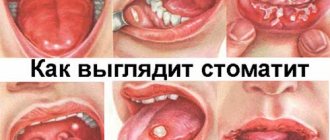
White plaque on the tonsils with fever and sore throat
Most often, white plaque on the tonsils, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, is associated with colds and infectious diseases (sore throat, acute respiratory infections, other infections).
Among various causes, advanced diseases, characteristic of a white coating without fever, are more often noted. Purulent tonsillitis, in fact, is tonsillitis in an advanced form. The main signs of the disease: fever, headache, lack of appetite, weakness, depression. The disease is difficult to treat, so it is easier to take preventive measures.
Let's look at the signs that differentiate a sore throat from tonsillitis.
In any case, it is better to start treatment in a timely manner rather than increase the chances of the acute process becoming chronic. You shouldn’t remove plaque yourself; it can make the problem worse. It is better to consult a specialist to avoid the disease becoming chronic and other complications.
Reference! The mouth and nasopharynx are entry points for pathogenic bacteria and microbes. Therefore, the presence of plaque on the oral mucosa in combination with temperature indicates an infectious disease. If you notice the first signs, in particular white plaque, you should urgently contact a pediatrician or otolaryngologist.
You should not ignore the appearance of white plaque on the tonsils; this fact in itself indicates some kind of health problem. Treatment is always more effective if it is provided in a timely manner in the early stages of the disease.
The absence of temperature is not the main sign of the inflammatory process, so there is no need to focus on this symptom.
Causes
White plaque on the larynx and tonsils appears due to the action of local immunity. The protective system is activated and begins to fight pathogenic microorganisms. If treatment is not started, the inflammation will go deeper, affecting the respiratory system.
White plaque in the throat of an adult without fever and with fever appears for the following reasons:
- Bacterial infections - pathogens usually affect the tonsils and oropharynx. Less commonly, the oral mucosa.
- Viruses - in this case, mucus forms on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and pharynx.
- Fungi - yeast-like microorganisms infect the pharynx. Activated due to weakened immunity.
Most often, whitish crusts appear due to exposure to staphylococci (especially aureus), streptococci, and Candida fungi.
Possible complications
If the disease is not treated and plaque on the tonsils is not removed, even if the adult or child does not have a fever, serious complications can occur. Severe infections, for example, diphtheria, can lead to the death of the patient. Incorrectly treated sore throat is fraught with negative consequences for various body systems and immunity.
Abscess in the throat
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3vIEdY3FRtc
When the throat hurts and a white coating appears on it, it becomes a source of infection that can penetrate the lower parts of the respiratory system, digestive organs, and through the bloodstream into any, even the most distant organ. If the pathology is not treated in time, in advanced cases the following complications are possible:
- Inflammation of the larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs.
- Development of otitis.
- Abscesses and mediastenitis in the pharynx are the spread of pus into deep tissues.
- Arthritis.
- Heart diseases.
- Kidney pathologies.
- Transition of the disease into a chronic form.
- With swelling of the larynx, the voice may become hoarse.
- Children may lose weight by refusing to eat if it hurts to swallow.
When the throat is red and very sore, a person immediately pays attention to it. In cases where there is no pain or fever, the pathology remains hidden, and while the patient does not notice it, it continues to negatively affect the immune system
Therefore, it is worth periodically examining the oral cavity in order to identify any violations in time and prevent dangerous consequences.
Localization and specificity
Where can plaque concentrations most often be observed? The most favorite places for the location of white plaque are the recesses of the tonsils. It is in such folds that food debris and pathogenic microorganisms accumulate. The proliferation of such microorganisms leads to the development
Plaque can also appear on the tonsils themselves in the form of a cheesy mass. If this plaque can be easily removed with a cotton swab, then the cause is the activity of a fungus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C0vU7E5Efnw
In the case of a whitish coating on the back of the throat, the problem is pharyngitis. As the disease progresses, the entire surface of the oropharynx becomes infected. If the plaque is in the form of a whitish mesh, then this indicates an autoimmune process.
