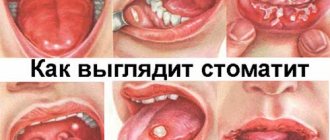
Associated symptoms
Plaque in the mouth, as well as pain during swallowing, is a symptom of many diseases.
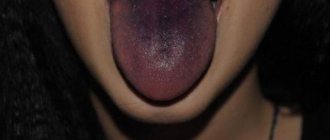
If a person has desquamative or geographic glossitis, his tongue is covered with a white or yellow layer with characteristic red specks. This disease indicates a high level of dysbiosis and other systemic disorders in the functioning of the body. This may also occur due to certain genetic changes or mutations. These symptoms may be caused by an allergic reaction to the presence of dentures or braces made of metal in the oral cavity. During wearing, a characteristic white tint appears on the oral mucosa and pimply spots.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MQPdS7IZ-xQ
A yellow tint to the tongue can be the result of the use of medications such as carboxylic acids, formaldehyde, antibiotics, various medicinal oils, as well as components of toothpastes and cosmetics.
Symptoms of pain can vary:
- Tingling sensations;
- Sharply increasing pain when swallowing;
- Conversation becomes very difficult;
- Difficulty swallowing (there are times when it is simply impossible to swallow);
- There are sensations of dryness and soreness in the throat;
- The lymph nodes are very enlarged;
- There are white spots in the throat on the tonsils;
- The voice becomes hoarse.
Infections that cause severe sore throat also have other nonspecific manifestations:
- Headache;
- Chills;
- Cough;
- Sneezing;
- Fever (the patient feels very cold);
- Body aches, joints and muscles twist.
Among the variety of manifestations characteristic of the described pathologies, common symptoms are noted. Among them:
- pain when swallowing saliva or food, as well as when talking;
- tingling in the throat;
- dryness and soreness;
- thirst;
- hoarseness or hoarseness of voice;
- violation of thermoregulation;
- cough;
- chilliness;
- pain in joints and muscles.
Clinical manifestations are observed separately, but their occurrence simultaneously is not excluded.
White coating in the throat
Healthy throat mucosa has a pinkish tint. The appearance of a white coating in the throat is not normal. First of all, this is a sign of an infectious disease. White plaque on the throat requires immediate analysis of the cause of the anomaly. It is equally important to take suitable preventive measures.
Causes of plaque
Most often, white spots form on the tonsils. The process of their occurrence is that when pathogenic bacteria penetrate the mucous membranes, the body’s susceptibility is triggered. The body's immune functions respond to the emerging danger and destroy the onset of bacteria, resulting in a white coating on the back of the throat.
It is important to understand the root causes of an emerging infection in time to obtain effective treatment. In this case, subsequent infection in the bronchi and lungs can be avoided.
The reasons may be the following:
1. Sore throat. In the case of this disease, white spots appear at the initial stage of the disease. The spots that appear may be yellow.
2. Hygienic reasons. A whitish film may appear due to non-compliance with hygienic rules for maintaining the oral cavity. After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth and brush your teeth.
3. Diphtheria. You may encounter the disease less often, but you shouldn’t rule it out. With this disease, the patient has a red throat with a white coating. The plaque is quite difficult to remove, so blood clots may be released. With the disease, an increase in temperature in an adult, swelling of the tonsils, and headaches are observed.
4. Leukoplakia. This type of plaque occurs in tobacco smokers. White spots are noticeable in the throat. The temperature does not rise. The spots are formed by dying mucosal cells. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. The reasons may be completely different.
5. Candidiasis. Children may have this disease due to weakened immunity. This type covers the entire oral cavity. A white coating appears in the throat and on the tonsils, but it does not bother the child at all.
6. Syphilis. It can be seen very rarely, but the disease should not be completely ruled out. White spots appear on the back wall of the throat. This symptom occurs already in the case of a severe stage of the disease.
7. Scarlet fever. With this disease, a white film appears on the larynx, but this is not the most unpleasant sign. Scarlet fever is accompanied by fever, pain in the head and throat. If this cause is identified in a timely manner, the multiplying bacteria can be quickly dealt with.
