Solder flux or solder paste - exist for the purpose of removing the metal oxide film before soldering, due to which the soldered surface is wetted with solder and it spreads, unhindered filling of the gap. The flux also takes on the function of protecting the metal from thermal oxidation during the soldering process.
Today there is a large range of fluxes, and every seller praises their product, but their features are not always ideal for specific personal purposes - you have to prepare them yourself. Therefore, in this article I would like to introduce you to the recipe, application and technology for preparing some fluxes:
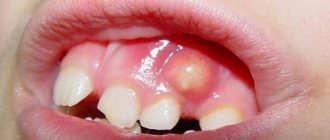
By what symptoms can periostitis be recognized?
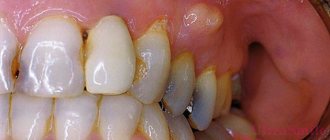
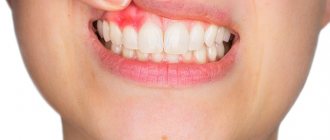
The cause of the appearance of flux on the gums is an infection that develops either in the cavity of the tooth itself or in the gum pocket. There are several stages during the course of the disease. First, toothache occurs when biting, then the gums become red and swollen. The tumor forms very quickly, as evidenced by the name of the disease: the German word “flux” means “flow” or “flow”.
The pus, which initially formed in the area of the tooth apex, tends to come out, so it creates a channel in the bone tissue to the periosteum. The inflammatory process developing in the tissues is accompanied by increasing throbbing pain, which begins to radiate to the ear, temple, and eyes. If you do not seek dental care at this stage, the periosteum will subsequently become inflamed.
The temperature rises, the pain becomes unbearable and is not relieved by painkillers, and swelling of the gums spreads to the jaw, cheeks, lips and leads to facial asymmetry. The temperature rises, typical signs of intoxication appear - from weakness and dry mouth to severe headache.
Some patients begin flux treatment at home and seriously progress the disease.
Let's figure out how self-treatment of purulent inflammation ends.
TYPES OF FLUXES
TYPES OF FLUXES
Fluxes. Complete collection: corrosive and non-corrosive, active and passive. The table below shows fluxes produced specifically for soldering.
| Photo of flux | Title and description | Compound |
| Pine rosin This simplest and cheapest neutral flux has already become a true “classic of the genre”! Cheap, has low leakage current and low corrosiveness. | ||
| Orthophosphoric acid is used in soldering as a flux (on oxidized copper, on ferrous metal, on stainless steel), for research in the field of molecular biology. It is also used to clean rust from metal surfaces. Forms a protective film on the treated surface, preventing further corrosion. | ||
| Soldering acid For soldering carbon and low-alloy steels, copper, nickel and their alloys. Active in the temperature range 290-350 °C. Washing with a 5% soda ash solution is recommended. | ||
| Soldering acid PET Application: soldering of carbon steels, copper, nickel and their alloys with low-melting solders at a temperature of 150 - 320°C. | ||
| Active soldering fat Used for soldering highly oxidized parts made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals Vaseline base | Ingredients: zinc chloride, ammonium chloride, hydrochloric acid, wetting additive “SOLINS”, deionized water. | |
| Neutral soldering fat Recommended for high-quality soldering of radio engineering devices. | ||
| Alcohol “Isopropanol” Absolute isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) is used in: printing, chemical, oil, furniture, wood chemical, and perfume industries. Isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) absolute is a good solvent for various essential oils, when washing high-tech components and assemblies, as a dehydrating and degreasing agent. | ||
| BORAHOUS Used for high-temperature soldering of carbon steels, cast iron, copper, hard alloys with copper and silver soldering alloys. | ||
| Glycerin flux TAGS This glycerin flux is used for soldering radio installation elements. When soldering printed circuit boards, it has residual resistance and requires mandatory cleaning with water or alcohol. | ||
| ZIL-2 Designed for soldering steel, cast iron, copper with low-tin solders or bismuth-based solders. | ||
| ZIL-2 PET Used for soldering brass, copper and its alloys | ||
| LTI-120 Flux LTI-120 - for soldering stainless steel, zinc, silver, copper and its alloys. Neutral, no cleaning required after soldering. Dissolves in alcohol and acetone. | Rosin – 25 Diethylamine hydrochloride – 5 Triethanolamine – 1 Ethyl alcohol – 69 | |
| LTI-120 PET Application: soldering of radio installation elements, printed circuit boards, carbon steels, zinc with fusible solders at temperatures of 200 - 300°C. Ingredients: pine rosin, alcohol, activators. | ||
| Soldering acid For soldering carbon and low-alloy steels, copper, nickel and their alloys. Active in the temperature range 290-350 °C. Washing with a 5% soda ash solution is recommended. | ||
