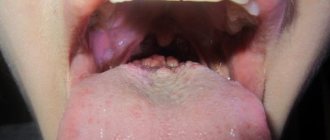
Why might a yellow coating appear on a child’s tongue?
Healthy children have a translucent coating on the tongue of a loose structure. If there is a change in color or density, you should consult a specialist, because the reasons can be quite serious.
More often, the tongue indicates problems in the digestive system
Parents should be alert to the following symptoms:
- maintaining yellowness on the tongue for a long time;
- changes in plaque parameters (increase in color intensity, size of the affected area, layer thickness);
- unpleasant odor from the mouth.
More often, the tongue indicates problems in the digestive system.
Characteristic manifestations can be supplemented by poor appetite, nausea, vomiting, as well as pain in the abdominal area.
When visiting a clinic, the doctor considers the presence of yellowness as one of the symptoms of the following diseases:
- jaundice (physiological in infants, hemolytic, hepatitis);
- poisoning;
- inflammations in the oral cavity of various types (stomatitis, caries, sore throat, gingivitis, glossitis);
- infectious diseases in which there is an increase in temperature;
- severe somatic pathology (diabetes, autoimmune processes, kidney disorders, etc.).
If yellowness is detected on the surface of the child’s tongue, in addition to consulting a pediatrician, the help of other specialists will be required.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of studies are carried out, and only on the basis of the collected tests is the true cause of the formation of yellow plaque on the mucous membrane determined.
Why it appears: reasons
There may be several reasons why a yellow coating appears on a baby’s tongue:
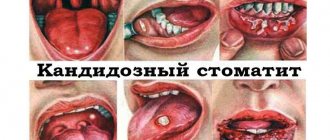
- fungal infection of the oral cavity. Thrush or candidiasis, caused by a fungus of the genus Candida, contributes to the appearance of whitish or yellow deposits that resemble a dense curdled mass;
- autoimmune diseases. They arise as a result of the destruction of the body’s tissues by the body’s own immune system and cause the appearance of many unpleasant symptoms;
- pathologies of the digestive system. Diseases of the stomach and intestines become one of the main reasons for the formation of a yellowish coating on the surface of the baby’s tongue;
- liver diseases. Pathological processes in the bile ducts lead to disruption of the exchange of bile pigment bilirubin, which causes staining of the tongue and skin;
- diabetes. At the initial stage, endocrine-metabolic disease is characterized by the appearance of a yellowish coating, restless behavior and poor weight gain;
- congenital yellowness of the skin and tongue. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the child’s body. Over time, the problem disappears;
- infectious diseases of the ENT organs. A sharp increase in body temperature causes cracking of the tongue and bleeding from small capillaries, which provokes the appearance of plaque;
- low-quality formula for feeding a newborn. Often affects the formation of white or yellow plaque and accompanies the little patient until the parents switch the baby to another formula;
- penetration into the child’s body of toxic substances present in the environment. Toxic substances can also enter the digestive system through mother’s milk;
- parasitic diseases. Toxins produced by helminths or giardia have a negative effect on the child’s body, causing the appearance of a dense yellow plaque.
One of the possible and most common reasons for the formation of yellow deposits in infants is the transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding.
Keep in mind! In this case, the symptom is temporary.
Danger
There is no need to worry when your tongue turns yellow in the following cases:
- Parents should be alerted to plaque that does not go away for a long time
when staining the mucous membranes and tissues in the oral cavity after consuming products with a coloring effect;
- if oral hygiene is not maintained;
- overeating food, in particular saturated fat;
- after taking medications.
This yellowness disappears after several procedures of cleaning the teeth and the mucous membrane with a special brush.
Parents should be alerted to plaque that does not go away for a long time, especially if other symptoms characteristic of the disease also appear.
This may be increased body temperature, nausea, gag reflex, frequent attacks of heartburn, decreased appetite, and abdominal pain. In this case, it is worth paying attention to the structure of the layer and its shade.
A thick, dense coating with a large localization zone and a green or dark brown tint does not bode well.
When examining the tongue, you can pay attention to the localization of the plaque.
Each place signals disturbances in the functioning of certain organs:
- if yellowness is concentrated on the back of the tongue, there is reason to suspect problems with the intestines;
- a yellow tip indicates a heart problem;
- an uneven plaque with cracks forms on the midline due to gastritis and ulcers;
- the extreme posterior points on the tongue indicate kidney dysfunction;
- coating of the front part and along the edges indicates diseases of the respiratory system;
- when diagnosing the spleen, yellowness is noted on the right, and liver problems are read on the left side;
- plaque over the entire surface with uneven coverage is a signal of decreased immunity.
