated with constant rubbing from braces or biting the tip. This is a unique type of callus that requires consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. In most cases, after removing metal structures and getting rid of a bad habit, the surface of the tongue is leveled within a few weeks without additional procedures or surgeries.
Prevention
In order not to suffer in the future with the inflammatory process, you should immediately show the child to the doctor at the first sign. The pediatrician will prescribe the necessary treatment. A few rules:
- to remove simple plaque from the gums, you just need to gently stroke it with a baby brush;
- calcium deficiency is also easily eliminated. You need to see a doctor and he will prescribe the necessary vitamins;
- stomatitis is treated only with medications;
- To ensure that there is no white residue left after feeding, you should rinse your baby’s mouth with boiled water;
- You can dilute baking soda in boiled water, and then soak a bandage in this water, wrap it around your finger and gently clean the baby’s mouth.
Read also: Why is there a black coating on the tongue?
To prevent your baby from getting white bumps in his mouth, you should follow certain rules.
- A balanced diet will provide the baby with the necessary vitamins and microelements. Artificial formulas are inferior in composition to natural breast milk.
- Compliance with the rules of oral hygiene. Otherwise, pathogenic bacteria will multiply, leading to inflammation.
- Before the appearance of their first teeth, babies put small things into their mouths. You need to carefully ensure that toys are clean, otherwise germs will get into your mouth.
- If one of your relatives has bad teeth or inflammatory processes in the mouth, you should limit the baby’s communication with this person. Infants are much more difficult to tolerate various diseases, including those of the oral cavity.
- The baby should only have his own cups, spoons, plates, and towels.
Atrophic glossitis in children
Bald spots on a child's tongue always indicate serious health problems. In medicine, there is even a separate concept of a “bald” tongue, which means the appearance of bare areas of different sizes. There are many reasons for their occurrence, so it is better to entrust the diagnosis to an experienced specialist:
| Problems with the immune system or malfunction of the body | · insufficient amount of hemoglobin in the blood; · chronic or dysplastic anemia; · beriberi disease; · scurvy; · poor nutrition, diet incorrectly chosen by parents, vegetarianism. |
| Inflammation of tissues on the tongue | · allergic reactions to dyes in sweets or foods; · use of “adult” toothpaste with a high content of fluoride or mint oil; · constant consumption of carbonated drinks, citrus fruits, sour fruit drinks. |
| Consequences of serious illnesses | · psoriasis; Allergy to antibiotics or certain medications; Dehydration after flu or diarrhea; · intestinal diseases. |
Bald spots on the tongue are almost impossible to get rid of. Such bald spots occur due to atrophic destruction of taste buds. Normally, it is the papillae that create an even texture and velvety surface and react to hot food by changing color. After dying, a smooth surface remains, which lasts for many years. Such children are less able to distinguish the tastes of foods and get less pleasure from food.
Treatment methods
After determining the reasons for the appearance of dots on the tongue and assessing all the features of the clinical picture, appropriate treatment is prescribed:
- Infectious diseases require local or general antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral therapy (taking into account the type of pathogen identified and its sensitivity to the selected drugs). The list of medicines may include Levomycetin, Clotrimazole, Acyclovir, Cholisal and others. In addition, local treatment of the oral cavity with antimicrobial and/or antiseptic drugs (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Tantum Verde spray or rinse solution, hydrogen peroxy, oxolinic ointment, etc.) is mandatory.
- For stomatitis of allergic origin, drugs with antihistamine action are prescribed (Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin, etc.).
- Treatment of nevus on the tongue is carried out only surgically. The mole is removed by laser, electrocoagulation, cryodestructive or any other method at the discretion of the doctor.
In case of complicated diseases of the oral cavity and tongue, or if the appearance of spots on the tongue is the result of some other disease (angina, intestinal dysbiosis, etc.), treatment is carried out jointly by specialists in the field of dentistry, otolaryngology, therapy or other medical fields.
Causes of redness on the tongue
The most common red spot on a child's tongue. This is a common symptom of many oral inflammations or infectious diseases. First of all, you should rule out an allergic reaction to foods or medications.
In some children, it manifests itself in a sharp rush of blood to the mucous membranes, the appearance of redness on the gums or palate. Sometimes color changes are caused by dyes contained in candies or juices.