If your throat is red
If a white formation occurs simultaneously with swelling and redness of the mucous membranes, this may be pathologies such as pharyngitis or tonsillitis. Pharyngitis is indicated by a white stripe on the back of the throat, and inflammation is noted.
At the very beginning, a sore throat with a white coating can be mistaken for a common cold, but the duration of the illness (more than seven days), high temperature and signs of general intoxication indicate a more serious cause of poor health.
Treatment
If the disease is caused by bacteria, your child may need antibiotics. Most often, treatment begins with antimicrobial agents of the penicillin group (“Augmentin”). If after three days there is no change in the child’s condition, the doctor may change the drug to a drug from another antimicrobial group, for example, a macrolide or a cephalosporin antibiotic. Treatment should be a course of treatment, minimum 5 days. If the baby feels better and the plaque begins to disappear before the end of the course of taking the drug, then treatment cannot be interrupted.
If the doctor determines that the plaque is the cause of a viral infection, he may recommend antiviral medications. Although their effectiveness has not been clinically proven to date. The most effective treatment will be associated with local treatment of the tonsils. To do this, use a balm, an antiseptic, and rinse with a furatsilin solution.
Fungal diseases in children are treated comprehensively - using local treatment and oral antifungal drugs. The drug is chosen depending on the type of fungus that is detected in the tests. A fungal infection can be cured completely and minimized only through early treatment, quick diagnosis and a fairly long course of medication - from 14 days. Then, after a short break, the course is usually repeated.
If the problem is an enlarged pharyngeal cavity, then the doctor will definitely determine the stage and degree of adenitis. The first degree does not require surgical intervention, grade 2 adenoids are a very individual situation. If breathing is not completely impaired, then the doctor will definitely take the opportunity and advise treating them at home. For grade 3 adenoids, they are usually removed. But since this is an important immune organ, any chance to preserve them is important for both the doctor and the child. An overgrown tonsil can be cut with a laser. This is the most gentle type of intervention.
Regardless of the reason that caused the appearance of white plaque, the child may be prescribed restorative and therapeutic physiotherapy during the recovery stage. This is heating, inhalation for non-bacterial and non-fungal diseases. The method of treating enlarged and inflamed tonsils with ultrasound has also proven effective.
The fact is that ultrasound has a surprisingly powerful effect on lymphoid tissue. It helps her recover, saturates her with oxygen, and helps her become more susceptible to medications. Before and after exposure to the sensor, the tonsils are washed, first with an antiseptic, and then with a solution prescribed by the doctor with a certain drug.
This method is not suitable for children whose disease is acutely infectious, but after recovery it will help to rehabilitate faster and restore the ability of the tonsils to maintain local immunity.
When does plaque really need to be removed?
In fact, a coating on the tongue after a sore throat requires some more or less serious measures only when it is caused by thrush and is, in fact, a symptom of a severe fungal infection. Here it is important to understand that you need to fight not with the plaque itself, but with the infection that caused it. If you do the opposite, the fight against the symptom will be endless, and all the results obtained will be temporary.
In fact, with thrush in the oral cavity (it is sometimes called fungal sore throat, if its main focus is in the pharynx), it is in the plaque that the largest number of microorganisms themselves that cause the infection are found. Consequently, in this case, it is the plaque and the tissues underneath that are subject to the most intensive treatment in order for the disease to be cured.
Severe candidiasis in an adult, requiring treatment with special drugs.
At the same time, the demand for treatment in this case is not always clear. For example, after the use of antibiotics, thrush develops very often as a side effect and ends without treatment when the microflora in the oral cavity normalizes. It often appears in young children due to an unformed microbiological background. In these cases, doctors often recommend doing nothing, since the microflora in the child’s mouth stabilizes on its own over time.
It is also useful to read: Why does your throat hurt after a sore throat or does it seem like something is bothering you, and what to do in such a situation?
But there are also cases when fungal sore throat and oral thrush actually require treatment. As a rule, this occurs in adults in whom the disease lasts long enough.