| SKF (FKSp) Alcohol rosin flux SKF with a brush (aka CE, FKEt, FKSp). Application: soldering of radio installation elements and printed circuit boards with low-melting solders at temperatures of 250-280°C. Ingredients: pine rosin - 20-30%, monohydric alcohol (ethyl or isopropyl, or a mixture) - 80-70%. | ||
| SKF (FKET) For soldering copper and its alloys. The temperature range of activity is 250-280 °C. Cleaning: alcohol, gasoline, acetone. | ||
| TAGS PET Application: soldering of carbon steels, copper, nickel and their alloys with low-melting solders at a temperature of 150 - 320°C. | ||
| F-38N PET The most active soldering flux on the market. If the flux activity is too high, dilute it with an equal amount of ethyl or isopropyl alcohol. Application: soldering of nichrome, constantan, manganin, beryllium and aluminum bronze, corrosion-resistant steels with fusible solders at a temperature of 300°C. contains phosphoric acid, glycols and organic hydrochlorides. | ||
| FIM For soldering copper, constantan, silver, platinum, stainless steel and ferrous metals. Requires washing with water. Chemically active in the temperature range 290-350 °C. | ||
| FIM PET Highly active soldering flux. Application: soldering of stainless steels and bronzes (especially aluminum and beryllium) with fusible solders at a temperature of 150 - 300°C. The flux contains phosphoric acid. | ||
| FIM (active) For soldering copper, constantan, silver, platinum, stainless steel and ferrous metals. Requires washing with water. Chemically active in the temperature range 290-350 °C. | ||
| FCDT. Designed for manual and mechanized soldering and tinning of electrical installation elements and other metal surfaces of printed circuit boards and electrical electronics terminals in electronic equipment products. Neutral, flux residues after soldering do not affect the insulation resistance of dielectrics. | ||
| FCT PET. Designed for manual and mechanized soldering and tinning of electrical installation elements and other metal surfaces of printed circuit boards and terminals of radio electronics elements in radio electronic equipment products. Neutral, flux residues after soldering do not affect the insulation resistance of dielectrics. Flux residues after soldering are not corrosive. | Made on the basis of extraction rosin “A” or “B” (GOST 19113-84), alcohol and a neutral wetting additive - dipentene tetrabromide (according to TU 13-0281078-140-93). | |
| FTS For soldering parts of radio-electronic equipment. Neutral, does not contain rosin, washes off easily with water. It has low corrosive activity, is heat-resistant, and does not smoke. | ||
| FTS PET. Manual and mechanized soldering of printed circuit boards. Tinning of electrical installation elements and other metal surfaces of printed circuit boards and electrical electronics terminals in electronic devices and electronic devices with low-melting solders at a temperature of 150 - 300°C. Removal of flux residues is required. | ||
| Orthophosphoric acid It is used as a flux or as a 5% aqueous solution as a rust converter. | ||
| Soldering paste “Tinol” is used for hot air soldering of SMD components. Provides high-quality soldering. Flux residues after soldering are non-hygroscopic, non-conductive and non-corrosive. The temperature of complete melting of solder is 200 °C. | ||
| For aluminum. No laundering. If necessary, excess flux can be wiped off with a rag. In addition to soldering aluminum, it can be used for soldering stainless steels, nickel, copper and other metals. | ||
| Neutral radio mounting flux-gel is used for soldering electronic components. Corrosively passive. Non-drying. Washable with alcohol and acetone. Bottle with dispenser cap. 10 ml. | ||
| Flux-gel TT. Used for high-quality soldering of electronic components. The flux contains an activity indicator. After installation, the red flux becomes discolored, which indicates the absence of an active component at the soldering site, and therefore there is no need for cleaning. | ||
| FTS (water-washable) Used for soldering parts of electronic equipment. Neutral, does not contain rosin, washes off easily with water. It has low corrosive activity, is heat-resistant, and does not smoke. | ||
| CT-61A acid-free solder paste Provides high-quality soldering. Flux residues after soldering are non-hygroscopic, non-conductive and non-corrosive. The temperature of complete melting of solder is 200 °C. CT-61B solder paste Solder paste for soldering electronic elements, circuits in computer and mobile equipment. CT-61C solder paste (rosin) Provides high-quality soldering. Flux residues after soldering are non-hygroscopic, non-conductive and non-corrosive. The temperature of complete melting of solder is 200 °C. Jar 10 g. | ||
| IF 9007 Interflux BGA soldering paste. Solder IF 9007´ is recommended for use in lead soldering. Its formula allows the third type of paste grit (25-45µ) to be applied using a syringe. It has No-clean properties with minimal halogen content. Leaves a thin, invisible layer of flux. | ||