Most often, such red or pinkish spots on the tongue occur for the following reasons:
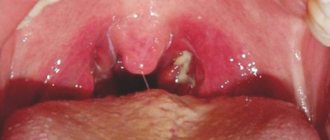
- Scarlet fever : accompanied by high fever and swelling, an increase in organ volume. It is difficult for the child to swallow, redness gradually spreads to the larynx, spasms and other unpleasant symptoms occur.
- Herpetic sore throat : rashes affect all mucous membranes and often cover the middle part of the tongue. Small dots fill with inflammatory fluid and burst after ripening. In their place, areas resembling a burn remain.
- Intestinal diseases : they are characterized by red spots on the root of the child’s tongue. The cause may be chronic dysbiosis, constipation, colitis or other disorders of the digestive system.
- Aphthous stomatitis : redness is the most pronounced and striking symptom along with rash and burning sensation in the mouth.
Sometimes the red spots are so pronounced that the doctor uses the term “geographic tongue.” It is necessary to begin treatment of the underlying disease as quickly as possible. After recovery, taste buds are gradually restored and acquire a natural shade.
Common causes
In certain cases, it is customary to separate pathology from the norm. Slight light spots may indicate mild dehydration or digestive problems. Moreover, such a manifestation should occur without disturbing the general condition and pain syndrome.
But if the problem does not disappear after a few days, then you should think about serious illnesses, even in the absence of general symptoms. Conventionally, all diseases that cause white spots on the tongue can be divided into 2 groups:
With a favorable prognosis:
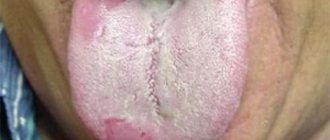
- Dehydration. Causes dry mouth and temporary white spots on the tongue, or rather a coating, which will disappear if you start drinking enough water. Medical assistance is not required in this case. But the white spots should not have a fuzzy texture or be enlarged in volume.
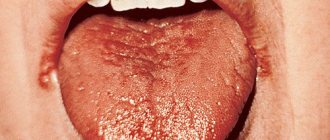
- Lack of oral hygiene. In this case, the tongue is covered with a thin white film - plaque. You can see this in children too, especially if they are still on dairy. You just need to clean your tongue and everything will be fine.
- Smokers' spots. Such changes are observed with excessive and long-term tobacco consumption. This occurs due to irritation of soft tissues. The affected areas appear denser and can sometimes become elevated. When you quit smoking, after a while everything returns to normal. But with prolonged exposure, the development of oncology directly under the formation is possible.
- ARVI, flu. Many people develop plaque in the form of spots a day or even a few hours before the onset of symptoms of these diseases. They may be subtle. Sometimes even the formation of blisters and pustules is observed.
- Pathologies of the spleen. Usually they are localized on the left side of the tongue. This may indicate spleen disease. So are the irregularities in her work.
- Gastrointestinal problems. In this case, the morphological formation is localized in the middle of the tongue. Indicates diseases of the liver or pancreas. With gastritis, a white coating is more often observed.
- Infectious diseases of the body.
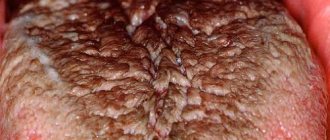
- Geographical language. These are inflammatory changes that can be caused by various factors, including the above-mentioned problems with the spleen, gastrointestinal tract, ARVI, as well as those associated with the circulatory and endocrine systems, acute infectious diseases and others. More often, the pathology manifests itself in the form of redness, around which a white rim (flaking tissue) forms.
- Stomatitis of various etiologies. They usually appear in a generalized manner, affecting, among other things, the mucous membrane of the tongue. In addition to spots, erosions, ulcers, blisters and pustules are observed.
- Taking certain medications. Long-term use (especially longer than prescribed) of antibiotics can also lead to the development of white spots on the tongue due to the death of beneficial bacteria on it. In addition, the formation can be caused by the use of steroid inhalers, immunosuppressants, alcohol-based mouthwashes, and creams.
With a cautious forecast:
- Candidiasis (thrush). A fungal disease caused by the yeast Candida Albicans, which is more often found on the genitals of women (less often than men). It appears as gray-white or yellowish spots on the tongue, tonsils or other parts of the mouth. The impetus for development is the deterioration of immunity due to taking antibiotics, chemotherapy, diabetes, etc. This is a relatively simple infection; the main thing is to contact a specialist in time to prevent the disease from developing into a more severe form.