8. Stomatitis. White coating on the tongue occurs without an increase in body temperature. White plaque in a child’s throat appears with more severe symptoms. There is a significant increase in body temperature.
9. Pharyngitis. A white coating appears in the throat without fever. Painful sensations may occur. There is often pain when swallowing food.
There are many diseases that can cause whitish spots to appear. But the main reason is reduced human immunity.
Without an increased temperature, the symptom may occur for the following reasons:
after a burn or injury;
· along with the personal characteristics of the organism;
· with a fungal infection;
· at the initial stage of development of any infection.
Localization and specificity
Where can plaque concentrations most often be observed? The most favorite places for the location of white plaque are the recesses of the tonsils. It is in such folds that food debris and pathogenic microorganisms accumulate.
The proliferation of such microorganisms leads to the development of purulent processes and the appearance of white plaque.
Plaque can also appear on the tonsils themselves in the form of a cheesy mass.
If this plaque can be easily removed with a cotton swab, then the cause is the activity of a fungus.
In the case of a whitish coating on the back of the throat, the problem is pharyngitis. As the disease progresses, the entire surface of the oropharynx becomes infected. If the plaque is in the form of a whitish mesh, then this indicates an autoimmune process.
Causes of plaque on the tongue and redness of the throat
Everyone has long been accustomed to the normal, natural colors of the organs of the oral cavity, but what does it mean that a suddenly white or yellow coating on the tongue or a red throat means?
It is worth understanding when these phenomena are the norm for a person. Speaking of the tongue, plaque on it is basically just the remains of food that has not decomposed, as well as a consequence of the activity of microbes and bacteria in the mouth. The same thing happens when a small amount of protein residues is present in saliva.
It is white or yellow plaque that in the vast majority of cases is the cause of bad breath. If the composition of saliva or the ongoing biological processes are disturbed, a slow whitening of the oral mucosa begins to occur, in rare cases in the throat, after which pain often appears when swallowing.
The most common reason why plaque appears on the tongue is a problem with the internal organs involved in digestion. In particular, due to the development of certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, bile stagnation occurs, as a result of which gastric juice is released into the esophagus.
If the patient has visible redness of the throat and pain when swallowing, these are most likely signs of a developing sore throat.
Changes in the color of the surface of the tongue and throat indicate that the mucous membrane has a lot of bacteria that multiply rapidly and lead to disruption of metabolic processes.
The main causes of pain are:
- Inflammatory processes, including those caused by pathogenic microflora.
- Allergy. Allergens can cause pain, redness and swelling in the tongue area. Manifestations can be characterized by swelling, tearing, coughing, rashes on the body, even dizziness. In normal cases, an allergy produces the listed symptoms when the substance that causes the sensitivity reaction enters the body together with food, medications, toxic fumes or smoke. As a rule, to eliminate such discomfort, it is necessary to identify which allergen causes such a reaction and stop all contact with it.
- Injuries received. Minor injuries to the mouth and tongue area can be caused by eating spicy or very hard foods. They occur quite often. As a rule, they cause mild pain and go away on their own.
- Burns of the oral mucosa occur relatively often. When consuming very hot food or drinks, the surface layer of the mucous membrane is injured. This manifests itself as pain and burning of the tongue, in the mouth in the throat area. Such burns also go away quickly, thanks to the body’s ability to restore mucosal cells.
- Severe burns are much less common. This affects the area of the mouth, throat and walls of the esophagus. With such burns, the pain becomes unbearable and it becomes difficult to swallow. If a person is burned, they should drink a glass of cold water, take pain medication, and immediately visit the emergency room.
- Infectious diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis).
- Neoplasms.
- Mental and neurological disorders.
- Missing vitamins and iron in the body.
- Diseases of the pancreas and thyroid glands.
In the article about glossalgia, you can read what to do when your tongue is burned.
White plaque on the back of the throat and on the tonsils is a waste product of bacterial and fungal flora.
Most often we are talking about the following microorganisms:
- Staphylococcus. Especially the golden variety of pathogenic agent. Causes severe acute lesions of the oropharynx.