In any case, both the need for treatment and the procedure itself should be prescribed by a doctor who can accurately diagnose the cause of the plaque. This reason is extremely difficult to determine at home without appropriate preparation, and attempts to get rid of plaque “on a whim” can be not only useless, but also dangerous.
Treatment of white plaque on tonsils and tonsils
When plaque appears on the tonsils, both with and without pain, it should be taken into account that this is only a symptom. It will not be possible to get rid of it with solely symptomatic therapy; complete treatment of the disease is necessary, which includes:
- Antibacterial therapy for diphtheria, bacterial sore throat, stomatitis of bacterial origin.
- Antiviral therapy for acute respiratory infections, sore throats and stomatitis of viral origin.
- Antifungal therapy for pharyngomycosis or thrush.
- Rinsing with disinfecting solutions to remove film from the tonsils and oral cavity.
- Washing off the purulent film from the tonsils using a special syringe with a solution (this is how plaque is removed only in a hospital).
- Antipyretics for fever.
- Painkillers for severe pain in the tonsils.
- Immunomodulators.
- Maintain a gentle regimen for the throat: avoid spicy foods, loud and long conversations.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Taking multivitamins if you have a weak immune system.
It is prohibited to independently select medications to remove the accumulation of pus from the tonsils. At home, without diagnosis and consultation with a specialist, it is impossible to determine the type of pathogen, and therefore the direction of treatment.
Washing and rinsing
Washing of the tonsils is performed by specialists only on an outpatient basis.
The procedure requires special care to avoid injury to the tonsils. It is unpleasant and a little painful, so it is especially difficult to wash off the white coating from the child’s throat
There are also contraindications for this procedure: it cannot be done during pregnancy, cancer, severe hypertension, open tuberculosis, or disorders of the autonomic nervous system. But proper rinsing effectively clears a white throat for various causes of plaque.
Washing tonsils in the clinic
Rinses can be varied: from cheap home remedies (soda-salt solution, chamomile decoction, furatsilin solution) to expensive pharmaceutical ones. The main condition is the frequency of manipulations. If you wash the tonsils rarely, the effect will not be achieved, since within a few hours the pus accumulates again.
Regular, frequent rinsing (once an hour or as prescribed by a doctor) allows you to remove germs, food debris, and immune cells, which eliminates the formation of a favorable environment for the life of microorganisms. Your tonsils will become less red and painful.
Why is a sore throat dangerous?
Since the white film in the oral cavity is exclusively a bacterial and microbial formation, it is foolish to expect that its presence on the oral mucosa will not in any way affect the general health of a person. Therefore, when unusual whitish formations appear on the tonsils, you need to get rid of them at the first opportunity.
Plaque predisposes a person to illness and poor health. The immune system is directly dependent on the tonsils. Violation of their condition can provoke:
- cardiac and articular rheumatism;
- lung diseases;
- kidney disease;
- complications of the heart valves;
- inflammation of the ear, nose and throat;
- allergies.
The presence of filmy bacterial formations in the pharynx can cause the appearance of ulcers, ulcers, inflammation and painful irritation.
When the first complications appear, it is too late to do anything on your own and try to get rid of the disease using home methods. In this case, you need to make a serious and complex decision, since rinsing with herbs will no longer help. Due to the microbial component of the white plaque, a person can get bacterial poisoning, which is called tonsillogenic intoxication. This can cause complications such as muscle and joint pain.
It is for these reasons that it is important to promptly seek advice from your doctor, who will help you choose the right treatment.
Actions upon detection of plaque
If you notice a white coating, you should definitely call a doctor. Preferably at home, since it may be a symptom of a disease that is quite contagious, and therefore sitting in line at the clinic is a selfish and unreasonable position.
Trying to diagnose yourself will most likely lead nowhere. After all, an experienced doctor knows fifty shades of white that can characterize plaque in a particular disease. For mothers, a white coating is just a white coating; it is impossible to discern the nuances without knowledge, experience and practice.
Even a good doctor, in order to confirm his assumption about the true cause, will take samples of this very plaque from the child for laboratory analysis. Usually scrapings are taken from the tongue, cheeks, and back of the larynx.