Most common reasons
Let's look at the most common reasons for the appearance of a yellow coating on a child's tongue:
| Yellowness on a child 's tongue | ||
| Cause | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Overeating the night before | Unpleasant sensations in the stomach, heaviness, nausea, dry mouth, yellowish coating on the tongue | A gentle diet, drinking and rest are prescribed. In case of constipation, an enema is recommended. |
| Inflammatory process of the oral cavity | Plaques on the tonsils, formation of aphthae, ulcers. A pronounced yellow coating is localized at the tip of the tongue and in the middle. | Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to eliminate the cause. The plaque goes away as the child recovers with the help of daily oral hygiene. |
| Infectious diseases | High body temperature, vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding cracks in the tongue and yellow-brown coating | First of all, the cause of yellowness in the tongue is eliminated. To remove plaque, it is recommended to follow generally accepted rules of hygiene: brushing your teeth and oral mucosa twice a day, rinsing the cavity after each meal. |
| Jaundice | Yellowing is observed not only on the mucous membrane, but also on the skin and whites of the eyes. In addition, weakness, lethargy, and pain in the right hypochondrium are noted. The coating forms on the mucous membrane of the tip of the tongue and its frenulum, the shade is close to lemon. | A blood test and liver biopsy are performed to determine the exact cause of the disease. Drug treatment is prescribed individually, taking into account the nature of the origin of the disease. The drugs used are: Silibor, Sirepar, Silibinin, etc. Phototherapy is also carried out, and a diet is recommended. When an obstructive form is diagnosed, surgery is prescribed. |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Symptoms: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, pain in the duodenum, heartburn, bad breath. Light yellowness (white-yellow or gray-yellow coating), located in the central part of the tongue. | Conducting drug treatment using drugs: Chamomill, Dioscorea, Magnesia phosphorica, Colocynth, etc. In addition to drugs, a diet rich in minerals and vitamins is developed, and a food intake regimen is established. |
| Insufficient oral hygiene | Yellowness on the tongue, teeth and gums, plaque has a dense structure. | Daily brushing of teeth and the surface of the tongue with toothpaste using a scraper and brush, which is intended for mucous membranes. Mouth rinsing is recommended after every meal. |
| Somatic pathologies | There is intoxication, disruption of the body's metabolic functions and other symptoms characteristic of a particular disease. The tongue is covered with a yellow coating with a slightly brownish tint, localized in a dense layer over almost the entire surface of the tongue. | Patients are prescribed a medicinal course of treatment, which is supplemented by psychotherapeutic influence to regulate the mechanism of development of the disease. A diet is also being developed to strengthen the body’s immune system and saturate it with vitamins. |
Possible causes of a yellow coating on a child’s tongue
The most extensive group of infectious diseases that are characteristic of childhood is considered:
- diphtheria;
- scarlet fever;
- foot and mouth disease;
- whooping cough;
- cholera;
- dysentery, etc.
Yellowing of the oral mucosa can have a different origin; it is not possible to determine the exact cause at home, unless, of course, it is the consumption of food with a coloring effect.
You can assess the situation and prescribe treatment only by understanding why the plaque appeared, after taking tests and performing an ultrasound.
Treatment methods
Treatment for yellow plaque will depend on the cause of its appearance. You should not try to cope with the problem without the help of a specialist. If the plaque has arisen for its own reasons, then to eliminate it it is enough to eliminate the provoking factor: stop consuming certain foods, medications, and avoid overeating. Regardless of the reason, you must follow the recommendations:
- When eating food, do not rush, chew everything,
- stick to fractional meals,
- eliminate soda from your diet,
- reduce the consumption of hot and spicy foods,
- can't be handed over overnight
- monitor the temperature of the food you eat,
- brush 2 times a day not only your teeth, but also your gums, palate, tongue,
- rinse your mouth after every meal.
If the cause is pathological, treatment will involve the use of drug therapy and folk remedies.
Drug therapy
Depending on the cause of yellowing of the tongue, doctors recommend taking medications:
- If the outflow of bile is impaired, choleretic drugs are used: Hologon, Cholenzym, Deholil.
- For viral hepatitis - antiviral agents: Intron, Altevir.
- For fungal glossitis - antifungal agents: Fluconazole, Mykosit.