- Streptococcus. They cause sluggish forms of the disease with scanty manifestations.
- Fungi. Usually, the genus Candide. They provoke the appearance of a white cheesy coating in the throat.
- Atypical flora such as chlamydia and other structures.
The appearance of a whitish coating is not typical for a viral infection.
In extremely rare cases, we can talk about keratinization of the mucous membranes. Visually it looks like whitish spots, but in fact these are atypically changed epithelial cells.
We suggest you read: Which teeth grow first in children?
Angina
Also called acute tonsillitis, it is the most common disease with these symptoms. By its nature, this is an infectious-inflammatory process involving the tonsils and, partially, the soft palate.
In the chronic form of tonsillitis, a white coating on the throat of an adult forms on the tonsils themselves, and its presence in the area of the back wall of the pharynx is characteristic of the catarrhal form. However, this is not the only symptom of the disease.
Manifestations include intense burning pain in the throat area. The patient experiences problems with inhalation and exhalation, cannot swallow normally, and feels a foreign body in the upper respiratory tract.
All this is due to enlarged tonsils. Swelling of the larynx or even laryngospasm may develop. These conditions are fraught with the development of suffocation and mechanical asphyxia. A fatal outcome in such a situation is very likely.
In addition, hyperthermia occurs - an increase in body temperature. Usually up to 38-39 degrees Celsius. It occurs only in an acute process; the chronic phase of the pathology or streptococcal infection of the throat occurs without temperature or with a minimal increase in temperature.
The disease is most often caused by staphylococci and streptococci (pyogenic flora). White plaque is a waste product of bacterial agents.
Treatment is carried out using broad-spectrum antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiseptics in the form of solutions and other drugs.
Diphtheria
Develops mainly in children. Slightly less common in adults. These days it is extremely rare and only if the person was not vaccinated in his early years.
The disease is provoked by the diphtheria bacillus and is characterized by the appearance of a dense, grayish-white coating on the back wall of the pharynx and soft palate.
When you try to clean it off, intense bleeding appears; the exudate itself does not dissolve in water, which is a pathognomonic (characteristic) sign of the disease.
In addition to the appearance of plaque, severe pain is also observed in the oropharynx area, which intensifies when swallowing and talking. Regional lymph nodes (cervical) enlarge, and secondary lymphadenitis begins.
Objectively, upon examination, abnormally overgrown structures of the oropharynx, white plaque, looseness of the posterior pharyngeal wall, etc. are revealed. The temperature rises, symptoms of general intoxication and difficulty breathing are possible.
Treatment is specific, using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, bacteriophages and antiseptics.
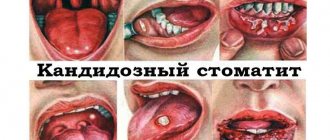
Candidiasis
Also called thrush. It most often appears in younger patients, especially infants. The throat has a white coating, especially the soft palate, the back wall of the pharynx, and the tonsils.
Also, exudate covers the entire oral cavity, cheeks, tongue, lips. As a rule, candidiasis in children is not accompanied by other symptoms. Plaque can be removed mechanically.
In adults, the disease is more severe, with the appearance of general symptoms: elevated body temperature, weakness, drowsiness and symptoms of intoxication of the body.
Pain in the throat is noted, the throat is red with a white coating, in rare cases there is suffocation, and an unpleasant sour odor from the mouth. This is due to the active proliferation of candida in the oral cavity.
The main reason for the development of the symptom lies in decreased immunity. To one degree or another, everyone is infected with fungi; they belong to the opportunistic flora. But not everyone gets sick.
Treatment must be systematic and comprehensive. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics to prevent secondary bacterial damage, antiseptic solutions, especially Miramistin, antimycotic agents and some other pharmaceuticals are used.
Pharyngomycosis
A close “relative” of candidiasis. By its nature it is an inflammatory lesion of the oropharynx and soft palate.
The velopharyngeal arch is covered with a white or grayish coating, which is cleaned off by mechanical action, as well as by lubrication with special antiseptic solutions.