A smear gives an accurate idea of the pathogen that caused the unpleasant symptom. This will make it possible to competently and accurately prescribe the necessary treatment.
Diseases of the tonsils in which plaque forms
Light plaque on the tonsils is observed in the following diseases:
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis;
- candidiasis;
- stomatitis.
All these diseases have one common cause - a decrease in immunity. The typical symptoms of each disease should be considered.
Tonsillitis
There is general weakness, lethargy and constant drowsiness
Sore throat is what people call tonsillitis. The disease can be acute or chronic, and inflammation of the tonsils occurs. Typical symptoms:
- white coating;
- redness and swelling;
- pain when swallowing;
- general malaise.
Tonsillitis can be unilateral or bilateral. In the first case, plaque and inflammation are observed only on one tonsil, in the second case, both organs are affected.
The acute form is accompanied by high fever, intoxication of the body and severe pain. Tonsillitis refers to inflammatory diseases of a bacterial nature.
Despite the severe symptoms, the acute form of the disease can be quickly and successfully treated with antibiotics and gargles. If the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations, there is a high risk of developing chronic tonsillitis. In this case, plaque on the tonsils is constantly observed. The abundance of microorganisms in the lacunae leads to the fact that the immune system ceases to cope with its function and “ignores” the inflamed area, as a result of which a permanent focus of infection appears in the human body. Over time, purulent plugs form in the gaps, bad breath appears, and the person constantly feels discomfort in the throat.
The problem with chronic tonsillitis is that it is very difficult to cure. The disease often worsens, medications are of little help, so the patient may be advised to have his tonsils removed.
Pharyngitis
No sputum when coughing
Pharyngitis is an “occupational” disease of smokers. The disease also occurs due to inhalation of air that is too hot or too cold.
Typical symptoms:
- redness and inflammation of the pharynx;
- sore throat;
- hoarseness of voice;
- dry cough;
- plaque on the tonsils;
- temperature is within 37.5-38 degrees.
The plaque is slightly expressed and appears due to the lack of timely treatment. Doctors call a sore throat the first symptom of the disease.
There is no high temperature with acute pharyngitis, the maximum is 38 degrees.
If the disease is not treated, it becomes chronic. The plaque on the tonsils becomes more pronounced, the patient feels constant dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa and discomfort when swallowing.
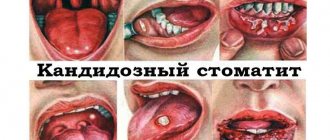
Candidiasis
Abundant thick plaque on the tonsils without fever in an adult or child is a typical symptom of candidiasis, or oral thrush. The cause of the disease is infection of the mucous membrane with a fungus of the genus Candida. This occurs against a background of decreased immunity due to long-term use of antibiotics or corticosteroids.
A typical symptom is a thick yellowish coating on the tonsils and tongue, which can be easily cleaned off with a cotton swab. True, after an hour, a thick coating appears on the cleaned area again. With candidiasis, you may feel a slight irritation of the throat and dryness, but there is no severe pain or soreness.
Stomatitis
The disease is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. Often develops due to advanced caries. It is quite difficult to distinguish stomatitis from tonsillitis. The only sure sign is the presence of ulcers or wounds on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips. In general, plaque on the tonsils is an exception rather than a typical symptom of stomatitis, and occurs only if the disease is left untreated.
Symptoms are moderate, body temperature does not rise. Pain is generally absent, but appears when swallowing. Discomfort may also occur when eating hot or hard foods.
White plaque in an adult
A white formation in the throat without fever is a sign of the initial stage of a sore throat, the presence of a fungal infection, stomatitis, a burn or a common injury.
With stomatitis, white spots appear on the palate, tongue, and inside of the cheeks. With advanced disease, the white formation can spread to the throat area.
A white coating on the throat with fever in most cases indicates inflammation of the tonsils or pharyngitis. If the separation of the gray-white plaque is difficult and is accompanied by bleeding, this is a sure sign of diphtheria.
The appearance of a white coating without pain may be one of the manifestations of thrush. Additionally, you can recognize it by bad breath. The process is not dangerous, but causes psychological discomfort.