- Leukoplakia. It appears as scattered white spots, or rather even plaques, due to the rapid growth of cells on the tongue or gums, which are often painful. The pathology is not always dangerous, but it is serious, as it is often an early form of cancer. It occurs in people who abuse tobacco, alcohol, and prefer too spicy and hot foods. The disease has several forms, but white spots most often appear with leukoplakia plana. They have varying transparency with diffuse boundaries.
- Lichen planus. This is a fairly common disease. Although from the name it may seem that the formations should be of a different color, in the oral cavity it often appears in the form of light spots. The disease has six clinical forms. When white spots appear, there are no other symptoms. Only in the case of erosions does the symptomatology increase sharply - a burning sensation and feelings of discomfort appear. This is a long-term immune system disorder (chronic), so white lacy stripes and spots in the mouth, including on the tongue, appear periodically in different places.
- Atrophic glossitis. Diagnosed in 1-3% of the population. Although red spots appear (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue), sometimes they can be subjectively called white, since there may be a light coating. The origin of the disease is unknown. Doctors tend to consider the psychosomatic nature of the occurrence of pathology. The spots are extensive, red in the center with a white border around the periphery.
- Decreased immunity.
- Occupational hazards.
- Chronic mechanical injury.
Such conditions require increased attention from doctors and the patient himself. It is necessary to eliminate the causes of these problems as quickly as possible.
The most serious:
HIV and AIDS. Symptoms may not be noticeable for many years before beginning to appear as white or other unusual patches on the tongue, other parts of the mouth or throat, enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits and neck, spots under the skin, eyelids, and nose. Other subsequent complications include neurological disorders such as memory loss, depression after severe brain damage.
Syphilis. In some cases, it can also cause light-colored lesions on the tongue, although more often it manifests itself in the form of fairly deep ulcers. Without treatment, it can have the most dire consequences.
Oral cancer. Risk groups include smokers, alcoholics and patients with human papillomavirus (HPV). It may begin as one or more white spots on or under the tongue, progressing to a painful, non-healing ulcer.
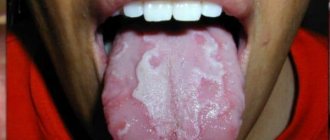
View photos of white spots on the tongue with description
A white coating on the tongue may be a result of poor hygiene or dehydration.
Small white dots are inflamed papillae. This condition is called tongue papillitis. The cause is usually trauma (burn, mechanical damage)
Candidiasis on the tongue - fungal infection
Stomatitis in the form of a light ulcer
Geographic tongue, which appears as redness surrounded by white stripes
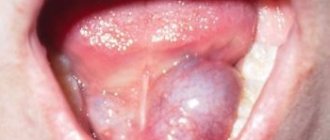
An unknown benign viral infection that appears as spots under the tongue. There are many infections that can lead to lesions in the mouth
Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue for various reasons. But these are more likely red spots accompanied by a light coating
The manifestation of syphilis in the form of light-colored formations. But more often this disease leads to the appearance of deep ulcers
Leukoplakia is an excessive growth of cells in the form of white spots that cannot be removed by scraping. May be an early form of cancer
Tongue cancer
Lichen planus on the tongue. In the right photo there is a child, which is very rare
White spots as a sign of stomatitis
A change in the color of the mucous membranes in some areas should alert attentive parents. White spots on the tongue, inside of the cheeks or lips are a clear symptom of candidal stomatitis. Fungal disease occurs in every second child under the age of 3 years. Gradually, the inflammation increases and merges into a homogeneous plaque, reminiscent of a film on milk. When you try to remove it with your finger, painful bright red ulcers are exposed.
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
If white spots and plaque have just appeared, the baby’s mouth and lips can be treated with a solution based on baking soda, and the tongue can be wiped with antiseptics:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Stomatophyte;
- Fukortsin;
- Betadine.
After the procedure, it is necessary to soak all ulcers and redness with Candide, 1% tannin or Nystatin ointment. They have a pronounced antifungal effect and stop the growth of pathogen colonies.
In more advanced situations, powerful antimycotics of the latest generation are used:
- Fluconazole;
- Flucytosine;
- Diflucan.