It dissolves in water, so the volume may decrease when rinsing.
Pharyngomycosis is associated with pain in the throat when swallowing, voice disturbances, up to its complete disappearance. The anatomical structures of the respiratory tract are red, hyperemic, and swollen. Treatment is identical to candidiasis.
Stomatitis
It is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The pharynx may also be involved in the pathological process.
A white coating covers the throat without fever, appears on the soft palate and is characterized by painlessness and is difficult to remove mechanically.
A pathognomonic sign is the appearance of whitish or yellow ulcers on the mucous membranes. In the necrotic form, a gray exudate is formed, tissue decomposition appears on the soft palate, is characterized by painlessness, but is difficult to remove mechanically.
Treatment is required by a dentist. If the pharyngeal epithelium is involved in the pathogenic process, the help of an otolaryngologist will be required.
Therapy is carried out with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiseptics, antibiotics, antifungal drugs, and antiviral agents.
Stomatitis can be bacterial, fungal, or viral, which leads to many possible treatment options.
If a necrotic process occurs, specialized drugs are prescribed that accelerate the process of rejection of pathogenic tissues. For example, Dioxidin is suitable.
Syphilis
If your throat hurts and there is a white coating on the back wall, the cause may be syphilis.
This is extremely rare, but the development of the disease cannot be completely ruled out, especially with recent unprotected sexual intercourse of an oral-genital nature.
It is characterized by painlessness and the impossibility of mechanical removal. You need to be examined and detect accompanying symptoms, they are quite specific.
We suggest you read: Warts on the tongue: causes and treatment
It is a neoplastic process. Typically, leukoplakia affects the genitals, the oral cavity is an uncharacteristic localization of the pathological process.
White coating on the tongue with a sore throat – City Clinic No. 2 of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution of the Novosibirsk Region
- White coating on the tongue combined with a sore throat occurs for many reasons .
- The most common of them are bacterial and fungal infections of the oral cavity , but there are a number of other factors that provoke this condition.
- What accompanying symptoms may occur if there is a white coating on the tongue and in what cases should you consult a doctor?
Know! How is diagnosis carried out and what treatment methods are available depending on the causes of the pathology? We'll figure it out in the article.
Sore throat or not? What does white plaque on the tonsils mean?
White plaque on the tonsils indicates the accumulation of pus. In 80% of cases, this is observed after ARVI, tonsillitis or pharyngitis. The deposits themselves are not a pathology, but require immediate medical intervention.
When is it not worth worrying?
White plaque on the tonsils sometimes appears due to the consumption of fermented milk products. In this situation, it is enough to rinse your mouth and wash away the deposits.
Sometimes a person, in a hurry or through negligence, injures the tonsils themselves, or the nearby mucous membranes. This happens when he eats too hard food, drinks very hot drinks, or accidentally swallows a fish bone.
A strong immune system quickly copes with the damage, and the wound gradually heals.
Otherwise, suppuration develops, and the person requires prompt medical intervention.