| FMKANC32-005. Flux cream is high-quality, rosin-based, no-clean, slightly activated FSW32, DIN8511, 5 ml syringe cartridge with piston and needle. Best results when soldering BGAs as well as QFPs using microwaves. | ||
| Soldering paste BS-10 (active). High activity allows you to solder even oxidized surfaces of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Not suitable for soldering printed circuit boards! Residues are easily washed off with Galosh gasoline or isopropanol. | Composition: - Vaseline (base) 80-90% - Paraffin 6-9% - Zinc chloride 4-6% - Ammonium chloride 1-3% - Water 2-4% | |
| IF 8001 Interflux Liquid soldering flux for lead-free SMD soldering. IF 8001 is a no-clean, high-quality alcohol-based synthetic flux. Does not contain halogens. Apply using a flux pen or brush. Does not require washing. If necessary, it can be easily removed using solvent-based removers. Guaranteed shelf life in a tightly closed container at a temperature of 5-35°C is 1 year. Yellow color | ||
| Pacific 2008 Interflux Liquid soldering flux Pacific 2008 is a harmless flux, specially designed for manual and selective soldering of poorly wetted, non-wettable and heat-intensive SMD components, because remains active for the additional time required when soldering such components. Does not contain halogens. Water washable. Does not require washing. Density at 20°C: 1.006 g/ml Colour: colorless Odour: sweet | ||
| Flux gel IF 8300 BGA Interflux (30cc) Flux gel BGA IF 8300-4 is used in lead-free soldering for mounting elements in BGA packages. The flux has rosin rheological properties. Halogen-free, which ensures reliable retention of elements on the printed circuit board. |
The fluxes presented above are presented as those specifically designed for soldering, as well as alternative ones that are not fluxes, but which can act as a flux. We have described a list of fluxes and recipes that are used for soldering. This reference material will undoubtedly be useful to both beginners and experienced radio amateurs. We are waiting for your comments, wishes, opinions. Continuation of the material here. Material provided by A. Kulibin
FORUM on amateur radio chemistry.
What does self-treatment of flux lead to?
Purulent inflammation of the periosteum requires an integrated approach. Since the abscess will not resolve on its own, an incision must be made near the diseased tooth, which will allow the purulent contents to come out. Then the oral cavity should be treated with an antiseptic, and the patient should be prescribed a course of antibiotics and, if necessary, physiotherapy.
In the absence of surgical and drug treatment, pus will accumulate in the soft tissues and cause an abscess, which will very quickly develop into phlegmon - no longer limited, but extensive purulent inflammation. Cellulitis can become a threat to the patient’s life, as the infection will spread further, and pus through the intermuscular space can penetrate into the neck and mediastinum, affecting the heart, aorta and lungs. The consequences of self-treatment of flux on the gums can be deadly sepsis (blood poisoning) or necrosis of the facial bones.
Diagnostic measures
Like any purulent pathology, flux spreads rapidly, so ignoring the problem is fraught with serious consequences, including sepsis and death. Periostitis is easily diagnosed during a dental examination. Additionally, an X-ray is taken to determine the volume of damaged tissue and a blood test to identify the pathogen, assess the stage of the inflammatory process and the level of leukocytes.
The x-ray will also show other problems (if any): cysts, periodontitis, unerupted teeth.
Procedures strictly prohibited for symptoms of periostitis
Traditional methods of treating gumboil with soda and herbal decoctions do not completely cure a diseased tooth. Their use is possible only at the initial stage, if the patient does not have the physical ability to immediately go to the clinic. During this period it is strictly prohibited:
- heat the area of the diseased tooth using a heating pad and warm compresses - heat promotes the spread of infection, so the flux will only increase, and the pus will penetrate into the soft tissues much faster;
- independently “prescribe” antibiotics to yourself, which may not have the expected effect on pathogens, but may cause an allergic reaction.
It is important to know: when you decide to see a dentist, you should stop taking analgesics so that the problem can be diagnosed more quickly.
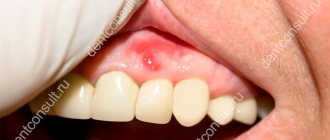
Features of surgical treatment of dental flux
Correctly prescribed by a doctor, treatment with antibiotics and painkillers at an early stage of the disease will relieve swelling and eliminate the source of inflammation. The cause of flux formation will also be identified and appropriate dental treatment will be carried out.