Smokers often develop white plaques in the throat. They are not dangerous in themselves, but if ignored they can develop into cancer.?
Methods of therapy
Antibiotics
For a sore throat that occurs without fever, or for chronic tonsillitis, it is necessary to take antibiotics to help cope with pathogenic bacteria. Antibiotics must destroy streptococci, and must be prescribed only by a doctor.
Washing
This procedure is an effective and simple (albeit quite unpleasant) measure for removing white plaque from the mouth. It is performed on an outpatient basis and involves mechanical washing out of plaque with a special solution.
The manipulation is carried out using a syringe with a tip. Children especially do not like this procedure, as it can sometimes be painful. It should be noted that rinsing is best used as one of the methods of complex treatment, and not as the only method. Find out more about vacuum rinsing of tonsils. The contents of this article will help.
Rinse
One of the mandatory methods of complex treatment of inflammation of the tonsils. This method perfectly washes out pus and plaque from the oral cavity, thereby speeding up recovery.
And the antibacterial components that are part of rinse solutions help destroy pathogens. The following components can be considered for preparing solutions:
- iodine;
- medicinal herbs;
- Furacilin.
- Soda. Rinsing with soda is good because this method perfectly “pulls out” pus from the surface of the tonsils.
But how to rinse the nasopharynx during inflammation and how to do it correctly is described in great detail in this article.
It is better to rinse more often: at least 10 times a day. If this condition is met, recovery will not take long. In addition to the methods listed above, special sprays for irrigating the throat are also a good option as an additional treatment.
If the cause of plaque is candidiasis, then rinsing with soda while taking antifungal medications helps.
When diagnosed with leukoplakia, competent and timely treatment is especially important due to the risk of developing cancer. But only a doctor should prescribe suitable therapy: in this case, it is especially dangerous to self-medicate
Causes of plaque on the tonsils
If there is a white coating on the tonsils, the absence of temperature is more alarming than pleasing. With fever, the cause is usually standard colds, but without it, the diagnosis is usually more difficult. And the causes of this symptom can be much more diverse and much more dangerous.
Purulent formations on the surface of the tonsils are a protective reaction of the body. These formations represent an accumulation of the results of the immune system’s fight against viruses. White plaque is usually located in the most inaccessible places of the tonsils, where it is most convenient for microbes to hide and multiply.
Often, having discovered a similar phenomenon in their throat, people usually decide that they have a sore throat. Although in fact there can be quite a few reasons for white plaque without fever, and a special type of sore throat is only one of them. Let's find out why white plaque appears on the tonsils in the absence of fever.
Angina Simanovsky-Vincent
This is the so-called atypical tonsillitis. Occurs less frequently than usual. With this type of disease there is almost never a high temperature, but a white coating on the tonsils is present.
This disease is also accompanied by a particularly fetid, putrid odor from the mouth. This type of sore throat is caused by bacteria and pathogenic bacilli that are spread by airborne droplets.
You may also be interested in the causes of purulent plugs.
Dental problems
If a person has advanced periodontal disease or equally advanced caries, then these diseases may well manifest themselves as small whitish ulcers on the oral mucosa. But this problem can be solved quite quickly - it is enough to simply eliminate the “dental” cause that gave rise to these manifestations. By the way, the level of immunity plays a significant role in this case.
If your immunity is “at its best,” then with any dental problems, ulcers are unlikely to appear. But when the body’s defenses are weak, this phenomenon occurs.
Chronic tonsillitis
In this case, a white coating on the tonsils will almost always be observed. If the disease is not in the acute stage, then there will be no fever.
Stomatitis
This disease is more common in children, however, in rare cases (if immunity is very low) it also occurs in adults. There is no temperature, but a white, sometimes quite abundant, coating is visible on the oral mucosa, including the tonsils.
Candidiasis
The disease is popularly called thrush. In this case, the white plaque in the mouth is caused by yeast-like fungi. They multiply very quickly, and in record time the oral mucosa, along with the tonsils and tongue, can be covered with a coating resembling cottage cheese.