Common Causes
The main reasons for the appearance of a white layer on the tonsils are presented in the table:
CauseDescriptionAdditional symptoms
| Acute tonsillitis (purulent tonsillitis) | Damage to the upper respiratory tract, characterized by the penetration of viruses or bacteria into the body. | White plaque with sore throat is combined with redness of the palatine arches. “Plugs”—caseous masses—appear inside the tonsils. A person has a severe sore throat, and the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. There is a soreness and burning sensation in the throat. The general temperature rises to 37-38 degrees. Against this background, there is severe pain in the joints and chills appear. |
| Pharyngitis | An inflammatory process affecting the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx. | White plaque on the tonsils is present on the left and right at the same time. It is accompanied by a feeling that a foreign object is stuck in the throat. This feeling intensifies during swallowing. Dry mouth appears, which is combined with a sensation of tickling, burning and soreness. The submandibular and occipital lymph nodes are enlarged. When you press them, a pain syndrome appears. |
| ARVI | A group of acute inflammatory pathologies of the respiratory system. Provocateurs are pneumotropic viruses. | White plaque on the tonsils is present on both one and both sides. Against the background of increased temperature, aches in the joints appear and headaches are present. There is a runny nose and a severe cough that does not go away for a long time. |
| Simanovsky-Vincent's tonsillitis (ulcerative membranous tonsillitis) | Acute inflammatory process affecting the palatine tonsils. The provocateur is the Plaut-Vincent wand. | The main symptom is a white coating on the tonsils with fever. It appears on the 3rd day of illness. After 4-5 days it peels off on its own. In its place, a specific spot appears, which looks like a crater-shaped ulcer with clear but uneven edges. The maxillary lymph nodes increase to 1.5 cm. Swallowing becomes difficult, there is a sore throat (usually on one side), and salivation increases. |
Source: https://clinica2.ru/otoskleroz/belyj-nalet-na-yazyke-pri-bolnom-gorle.html
Diagnostic methods
Differentiation of diseases necessary for choosing treatment tactics involves the following procedures:
- preliminary inspection;
- clinical and biochemical analysis of blood and urine;
- throat swab to rule out diphtheria and scarlet fever;
- X-rays of light;
- PCR test;
- serological studies.
A thorough examination of the patient allows us to make an objective diagnosis and prescribe an adequate course of therapy.
Based on the examination results and taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, the doctor prescribes:
- A course of antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics are used only for bacterial etiologies of the disease. Among the effective drugs in this group are Augmentin, Ciprofloxacin, Sumamed.
- Antiviral drugs. Their use is due to the viral origin of the disease. The most effective are Anaferon, Cycloferon, Isoprinosine.
- Antiseptics. Local use of sprays, rinses, and absorbable tablets helps eliminate pathogenic microflora. This is Doctor Mom, Strepsils, Chlorophyllipt.
- Antipyretic. The use of these drugs is recommended at temperatures above 38°. Nimesil, Panadol, Paracetamol are very popular.
- Rinse with medicinal preparations. Inhalipt, Rotokan, Lugol's solution are recognized as the best.
Oncological diseases require additional diagnosis and treatment using radiation therapy, chemotherapy or surgery.
If a white coating appears on the tongue, you should consult a dentist or gastroenterologist. The first specialist conducts a thorough examination of the oral cavity, the condition of the teeth, and palpates the lymph nodes. A gastroenterologist can refer you for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs or gastroduodenoscopy. It is also necessary to take a general blood, urine and stool test.
During the examination, the doctor may take a scraping from the tongue to identify the causative agent of the disease.
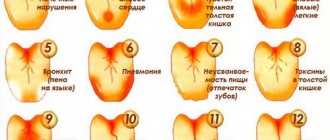
There are few methods for examining the tongue - mainly complaints and external examination. They begin studying the work by collecting complaints. Damage to the tongue is possible when the whole body suffers from dehydration, poisoning, with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer, gastroenteritis), cardiovascular (stroke, heart failure), central and peripheral nervous system (paralysis). The patient may complain of paresthesia, decreased mobility, or pain in the tongue.
When examining, pay attention to the condition of the mucous membrane - its moisture, color, the presence of damage or rashes, erosions, foci of hyperkeratosis, the severity of the papillae, the degree of mobility of the tongue, the presence of tooth marks on it.
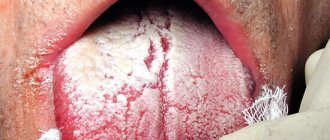
The tongue may have coating of different colors and severity. A white coating on the tongue in its middle third with cracks of different sizes most likely indicates damage to the gastrointestinal tract (gastroenteritis, ulcer). If plaque is found along the edges of the tongue on its anterior third, then most likely the person has a chronic pathology of the respiratory system (bronchitis, emphysema).
A yellow coating on the tongue may indicate damage to the digestive system, in particular the pancreas, liver and bile ducts. This color is given to it by breakdown products or bilirubin. A yellow coating on the tongue also occurs in healthy people who drink a lot of tea, coffee or smoke. In this case, the teeth also turn yellow, especially their back surface facing the tongue.