If the patient delays and goes to the clinic at an acute stage, when an abscess has already formed, surgical intervention will become inevitable. Severe pain in the area of inflammation makes it necessary to use local anesthesia. But if necessary or at the request of the client, dental treatment can be performed under general anesthesia .
The gums, and sometimes the bone tissue near the diseased tooth, are cut to release accumulated pus, and the affected area is treated with antiseptic solutions. To prevent the edges of the incision from merging and the wound to remain open until complete cleansing, drainage is used - a special latex strip.
Only competent actions of the surgeon and subsequent drug therapy can save the tooth. After removal of the drainage, the bone tissue is quickly restored and the gums heal. If the surgery was extensive, stitches may be placed on the gums. After surgery, usually a few weeks later, a resection of the apex of the tooth root is performed.
If, based on the results of the examination, restoration of a seriously damaged tooth is considered inappropriate, the doctor will recommend its removal. You should not be afraid of this procedure. , tooth extraction under general anesthesia may be offered .
What dentists recommend
The first thing to do when the above symptoms appear is to consult a doctor. The dentist will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe a set of medications to stop the spread of inflammation.
Experts also advise the following:
- rinse the mouth with a soda solution, sage decoction or herbal mixture, which will reduce the manifestations of the inflammatory process,
- We try to identify incipient flux in the early stages. If detected, we do not hesitate to treat the disease with a specialist,
- We do not self-medicate under any circumstances - it is fraught with dangerous consequences,
- we do not apply hot compresses - when heated, the pus will very quickly leave the sac, spread throughout the entire jaw and even throughout the body,
- We pay key attention to oral hygiene. We monitor the appearance of carious spots and treat them in a timely manner. We regularly visit the dentist's office for preventive examinations.
Treatment of flux
Summarizing everything that has been said regarding flux, let us recall that the sooner the symptoms of periostitis are recognized and its treatment is started, the less time and money will have to be spent on dealing with unpleasant consequences.
How does tooth flux occur?
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 4.50 out of 5)
flux
Consulting specialist
Vakhrushev Alexander Viktorovich
Doctor rating: 9.8 out of 10 (4) Specialization: Surgeon, implantologist, periodontist, orthopedist, therapist Experience: 30 years
Drug treatment: antibacterial therapy + antiseptic care
After opening the abscess, the patient quickly returns to normal temperature and the excruciating pain subsides. But the swelling may even increase and will decrease only on the second or third day. In order for the consequences to disappear completely, after surgery, flux treatment must be prescribed with antibiotics that suppress inflammation and prevent the spread of infection.
The choice of a specific drug that is sensitive to certain types of microorganisms, its dosage and the duration of the treatment course must be made by the doctor. Only a specialist can choose the optimal antibiotic that matches the severity of the disease and the patient’s health characteristics. In case of severe postoperative pain, pharmaceuticals with analgesic and powerful anti-inflammatory effects are prescribed in parallel.
The importance of antiseptic care is explained by the need to minimize the possibility of repeated accumulation of pus and the occurrence of complications. The patient is prescribed rinses with solutions of baking soda, rotokan and chlorhexidine. The latter drug not only has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect, but also activates the growth of new cells that promote rapid healing of wounds in the oral cavity.
Etiology of the disease
Periostitis can be caused by many problems, in particular:
- advanced caries;
- injury to the gums or tooth;
- infections of various types;
- sinusitis;
- angina;
- dental diseases;
- pathological growth of teeth or their prolonged eruption;
- improper or insufficient oral care;
- furunculosis;
- hypothermia of the body;
- nervous breakdowns.
Depending on the cause that triggered the development of periostitis of the jaw, there are 4 forms of the disease:
Inflammatory
A complication after dental therapy or a concomitant problem of untreated dental diseases.
Specific
Consequence of systemic pathologies of the body.
Traumatic
Damage to the tooth or gum tissue due to mechanical impact.
Toxic
Infectious lesions (stomatitis, sore throat, etc.).
In any of the above cases, the clinical picture is manifested by the development of inflammation and rapid infection of tissues by pathogenic microorganisms.
How to prevent recurrence of periostitis
Despite the fact that today it is possible to treat teeth under sedation or with reliable local anesthesia, it is unlikely that anyone would want to undergo inflammation of the periosteum again. To do this, it is enough to follow the basic rules of oral hygiene: visit your doctor twice a year for a preventive examination and professional teeth cleaning, brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day, and after eating, rinse your mouth with water or mouthwash to wash away food debris.
Quick appointment Free consultation