It should be noted that this disease (pharyngomycosis) often occurs due to improper use of antibiotic medications. If you are used to swallowing antibiotics whenever you sneeze, then you are at risk. In addition to this reason, a child may also develop oral thrush due to neglect of hygiene rules.
Read how to treat chronic tonsillitis in adults here.
Pharyngitis, acute respiratory infection
These common diseases in chronic form can also manifest themselves as a white coating on the tonsils in the absence of fever.
Cysts in the nose and throat
Here, although outwardly the manifestations look like a white dotted plaque, however, these are actually compactions from overgrown soft tissue of the tonsil mucosa. They are not caused by viruses and bacteria, so they do not contain infections.
However, these formations make it difficult to swallow fully and create a sensation of soreness and a lump in the throat.
Trauma or burn
Sometimes the tonsils or mucous membranes next to them are injured or burned by too hot food/drinks.
Tissues can be injured by a fish bone, for example, or a hard cracker.
If the immune system is good, then the person will not even notice such an injury - the wound will quickly heal. But if your health fails, then the wound may begin to fester.
Leukoplakia
One of the most serious and requiring special attention causes of plaque. In this case, the plaque is the keratinized upper tissue of the tonsils. In addition, pus appears in the oral cavity and ulcers form. This symptom may indicate the first stage of cancer development.
Leftovers
Sometimes, after drinking fermented milk drinks, a whitish coating appears in the mouth. To get rid of it, you just need to rinse your mouth thoroughly. If the plaque has not gone away, then the reason is more serious.
How to overcome the disease?
If a child has a sore throat and a white coating appears on the tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor. Before the doctor’s visit, you can ease the well-being of your son or daughter using available means. For redness of the pharynx, the following help well:
- rinsing with chamomile infusion and a water-salt solution - soothe irritated mucous membranes, stop the inflammatory process, and have a softening effect;
- Drinking plenty of fluids prevents dehydration, normalizes water balance, and helps remove toxins from the body.
White plaque on the tongue is removed with a toothbrush. Drinking also helps reduce the amount of buildup. You can cope with a sore throat using ordinary vegetable oil. One teaspoon of liquid at room temperature should be given to the child to hold in the mouth and then swallow.
Medicinal preparations for rinsing
Despite the fact that you can remove ulcers by rinsing your throat with plain water, it is best to use special means for this purpose. Thanks to this, it is possible to achieve a triple effect in 1 time. Not only remove plaque, but also have a healing effect on the mucous membrane of the throat and a destructive effect on the causative agent of the disease.
The most popular and effective means for rinsing the larynx when pus occurs on the tonsils:
- Potassium permanganate solution. To prepare it, you need to dilute several grains of potassium permanganate in 1 glass of warm water. It is advisable to strain the liquid so that the remaining crystals do not damage the mucous membrane of the throat. You need to rinse your larynx 3-4 times a day, each time preparing a new remedy.
- 1% boric acid solution. To prepare the medicine, you need to dilute 2.5 g of dry powder in 1 glass of warm water. Mix the product well and use for rinsing 3-5 times a day. The medicine has pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, creating unfavorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and promoting a speedy recovery of the patient.
- Saline solution. The most popular gargle for sore throat. To prepare it, you need to dilute 1 tsp. salt and soda in 1 glass of warm water. In order to enhance the therapeutic effect, it is necessary to add a few drops of iodine, a known antiseptic. The product has an anti-inflammatory, disinfectant, and wound-healing effect. The medicine must be used 3-4 times a day, alternating with the use of other medicines.
- Furacilin solution. Has antimicrobial and antiseptic effects. To gargle, dilute 1 tablet of medication in 200 ml of warm water. First you need to crush it well so that there are no small crystals left. Use the product 2-4 times a day, depending on the patient’s well-being.