A brown coating on the tongue occurs with chronic alcohol abuse. The plaque acquires a greenish color when taking certain antibiotics, steroids and other drugs that suppress the immune system. Gray plaque indicates the ulcerative nature of the gastrointestinal tract lesion.
When to see a doctor
Indications for an immediate visit to an otolaryngologist are the following manifestations:
- intense sore throat;
- difficulty breathing;
- high temperature that does not decrease after taking antipyretics;
- the presence of purulent plaque on the tonsils;
- formation of ulcers on the tongue.
Pain in the throat and tongue clearly indicates that there is a malfunction in the body. These sensations do not arise on their own and, naturally, do not go away. Of course, many people have neither the time nor the desire to immediately rush to see a doctor.
The first thing you need to do is try to identify the causes of pain: these could be colds and allergic reactions, drinking alcohol and frequent smoking can also cause severe pain.
And if a person begins to develop cancer, there is no way to delay identifying the causes. Therefore, if pain does not go away within a few days, you should make an appointment with a doctor to identify the causes and prompt treatment.
There are a lot of diseases that occur in the area of the tongue and throat; they should be identified immediately. After all, if you ignore pain in the tongue, cracks in the tongue and ulcers will subsequently appear on it, and this, in turn, leads to the development of diseases such as measles, diphtheria, scarlet fever, etc.
For an appointment, you need to come to a therapist, and he will issue directions for various tests to identify the causes of the disease and, if necessary, refer you to another specialist.
Many patients complain of excessive sensitivity, discoloration of enamel and caries. Toothpaste with a filling effect does not thin the enamel, but, on the contrary, strengthens it as much as possible.
Thanks to hydroxyapatite, it firmly plugs microcracks on the enamel surface. The paste prevents early tooth decay. Effectively removes plaque and prevents the formation of caries. I recommend.
Specific examinations are carried out as prescribed by the treating specialist. First of all, it is recommended to consult a therapist.
He will help you decide on further diagnostic tactics and carry out routine activities, such as an initial examination of the pharynx, measuring body temperature, listening to lung sounds (perhaps this is a secondary process).
In the future, you need to contact specialized specialists:
- Otolaryngologist.
- To the dentist.
- Oncologist (for leukoplakia),
We suggest you read: How to clean plaque from cigarettes on teeth
At the initial consultation, any doctor conducts an oral survey of the patient regarding complaints. It is important to record all information for further analysis.
Next, the specialist collects anamnesis: finds out what the patient has suffered or is currently suffering from. It is especially important to establish the facts of the presence of chronic diseases of any type and nature and some others.
To make and verify the diagnosis, you will need to conduct a number of studies:
- General blood analysis. In the case of infectious lesions, it demonstrates an inflammatory process. It is indicated by leukocytosis, a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Biochemistry of venous blood. Alkaline phosphatase and some other indicators increase.
- Examination of the oral cavity, assessment of the condition of the pharynx (at appointments with the dentist and ENT doctor).
- Laryngoscopy. For an objective assessment of the condition of the larynx.
- Throat swab, plaque examination. Bacteriological culture and serological assessment are carried out.
- Biopsy of the leukoplakia area.
- Histological examination of cellular structures. It is also prescribed for hyperkeratosis.
It is not necessary to take all tests. In most situations, a visual examination and a throat swab are enough, since we are talking about tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
However, if the reason remains unclear, in addition to these examinations, the doctor may prescribe other manipulations.
What should not be done if pain occurs?
Sore throat and tongue are often accompanied by high fever, coughing, and sneezing.
What not to do if pain occurs:
- Delay in identifying the causes of severe pain.
- Self-medicate, because this will lead to failure.
- The use of any medicine is aimed at treating certain diseases, and there is no need to choose it based on advertising;
- The development of the disease provokes the proliferation of microbes, which can be suppressed by taking antibiotics, and only a doctor should choose them, because there are a huge number of them;
- Independent choice of medications will harm the entire body and, first of all, the liver;
- A medicine may not help if you choose it on the advice of friends, because each patient has his own symptoms and must be treated individually;
- Tablets will help relieve the symptoms of tickling and hoarseness for a short time, but they will not be able to get rid of the disease completely; only an experienced doctor can help eliminate these pains.