- For infectious diseases - antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Tetracycline, Levofloxacin.
- With increased tone of the bile ducts - antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Sorbitol.
- To restore hepatocytes - hepatoprotectors: Karsil, Essentiale, Hepatosan.
- In case of dehydration - 5% glucose solution and electrolyte solutions: Acesol, Chlosol.
- In case of poisoning - adsorbents: Enterosgel, Sorbex.
Medicines may be prescribed to relieve symptoms: pain, diarrhea, vomiting, heaviness.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?YesNo
To temporarily remove plaque, you can use the following means:
- Rinsing the mouth with a decoction of chamomile and sage.
- Using bee products helps get rid of bacteria.
- Taking an infusion of flax seeds helps normalize the activity of the gastrointestinal tract. You need to pour 20 grams of seeds with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for at least 5 hours.
- Rinsing with soda and eating solid foods can temporarily eliminate hard plaque.
- Drinking an infusion of corn silk helps normalize bile secretion. To prepare it, you need to pour 1 tablespoon of stigmas into 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 1 hour.
The products bring a positive effect, but for a few hours. To get rid of plaque, you need to eliminate the root cause.
To prevent plaque from occurring, you need to remember some rules:
- You need to teach your child to brush not only their teeth, but also their tongue. Modern toothbrushes are adapted to this. Bacteria will then not accumulate on the tongue, which means plaque will be avoided. Additionally, you need to use dental floss and an irrigator.
- You should not allow your child to eat a lot of fatty foods. Sweets in large quantities also negatively affect the digestive system.
- When the first symptoms of digestive system diseases appear, you should visit a doctor's office.
- Products containing dyes should be limited. This is especially true for sweet carbonated drinks.
By following simple rules, the appearance of yellow plaque can be avoided. Parents should monitor their child's diet very carefully.
Often plaque appears due to digestive problems. You should not allow your baby to eat junk food. A healthy diet will help protect your child from a yellow coating on the tongue.
With the birth of a child, parents try to control any changes in his behavior and well-being.
Therefore, even minor symptomatic manifestations in a baby can become a serious cause for concern.
A yellow coating on the tongue of a baby is a common phenomenon, indicating both diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, and the need to replace a formula that is not suitable for the baby.
Note! In order not to worry about the baby’s health, it is worth taking a closer look at the causes of the symptom.
Diagnostics
If a child has noticed a change in the color of the mucous membrane on the tongue, it is necessary to first exclude everyday incidents that led to this effect.
If a child has noticed a change in the color of the mucous membrane on the tongue, it is necessary to first exclude everyday incidents that led to such an effect.
It is impossible to eliminate dangerous situations on your own, so it is recommended to contact your local pediatrician.
After the examination, you may need to consult a dentist or gastroenterologist.
If severe somatic pathologies are detected, the child is referred to a specialized specialist (endocrinologist, hepatologist, nephrologist, hematologist).
To confirm or refute a preliminary diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- blood, stool and urine tests;
- a detailed biochemical blood test (for the level of glucose, bilirubin, ALT, AST, creatinine, urea, etc.);
- Ultrasound of organs involved in the functioning of the digestive system, and, if necessary, the abdominal cavity;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Vegetables and fruits that are yellow can cause your tongue to turn yellow.
Treatment
There is no need to treat yellow plaque without eliminating the causes that caused this effect. Therefore, after examination by a doctor (or several specialists), the patient is prescribed medication.
Since most of the causes are associated with disruption of the digestive system, in particular the correct outflow of bile, a series of studies are prescribed, based on the results of which treatment tactics are developed.
Therapeutic therapy is carried out in inpatient and outpatient settings. This issue can only be resolved by a specialist. In addition to medications, a dietary diet is recommended, including lean protein and vegetable foods.
Therapy is often enhanced with phototherapy, sanatorium treatment, and folk methods involving the use of decoctions based on medicinal herbs.
The following components are considered the most effective:
- bee products (propolis, honey);
- a decoction of sage and chamomile for rinsing the mouth;
- eating coarsely chopped vegetables (hard structure removes plaque).
Preventive measures
Measures to prevent the formation of yellowness on the tongue include the following recommendations:
- Daily oral hygiene will help avoid the appearance of unwanted plaque on the tongue.