- Gargling with chlorophyllipt shows good results. This is a natural medicine that contains eucalyptus and myrtle. The effectiveness of the drug is due to its healing properties: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, regenerating, antihypoxic and immunostimulating. An additional advantage of this product is its antipyrogenic properties, due to which the formation of pus and mucus is reduced, and the accumulations present are quickly removed from the body. To gargle, you need to prepare the following composition: dilute 1 tsp. chlorophyllipt solution in a glass of warm water. The frequency of the procedure is 2-3 sessions per day.
- "Stopangin." It has an antiseptic, enveloping and analgesic effect. For rinsing, it is used in its pure form and does not require additional dilution. The frequency of use is from 2 to 4 times a day.
- 0.05% chlorhexidine solution. This drug is a well-known antiseptic. To enhance the effectiveness of the medicine, it is necessary to brush your teeth well and rinse your mouth with ordinary boiled water before using it. The rinsing procedure with chlorhexidine should be done for 20-30 seconds, after which the solution should be spat out. Under no circumstances should it be swallowed. It is not advisable to eat food for 2 hours after the procedure.
To remove pus from the tonsils, you cannot indiscriminately use all kinds of medications. Some drugs may do more harm than good. For example, Lugol's solution and Inhalipt have increased viscosity, as a result of which the discharge of purulent accumulations from the tonsils slows down.
How to remove white plaque on the tonsils?
The main methods are washing and rinsing.
The washing procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis. The doctor washes out the white deposits using a syringe with a special tip.
You cannot remove plaque at home if it is accompanied by the appearance of specific symptoms. If its appearance is not associated with the development of a particular disease, it disappears within a few hours.
The product has a strong antibacterial effect and helps destroy pathogenic organisms. The optimal number of procedures is 2-3/24 hours. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the clinical picture.
Oral and local use of medications is recommended.
Should be taken orally:
- Nystatin. The main effects are antifungal, fungistatic;
- Fluconazole. Triazole antifungal drug is a powerful selective inhibitor of sterol synthesis in fungal cells;
- Levorin. Antibiotic with polyene structure. Has a fungicidal effect.
Miconazole gel, levorin and nystatin ointments are used locally.
Considering that it appeared due to the activity of bacterial flora, the doctor prescribes antibiotics to the patient:
- Isofra. Belongs to the group of aminoglycosides. The main component is framycetin sulfate. Effect: bactericidal, antibacterial, broad spectrum antibacterial.
- Azithromycin. Belongs to the group of macrolides and azalides. Has a broad spectrum antibacterial effect.
During the period of treatment you should avoid eating hard, spicy and hot foods. You need to drink more liquids, giving preference to weak tea, chicken broth, warm compotes and fruit drinks.
Treatment of bacterial sore throat
The antibiotics of first choice in the treatment of sore throat are penicillins, for example, Amoxiclav. This drug contains the antibiotic amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, which prevents the development of bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. The course of treatment for sore throat with Amoxiclav is 10-14 days.
There is no need to purposefully remove plaque from the inflamed tonsils - with the correct selection of antibiotics, it disappears on its own within 5-7 days.
To speed up the process of clearing the tonsils, it is recommended to gargle. For this purpose, you can use an aqueous solution of soda (1 teaspoon per glass of warm water). Soda acts like a mucolytic, thinning mucus and promoting its removal. In addition, baking soda has an antifungal effect. A good therapeutic effect is achieved by adding antiseptics to water - tinctures of propolis, chlorophyllipt, eucalyptus essential oil, decoctions of medicinal plants (calendula, chamomile, pine buds, etc.).
Diagnostics
Not many pathological conditions can cause the appearance of a layer on the tonsils, which is why an experienced specialist will not have difficulty establishing the correct diagnosis. The exception is plaque on the tonsils without fever.
Palpation of cervical lymph nodes
- conducting a detailed survey of the patient or his parents - to obtain a complete clinical picture for the clinician. It is necessary to inform the doctor about the first time of onset and intensity of symptoms;
- the doctor's examination of the patient's medical history and life history - this is necessary to search for predisposing factors;
- palpation of the neck - to identify enlarged lymph nodes;
- examination of the throat using special ENT instruments;
- laboratory blood tests will indicate the occurrence of a pathological process in the body;
- taking a smear from the tonsils for subsequent bacterial culture;
- PCR - to detect the pathogen that could cause the appearance of a pathological layer on the tonsils.