Is it possible to swallow your tongue
Date of publication: August 10, 2020. Category: Questions from the Internet.
Rating 4.36 [7 vote(s)]
The introductory part of the emergency medicine course states that when providing emergency care, you should open the person's mouth and grab his tongue with something, holding it, and in some cases even pinning it to his collar or lip,
to prevent the victim from swallowing the tongue. Then it is recommended to place an object in the victim’s mouth to prevent him from biting something on himself or you. But before you do this in an emergency, you should know: putting something in the mouth of someone having a seizure or convulsion is actually the worst thing you could do. Instead of helping, it will most likely cause injury to the tongue and mouth, make it difficult to breathe, and may cause suffocation.
However, the question remains: is it actually possible to swallow your tongue? To find out the answer, let's look at the anatomy of the mouth.
Inside it there is a key structure called the frenulum linguae. This mucous bridge is located in the front part of the oral cavity behind the teeth below and is attached to the tongue. If you lift your tongue up in front of a mirror, you will see your frenulum underneath it. At the front, it attaches the tongue to the gums, creating a fold called the sublingual papilla, which contains the salivary glands. The same bar runs down the midline of the lower part of the tongue and attaches it to the bottom of the mouth. This is especially important to note because it is at the bottom of the tongue that this structure holds the tongue in the desired position, unless a frenulectomy has previously been performed - surgery to completely remove the frenulum.
Whether you're doing handstands, skydiving, or performing circus tricks with your tongue, the frenulum will keep it attached to the bottom of your mouth. Your tongue will never be completely free, it will not be able to fall out or fall inside. This is an anchor forever. And for this reason you will not be able to swallow it.
However, sometimes the bridle does its job too well. Some babies are born with a condition called ankyloglossia, more commonly known as tongue-tied condition. The frenulum itself is small, moreover, very flexible and elastic, and in the case of ankyloglossia it has a denser structure and attaches the tongue too close to the floor of the oral cavity. Such a defect is not dangerous, but it creates some difficulties, limiting the mobility of the tongue: the baby cannot grasp the mother’s nipple tightly enough when breastfeeding or a bottle nipple, it is difficult for him to swallow, and at the stage of speech development, such a frenulum will prevent the child from pronouncing words normally.
In some children, this defect disappears on its own over time. Sometimes the conditions require a frenulotomy, a minor surgical procedure to cut the frenulum. The minute-long operation does not require hospitalization, special preparation or even pain relief, and after it children are advised to visit a speech therapist to correct speech defects. In order to reduce the consequences, surgery is recommended at an early age.
So is it possible to swallow your tongue? Not if it's still attached to your mouth! Theoretically, this is possible if you cut it off and then swallow it, but such a scene can only be seen in a gangster film.
Your tongue may be extremely flexible, but rest assured that it is securely secured in your mouth.
Prevention
In some cases, it is impossible to predict the appearance of a white coating on the tongue. However, there are general recommendations that will help reduce the likelihood of its formation:
- First of all, get rid of bad habits. It is very important to give up cigarettes and alcohol consumption;
- drink about two liters of clean drinking water every day. This will help improve your health and quickly eliminate toxins and waste accumulated in the body;
- undergo preventive examinations at the dentist, monitor the condition of your teeth;
- after eating food, use a mouthwash and clean your tongue with a toothbrush or scraper;
- carry out timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract, undergo examinations by a gastroenterologist;
- watch your diet, try to reduce your consumption of sweet, fatty and other unhealthy foods;
- Brush your teeth thoroughly at least twice a day. Find a toothpaste and mouthwash that's right for you.
Following simple recommendations will help prevent a sore throat and tongue from occurring:
- daily sanitation of the oral cavity and nose;
- feasible physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits.
An active lifestyle, a positive attitude and timely consultation with a doctor in case of any painful sensations, as well as strict adherence to his instructions, are the key to good health.