To reduce pain, wounds are lubricated with gels with an analgesic: Cholisal, Dentinox N, Dentol Baby. After an acute period, you can moisturize the surface of the tongue with Solcoseryl ointment. It heals the affected areas well, restores the functionality of the receptors and makes the surface smoother.
Parents should take care of strengthening the immune defense, review the diet in favor of healthy and nutritious dishes, and monitor the hygiene and cleanliness of the child’s toys.
What to do with all this
The most important thing that doctors (including Dr. Komarovsky) advise in such a situation is not to panic and try to treat the child with traditional methods or advice from the Internet. In any case, you should visit your pediatrician for an examination and possible further examination. This is especially true if the child complains of weakness and high temperature.
- The effect of food coloring. It is necessary to temporarily remove all coloring foods from the baby’s diet and everything will go away on its own and without a trace. To speed up this process, you can thoroughly clean the surface of the tongue with a soft toothbrush and continue to monitor the quality of your child’s oral hygiene.
- Plaque of fungal origin. You should not try to remove it. Treatment in such cases will consist of taking antifungal drugs in combination with treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions.
- Pathology of the digestive system. Elimination of the root cause leads to the rapid disappearance of any manifestations of black tongue. In the treatment of dysbiosis, eubiotic preparations (Linnex, Lacidofil, Bifidumbacterin and others) are good helpers, as well as following a gentle but rational diet.
- Hypovitaminosis. They are well corrected with complex vitamin preparations, with treatment with which all symptoms go away very quickly.
- Black hairy tongue. In this case, there is no specific therapy. This phenomenon most often goes away on its own. It is necessary to apply only preventive measures and treat the child’s oral cavity with antiseptic solutions.
Despite the fact that most often the causes of a black tongue in a child do not threaten his health, a visit to the pediatrician’s office should not be ignored. Only a specialist will help determine why such a problem appeared and how quickly it can be solved.
Hello, I would like to get a consultation from Dr. O.E. Komarovsky, I of course understand that the doctor is very busy, but hope, as they say, dies last, so I’ll take a risk.
My son, who turned one year old on December 22, 2013, noticed a month ago that his tongue had become black, although not all of it, but closer to the throat. Since we just had a routine annual medical examination, when we went to the ENT specialist I asked what it could be, the doctor replied that we needed to see a pediatrician and get a stool test.
On the same day, we went to an appointment with the local pediatrician, after listening to us, he looked at the tongue and said that he did not see any plaque on the tongue, I explained that the blackness on the tongue is mainly at the throat, and we must take into account that the child is small, he Doesn't let you see the tongue well. The doctor asked how the child was feeling, I replied that it was good, to which the doctor replied that he did not see any problems for concern, most likely the child had eaten something.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with 10 types of tongue glossitis with photos that will make everyone wary
I asked if I could clean off the plaque with a soda solution, the doctor said try it, and we left. At home, I cleaned off as much of the plaque as I could. However, since the plaque did not completely disappear, after three weeks, I again turned to the pediatrician with a request to prescribe a stool test for scatology. The analysis did not reveal any deviations.
Then I began to observe that our newly emerged upper teeth turned gray in places with black dots, the lower ones did not, I went to the dentist and explained that we periodically have a black coating on our tongue, to a greater or lesser extent, so perhaps the teeth turned gray from plaque. I would like to add that the color of the teeth began to change as soon as a black coating appeared on the tongue; before that, the teeth were white.
The dentist examined the child and said that perhaps he had a “hairy tongue,” and they began to brush his teeth with a brush and children’s toothpaste, but the teeth were still gray and remained that way. I would like to add that the child did not have any illnesses during this period and did not take any medications. My question to the doctor is that, has he encountered similar cases in his practice (our pediatrician, as I understand it, he has not) what a black coating on the tongue can mean, should we be worried, and what should we do?
Thank you in advance for your attention Doctor!
A child's black tongue does not look the best. Even a little creepy.
A child may turn black for completely peaceful reasons: he ate too much blueberries or blackberries, drank currant compote, etc. Moreover, food staining of the tongue black is caused not only by dark-colored food and drink.
Did you know that regular tomato juice, as well as taking certain medications, for example, activated carbon, can lead to dark coloration?
But all these cases are absolutely safe, the blackness disappears after a couple of days without a trace.
But if a child’s black tongue persists for a long time, there may be health problems that need to be treated.