Only after the otolaryngologist has familiarized himself with the results of all examinations, can he prescribe an individual tactic on how to remove plaque from the tonsils.
To determine whether you have this symptom, you need to look into the mirror opposite the light source with your mouth wide open. If there is a film on the tonsils and the back of the throat, you need to go to the doctor. When contacting an otolaryngologist to make a correct diagnosis, the following examinations may be necessary:
- Studying the medical history: whether your throat hurts or not, whether your body temperature is elevated, how long ago the complaints arose.
- Examination of the oral cavity and back of the throat, determining the properties of plaque, its consistency, shade, and nature of distribution in the oral cavity.
- Palpation of lymph nodes.
- Blood analysis.
- Taking biological material from the tonsils to identify the causative agent of the disease - a smear from the tonsils.
- Analysis of urine.
Often the disease is quite easily determined by the appearance of the tonsils. A qualified specialist can make a diagnosis by examining the tonsils and identifying associated symptoms
But it is equally important to determine the type of pathogen - that’s why a throat swab is taken
What types of sore throat can there be?
Since a disease of the pharynx can occur with various symptoms, experts distinguish the following types of sore throat:
- Catarrhal . It is characterized by the presence of soreness, dry mouth, some swelling of the pharynx and lymph nodes. In this case, accompanying symptoms will be chills, fever, brittle limbs and severe headache. If treatment for this form is not started in a timely manner, then there is a high probability of developing a more serious type of illness - purulent tonsillitis.
- Purulent . It has the same symptoms as catarrhal disease, but in addition to them, strong white plaque formations appear on the tonsils, accompanied by vomiting, fever, and the procedure for swallowing saliva is excessively painful.
- Ulcerative-membranous . It does not always occur with elevated body temperature and severe deterioration in health, but, as a rule, it develops on one of the tonsils and all inflammation processes look like an unpleasant dirty white coating on the tongue with the subsequent appearance of ulcers.
- Necrotic . Its main symptoms are severe nausea and vomiting.
With sore throat, there may also be a yellow coating on the tongue with a greenish tint. When the patient tries to remove it with his own hands, the surface begins to bleed. This occurs due to the fact that due to the spread of infection, the mucous membrane of the tonsils begins to reject the surface tissue and causes its necrosis. Such a pathogenic layer can spread to the entire oral cavity.
Based on the types of the disease, it can be established that the main symptom of the disease is the resulting white layer. It causes the patient a lot of inconvenience and pain. Therefore, the question becomes urgent: how to get rid of it?
Plaque in the throat: white, gray, yellow
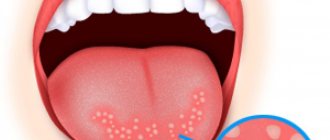
Plaque in the throat is usually called plaque on the tonsils (tonsils). This is an organ (paired) located between the pharynx and mouth. The tonsils are easy to see if you open your mouth. There are also tonsils, which are located under the tongue, deeper in the throat, and also in the nose. They are no longer visible.
The tonsils also belong to the immune system; they take part in the development of immunity. They also perform a hematopoietic function.
The tonsils are a fairly sensitive organ, especially in the cold. With reduced immunity, a person begins to have a sore throat, and the tonsils may become covered with a specific coating. Thus, they neutralize germs and viruses that enter the body through the mouth.
That is why the tonsils are called the first shield on the way to the body of harmful microorganisms. However, the role of tonsils in the immune system is not yet fully understood.
What are tonsils
This is a paired organ, also called tonsils.
They are located in the middle between the oral cavity and pharynx. They protect the body from viruses, thereby developing immunity. The tonsils are very sensitive and at the slightest decrease in immunity, pain appears and becomes covered with plaque. Thus, they are the “first shield” that neutralizes microorganisms that have penetrated the oral cavity. Plaque on the tonsils can be noticed when brushing your teeth; if it is easily removed and does not cause discomfort, there is no need to worry; after hygiene procedures it will disappear without a trace.