Clean your teeth and oral cavity every day with a special scraper;
- Minimize consumption of products containing artificial or natural dyes;
- balance your diet by adding only healthy foods;
- minimize the consumption of carbonated drinks, black tea, coffee (although such drinks are generally not recommended for children);
- do not include smoked and fried dishes in the menu;
- do not overeat while eating;
- Regularly treat dishes and nipples for infants at high temperatures to kill bacteria.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of plaque on a child’s tongue, there are a number of preventive measures that many experts focus on:
- The room in which the child lives should always be clean, well ventilated and humidified.
- You should not prescribe antibiotics to your child yourself. The use of such medications must be strictly justified.
- It is necessary to closely monitor the baby's health. If the slightest symptoms appear that indicate a possible disease from the internal organs, you should urgently seek medical help.
- Limit your child's consumption of sweets containing synthetic coloring pigments: sweet carbonated drinks, candies, chewing gum. This will not only prevent the appearance of active staining of the tongue, but will also preserve the health of delicate children's teeth.
If plaque does appear on the tongue, there is no need to try to remove or treat it yourself. Consult your doctor about the possible causes of this phenomenon and the necessary treatment for it.
Posted in For parents by biglamed
Yellow coating on the tongue of a baby
The discovery of a yellow coating on the tongue of a baby should alert parents. This symptom often indicates a problem in the body. The location of a dense layer on the back part indicates jaundice, and if localized in the left half in the middle, suspicions fall on the liver.
One of the main reasons for discoloration of the oral mucosa of an infant is the accumulation of bacteria. The main number of them accumulates at the root of the tongue.
This localization is explained simply - during feeding, the front part is involved, while the back remains motionless, which eliminates its cleansing. It is easy to prevent the development of bacteriosis by following daily hygiene procedures.
But in any case, it is better to consult a doctor about yellowness so as not to waste precious time.
Signs of newborn jaundice
In a teenager
For a teenager, in addition to the reasons listed, there is another one related to the transition period. The growing up of boys and girls at this stage is accompanied by a hormonal surge. This effect does not have the best effect on the functionality of internal organs.
If the formation and outflow of bile is disrupted, yellowing of the tongue is observed. This symptom does not require treatment; it is enough to manage with hygiene procedures.
Based on the information presented, it should be noted that yellowness on the tongue should at least alert you. You should not rely on chance and wait until the problem disappears on its own. The child’s body is not yet strong enough to cope without the help of specialists.
What is a raid?
Microflora is always present on the tongue, and there is more of it on the back of the organ. If a person monitors hygiene and takes care of his oral cavity, then practically no plaque is observed. Normally, the tongue is pink and mobile, and taste buds are visible through the coating, if present. The surface and structure should be clearly visible. Light deposits are not a pathology, and their color and intensity vary depending on the climate, place of residence, season of the year, eating habits and even gender. For example, some increase in sediment intensity is normal during the hot season and is not something to worry about. Short-term staining of the tongue due to medication is also not dangerous. But if brushing your teeth is irregular, bad habits take place (especially smoking), then the plaque becomes thick and acquires an unpleasant odor due to the increased proliferation of bacteria. An unusual color of plaque, the inability to clean it, spots on the tongue indicate possible chronic diseases, infectious processes or parasitic infestation. Let's analyze the types of plaque by color and find out the reasons for the appearance of one or another type of deposit.
White-yellow coating on the tongue
The reasons for the appearance of light deposits with a yellowish tint are different:
- Chronic constipation - plaque is thick, dense, and has a repulsive odor.
- Gastrointestinal diseases (peptic ulcers, gastritis, colitis) - mainly the middle and root of the tongue are coated.
- Kidney pathology - plaque is located on the sides or in front.
- Infectious lesion - a coated tongue is accompanied by an increase in temperature and symptoms of intoxication.
- Jaundice and liver disease - predominantly yellow plaque. If there is stagnation of bile, the deposits may at times take on a greenish tint.
White-yellow coating on a child’s tongue
If you notice a build-up of mucous membranes in an infant, and the deposits are predominantly white, cheesy, and cannot be removed, then it is possible that this is candidiasis (thrush). Usually the inner parts of the cheeks are also affected, and the baby becomes capricious and restless.
Small pinpoint rashes are characteristic of stomatitis, and if the plaque is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition, fever, and spreads to the tonsils, the child most likely has an infection (scarlet fever, tonsillitis, flu, etc.).
For older children, changes in the color of the oral mucosa are more associated with poor hygiene and dietary disorders. Noticeable yellowishness may indicate stagnation of bile in a child; in this case, it is advisable to check the condition of the biliary tract. Also, yellow color is detected after long-term vitamin therapy.